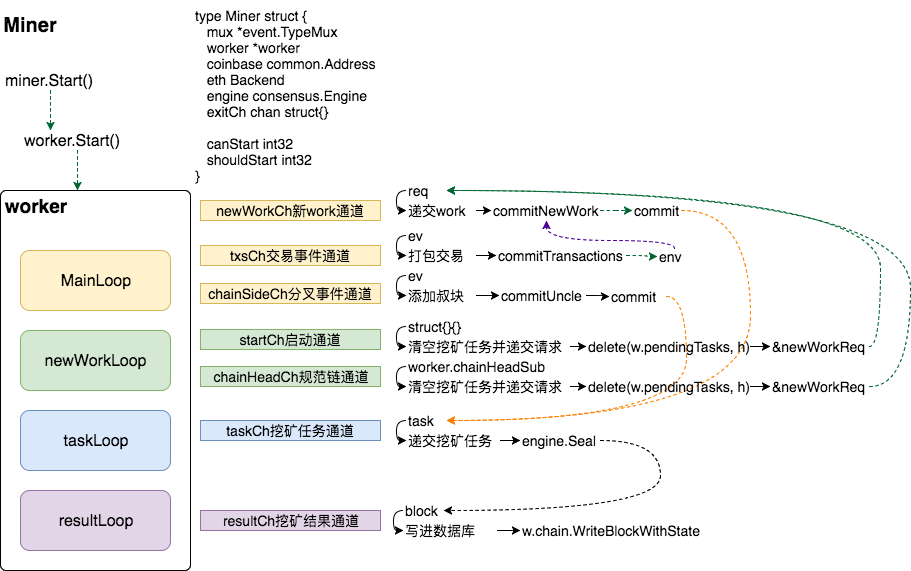
最新的以太坊源码Miner模块有较大的改动,取消了原来的agent模块以及work对象,但是基本上的逻辑还是一样的。Miner模块的主要执行部分在worker中,Miner对象及其方法主要控制着模块的开关和外部接口。
一、Miner模块
type Miner struct {
mux *event.TypeMux
worker *worker
coinbase common.Address
eth Backend
engine consensus.Engine
exitCh chan struct{}
canStart int32 // can start indicates whether we can start the mining operation
shouldStart int32 // should start indicates whether we should start after sync
}1)worker:worker模块,用于支持主要的挖矿流程;
2)coinbase:矿工地址;
3)eth:以太坊命令终端;
4)engine:共识引擎;
5)canStart、shouldStart:两个调控Miner模块是否运行的开关。
miner.update()方法监听downloader事件,控制着canStart和shouldStart这两个开关,用于抵挡DOS攻击。
1、当监听到downloader的StartEvent事件时,canStart设置为0,表示downloader同步时不可进行挖矿,如果正在挖矿(miner.mining == ture),停止挖矿,同时将shouldStart设置为1,以便下次直接开始挖矿;
2、当监听到downloader的DoneEvent事件或者FailedEvent事件,判断shouldStart是否打开。如果是打开的,则再打开canStart,将shouldStart关闭。此时,将挖矿的控制权完全交给miner.Start()方法。
func (self *Miner) update() {
events := self.mux.Subscribe(downloader.StartEvent{}, downloader.DoneEvent{}, downloader.FailedEvent{})
defer events.Unsubscribe()
for {
select {
case ev := <-events.Chan():
if ev == nil {
return
}
switch ev.Data.(type) {
case downloader.StartEvent:
atomic.StoreInt32(&self.canStart, 0)
if self.Mining() {
self.Stop()
atomic.StoreInt32(&self.shouldStart, 1)
log.Info("Mining aborted due to sync")
}
case downloader.DoneEvent, downloader.FailedEvent:
shouldStart := atomic.LoadInt32(&self.shouldStart) == 1
atomic.StoreInt32(&self.canStart, 1)
atomic.StoreInt32(&self.shouldStart, 0)
if shouldStart {
self.Start(self.coinbase)
}
// stop immediately and ignore all further pending events
return
}
case <-self.exitCh:
return
}
}
}Miner的启动也很简单,打开shouldStart,设置coinbase,然后启动worker。
func (self *Miner) Start(coinbase common.Address) {
atomic.StoreInt32(&self.shouldStart, 1)
self.SetEtherbase(coinbase)
if atomic.LoadInt32(&self.canStart) == 0 {
log.Info("Network syncing, will start miner afterwards")
return
}
self.worker.start()
}二、Worker模块
先来看看Worker的数据结构比较重要的东西:
type worker struct {
engine consensus.Engine // 公式引擎
eth Backend // 以太坊终端
chain *core.BlockChain // 区块链对象
gasFloor uint64
gasCeil uint64
// Subscriptions
mux *event.TypeMux
txsCh chan core.NewTxsEvent // 交易池更新事件
txsSub event.Subscription
chainHeadCh chan core.ChainHeadEvent // 区块头更新事件
