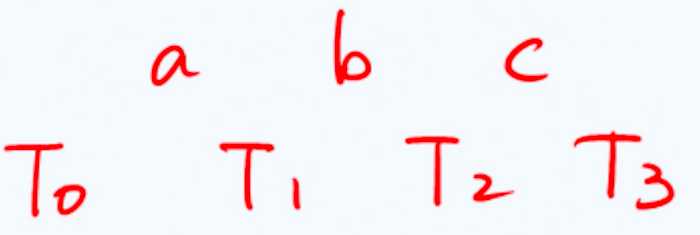个人技术博客:http://blog.ztgreat.cn
平衡二叉树(Balanced BinaryTree)又被称为AVL树。它具有以下性质:它是一棵空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差的绝对值不超过1,并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
平衡二叉树一般是一个有序树,它具有二叉树的所有性质,其遍历操作和二叉树的遍历操作相同。但是由于其对二叉树施加了额外限制,因而其添加、删除操作都必须保证平衡二叉树的因子被保持。
平衡二叉树中引入了一个概念:平衡二叉树节点的平衡因子,它指的是该节点的两个子树,即左子树和右子树的高度差,即用左子树的高度减去右子树的高度,如果该节点的某个子树不存在,则该子树的高度为0,如果高度差的绝对值超过1就要根据情况进行调整。
为了更好的明白下面的图解和代码,这里我先给出平衡二叉树结构定义:
typedef struct AVLNode *Tree;
typedef int ElementType;
struct AVLNode
{
int depth; //深度,这里计算每个结点的深度,通过深度的比较可得出是否平衡
Tree parent; //该结点的父节点,方便操作
ElementType val; //结点值
Tree lchild;
Tree rchild;
AVLNode(int val=0) //默认构造函数
{
parent=NULL;
depth=0;
lchild=rchild=NULL;
this->val=val;
}
};
平衡的调整共有四种情况:分别为LL,LR,RR,RL。
下面我们通过不断插入数据来说明几种不同的旋转方式:
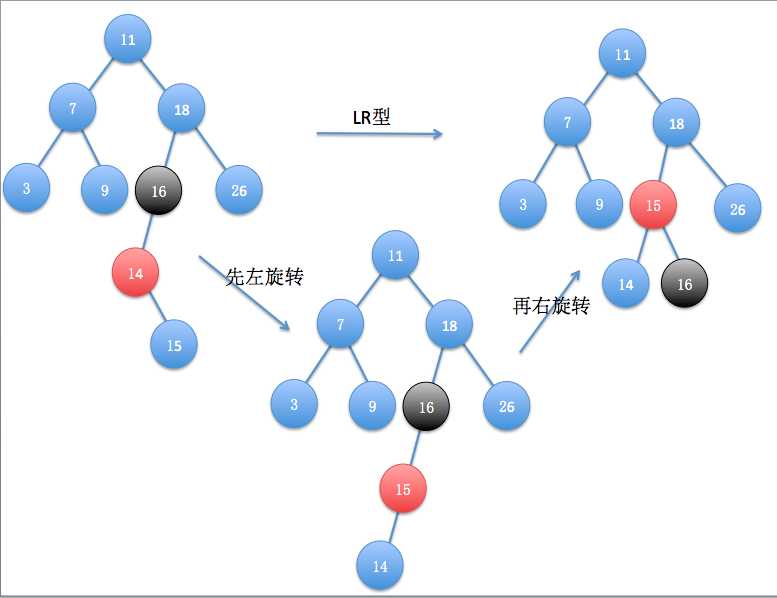
注意:橘黄色的结点为旋转中心,黑色结点的为离插入结点最近的失衡结点。
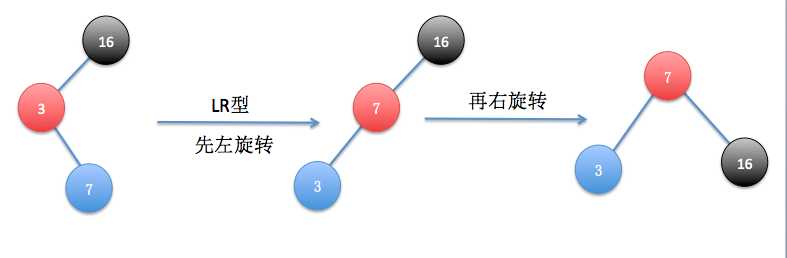
(1)LR型
最开始插入数据16,3,7后的结构如上图所示,结点16失去了平衡,3为16的左孩子,7为失衡结点的左孩子的右孩子,所以为LR型,接下来通过两次旋转操作复衡,先通过以3为旋转中心,进行左旋转,结果如图所示,然后再以7为旋转中心进行右旋转,旋转后恢复平衡了。
//LR型,先左旋转,再右旋转
//返回:新父节点
Tree LR_rotate(Tree node)
{
RR_rotate(node->lchild);
return LL_rotate(node);
}
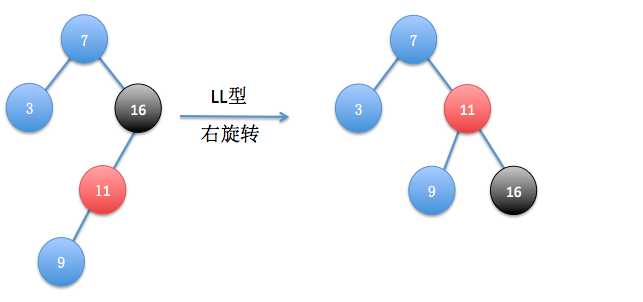
(2)LL型
在上面恢复平衡后我们再次插入数据11和9,发现又失去平衡了,这次失衡结点是16,11是其左孩子,9为其失衡结点的左孩子的左孩子,所以是LL型,以失衡结点的左孩子为旋转中心进行一次右旋转即可。
//LL型调整函数
//返回:新父节点
Tree LL_rotate(Tree node)
{
//node为离操作结点最近的失衡的结点
Tree parent=NULL,son;
//获取失衡结点的父节点
parent=node->parent;
//获取失衡结点的左孩子
son=node->lchild;
//设置son结点右孩子的父指针
if (son->rchild!=NULL)
son->rchild->parent=node;
//失衡结点的左孩子变更为son的右孩子
node->lchild=son->rchild;
//更新失衡结点的高度信息
update_depth(node);
//失衡结点变成son的右孩子
son->rchild=node;
//设置son的父结点为原失衡结点的父结点
son->parent=parent;
//如果失衡结点不是根结点,则开始更新父节点
if (parent!=NULL)
{
//如果父节点的左孩子是失衡结点,指向现在更新后的新孩子son
if (parent->lchild==node)
parent->lchild=son;
else //父节点的右孩子是失衡结点
parent->rchild=son;
}
//设置失衡结点的父亲
node->parent=son;
//更新son结点的高度信息
update_depth(son);
return son;
}
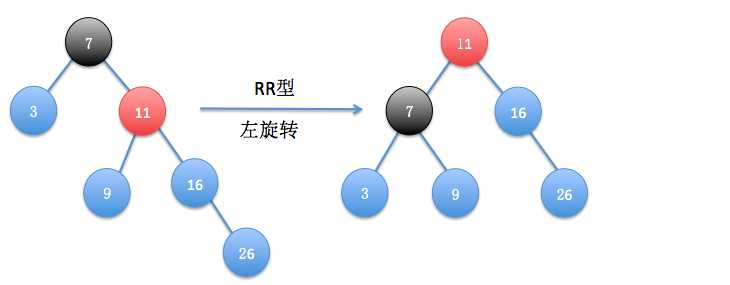
(3)RR型
