欢迎关注:glmapper_2018
引言
先来看下nginx在web服务器排名上的趋势:

存在即合理,那为什么要使用nginx呢?这得看看nginx能帮我们做些什么。
首先,nginx能做反向代理【关于反向代理和正向代理此处不做说明了,感兴趣的小伙伴自行谷歌】;比方说,我想在本地使用 www.glmapper1.com 的域名去访问www.taobao.com。那么这个时候我们就可以通过nginx去实现。
再者,nginx能实现负载均衡,什么是负载均衡呢?就是说应用部署在不同的服务器上,但是通过统一的域名进入,nginx则对请求进行分发,将请求分发到不同的服务器上去处理,这样就可以有效的减轻了单台服务器的压力。
在上面这两种情况下,nginx服务器的作用都只是作为分发服务器,真正的内容,我们可以放在其他的服务器上,这样来,还能起到一层安全隔壁的作用,nginx作为隔离层。
解决跨域问题
同源:URL由协议、域名、端口和路径组成,如果两个URL的协议、域名和端口相同,则表示他们同源。
浏览器的同源策略:浏览器的同源策略,限制了来自不同源的”document”或脚本,对当前”document”读取或设置某些属性。从一个域上加载的脚本不允许访问另外一个域的文档属性。
因为nginx和tomcat不能共用同一端口,url一样,端口不同,这样就会有跨域问题。
PS:点到为止,这里本次测试没有涉及,就不妄自菲薄了!!!
配置文件解析
配置文件主要由四部分组成:
- main(全区设置)
- server(主机配置)
- http(控制着nginx http处理的所有核心特性)
- location(URL匹配特定位置设置)。
- upstream(负载均衡服务器设置)
下面以默认的配置文件来说明下具体的配置文件属性含义:
#Nginx的worker进程运行用户以及用户组
#user nobody;
#Nginx开启的进程数
worker_processes 1;
#定义全局错误日志定义类型,[debug|info|notice|warn|crit]
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#指定进程ID存储文件位置
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
#事件配置
events {
#use [ kqueue | rtsig | epoll | /dev/poll | select | poll ];
#epoll模型是Linux内核中的高性能网络I/O模型,如果在mac上面,就用kqueue模型。
use kqueue;
#每个进程可以处理的最大连接数,理论上每台nginx服务器的最大连接数为worker_processes*worker_connections。理论值:worker_rlimit_nofile/worker_processes
worker_connections 1024;
}
#http参数
http {
#文件扩展名与文件类型映射表
include mime.types;
#默认文件类型
default_type application/octet-stream;
#日志相关定义
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#连接日志的路径,指定的日志格式放在最后。
#access_log logs/access.log main;
#开启高效传输模式
sendfile on;
#防止网络阻塞
#tcp_nopush on;
#客户端连接超时时间,单位是秒
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#开启gzip压缩输出
#gzip on;
#虚拟主机基本设置
server {
#监听的端口号
listen 80;
#访问域名
server_name localhost;
#编码格式,如果网页格式与当前配置的不同的话将会被自动转码
#charset koi8-r;
#虚拟主机访问日志定义
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
#对URL进行匹配