chainHeadSub event.Subscription
chainSideCh chan core.ChainSideEvent // 区块链分叉事件
chainSideSub event.Subscription
// Channels
newWorkCh chan *newWorkReq
taskCh chan *task
resultCh chan *types.Block
startCh chan struct{}
exitCh chan struct{}
resubmitIntervalCh chan time.Duration
resubmitAdjustCh chan *intervalAdjust
current *environment // 当前挖矿生命周期的执行环境
localUncles map[common.Hash]*types.Block // 本地分叉区块作为潜在叔块
remoteUncles map[common.Hash]*types.Block // 分叉区块中潜在的叔块
unconfirmed *unconfirmedBlocks // 本地产生但尚未被确认的区块
mu sync.RWMutex // The lock used to protect the coinbase and extra fields
coinbase common.Address
extra []byte
pendingMu sync.RWMutex
pendingTasks map[common.Hash]*task // 挖矿任务map
snapshotMu sync.RWMutex
snapshotBlock *types.Block // 快照的区块
snapshotState *state.StateDB // 快照的状态
// atomic status counters
running int32 // 判断共识引擎是否启动
newTxs int32 // 记录上次递交任务后新来的区块数量
}在初始化miner的时候就会新建worker,即调用newWorker()函数。该函数首先配置了worker对象,然后订阅交易池事件、规范链更新事件和分叉事件。最后启动了4个goroutine。
func newWorker(config *params.ChainConfig, engine consensus.Engine, eth Backend, mux *event.TypeMux, recommit time.Duration, gasFloor, gasCeil uint64, isLocalBlock func(*types.Block) bool) *worker {
worker := &worker{
...
}
worker.txsSub = eth.TxPool().SubscribeNewTxsEvent(worker.txsCh)
worker.chainHeadSub = eth.BlockChain().SubscribeChainHeadEvent(worker.chainHeadCh)
worker.chainSideSub = eth.BlockChain().SubscribeChainSideEvent(worker.chainSideCh)
// Sanitize recommit interval if the user-specified one is too short.
if recommit < minRecommitInterval {
log.Warn("Sanitizing miner recommit interval", "provided", recommit, "updated", minRecommitInterval)
recommit = minRecommitInterval
}
go worker.mainLoop()
go worker.newWorkLoop(recommit)
go worker.resultLoop()
go worker.taskLoop()
// Submit first work to initialize pending state.
worker.startCh <- struct{}{}
return worker
}最后通过向startCh中传入一个struct{}{},直接进入newWorkLoop的逻辑。
newWorkLoop
newWorkLoop主要监听两个重要的通道,一个是startCh通道,一个是chainHeadCh,这两个通道均用于清理特定父区块的pending tasks列表,然后递交基于父区块的挖矿task)。区别在于startCh通道启动是基于当前的currentBlock,而chainHeadCh是基于新传来的区块头。
func (w *worker) newWorkLoop(recommit time.Duration) {
var (
interrupt *int32
minRecommit = recommit // minimal resubmit interval specified by user.
timestamp int64 // timestamp for each round of mining.