进一步插入数据26后又再次失衡了,失衡结点为7,很明显这是RR型,以失衡结点的右孩子为旋转中心左旋转一次即可。
代码:
//RR型调整函数
//返回新父节点
Tree RR_rotate(Tree node)
{
//node为离操作结点最近的失衡的结点
Tree parent=NULL,son;
//获取失衡结点的父节点
parent=node->parent;
//获取失衡结点的右孩子
son=node->rchild;
//设置son结点左孩子的父指针
if (son->lchild!=NULL)
son->lchild->parent=node;
//失衡结点的右孩子变更为son的左孩子
node->rchild=son->lchild;
//更新失衡结点的高度信息
update_depth(node);
//失衡结点变成son的左孩子
son->lchild=node;
//设置son的父结点为原失衡结点的父结点
son->parent=parent;
//如果失衡结点不是根结点,则开始更新父节点
if (parent!=NULL)
{
//如果父节点的左孩子是失衡结点,指向现在更新后的新孩子son
if (parent->lchild==node)
parent->lchild=son;
else //父节点的右孩子是失衡结点
parent->rchild=son;
}
//设置失衡结点的父亲
node->parent=son;
//更新son结点的高度信息
update_depth(son);
return son;
}
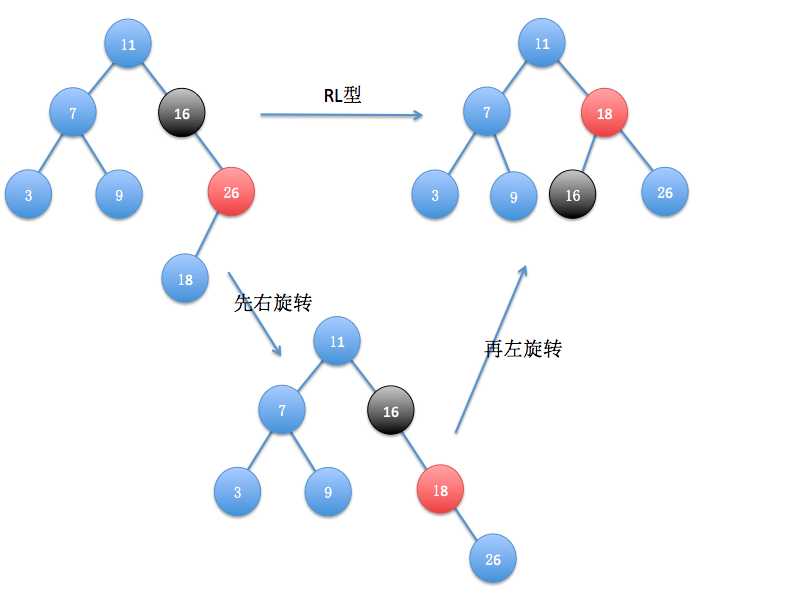
(4)RL型
再插入18后又再次失衡了,失衡结点为16,26为其右孩子,18为其右孩子的左孩子,为RL型,以失衡结点的右孩子为旋转中心,进行一次右旋转,然后再次已失衡结点的右孩子为旋转中心进行一次左旋转变恢复了平衡。
//RL型,先右旋转,再左旋转
//返回:新父节点
Tree RL_rotate(Tree node)
{
LL_rotate(node->rchild);
return RR_rotate(node);
}
这就是4中旋转方式,其实只有两种,RR和LL,RL和LR本质上是一样的。下面我们再次插入数据14,15,完成我们最后数据的插入操作:
又是一次LR型,按前面操作就可以了。
一、平衡二叉树的建立
说完了平衡二叉树的4个基本调整,基本问题就解决一大半了,接下来我们再来说说其它的操作函数,首先我们得建树对吧,既然要建树,那么就得插入数据呀,来看看我们的插入函数:
//向AVL树中插入val
//参数:根,插入数据value
//返回:新根结点
Tree Insert(Tree &root,ElementType val)
{
Tree temp=NULL;
Tree node=new AVLNode(val);
//插入结点
temp=insert_val(root,node,NULL); //调用真正的插入函数
if (temp)
{
update_depth(temp);
root=AVLTree(root,temp); //检查树是否该调整
}
else //无需插入,释放结点
delete temp;
return root;
}
这里我们看到,我们在插入数据里面还有一个真正的插入函数,以及高度更新操作,还有我们AVL树调整操作,而我们刚刚的插入函数封装了封装了这两个函数,这样方便我们的调用,我们可以先不管其细节如果,先理解上面的逻辑结构,我们在函数里面创建一个结点,然后插入这个数据,当然不一定成功呢,如果这个AVL树中有了这个数据,那么插入就会失败,temp将等于空,所以我们对temp可以进行判断,再进行操作,当插入成功后,我们更新插入结点的高度信息,其实这个结点肯定是叶子结点,不用更新也可以,因为我们在构造函数里面已经初始化了。高度更新后,我们便开始看是否需要调整树结构,将调整后的新根结点返回来。这就是这段代码的逻辑结构,很简单吧,接下来我们在分析其分支结构。
//更新当前深度
void update_depth(Tree node)
{
if (node==NULL)
return;
else
{
int depth_Lchild=get_balance(node->lchild); //左孩子深度
int depth_Rchild=get_balance(node->rchild); //右孩子深度
node->depth=max(depth_Lchild,depth_Rchild)+1;
}
}这便是我们的高度更新函数,这里面又有一个新函数,就是获取左右子树的高度,然后再更新当前结点的高度信息。很简单吧。接下来看看我们的获取高度的函数.
