思维导图:

一 offset 系列
1.1 定位元素
定位元素(positioned element)是指该元素计算后位置(position)属性为 relative, absolute, fixed 或 sticky 的一个元素。同时定位属性又细分为以下几种:
- 相对定位元素(relatively positioned element): 指该元素计算后位置(position)属性为 relative 的元素
- 绝对定位元素(absolutely positioned element): 指该元素计算后位置(position)属性为 absolute 或 fixed 的元素
- 粘性定位元素(stickily positioned element): 指该元素计算后位置(position)属性为 sticky 的元素
对于绝对定位元素(position 属性为 absolute 或 fixed 的元素 ), 在未设置 height 和 width 或者为 auto 的情况下,允许通过 top bottom left right 来填充容器可用的空间, 只是 top bottom left right 的参考对象不同而已;
1.2 Element.offsetParent
Element.offsetParent 是一个只读属性, 返回当前元素最近的一个父级定位元素。同时又有下列几种特殊情况:
- 如果当前元素没有父级定位元素,则 offsetParent 为最近的标准单元格元素( td 元素)
- 如果当前元素最近也没有标准单元格元素,则为 body 元素。(有种说法: 标准模式下为 offsetParent 为 html 元素, quirks 模式下但是经过测试好像都是 body 元素)
- 在 WebKit 为核心的浏览器上,如果元素是隐藏的(style.display=’none’)或者元素 style.position=’fixed’,则该元素 offsetParent 为 null
- 在IE(9)上只有当元素 style.position=’fixed’ 时 offsetParent 才会返回 null, 即使元素 display = ‘none’ 也是不会影响返回结果
1.3 Element.offsetLeft && Element.offsetTop
Element.offsetLeft 和 Element.offsetTop 是一个只读属性,返回当前**元素边界(border)**相对于 Element.offsetParent 节点的偏移的像素值。
- 示意图:
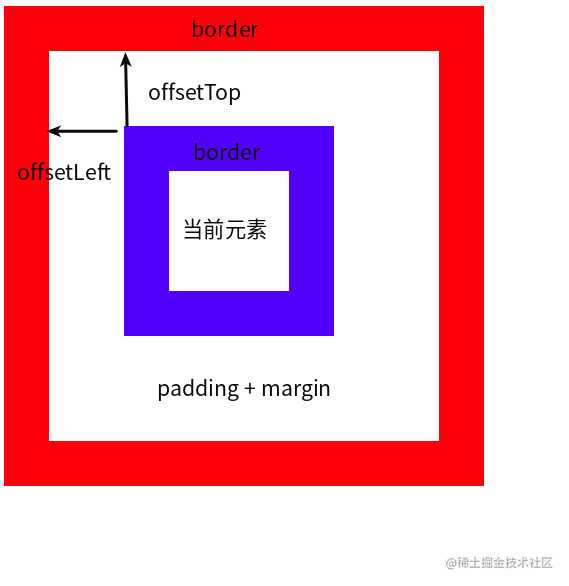
- 上图演示代码:
<style> #parent{ position: relative; border: 30px solid red; padding: 30px; width: 200px; height: 200px; } #child{ border: 30px solid blue; padding: 30px; margin: 20px; width: 20px; height: 20px; } </style>
<div id="parent">
<div id="child"></div>
</div>
<script> const dom = document.getElementById('child'); console.log(dom.offsetParent); // <div id="parent"></div> console.log(dom.offsetTop); // 50 </script>
1.4 Element.offsetWidth && Element.offsetHeight
Element.offsetWidth 和 Element.offsetHeight 是一个只读属性,返回一个元素布局的宽高(元素布局包括: border、滚动条、padidng、内容块), 该属性返回的值为一个四舍五入的整数
- 示意图:
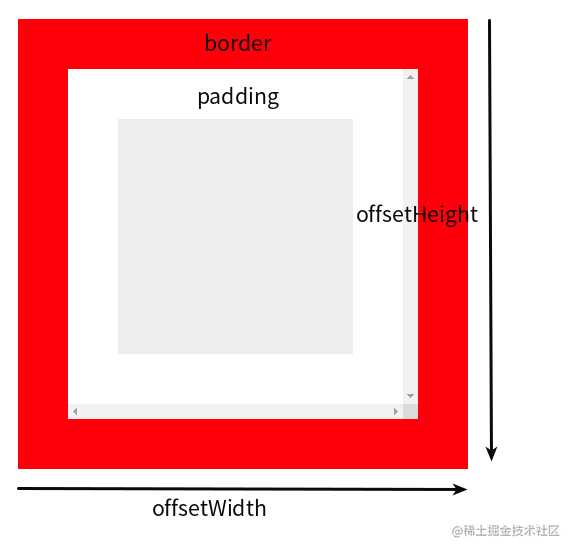
- 上图演示代码:
<style> #parent{ margin: 10px; border: 20px solid red; padding: 20px; width: 100px; height: 100px; overflow: scroll; } #child{ width: 100%; height: 100%; background: #eee; } </style>
<div id="parent">
<div id="child"></div>
</div>
<script> const dom = document.getElementById('parent'); console.log(dom.offsetParent); // <body></body> console.log(dom.offsetHeight); // 180 console.log(dom.offsetWidth) // 180 </script>
1.5 内联元素下的特殊行为
上文关于 Element offset 系列属性的描述都是针对块级元素进行的,至于内联元素又有一定的区别:
- 示意图:
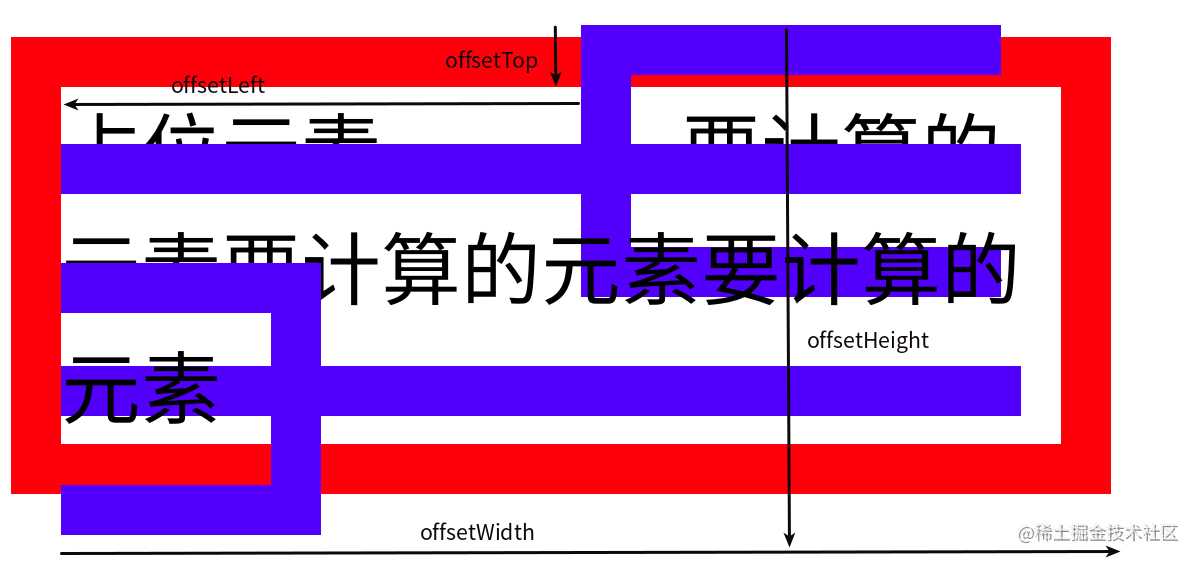
- 上图演示代码:
<style> #parent{ position: relative; width: 200px; border: 10px solid red; } #Placeholder{ display: inline-block; width: 100px; } #child{ border: 10px solid blue; padding: 10px; } </style>
<div id="parent">
<span id="Placeholder">占位元素</span>
<span id="child">
要计算的元素要计算的元素要计算的元素
</span>
</div>
<script> const dom = document.getElementById('child'); console.log(dom.offsetParent); console.log(dom.offsetTop); // -12 console.log(dom.offsetLeft); // 104 console.log(dom.offsetWidth); // 192 console.log(dom.offsetHeight); // 102 </script>
二 client 系列
- Element.clientTop 和 Element.clientLeft 获取可视区域的偏移值(实际上就等于元素上下 border 值) 四舍五入(整数)后的结果;
- Element.clientWidth 和 Element.clientHeight 获取可视区域(padding + 元素内容区域的宽高,不包含滚动条)的宽高
- 示意图:
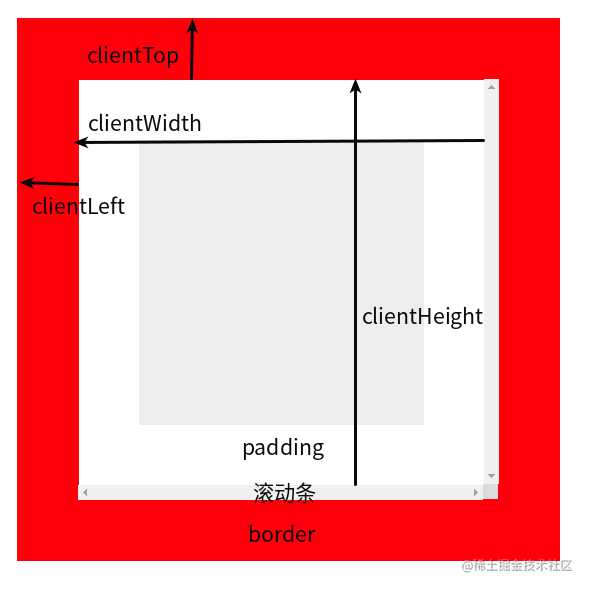
- 上图演示代码:
<style> #parent{ margin: 10px; border: 20.5px solid red; padding: 20px; width: 100px; height: 100px; overflow: scroll; } #child{ width: 100%; height: 100%; background: #eee; } </style>
<div id="parent">
<div id="child"></div>
</div>
<script> const dom = document.getElementById('parent'); console.log(dom.clientTop); // 21 console.log(dom.clientLeft); // 21 console.log(dom.clientWidth); // 125 console.log(dom.clientHeight); // 125 </script>
三 scroll 系列(用于对可滚动元素进行求值)
3.1 Element.scrollTop && Element.scrollLeft(可写)