)
timer := time.NewTimer(0)
<-timer.C // discard the initial tick
// commit aborts in-flight transaction execution with given signal and resubmits a new one.
commit := func(noempty bool, s int32) {
if interrupt != nil {
atomic.StoreInt32(interrupt, s)
}
interrupt = new(int32)
w.newWorkCh <- &newWorkReq{interrupt: interrupt, noempty: noempty, timestamp: timestamp}
timer.Reset(recommit)
atomic.StoreInt32(&w.newTxs, 0)
}
...
// clearPending cleans the stale pending tasks.
clearPending := func(number uint64) {
w.pendingMu.Lock()
for h, t := range w.pendingTasks {
if t.block.NumberU64()+staleThreshold <= number {
delete(w.pendingTasks, h)
}
}
w.pendingMu.Unlock()
}
for {
select {
case <-w.startCh:
clearPending(w.chain.CurrentBlock().NumberU64())
timestamp = time.Now().Unix()
commit(false, commitInterruptNewHead)
case head := <-w.chainHeadCh:
clearPending(head.Block.NumberU64())
timestamp = time.Now().Unix()
commit(false, commitInterruptNewHead)清理残留挖矿任务后,就要构建新的挖矿任务,这时候调用commit函数,构建一个newWorkReq对象,传入newWorkCh通道,进入MainLoop协程。MainLoop()监听三个重要的通道,newWorkCh(新work请求通道)、txsCh(交易池更新事件通道)以及chainSideCh(区块链分叉事件通道)。
MainLoop:
for {
select {
// task1:直接启动commitNewWork,进一步递交挖矿task
case req := <-w.newWorkCh:
w.commitNewWork(req.interrupt, req.noempty, req.timestamp)
// task2:出现分叉后,处理叔块
case ev := <-w.chainSideCh:
// 检验该hash的区块是否已经被当做潜在叔块,如果是,则忽略
if _, exist := w.localUncles[ev.Block.Hash()]; exist {
continue
}
if _, exist := w.remoteUncles[ev.Block.Hash()]; exist {
continue
}
// 将该区块作为潜在叔块加入叔块map,key为该区块的矿工地址
if w.isLocalBlock != nil && w.isLocalBlock(ev.Block) {
w.localUncles[ev.Block.Hash()] = ev.Block
} else {
w.remoteUncles[ev.Block.Hash()] = ev.Block
}
// 如果我们正在mining的区块少于两个uncles,则添加新的uncles并重新生成mining block
if w.isRunning() && w.current != nil && w.current.uncles.Cardinality() < 2 {
start := time.Now()
if err := w.commitUncle(w.current, ev.Block.Header()); err == nil {
var uncles []*types.Header
w.current.uncles.Each(func(item interface{}) bool {
hash, ok := item.(common.Hash)
if !ok {
return false
}
uncle, exist := w.localUncles[hash]
if !exist {
uncle, exist = w.remoteUncles[hash]
}
if !exist {
return false
}
uncles = append(uncles, uncle.Header())
return false
})
w.commit(uncles, nil, true, start)
}
}
// task3:交易池更新后
case ev := <-w.txsCh:
// 待挖矿停止,执行该交易并更新世界状态
// 如果该交易与正在mining的交易不连续,则直接忽略
if !w.isRunning() && w.current != nil {
w.mu.RLock()
coinbase := w.coinbase
w.mu.RUnlock()
txs := make(map[common.Address]types.Transactions)
for _, tx := range ev.Txs {
acc, _ := types.Sender(w.current.signer, tx)
txs[acc] = append(txs[acc], tx)
}
txset := types.NewTransactionsByPriceAndNonce(w.current.signer, txs)
w.commitTransactions(txset, coinbase, nil)
w.updateSnapshot()
} else {
// If we're mining, but nothing is being processed, wake on new transactions
if w.config.Clique != nil && w.config.Clique.Period == 0 {
w.commitNewWork(nil, false, time.Now().Unix())
}
}
atomic.AddInt32(&w.newTxs, int32(len(ev.Txs)))接着上面的的流程,newWorkCh通道传出req后,直接启动了commitNewWork()函数。
commitNewWork()函数的主要功能是递交一个新的task:
1)初始化一个新区块头给待挖矿的区块
2)为当前挖矿周期初始化一个工作环境work
3)获取交易池中每个账户地址的交易列表中的第一个交易后排序,然后应用这些交易
4)获取两个叔块
6)将区块递交给commit,用于生成task
7)更新状态快照,供前端查询
func (w *worker) commitNewWork(interrupt *int32, noempty bool, timestamp int64) {
w.mu.RLock()
defer w.mu.RUnlock()
tstart := time.Now()
parent := w.chain.CurrentBlock()