//获取当前结点的深度
int get_balance(Tree node)
{
if (node==NULL)
return 0;
return node->depth;
}可以看到这个函数非常的简单,就是直接返回当前结点的高度而已,单独写个函数,只是为了便于梳理逻辑结构,便于调用,也许大家这里就有问题了,我们每次都是获取当前结点里面的高度,但是怎么确保我们里面每个结点的高度信息都是准确的呢,为了我们每个结点高度信息的准确,所以我们每插入一个结点就得一层一层的更新结点的高度信息,因为建树过程是从无到有,我们最开始就慢慢维护好每个结点的高度,一旦变动我们就更新一下,不管是否需要,这样我们就可以保证准确性了,其实这个问题我们可以放在后面再来理解的。
OK,到了这里我们还有一个个非常重要的函数没有讲解,就是AVLTree,AVL树调整函数,里面了前面的逻辑结构我们现在就往下看:
//AVL树调整函数
//参数:根结点,插入结点
//返回:调整后的根结点
Tree AVLTree(Tree &root,Tree node)
{
int balance=0; //平衡因子
while (node!=NULL) //检查其祖先是否需要调整,更新
{
update_depth(node); //更新当前结点的高度信息
balance=is_balance(node); //获取当前结点的平衡因子情况
if (balance>1 || balance<-1) //平衡因子超标
{
if (balance>1) //左子树高
{
if (is_balance(node->lchild)>0) //LL型
node=LL_rotate(node);
else //LR型
node=LR_rotate(node);
}
else //右子树高
{
if (is_balance(node->rchild)<0) //RR型
node=RR_rotate(node);
else //RL型
node=RL_rotate(node);
}
if (node->parent==NULL) //到达根结点
{
root=node; //设置新的根结点
break; //退出
}
}
node=node->parent; //依次找到其父节点
}
return root; //返回新根
}
重要看到其真面目了,很惊讶的是,怎么这么短呢,其实我们把各个功能分开了,这样方便编写,不然很混乱,这里我们终于看到了我们的平衡因子,这里的平衡因子我们由树的高度得出,判断当前这个树是否平衡,那么我们只要得出这个树的左右子树的高度变可以判断这颗树是否平衡了,如果不平衡,那么我们就判断是4中类型的那种,然后进行相应操作即可了,代码里面的注释我觉得我还是写得很详细了,只要认真看,结合图解肯定是看得懂的。最后我们看到这里有个while循环,其实这个循环就是一层一层检查祖先是否平衡,以及更新他们的高度信息,这样我们就能维护好一颗树啦,注意根结点的父节点是为空的,这样我们最后便可以顺利的退出来啦。
这里的4种操作我在前面就给出来了,这里就不在重复给出来了,可以看看前面,注释很详细的。
到这里平衡二叉树的建树过程就完成了,只需平衡二叉树的查找函数很简单,这里就不在给出来,其实自己也没有写,当然这个可以完全自己写,平衡二叉树也是一颗BST树,BST的查找函数完全适用。
二、平衡二叉树的删除
前面我们说了平衡二叉树的建树过程,只要明白怎么旋转,以及怎么进行平衡的判断其实很简单的,不同的判断方法可能导致代码差别很大,所以选择好的判断方式还是很重要的。AVL树的删除操作其实比较简单的,因为这里我们以及有了调整函数,这样我们再删除的过程中如果一旦判断不平衡了,那么我们就通过平衡调整函数进行调整即可。平衡二叉树的删除方式和BST的删除方式是一样的,都是化繁为简,如果看到这里不知道BST怎么删除元素的可以参考这篇博客:BST的建立于删除
OK,我们这里假设大家已经会了BST的删除操作,我们直接进行AVL树的操作,先看一下删除函数:
//找到删除的结点,执行删除操作,并根据情况调整AVL树
//参数:根,需要删除的val
//返回:找到删除结点的情况则返回新根,否则返回NULL
Tree remove(Tree &root,ElementType val)
{
static Tree *temp=NULL;
if (root==NULL)
{
temp=NULL;
return NULL;
}
else if(root->val<val) //在右子树查找
remove(root->rchild, val);
else if(root->val>val) //在左子树查找
remove(root->lchild, val);
else //找到了,标记一下
temp=&root;
if (temp)
{
if (!root->parent) //如果已经返回到最后一次(也就是root是真正的树根)
{
Tree tmp=NULL;
tmp=remove_val(root,*temp); //执行删除操作
return AVLTree(root,tmp); //更新AVL树
}
return *temp;
}
return NULL;
}
OK,认真看还是很简单的,这里一直查找这个需要删除的结点,然后赋值给这个temp,这样我们再函数即将退出的时候,进行相应的判断操作,如果找了,那么我们调用一个删除函数,进行删除,删除后调整一下AVL树,注意这里的temp是个二级结构体指针,会引用需要删除的结点。
//删除操作
//参数:根,需要删除的结点
//返回值: 返回删除结点的父节点
Tree remove_val(Tree &root,Tree &node)
{
Tree parent=node->parent;
Tree temp=NULL;
//只有左孩子
if (node->rchild==NULL && node->lchild!=NULL)
{
temp=node;
node=node->lchild; //指向左孩子
node->parent=temp->parent;
delete temp; //释放结点
update_depth(node); //更新当前结点信息
}
else if(node->lchild==NULL && node->rchild!=NULL) //只有右孩子
{
temp=node;
node=node->rchild; //指向右结点
node->parent=temp->parent;
delete temp; //释放结点
update_depth(node); //更新当前结点信息
}
else if(node->rchild==NULL && node->lchild==NULL) //叶子结点
{
parent=node->parent; //找到其父节点
if (parent) //如果父节点存在
{
/*
if (parent->lchild==node)//当前结点是父节点的左孩子
{
parent->lchild=0; //删掉左孩子
delete node; //释放空间
}
else //当前结点是父节点的右孩子
{
parent->rchild=0;
delete node;
}
*/
delete node;
node=NULL;
update_depth(parent); //更新父节点高度信息
}
else //删除的是根
{
delete root;
root=NULL;
}
}
else //既有左孩子也有右孩子,化繁为简
{
Tree *tmp=Find_Min(node->rchild); //找到替代元素,temp为叶子结点
node->val=(*tmp)->val; //更新值
//判断当前叶子结点是左孩子还是右孩子。
parent=(*tmp)->parent;
/*
if (parent->lchild==temp)
{
parent->lchild=0;
delete temp;
}
else
{
parent->rchild=0;
delete temp;
}
*/
delete *tmp;
*tmp=NULL;
update_depth(parent);
}
return parent;
}这便是我们真正的删除函数,里面分了几种不同的情况,同时对于复杂的情况我们化繁为简,这里大家注意到,我们注释了一段代码,这是在开始的时候,我没有引用删除结点指针,这样需要通过父节点来进行操作,需要判断是父节点的左孩子还是右孩子,然后再进行相应的操作,后来为了统一,把Find_Min函数改为返回其引用结构,这样就可以不用判断了,这样变可以简化很多(这和BST里面是一样的),不过也极容易操作出错,而影响树结构,可以看看几种旋转操作,为了方便理解,没有改成这种结构。
