写一个查询天气的demo。
代码github地址:github.com/koudle/GDG_…
1.创建工程
在Android Studio中,File -> New ->New Flutter Project -> Flutter Application
创建完工程后,有三个目录
android:Android工程的目录
ios:iOS工程的目录
lib: Flutter工程的目录
其中android、ios下的文件我们都不动,我们只改动lib目录下的dart文件。
2.运行Flutter工程
- 连接手机
- 这里不建议用模拟器,因为模拟器在用GPU渲染时可能会出问题,导致图片渲染不出来。
- 然后按
Run在手机上把程序跑起来。
3.天气API接口申请
注册地址console.heweather.com/register
注册完后,再看API文档 www.heweather.com/documents
demo这里用的是,获取当天天气情况的API:www.heweather.com/documents/a…
用的请求URL如下:
https://free-api.heweather.com/s6/weather/now?location=广州&key=******
4.界面编写
在创建的工程里,有个main.dart里面有一段显示界面的代码如下:
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
// This is the theme of your application.
//
// Try running your application with "flutter run". You'll see the
// application has a blue toolbar. Then, without quitting the app, try
// changing the primarySwatch below to Colors.green and then invoke
// "hot reload" (press "r" in the console where you ran "flutter run",
// or press Run > Flutter Hot Reload in a Flutter IDE). Notice that the
// counter didn't reset back to zero; the application is not restarted.
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'),
);
}
}
其中home 就是要显示的界面,这里我们要把MyHomePage换成我们自己的。
4.1 创建WeatherWidget
通过 new -> Dart File 在lib目录下创建WeatherWidget
class WeatherWidget extends StatefulWidget{
@override
State<StatefulWidget> createState() {
// TODO: implement createState
return new WeatherState();
}
}
class WeatherState extends State<WeatherWidget>{
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// TODO: implement build
return Scaffold(
);
}
}
创建完后,在main.dart中将home改为WeatherWidget,如下:
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: WeatherWidget(),
);
}
4.2 HotReload
在写UI的工程中,我们可以用到Flutter的hot reload的特性,写布局的时候,按ctrl+s或cmd+s就可以在手机上实时看到界面的变化。
这个功能很好用。
4.3添加图片资源
Flutter可以添加不同的资源,例如图片、文本、配置文件、静态数据等。
添加资源时,需要在pubspec.yaml文件中的flutter属性下添加assets,并标明要添加资源的路径,例如,我们要加入指定的图片时,可以这么写:
flutter:
assets:
- assets/my_icon.png
- assets/background.png
如果要添加的资源太多,也可以添加文件夹,例如:
flutter:
assets:
- assets/
在本demo中,要添加一个背景图,我们在工程的根目录下创建images目录,将背景图放在images目录下,然后在pubspec.yaml中添加:
flutter:
# The following line ensures that the Material Icons font is
# included with your application, so that you can use the icons in
# the material Icons class.
uses-material-design: true
assets:
- images/
4.4 写WeatherWidget的UI布局
在Scaffold中添加body的属性,来写UI的布局,如下:
class WeatherState extends State<WeatherWidget>{
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
// TODO: implement build
return Scaffold(
body: new Stack(
fit: StackFit.expand,
children: <Widget>[
new Image.asset("images/weather_bg.jpg",fit: BoxFit.fitHeight,),
new Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.center,
children: <Widget>[
new Container(
width: double.infinity,
margin: EdgeInsets.only(top: 40.0),
child: new Text(
"广州市",
textAlign: TextAlign.center,
style: new TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 30.0,
),
),
),
new Container(
width: double.infinity,
margin: EdgeInsets.only(top: 100.0),
child: new Column(
children: <Widget>[
new Text(
"20 °",
style: new TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 80.0
)),
new Text(
"晴",
style: new TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 45.0
)),
new Text(
"湿度 80%",
style: new TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 30.0
),
)
],
),
)
],
)
],
),
);
}
}
按ctrl+s,在手机上就可以看到写好的UI,但这时候的数据是写死的,下来看如何通过http获取数据。
5.通过http获取数据
要通过http数据,我们首先要添加http的依赖库,在pubspec.yaml中的dependencies添加如下:
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
# The following adds the Cupertino Icons font to your application.
# Use with the CupertinoIcons class for iOS style icons.
cupertino_icons: ^0.1.2
http: ^0.12.0
然后在当前工程目录下运行以下命令行:
$ flutter packages get
或者在Android Stuido 打开pubspec.yaml 文件,点击上面的packages get
这里操作的意义是,拉取http的库。
5.1 创建WeatherData类
通过 new -> Dart File 在lib目录下创建WeatherData
class WeatherData{
String cond; //天气
String tmp; //温度
String hum; //湿度
WeatherData({this.cond, this.tmp, this.hum});
factory WeatherData.fromJson(Map<String, dynamic> json) {
return WeatherData(
cond: json['HeWeather6'][0]['now']['cond_txt'],
tmp: json['HeWeather6'][0]['now']['tmp']+"°",
hum: "湿度 "+json['HeWeather6'][0]['now']['hum']+"%",
);
}
factory WeatherData.empty() {
return WeatherData(
cond: "",
tmp: "",
hum: "",
);
}
}
5.2 数据获取
class WeatherState extends State<WeatherWidget>{
WeatherData weather = WeatherData.empty();
WeatherState(){
_getWeather();
}
void _getWeather() async{
WeatherData data = await _fetchWeather();
setState((){
weather = data;
});
}
Future<WeatherData> _fetchWeather() async{
final response = await http.get('https://free-api.heweather.com/s6/weather/now?location=广州&key=ebb698e9bb6844199e6fd23cbb9a77c5');
if(response.statusCode == 200){
return WeatherData.fromJson(json.decode(response.body));
}else{
return WeatherData.empty();
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
...
}
}
5.3 将之前写死的数据换成WeatherData
...
child: new Column(
children: <Widget>[
new Text(
weather?.tmp,
style: new TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 80.0
)),
new Text(
weather?.cond,
style: new TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 45.0
)),
new Text(
weather?.hum,
style: new TextStyle(
color: Colors.white,
fontSize: 30.0
),
)
],
),
...
6.运行界面
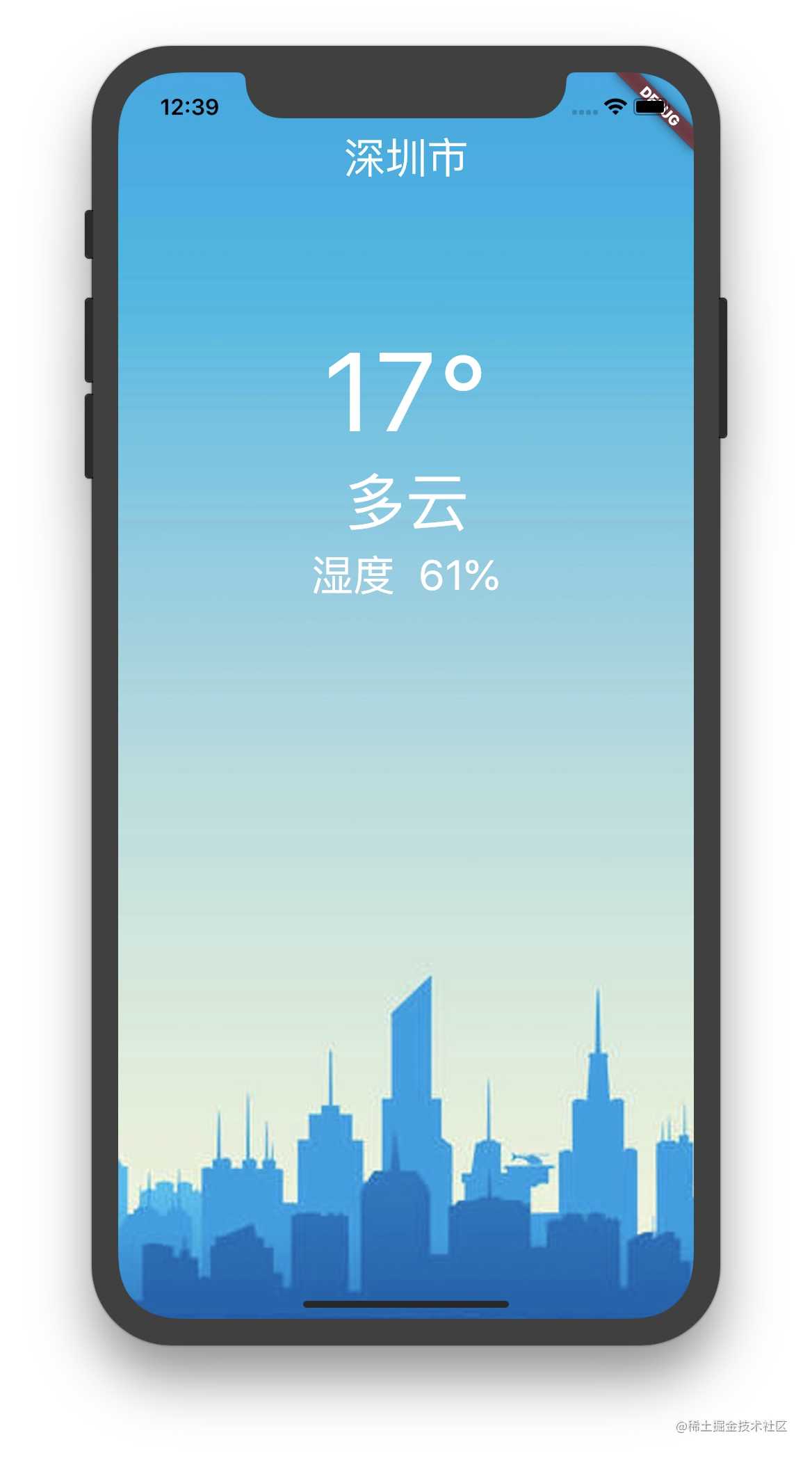
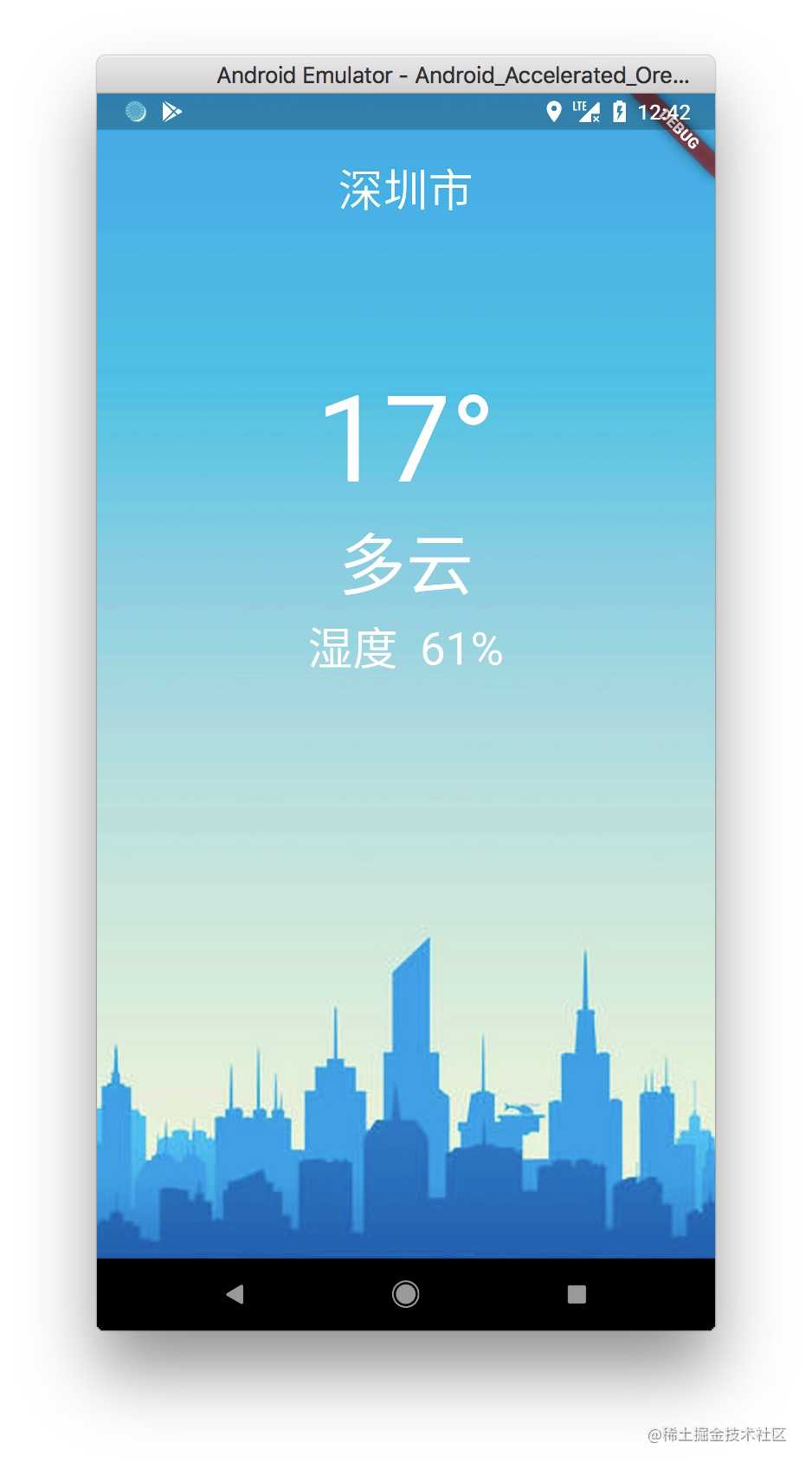
今天的文章Flutter实战1 — 写一个天气查询的APP分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/21929.html