// 如果父区块的时间比现在的时间还大,将当前时间设置为父区块时间+1
if parent.Time().Cmp(new(big.Int).SetInt64(timestamp)) >= 0 {
timestamp = parent.Time().Int64() + 1
}
// 如果父区块时间大于本地时间,就等一会
if now := time.Now().Unix(); timestamp > now+1 {
wait := time.Duration(timestamp-now) * time.Second
log.Info("Mining too far in the future", "wait", common.PrettyDuration(wait))
time.Sleep(wait)
}
// task1:初始化区块头给待挖矿的区块,调用core.CalcGasLimit方法,计算gas限额
// 如果父区块使用的gas大于父区块gasLimit的2/3,那么当前区块的gasLimit就会增加
num := parent.Number()
header := &types.Header{
ParentHash: parent.Hash(),
Number: num.Add(num, common.Big1),
GasLimit: core.CalcGasLimit(parent, w.gasFloor, w.gasCeil),
Extra: w.extra,
Time: big.NewInt(timestamp),
}
// 共识引擎启动后才能设置coinbase到区块头 (avoid spurious block rewards)
if w.isRunning() {
if w.coinbase == (common.Address{}) {
log.Error("Refusing to mine without etherbase")
return
}
header.Coinbase = w.coinbase
}
// 计算挖矿难度值
if err := w.engine.Prepare(w.chain, header); err != nil {
log.Error("Failed to prepare header for mining", "err", err)
return
}
// 处理DAO事件分叉
if daoBlock := w.config.DAOForkBlock; daoBlock != nil {
...
}
// task2:设置当前任务的environment,其中获取了7个ancestors和与之直接相连的familily
err := w.makeCurrent(parent, header)
if err != nil {
log.Error("Failed to create mining context", "err", err)
return
}
// 创建当前work task
env := w.current
if w.config.DAOForkSupport && w.config.DAOForkBlock != nil && w.config.DAOForkBlock.Cmp(header.Number) == 0 {
misc.ApplyDAOHardFork(env.state)
}
// task3:添加两个叔块到当前mining block中
uncles := make([]*types.Header, 0, 2)
commitUncles := func(blocks map[common.Hash]*types.Block) {
// 先清除之前的uncle
for hash, uncle := range blocks {
if uncle.NumberU64()+staleThreshold <= header.Number.Uint64() {
delete(blocks, hash)
}
}
for hash, uncle := range blocks {
if len(uncles) == 2 {
break
}
if err := w.commitUncle(env, uncle.Header()); err != nil {
log.Trace("Possible uncle rejected", "hash", hash, "reason", err)
} else {
log.Debug("Committing new uncle to block", "hash", hash)
uncles = append(uncles, uncle.Header())
}
}
}
// 优先选择本地叔块
commitUncles(w.localUncles)
commitUncles(w.remoteUncles)
if !noempty {
// 如果noempty参数为false,根据临时复制状态创建一个空块,以便在不等待块执行完成的情况下提前创建block
w.commit(uncles, nil, false, tstart)
}
// task4:从交易池pending列表中向区块中添加可用的交易
pending, err := w.eth.TxPool().Pending()
if err != nil {
log.Error("Failed to fetch pending transactions", "err", err)
return
}
// 如果没有可用的交易,更新一下状态快照
if len(pending) == 0 {
w.updateSnapshot()
return
}
// 将交易分为local和remote,分别执行commitTransaction,将交易执行并传入block
localTxs, remoteTxs := make(map[common.Address]types.Transactions), pending
for _, account := range w.eth.TxPool().Locals() {
if txs := remoteTxs[account]; len(txs) > 0 {
delete(remoteTxs, account)
localTxs[account] = txs
}
}
if len(localTxs) > 0 {
txs := types.NewTransactionsByPriceAndNonce(w.current.signer, localTxs)
if w.commitTransactions(txs, w.coinbase, interrupt) {
return
}
}
if len(remoteTxs) > 0 {
txs := types.NewTransactionsByPriceAndNonce(w.current.signer, remoteTxs)
if w.commitTransactions(txs, w.coinbase, interrupt) {
return
}
}
// task5:递交
w.commit(uncles, w.fullTaskHook, true, tstart)
}
最后是commit方法计算挖矿奖励,更新block,将上面生成的block递交到一个挖矿task,最后将task传入taskCh通道。
func (w *worker) commit(uncles []*types.Header, interval func(), update bool, start time.Time) error {
// Deep copy receipts here to avoid interaction between different tasks.