OK到这里,我们就把二叉平衡树的删除操作说完了,相对来说只要旋转有了,那么删除也很简单了,只是细节处理稍微麻烦点,反正一旦处理了某个结点,那么一定要层层更新。维护好树结构。特别是删除操作。有可能最近祖先没有失衡,但是稍远的祖先确失衡了。至于删除的图解应该不用话出来了吧,后面我给出数据,然后自己可以在纸上画一下,看看是否正确。
看看main函数:
int main()
{
Tree root=NULL;
root = Insert(root, 16);
root = Insert(root, 3);
//插入7后LR调整
root = Insert(root, 7);
root = Insert(root, 11);
//插入9后LL调整
root = Insert(root, 9);
//插入26后RR调整
root = Insert(root, 26);
//插入28后RL调整
root = Insert(root, 18);
root = Insert(root, 14);
//插入15后LR调整
root = Insert(root, 15);
printf("插入:\n");
printf("前序:");
PreOrder(root); // 11 7 3 9 18 15 14 16 26
printf("\n");
printf("中序:");
InOrder(root); // 3 7 9 11 14 15 16 18 26
printf("\n");
printf("删除:\n");
//测试删除叶子结点
// remove(root, 16);
//测试删除只有左孩子的结点
// remove(root, 16);
// remove(root, 15);
//测试删除只有右孩子的结点
// remove(root, 14);
// remove(root, 15);
//测试删除有左右孩子的结点
// remove(root, 18);
//删除26后进行LR型调整
remove(root, 26);
//删除18后进行RR型
remove(root, 18);
remove(root, 3);
remove(root, 9);
//删除7过进行RL调整
remove(root, 7);
//删除11后进行LL调整
remove(root, 11);
//把结点删除完
// remove(root, 15);
// remove(root, 14);
// remove(root, 16);
printf("前序:");
PreOrder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("中序:");
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
前面的插入就不说了,只要说说删除,因为测试的时候,数据很重要,开始就是测试的不够好,导致错误代码混过去了,后来改正了,不过可能还是有bug,忘各位不吝指出。
//测试删除叶子结点
// remove(root, 16);
//测试删除只有左孩子的结点
// remove(root, 16);
// remove(root, 15);
//测试删除只有右孩子的结点
// remove(root, 14);
// remove(root, 15);
//测试删除有左右孩子的结点
// remove(root, 18);这几个测试点,是单独测试的,也就是它们之间是独立的,分别测试4种不同的情况,比如测试第二种的是否,请注释第一组和其它组,不过乱测试还是可以的,后面的旋转测试,是一步接着一步的,不是独立的。
OK,终于说完了,下面贴出全部代码,希望和大家一起学习,如果有问题,希望各位可以指出,谢谢啦。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct AVLNode *Tree;
typedef int ElementType;
struct AVLNode
{
int depth; //深度,这里计算每个结点的深度,通过深度的比较可得出是否平衡
Tree parent; //该结点的父节点,方便操作
ElementType val; //结点值
Tree lchild;
Tree rchild;
AVLNode(int val=0) //默认构造函数
{
parent=NULL;
depth=0;
lchild=rchild=NULL;
this->val=val;
}
};
Tree insert_val(Tree&,Tree,Tree);
Tree remove(Tree&,ElementType);
Tree remove_val(Tree &,Tree &);
void update_depth(Tree);
Tree AVLTree(Tree&,Tree);
Tree LL_rotate(Tree);
Tree RL_rotate(Tree);
Tree RR_rotate(Tree);
Tree LR_rotate(Tree);
int get_balance(Tree);
int is_balance(Tree);
Tree *Find_Min(Tree&);
//向AVL树中插入val
//参数:根,插入数据value
//返回:新根结点
Tree Insert(Tree &root,ElementType val)
{
Tree temp=NULL;
Tree node=new AVLNode(val);
//插入结点
temp=insert_val(root,node,NULL); //调用真正的插入函数
if (temp)
{
update_depth(temp);
root=AVLTree(root,temp); //检查树是否该调整
}
else //无需插入,释放结点
delete temp;
return root;
}
//插入函数
//参数:根节点,待插结点,待插结点的父节点
//返回:插入结点
Tree insert_val(Tree &root,Tree node,Tree parent)
{
if (root==NULL)
{
root=node;
node->parent=parent; //设置当前结点的父结点
return root; //返回插入结点
}
if (node->val<root->val) //插左子树
return insert_val(root->lchild, node,root);
else if(node->val>root->val) //插右子树
return insert_val(root->rchild, node,root);
else //已存在该结点,停止插入操作,返回NULL
return NULL;
}
//AVL树调整函数
//参数:根结点,插入结点
//返回:调整后的根结点
Tree AVLTree(Tree &root,Tree node)
{
int balance=0; //平衡因子
while (node!=NULL) //检查其祖先是否需要调整,更新
{
update_depth(node); //更新当前结点的高度信息
balance=is_balance(node); //获取当前结点的平衡因子情况
if (balance>1 || balance<-1) //平衡因子超标
{
if (balance>1) //左子树高
{
if (is_balance(node->lchild)>0) //LL型
node=LL_rotate(node);
else //LR型
node=LR_rotate(node);
}
else //右子树高
{
if (is_balance(node->rchild)<0) //RR型
node=RR_rotate(node);
else //RL型
node=RL_rotate(node);
}
if (node->parent==NULL) //到达根结点
{
root=node; //设置新的根结点
break; //退出
}
}
node=node->parent; //依次找到其父节点
}
return root; //返回新根
}
//查找最小结点
Tree *Find_Min(Tree &root)
{
if (root->lchild)
{
return Find_Min(root->lchild);
}
return &root;