location / {
#访问路径,可相对也可绝对路径
root html;
#首页文件,匹配顺序按照配置顺序匹配
index index.html index.htm;
}
#错误信息返回页面
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
#访问URL以.php结尾则自动转交给127.0.0.1
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
#php脚本请求全部转发给FastCGI处理
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
#禁止访问.ht页面
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
#第二个虚拟主机配置
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
#HTTPS虚拟主机定义
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
include servers/*;
}
反向代理实例
假设我现在需要本地访问www.baidu.com;配置如下:
server {
#监听80端口
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
# individual nginx logs for this web vhost
access_log /tmp/access.log;
error_log /tmp/error.log ;
location / {
proxy_pass http://www.baidu.com;
}
验证结果:
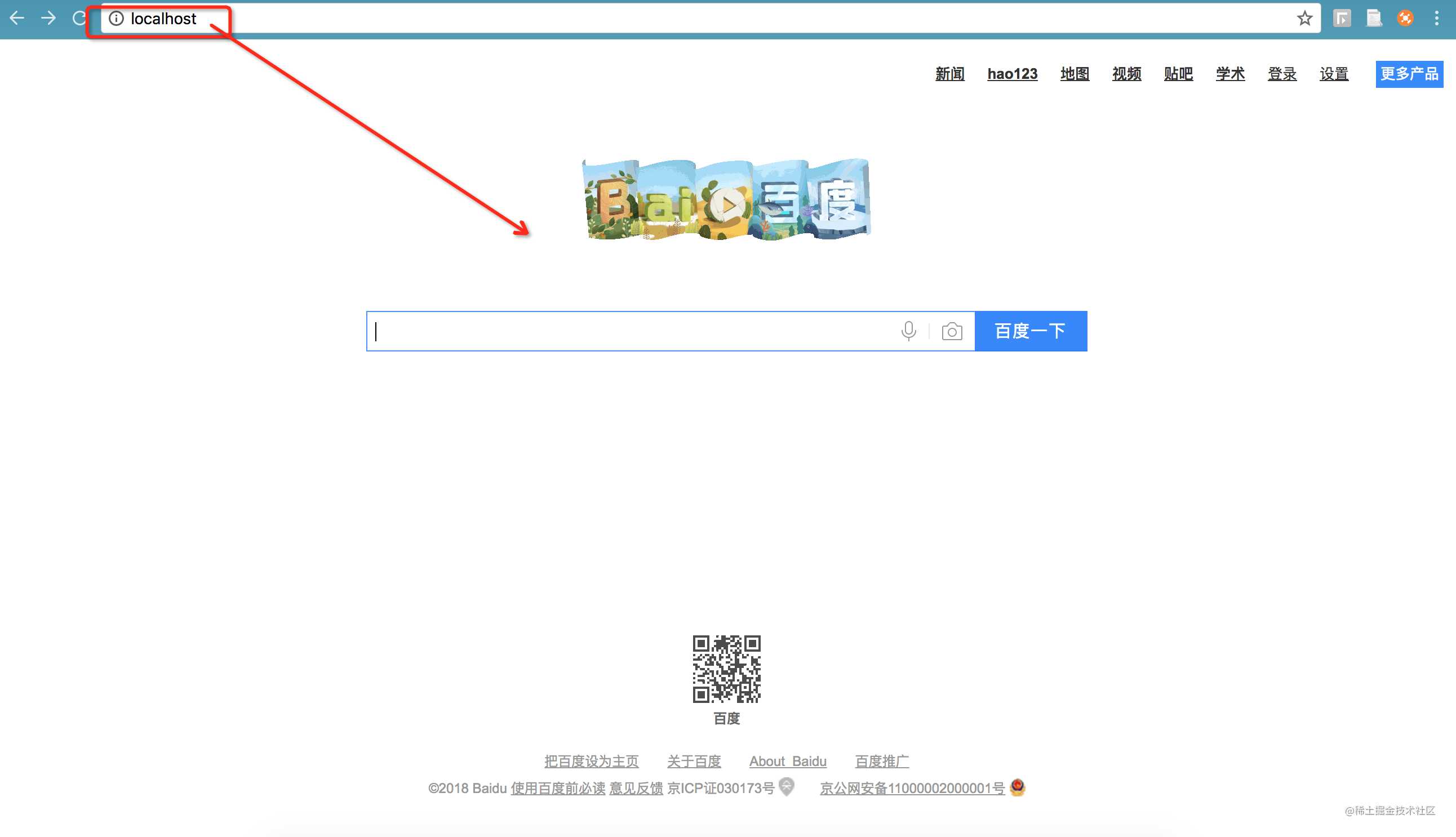
可以看到,我在浏览器中使用localhost打开了百度的首页…
负载均衡实例
下面主要验证最常用的三种负载策略。虚拟主机配置:
server {
#监听80端口
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
# individual nginx logs for this web vhost
access_log /tmp/access.log;
error_log /tmp/error.log ;
location / {
#负载均衡
#轮询
#proxy_pass http://polling_strategy;
#weight权重
#proxy_pass http://weight_strategy;
#ip_hash
# proxy_pass http://ip_hash_strategy;
#fair
# proxy_pass http://fair_strategy;
#url_hash
# proxy_pass http://url_hash_strategy;
#重定向
#rewrite ^ http://localhost:8080;
}
轮询策略
# 1、轮询(默认)
# 每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除。
upstream polling_strategy {
server glmapper.net:8080; # 应用服务器1
server glmapper.net:8081; # 应用服务器2
}
测试结果(通过端口号来区分当前访问):
8081:hello
8080:hello
8081:hello
8080:hello
权重策略
#2、指定权重
#指定轮询几率,weight和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况。
upstream weight_strategy {
server glmapper.net:8080 weight=1; # 应用服务器1
server glmapper.net:8081 weight=9; # 应用服务器2
}
测试结果:总访问次数15次,根据上面的权重配置,两台机器的访问比重:2:13;满足预期!