receipts := make([]*types.Receipt, len(w.current.receipts))
for i, l := range w.current.receipts {
receipts[i] = new(types.Receipt)
*receipts[i] = *l
}
s := w.current.state.Copy()
// 计算挖矿奖励(包括叔块奖励)
block, err := w.engine.Finalize(w.chain, w.current.header, s, w.current.txs, uncles, w.current.receipts)
if err != nil {
return err
}
if w.isRunning() {
if interval != nil {
interval()
}
select {
// 生成task,传入taskCh通道
case w.taskCh <- &task{receipts: receipts, state: s, block: block, createdAt: time.Now()}:
w.unconfirmed.Shift(block.NumberU64() - 1)
feesWei := new(big.Int)
for i, tx := range block.Transactions() {
feesWei.Add(feesWei, new(big.Int).Mul(new(big.Int).SetUint64(receipts[i].GasUsed), tx.GasPrice()))
}
feesEth := new(big.Float).Quo(new(big.Float).SetInt(feesWei), new(big.Float).SetInt(big.NewInt(params.Ether)))
log.Info("Commit new mining work", "number", block.Number(), "sealhash", w.engine.SealHash(block.Header()),
"uncles", len(uncles), "txs", w.current.tcount, "gas", block.GasUsed(), "fees", feesEth, "elapsed", common.PrettyDuration(time.Since(start)))
case <-w.exitCh:
log.Info("Worker has exited")
}
}
if update {
w.updateSnapshot()
}
return nil
}
taskLoop
task进入taskLoop后,被加入pendingTasks列表:
case task := <-w.taskCh:
if w.newTaskHook != nil {
w.newTaskHook(task)
}
// 计算header数据的RLP hash值,判断是否有相同的块已经在挖矿中了,如果是则放弃;如果不是,则终止之前的挖矿
sealHash := w.engine.SealHash(task.block.Header())
if sealHash == prev {
continue
}
// Interrupt previous sealing operation
interrupt()
stopCh, prev = make(chan struct{}), sealHash
if w.skipSealHook != nil && w.skipSealHook(task) {
continue
}
w.pendingMu.Lock()
w.pendingTasks[w.engine.SealHash(task.block.Header())] = task
w.pendingMu.Unlock()
// 最后执行挖矿,结果会通过resultCh传入resultLoop
if err := w.engine.Seal(w.chain, task.block, w.resultCh, stopCh); err != nil {
log.Warn("Block sealing failed", "err", err)
}resultLoop
最后是resultLoop,挖矿结果传入resultLoop,先从pendingTasks列表中取出刚执行挖矿的task,更新收据日志中的blockHash。然后将区块存入数据库,最后将区块广播出去。
func (w *worker) resultLoop() {
for {
select {
case block := <-w.resultCh:
// Short circuit when receiving empty result.
if block == nil {
continue
}
// Short circuit when receiving duplicate result caused by resubmitting.
if w.chain.HasBlock(block.Hash(), block.NumberU64()) {
continue
}
var (
sealhash = w.engine.SealHash(block.Header())
hash = block.Hash()
)
w.pendingMu.RLock()
task, exist := w.pendingTasks[sealhash]
w.pendingMu.RUnlock()
if !exist {
log.Error("Block found but no relative pending task", "number", block.Number(), "sealhash", sealhash, "hash", hash)
continue
}
// Different block could share same sealhash, deep copy here to prevent write-write conflict.