}
//删除操作
//参数:根,需要删除的结点
//返回值: 返回删除结点的父节点
Tree remove_val(Tree &root,Tree &node)
{
Tree parent=node->parent;
Tree temp=NULL;
//只有左孩子
if (node->rchild==NULL && node->lchild!=NULL)
{
temp=node;
node=node->lchild; //指向左孩子
node->parent=temp->parent;
delete temp; //释放结点
update_depth(node); //更新当前结点信息
}
else if(node->lchild==NULL && node->rchild!=NULL) //只有右孩子
{
temp=node;
node=node->rchild; //指向右结点
node->parent=temp->parent;
delete temp; //释放结点
update_depth(node); //更新当前结点信息
}
else if(node->rchild==NULL && node->lchild==NULL) //叶子结点
{
parent=node->parent; //找到其父节点
if (parent) //如果父节点存在
{
/*
if (parent->lchild==node)//当前结点是父节点的左孩子
{
parent->lchild=0; //删掉左孩子
delete node; //释放空间
}
else //当前结点是父节点的右孩子
{
parent->rchild=0;
delete node;
}
*/
delete node;
node=NULL;
update_depth(parent); //更新父节点高度信息
}
else //删除的是根
{
delete root;
root=NULL;
}
}
else //既有左孩子也有右孩子,化繁为简
{
Tree *tmp=Find_Min(node->rchild); //找到替代元素,temp为叶子结点
node->val=(*tmp)->val; //更新值
//判断当前叶子结点是左孩子还是右孩子。
parent=(*tmp)->parent;
/*
if (parent->lchild==temp)
{
parent->lchild=0;
delete temp;
}
else
{
parent->rchild=0;
delete temp;
}
*/
delete *tmp;
*tmp=NULL;
update_depth(parent);
}
return parent;
}
//找到删除的结点,执行删除操作,并根据情况调整AVL树
//参数:根,需要删除的val
//返回:找到删除结点的情况则返回新根,否则返回NULL
Tree remove(Tree &root,ElementType val)
{
static Tree *temp=NULL;
if (root==NULL)
{
temp=NULL;
return NULL;
}
else if(root->val<val) //在右子树查找
remove(root->rchild, val);
else if(root->val>val) //在左子树查找
remove(root->lchild, val);
else //找到了,标记一下
temp=&root;
if (temp)
{
if (!root->parent) //如果已经返回到最后一次(也就是root是真正的树根)
{
Tree tmp=NULL;
tmp=remove_val(root,*temp); //执行删除操作
return AVLTree(root,tmp); //更新AVL树
}
return *temp;
}
return NULL;
}
//获取当前结点的深度
int get_balance(Tree node)
{
if (node==NULL)
return 0;
return node->depth;
}
//返回当前平衡因子
int is_balance(Tree node)
{
if (node==NULL)
return 0;
else
return get_balance(node->lchild)-get_balance(node->rchild);
}
//RR型调整函数
//返回新父节点
Tree RR_rotate(Tree node)
{
//node为离操作结点最近的失衡的结点
Tree parent=NULL,son;
//获取失衡结点的父节点
parent=node->parent;
//获取失衡结点的右孩子
son=node->rchild;
//设置son结点左孩子的父指针
if (son->lchild!=NULL)
son->lchild->parent=node;
//失衡结点的右孩子变更为son的左孩子
node->rchild=son->lchild;
//更新失衡结点的高度信息
update_depth(node);
//失衡结点变成son的左孩子
son->lchild=node;
//设置son的父结点为原失衡结点的父结点
son->parent=parent;
//如果失衡结点不是根结点,则开始更新父节点
if (parent!=NULL)
{
//如果父节点的左孩子是失衡结点,指向现在更新后的新孩子son
if (parent->lchild==node)
parent->lchild=son;
else //父节点的右孩子是失衡结点
parent->rchild=son;
}
//设置失衡结点的父亲
node->parent=son;
//更新son结点的高度信息
update_depth(son);
return son;
}
//LL型调整函数
//返回:新父节点
Tree LL_rotate(Tree node)
{
//node为离操作结点最近的失衡的结点
Tree parent=NULL,son;
//获取失衡结点的父节点
parent=node->parent;
//获取失衡结点的左孩子
son=node->lchild;
//设置son结点右孩子的父指针
if (son->rchild!=NULL)
son->rchild->parent=node;
//失衡结点的左孩子变更为son的右孩子
node->lchild=son->rchild;
//更新失衡结点的高度信息
update_depth(node);
//失衡结点变成son的右孩子
son->rchild=node;
//设置son的父结点为原失衡结点的父结点
son->parent=parent;
//如果失衡结点不是根结点,则开始更新父节点
if (parent!=NULL)
{
//如果父节点的左孩子是失衡结点,指向现在更新后的新孩子son
if (parent->lchild==node)
parent->lchild=son;
else //父节点的右孩子是失衡结点
parent->rchild=son;
}
//设置失衡结点的父亲
node->parent=son;
//更新son结点的高度信息
update_depth(son);
return son;
}
//LR型,先左旋转,再右旋转
//返回:新父节点
Tree LR_rotate(Tree node)
{
RR_rotate(node->lchild);
return LL_rotate(node);
}
//RL型,先右旋转,再左旋转
//返回:新父节点
Tree RL_rotate(Tree node)
{
LL_rotate(node->rchild);
return RR_rotate(node);
}
//更新当前深度
void update_depth(Tree node)
{
if (node==NULL)
return;
else
{
int depth_Lchild=get_balance(node->lchild); //左孩子深度
int depth_Rchild=get_balance(node->rchild); //右孩子深度
node->depth=max(depth_Lchild,depth_Rchild)+1;
}
}
//前序
void PreOrder(Tree root)
{
if (root==NULL)
return;
printf("%d ",root->val);
PreOrder(root->lchild);
