in和exists哪个性能更优
sql脚本:
/*建库*/
create database testdb6;
use testdb6;
/* 用户表 */
drop table if exists users;
create table users(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20)
);
insert into users(name) values ('A');
insert into users(name) values ('B');
insert into users(name) values ('C');
insert into users(name) values ('D');
insert into users(name) values ('E');
insert into users(name) values ('F');
insert into users(name) values ('G');
insert into users(name) values ('H');
insert into users(name) values ('I');
insert into users(name) values ('J');
/* 订单表 */
drop table if exists orders;
create table orders(
id int primary key auto_increment,/*订单id*/
order_no varchar(20) not null,/*订单编号*/
title varchar(20) not null,/*订单标题*/
goods_num int not null,/*订单数量*/
money decimal(7,4) not null,/*订单金额*/
user_id int not null /*订单所属用户id*/
)engine=myisam default charset=utf8 ;
delimiter ?
drop procedure batch_orders ?
/* 存储过程 */
create procedure batch_orders(in max int)
begin
declare start int default 0;
declare i int default 0;
set autocommit = 0;
while i < max do
set i = i + 1;
insert into orders(order_no,title,goods_num,money,user_id)
values (concat('NCS-',floor(1 + rand()*1000000000000 )),concat('订单title-',i),i%50,(100.0000+(i%50)),i%10);
  end while;
commit;
end ?
delimiter ;
/*插入1000万条订单数据*/
call batch_orders(10000000); /*插入数据的过程根据机器的性能 花费的时间不同,有的可能3分钟,有的可能10分钟*/
上面的sql中 订单表中(orders) 存在user_id,而又有用户表(users),所以我们用orders表中user_id和user表中的id 来in 和 exists。
结果
1.where后面是小表
(1)select count(1) from orders o where o.user_id in(select u.id from users u);
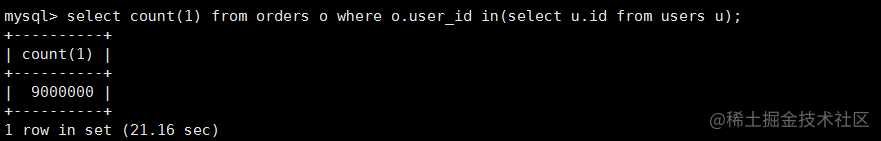
(2)select count(1) from orders o where exists (select 1 from users u where u.id = o.user_id);
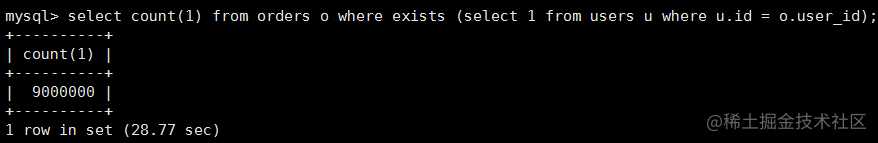
2.where后面是大表
(1)select count(1) from users u where u.id in (select o.user_id from orders o);

(2)select count(1) from users u where exists (select 1 from orders o where o.user_id = u.id);

分析
我们用下面的这两条语句分析:
select count(1) from orders o where o.user_id in(select u.id from users u);
select count(1) from orders o where exists (select 1 from users u where u.id = o.user_id);
1.in:先查询in后面的users表,然后再去orders中过滤,也就是先执行子查询,结果出来后,再遍历主查询,遍历主查询是根据user_id和id相等查询的。
即查询users表相当于外层循环,主查询就是外层循环
小结:in先执行子查询,也就是in()所包含的语句。子查询查询出数据以后,将前面的查询分为n次普通查询(n表示在子查询中返回的数据行数)
2.exists:主查询是内层循环,先查询出orders,查询orders就是外层循环,然后会判断是不是存在order_id和 users表中的id相等,相等才保留数据,查询users表就是内层循环
这里所说的外层循环和内层循环就是我们所说的嵌套循环,而嵌套循环应该遵循“外小内大”的原则,这就好比你复制很多个小文件和复制几个大文件的区别
小结:如果子查询查到数据,就返回布尔值true;如果没有,就返回布尔值false。返回布尔值true则将该条数据保存下来,否则就舍弃掉。也就是说exists查询,是查询出一条数据就执行一次子查询
结论
小表驱动大表。
in适合于外表大而内表小的情况,exists适合于外表小而内表大的情况。
欢迎关注我的公众号,第一时间接收最新文章~ 搜索公众号: 码咖 或者 扫描下方二维码:

版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/14409.html