var (
receipts = make([]*types.Receipt, len(task.receipts))
logs []*types.Log
)
for i, receipt := range task.receipts {
receipts[i] = new(types.Receipt)
*receipts[i] = *receipt
// Update the block hash in all logs since it is now available and not when the
// receipt/log of individual transactions were created.
for _, log := range receipt.Logs {
log.BlockHash = hash
}
logs = append(logs, receipt.Logs...)
}
// Commit block and state to database.
stat, err := w.chain.WriteBlockWithState(block, receipts, task.state)
if err != nil {
log.Error("Failed writing block to chain", "err", err)
continue
}
log.Info("Successfully sealed new block", "number", block.Number(), "sealhash", sealhash, "hash", hash,
"elapsed", common.PrettyDuration(time.Since(task.createdAt)))
// Broadcast the block and announce chain insertion event
w.mux.Post(core.NewMinedBlockEvent{Block: block})
var events []interface{}
switch stat {
case core.CanonStatTy:
events = append(events, core.ChainEvent{Block: block, Hash: block.Hash(), Logs: logs})
events = append(events, core.ChainHeadEvent{Block: block})
case core.SideStatTy:
events = append(events, core.ChainSideEvent{Block: block})
}
w.chain.PostChainEvents(events, logs)
// Insert the block into the set of pending ones to resultLoop for confirmations
w.unconfirmed.Insert(block.NumberU64(), block.Hash())
case <-w.exitCh:
return
}
}
}三、其他函数中一些值得注意的函数
1、commitTransaction
a)gasPool的设置
w.current.gasPool = new(core.GasPool).AddGas(w.current.header.GasLimit)b)进入交易执行循环
交易执行的过程中有三种情况会被打断:(1)交易还在执行,但是新的区块已经经过广播到达本地,interrupt信号为1;(2)worker start或者restart,interrupt信号为1;(3)worker重新构造区块,包含了新到的交易,interrupt信号为2。
对于前两种,worker的本次执行就会终止,但对于第三种情况,本次执行依然会被递交到consensus engine。
c)如果区块工作环境剩余gas小于21000,则退出循环;否则从排好序的列表里取出交易;
if w.current.gasPool.Gas() < params.TxGas {
log.Trace("Not enough gas for further transactions", "have", w.current.gasPool, "want", params.TxGas)
break
}
// Retrieve the next transaction and abort if all done
tx := txs.Peek()
if tx == nil {
break
}d)执行交易并处理错误
// 首先准备当前世界状态
w.current.state.Prepare(tx.Hash(), common.Hash{}, w.current.tcount)
// 使用commitTransaction去调用交易执行的方法core.ApplyTransaction,得到收据并放入当前执行环境
logs, err := w.commitTransaction(tx, coinbase)
switch err {
case core.ErrGasLimitReached:
// gasPool不够执行交易,则将当前交易从txs中移除
log.Trace("Gas limit exceeded for current block", "sender", from)
txs.Pop()
case core.ErrNonceTooLow:
// 交易nonce太低,则取下一个交易替换处理列表中的第一个交易
log.Trace("Skipping transaction with low nonce", "sender", from, "nonce", tx.Nonce())
txs.Shift()
case core.ErrNonceTooHigh:
// 交易Nonce太高,则将当前交易从txs列表中移除
log.Trace("Skipping account with hight nonce", "sender", from, "nonce", tx.Nonce())
txs.Pop()
case nil:
// 一切正常,收集日志,统计执行成功的交易技术
coalescedLogs = append(coalescedLogs, logs...)
w.current.tcount++
txs.Shift()
default:
// Strange error, 如果当前交易发送者账户里还有交易,则取下一个交易替换列表中第一个交易,重新排序
log.Debug("Transaction failed, account skipped", "hash", tx.Hash(), "err", err)
txs.Shift()
}
今天的文章以太坊imtoken_mc源代码公开分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/88146.html