PreOrder(root->rchild);
}
//中序
void InOrder(Tree root)
{
if (root==NULL)
return;
InOrder(root->lchild);
printf("%d ",root->val);
InOrder(root->rchild);
}
int main()
{
Tree root=NULL;
root = Insert(root, 16);
root = Insert(root, 3);
//插入7后LR调整
root = Insert(root, 7);
root = Insert(root, 11);
//插入9后LL调整
root = Insert(root, 9);
//插入26后RR调整
root = Insert(root, 26);
//插入28后RL调整
root = Insert(root, 18);
root = Insert(root, 14);
//插入15后LR调整
root = Insert(root, 15);
printf("插入:\n");
printf("前序:");
PreOrder(root); // 11 7 3 9 18 15 14 16 26
printf("\n");
printf("中序:");
InOrder(root); // 3 7 9 11 14 15 16 18 26
printf("\n");
printf("删除:\n");
//测试删除叶子结点
// remove(root, 16);
//测试删除只有左孩子的结点
// remove(root, 16);
// remove(root, 15);
//测试删除只有右孩子的结点
// remove(root, 14);
// remove(root, 15);
//测试删除有左右孩子的结点
// remove(root, 18);
//删除26后进行LR型调整
remove(root, 26);
//删除18后进行RR型
remove(root, 18);
remove(root, 3);
remove(root, 9);
//删除7过进行RL调整
remove(root, 7);
//删除11后进行LL调整
remove(root, 11);
//把结点删除完
// remove(root, 15);
// remove(root, 14);
// remove(root, 16);
printf("前序:");
PreOrder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("中序:");
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
程序我反复测试过,目前还没有发现问题,当然也是还存在bug,不管是代码还是思考过程,如果有问题,还希望各位不吝指教。感谢。
main函数太长
三、平衡树的3+4重构
平衡二叉树也是一颗BST树,那么BST的特点,平衡二叉树也应该具有,那么BST树又有什么特点呢,特点是有序,什么有序呢,中序遍历序列有序,也就是说BST树的中序序列是单调的,这个很容易就证明了,对根节点而已,其左子树的肯定比它本身要小,其右子树的值肯定比其值要大,而中序序列是左根右,所以BST树的中序序列肯定是单调的。这个是非常重要的性质,稍后我们将用到它。
我们设g(x)为最低的失衡结点,考察祖孙三代:g~p~v,按照中序遍历次序将其重命名为:a<b<c。
它们总共拥有互不相交的四颗(可能为空的)子树,按照中序遍历次序,将其重命名为:T0<T1<T2<T3。
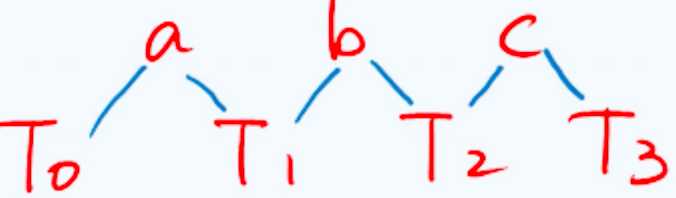
此时,如果我们依然按照中序的遍历次序将这两个序列混合起来,就可以得到一个长度为7的序列。在这个序列中三个结点a,b,c,必然是镶嵌于这4棵子树之间
实际上无论是哪种具体的情况,经过这样的重命名之后,按照中序遍历的次序,必然是从T0到a,再从a到T1,再从T1到b,然后从b到T2,再从T2到c,最终由c到T3,这就是BST单调性的体现
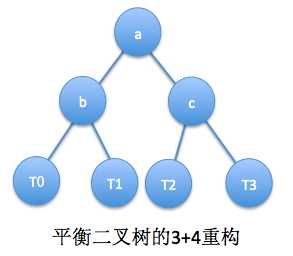
因此我们可以统一的将这三个顶点abc以及这4棵子树,按照下面的拓扑关系直接的拼接起来,这样的一种拼接是针对于三个结点,以及下属的4棵子树而言的,所以也称作3+4重构
无论是插入还是删除,无论是单旋还是双旋,最终的效果都应该是这样一种形式。
下面我们给出我们的3+4重构函数的代码:
//3+4重构函数
//参数:见分析
//返回:新根
Tree connect34(Tree &a,Tree &b,Tree &c,Tree &T0,Tree &T1,Tree &T2,Tree &T3)
{
a->lchild=T0;
if (T0)
T0->parent=a;
a->rchild=T1;
if(T1)
T1->parent=a;
update_depth(a);
c->lchild=T2;
if(T2)
T2->parent=c;
c->rchild=T3;
if(T3)
T3->parent=c;
update_depth(c);
b->lchild=a;
a->parent=b;
b->rchild=c;
c->parent=b;
update_depth(b);
return b;
}可以看见很简单,从此以后我们就不用各种旋转了,因此对于调整AVL树结构的函数,也需要改,不过我们就再原来的基础上调整一下就就可以了。
Tree rotateAt(Tree &root,Tree &node)
{
Tree son,temp;
Tree grandson;
int balance=0; //平衡因子
while (node!=NULL) //检查其祖先是否需要调整,更新
{
update_depth(node); //更新当前结点的高度信息
balance=is_balance(node); //获取当前结点的平衡因子情况
if (balance>1 || balance<-1) //平衡因子超标
{
if (balance>1) //左子树高
{
if (is_balance(node->lchild)>0) //LL型
{
//找祖孙三代,后面的类似
son=node->lchild; //找其左孩子
grandson=son->lchild; //找其左孩子的左孩子
son->parent=node->parent; //设置更新后的son的父节点
temp=node;
//重构
node=connect34(grandson, son, node, grandson->lchild, grandson->rchild, son->rchild, node->rchild);
setchild(son, temp, node);//设置son父节点的孩子为node
}
else //LR型
{
son=node->lchild;
grandson=son->rchild;
grandson->parent=node->parent;
temp=node;
node=connect34(son, grandson, node, son->lchild, grandson->lchild, grandson->rchild, node->rchild);
setchild(grandson, temp, node); //设置grandson父节点的孩子为node
}
}
else //右子树高
{
if (is_balance(node->rchild)<0) //RR型
{
son=node->rchild;
grandson=son->rchild;
son->parent=node->parent;
temp=node;
node=connect34(node, son, grandson, node->lchild, son->lchild, grandson->lchild, grandson->rchild);
setchild(son, temp, node); //设置son父节点的孩子为node
}
else //RL型
{
son=node->rchild;
grandson=son->lchild;
grandson->parent=node->parent;
temp=node;
node=connect34(node, grandson, son, node->lchild, grandson->lchild, grandson->rchild, son->rchild);