Element.scrollTop 和 Element.scrollLeft 用于获取或设置元素被卷起的宽高(子元素顶部或左侧到当前元素可视区域顶部或左侧的距离)
- 示意图:以 scrollTop 为例
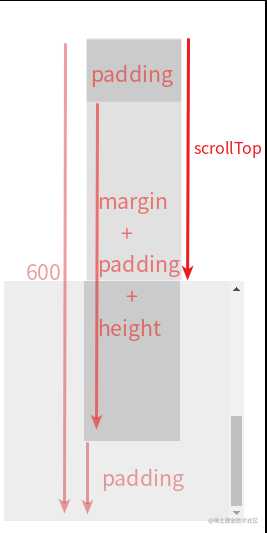
- 上图演示代码:
<style> #parent{ width: 200px; height: 200px; padding: 50px; background: #eee; overflow: auto; } #child { height: 400px; margin: 50px; padding: 50px; width: 20px; background: #ccc; } </style>
<body>
<div id="parent">
<div id="child"></div>
</div>
</body>
<script> window.onload = () => { const dom = document.getElementById('parent'); dom.onscroll= () => { console.log(dom.scrollTop); } } </script>
- 补充:
- 对于不可滚动的元素 Element.scrollTop 和 Element.scrollLeft 值为 0
- 如果给 scrollTop(scrollLeft) 设置的值小于0,那么 scrollTop(scrollLeft) 的值将变为0。
- 如果给 scrollTop(scrollLeft) 设置的值大于元素内容最大宽度,那么 scrollTop(scrollLeft) 的值将被设为元素最大宽度(高度)。
3.2 Element.scrollWidth && Element.scrollHeight
- Element.scrollWidth 和 Element.scrollHeight 是只读属性, 表示元素可滚动区域的宽高; 实际上又等于 clientHeight/clientWidth + 未显示在屏幕中内容的宽高;
- 它们的值等于元素在不使用水平滚动条的情况下适合视口中的所有内容所需的最小宽度。
- 测量方式与 clientWidth(clientHeight) 相同:它包含元素的内边距,但不包括边框,外边距或垂直滚动条(如果存在)。 它还可以包括伪元素的宽度,例如::before或::after。
- 如果元素的内容可以适合而不需要水平滚动条,则其 scrollWidth 等于 clientWidth; (最小值为元素的可视区域宽高: clientWidth (clientHeight))
- 示意图:以 scrollHeight 为例
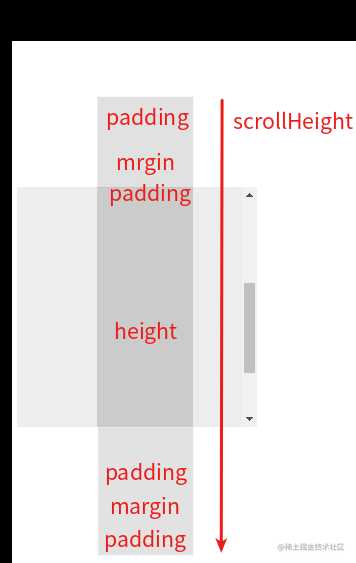
- 上图演示代码:
<style> #parent{ width: 200px; height: 200px; padding: 50px; background: #eee; overflow: auto; } #child { height: 400px; margin: 50px; padding: 50px; width: 20px; background: #ccc; } </style>
<body>
<div id="parent">
<div id="child"></div>
</div>
</body>
<script> window.onload = () => { const dom = document.getElementById('parent'); console.log(dom.scrollHeight); // 700 } </script>
补充:
- 虽然 scrollWidth 计算方式和 scrollHeight 是一样的, 但是如果在可滚动元素中其子元素使用了 margin-right 则会发生 margin 塌陷等问题, 这时实际计算出的 scrollWidth 会有所不同
今天的文章元素 offset client scroll 相关属性简介分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/19025.html