ip hash策略
#3、IP绑定 ip_hash
#每个请求按访问ip的hash结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,
#可以解决session的问题;在不考虑引入分布式session的情况下,
#原生HttpSession只对当前servlet容器的上下文环境有效
upstream ip_hash_strategy {
ip_hash;
server glmapper.net:8080; # 应用服务器1
server glmapper.net:8081; # 应用服务器2
}
iphash 算法:ip是基本的点分十进制,将ip的前三个端作为参数加入hash函数。这样做的目的是保证ip地址前三位相同的用户经过hash计算将分配到相同的后端server。作者的这个考虑是极为可取的,因此ip地址前三位相同通常意味着来着同一个局域网或者相邻区域,使用相同的后端服务让nginx在一定程度上更具有一致性。
为什么说要解释下iphash,因为采坑了;和猪弟在进行这个策略测试时使用了5台机器来测试的,5台机器均在同一个局域网内【192.168.3.X】;测试时发现5台机器每次都路由到了同一个服务器上,一开始以为是配置问题,但是排查之后也排除了这个可能性。最后考虑到可能是对于同网段的ip做了特殊处理,验证之后确认了猜测。
其他负载均衡策略
这里因为需要安装三方插件,时间有限就不验证了,知悉即可!
#4、fair(第三方)
#按后端服务器的响应时间来分配请求,响应时间短的优先分配。
upstream fair_strategy {
server glmapper.net:8080; # 应用服务器1
server glmapper.net:8081; # 应用服务器2
fair;
}
#5、url_hash(第三方)
#按访问url的hash结果来分配请求,使每个url定向到同一个后端服务器,
#后端服务器为缓存时比较有效。
upstream url_hash_strategy {
server glmapper.net:8080; # 应用服务器1
server glmapper.net:8081; # 应用服务器2
hash $request_uri;
hash_method crc32;
}
重定向rewrite
location / {
#重定向
#rewrite ^ http://localhost:8080;
}
验证思路:本地使用localhost:80端口进行访问,根据nginx的配置,如果重定向没有生效,则最后会停留在当前localhost:80这个路径,浏览器中的地址栏地址不会发生改变;如果生效了则地址栏地址变为localhost:8080;
通过验证,满足预期!
总结
本文先对nginx的作用和基本的配置做了简单说明;然后通过负载均衡的实例测试了不同负载均衡算法的具体应用反馈结果。帮助自己更加深刻的理解nginx服务器中的一些配置细节。感谢刘秘提供的helloworld程序【基于springboot的脚手架,有需要的可以联系他获取;还有就是刘秘是个男的…😜】
参考
- http://nginx.org/
- https://www.nginx.com/
- http://www.sohu.com/a/161411719_324809
今天的文章nginx反向代理和负载均衡策略实战案例分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/16980.html