setchild(grandson, temp, node); //设置grandson父节点的孩子为node
}
}
if (node->parent==NULL) //到达根结点
{
root=node; //设置新的根结点
break; //退出
}
}
node=node->parent; //依次找到其父节点
}
return root; //返回新根
}额,看着好复杂的样子,其实仔细观察,不难看出,我们只是在原来的基础上删除了旋转操作,然后把3+4重构函数加了进来,在进行重构之前,首先需要找到abc,以及T0,T1,T2,T3,这个看一下程序就明白了,不够值得注意的是,要重新设置它们的连接关系,尤其是abc,后它们祖先的关系,这里还有一个setchild函数,就是用来连接abc和它们祖先的函数,abc的拓扑在变,也就是最后son可能就成parent了,所以需要更新son的父节点。
void setchild(Tree &g,Tree &temp,Tree &node)
{
if (g->parent)
{
if (g->parent->lchild==temp)
g->parent->lchild=node;
else
g->parent->rchild=node;
}
}OK,这就是setchild函数,到这里平衡二叉树的3+4重构就讲完了,简单吧,下面给出其总代码,测试方式同上面的旋转的平衡二叉树。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef struct AVLNode *Tree;
typedef int ElementType;
struct AVLNode
{
int depth; //深度,这里计算每个结点的深度,通过深度的比较可得出是否平衡
Tree parent; //该结点的父节点,方便操作
ElementType val; //结点值
Tree lchild;
Tree rchild;
AVLNode(int val=0) //默认构造函数
{
parent=NULL;
depth=0;
lchild=rchild=NULL;
this->val=val;
}
};
Tree insert_val(Tree&,Tree,Tree);
Tree remove(Tree&,ElementType);
Tree remove_val(Tree &,Tree &);
void update_depth(Tree);
int get_balance(Tree);
int is_balance(Tree);
Tree *Find_Min(Tree&);
Tree connect34(Tree&,Tree&,Tree&,Tree&,Tree&,Tree&,Tree&);
Tree rotateAt(Tree&,Tree&);
void setchild(Tree &,Tree &,Tree &);
//向AVL树中插入val
//参数:根,插入数据value
//返回:新根结点
Tree Insert(Tree &root,ElementType val)
{
Tree temp=NULL;
Tree node=new AVLNode(val);
//插入结点
temp=insert_val(root,node,NULL); //调用真正的插入函数
if (temp)
{
update_depth(temp);
root=rotateAt(root, temp);//检查树是否该调整
}
else //无需插入,释放结点
delete temp;
return root;
}
//插入函数
//参数:根节点,待插结点,待插结点的父节点
//返回:插入结点
Tree insert_val(Tree &root,Tree node,Tree parent)
{
if (root==NULL)
{
root=node;
node->parent=parent; //设置当前结点的父结点
return root; //返回插入结点
}
if (node->val<root->val) //插左子树
return insert_val(root->lchild, node,root);
else if(node->val>root->val) //插右子树
return insert_val(root->rchild, node,root);
else //已存在该结点,停止插入操作,返回NULL
return NULL;
}
//3+4重构函数
//参数:见分析
//返回:新根
Tree connect34(Tree &a,Tree &b,Tree &c,Tree &T0,Tree &T1,Tree &T2,Tree &T3)
{
a->lchild=T0;
if (T0)
T0->parent=a;
a->rchild=T1;
if(T1)
T1->parent=a;
update_depth(a);
c->lchild=T2;
if(T2)
T2->parent=c;
c->rchild=T3;
if(T3)
T3->parent=c;
update_depth(c);
b->lchild=a;
a->parent=b;
b->rchild=c;
c->parent=b;
update_depth(b);
return b;
}
Tree rotateAt(Tree &root,Tree &node)
{
Tree son,temp;
Tree grandson;
int balance=0; //平衡因子
while (node!=NULL) //检查其祖先是否需要调整,更新
{
update_depth(node); //更新当前结点的高度信息
balance=is_balance(node); //获取当前结点的平衡因子情况
if (balance>1 || balance<-1) //平衡因子超标
{
if (balance>1) //左子树高
{
if (is_balance(node->lchild)>0) //LL型
{
//找祖孙三代,后面的类似
son=node->lchild; //找其左孩子
grandson=son->lchild; //找其左孩子的左孩子
son->parent=node->parent; //设置更新后的son的父节点
temp=node;
//重构
node=connect34(grandson, son, node, grandson->lchild, grandson->rchild, son->rchild, node->rchild);
setchild(son, temp, node);//设置son父节点的孩子为node
}
else //LR型
{
son=node->lchild;
grandson=son->rchild;
grandson->parent=node->parent;
temp=node;
node=connect34(son, grandson, node, son->lchild, grandson->lchild, grandson->rchild, node->rchild);
setchild(grandson, temp, node); //设置grandson父节点的孩子为node
}
}
else //右子树高
{
if (is_balance(node->rchild)<0) //RR型
{
son=node->rchild;
grandson=son->rchild;
son->parent=node->parent;
temp=node;
node=connect34(node, son, grandson, node->lchild, son->lchild, grandson->lchild, grandson->rchild);
setchild(son, temp, node); //设置son父节点的孩子为node
}
else //RL型
{
son=node->rchild;
grandson=son->lchild;
grandson->parent=node->parent;
temp=node;
node=connect34(node, grandson, son, node->lchild, grandson->lchild, grandson->rchild, son->rchild);
setchild(grandson, temp, node); //设置grandson父节点的孩子为node
}
}
if (node->parent==NULL) //到达根结点
{
root=node; //设置新的根结点
break; //退出
}
}
node=node->parent; //依次找到其父节点
}
return root; //返回新根
}
void setchild(Tree &g,Tree &temp,Tree &node)
{
if (g->parent)
{
if (g->parent->lchild==temp)
g->parent->lchild=node;
else
g->parent->rchild=node;
}
}
//查找最小结点
Tree *Find_Min(Tree &root)
{
if (root->lchild)
{
return Find_Min(root->lchild);
}
return &root;
}
//删除操作
//参数:根,需要删除的结点
//返回值: 返回删除结点的父节点
Tree remove_val(Tree &root,Tree &node)
{
Tree parent=node->parent;
Tree temp=NULL;
//只有左孩子
if (node->rchild==NULL && node->lchild!=NULL)
{
temp=node;
node=node->lchild; //指向左孩子
node->parent=temp->parent;
delete temp; //释放结点
update_depth(node); //更新当前结点信息
}
else if(node->lchild==NULL && node->rchild!=NULL) //只有右孩子
{
temp=node;
node=node->rchild; //指向右结点
node->parent=temp->parent;
delete temp; //释放结点
update_depth(node); //更新当前结点信息
}
else if(node->rchild==NULL && node->lchild==NULL) //叶子结点
{
parent=node->parent; //找到其父节点
if (parent) //如果父节点存在
{
delete node;
node=NULL;
update_depth(parent); //更新父节点高度信息
}
else //删除的是根
{
delete root;
root=NULL;
}
}
else //既有左孩子也有右孩子,化繁为简
{
Tree *tmp=Find_Min(node->rchild); //找到替代元素,temp为叶子结点
node->val=(*tmp)->val; //更新值
//判断当前叶子结点是左孩子还是右孩子。
parent=(*tmp)->parent;
delete *tmp;
*tmp=NULL;
update_depth(parent);
}
return parent;
}
//找到删除的结点,执行删除操作,并根据情况调整AVL树
//参数:根,需要删除的val
//返回:找到删除结点的情况则返回新根,否则返回NULL
Tree remove(Tree &root,ElementType val)
{
static Tree *temp=NULL;
if (root==NULL)
{
temp=NULL;
return NULL;
}
else if(root->val<val) //在右子树查找
remove(root->rchild, val);
else if(root->val>val) //在左子树查找
remove(root->lchild, val);
else //找到了,标记一下
temp=&root;
if (temp)
{
if (!root->parent) //如果已经返回到最后一次(也就是root是真正的树根)
{
Tree tmp=NULL;
tmp=remove_val(root,*temp); //执行删除操作
return rotateAt(root, tmp);
}
return *temp;
}
return NULL;
}
//获取当前结点的深度
int get_balance(Tree node)
{
if (node==NULL)
return 0;
return node->depth;
}
//返回当前平衡因子
int is_balance(Tree node)
{
if (node==NULL)
return 0;
else
return get_balance(node->lchild)-get_balance(node->rchild);
}
//更新当前深度
void update_depth(Tree node)
{
if (node==NULL)
return;
else
{
int depth_Lchild=get_balance(node->lchild); //左孩子深度
int depth_Rchild=get_balance(node->rchild); //右孩子深度
node->depth=max(depth_Lchild,depth_Rchild)+1;
}
}
//前序
void PreOrder(Tree root)
{
if (root==NULL)
return;
printf("%d ",root->val);
PreOrder(root->lchild);
PreOrder(root->rchild);
}
//中序
void InOrder(Tree root)
{
if (root==NULL)
return;
InOrder(root->lchild);
printf("%d ",root->val);
InOrder(root->rchild);
}
int main()
{
Tree root=NULL;
root = Insert(root, 16);
root = Insert(root, 3);
//插入7后LR调整
root = Insert(root, 7);
root = Insert(root, 11);
//插入9后LL调整
root = Insert(root, 9);
//插入26后RR调整
root = Insert(root, 26);
//插入18后RL调整
root = Insert(root, 18);
root = Insert(root, 14);
//插入15后LR调整
root = Insert(root, 15);
printf("插入:\n");
printf("前序:");
PreOrder(root); // 11 7 3 9 18 15 14 16 26
printf("\n");
printf("中序:");
InOrder(root); // 3 7 9 11 14 15 16 18 26
printf("\n");
printf("删除:\n");
//测试删除叶子结点
// remove(root, 16);
//测试删除只有左孩子的结点
// remove(root, 16);
// remove(root, 15);
//测试删除只有右孩子的结点
// remove(root, 14);
// remove(root, 15);
//测试删除有左右孩子的结点
// remove(root, 18);
//删除26后进行LR型调整
remove(root, 26);
//删除18后进行RR型
remove(root, 18);
remove(root, 3);
remove(root, 9);
//删除7过进行RL调整
remove(root, 7);
//删除11后进行LL调整
remove(root, 11);
//把结点删除完
// remove(root, 15);
// remove(root, 14);
// remove(root, 16);
printf("前序:");
PreOrder(root);
printf("\n");
printf("中序:");
InOrder(root);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
程序我反复测试过,目前还没有发现问题,当然也是还存在bug,不管是代码还是思考过程,如果有问题,还希望各位不吝指教。感谢。
注:程序中大量使用了引用和指针,如果对指针有疑惑的可以参考C语言指针初探
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/35839.html