前言
在做一个Node监控系统的时候要做了一个邮件报警的需求,这时候就需要自定义一套规则来书写触发报警的表达式,本文就介绍一下如何编写一个简易的表达式解析器。 附上界面截图,图中就是一个表达式的例子。

参考书籍:《编程语言实现模式》
确定一些基本规则
在开始编写之前你需要确定你的表达式需要拥有些什么能力。本文的表达式是判断是否触发报警的条件,表达式的规则不应该过于复杂。同时,由于书写表达式的用户是前端开发或者node开发,所以语法贴近js表达式语法最合适:
- 支持变量,这里规定变量以@开头,由字母和数字组成,如: @load15
- 支持常量:布尔值、数字、字符串
- 支持加法(+)、减法(-)、乘法(*)、除法(/)、取余(%)运算
- 支持全等(===)、不等(!==)、大于(>)、小于(<)、大于等于(>=)、小于等于(<=)等比较运算
- 支持与(&&)、或(||)、非(!)等逻辑运算
- 扩展字符串包含include运算
- 支持括号()
构建抽象语法树(AST)
构建抽象语法树的目的是设计一种数据结构来说明一个表达式的含义。比如@var > 5,在代码中它作为一个字符串,是没有规定其是怎样去进行运算的。
如果解析成如下抽象语法树:
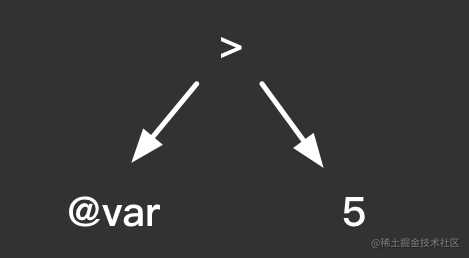
根节点为运算符,子节点为运算对象,这样我们就用二叉树抽象了一个运算。
当然,上面的例子是一个较为简单的运算表达式,一旦表达式变得复杂,无法避免的是运算的优先级,那么二叉树如何来表示运算的优先级呢?
我们用两个表达式来说明:
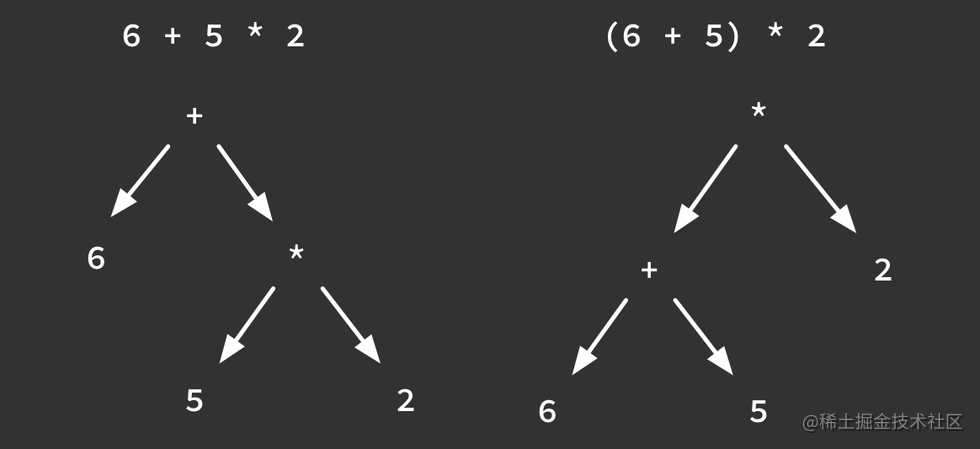
从图中可以看出,第二个表达式加入括号后改变了原来的运算顺序,对应的抽象语法树也发生了变化,不难看出:运算的优先级越高,在语法树中的位置越低。
AST的数据结构举个例子来看,如以下表达式
@load > 1 + 5
解析成的token为:
{
"type": "LOGICAL_EXP",
"operator": ">",
"left": {
"type": "VARIABLE",
"value": "load",
"raw": "@load"
},
"right": {
"type": "BINARY_EXP",
"operator": "+",
"left": {
"type": "NUMBER",
"value": 1,
"raw": "1"
},
"right": {
"type": "NUMBER",
"value": 5,
"raw": "5"
}
}
}
确定了抽象语法树的结构,我们就可以开始考虑怎么去解析表达式字符串了。
使用LL(1)递归下降词法解析器
词法单元(tokenizing)是指字符的语法,类似我们用字母以一定的语法拼成一个单词一样。
LL(1)递归下降词法解析器是向前看一个词法单元的自顶向下的解析器,LL中的两个L都是”left-to-right”,第一个L表示解析器按”从做到右”的顺序解析输入内容,第二个L表示下降解析时也时从左到右遍历子节点。
这个是最简单的解析器,能够满足需求的情况下,使用这个模式更为通俗易懂。
词法单元罗列
既然要向前看一个词法单元,那么我们首先应该罗列出这个表达式可能拥有的词法单元,本文的表达式可能拥有如下词法单元:
- 变量词法单元,标志:以”@”开头
- 数字词法单元,标志:以0-9开头或者”.”开头
- 字符串词法单元,标志:以单引号或者双引号开头
- 括号词法单元,标志:以左括号为开头
- 一元运算符词法单元,标志:以”!”、”+”、”-“开头
下面我们就可以正式开始写代码了。
寻找递归点
一个表达式可以分解成多个没有括号的表达式,如以下表达式:
5 * (3 + 2 * (5 + 6))
我们可以把它分解成以下表达式:
5 * expression_a
3 + 2 * expression_b // expression_a
5 + 6 // expression_b
整个字符串表示的就是一个表达式,这就是我们要找的递归点,定义一个函数eatExpression去解析一个表达式,遇到括号就递归eatExpression,直到无法匹配任何词法单元。
下面开始撸代码。
class ExpressionParser
class ExpressionParser {
constructor(expr) {
if (typeof expr !== 'string') {
throw new Error(`[expression-parser] constructor need a string parameter, but get [${typeof expr}]`);
}
this.expr = expr;
this.parse();
}
parse() {
this.index = 0;
this.tokens = this.eatExpression();
if (this.index < this.expr.length) {
this.throwError(`非法字符"${this.charAt()}"`);
}
}
}
const expression
const parser = new ExpressionParser(expression)
这是解析器类,初始工作就是保存expression,然后使用eatExpression去解析,当我们开始解析的时候,我们是一位一位字符地查看,我们形象地用”eat”来表示遍历这个动作,因此要有几个辅助参数和辅助函数:
this.index // 标记当前遍历的字符的下标
// 获取当前遍历字符
charAt(index = this.index) {
return this.expr.charAt(index);
}
// 获取当前字符的 Unicode 编码
charCodeAt(index = this.index) {
return this.expr.charCodeAt(index);
}
ExpressionParser.prototype.eatExpression
这个函数是整个解析器的入口,这个函数的思路很重要。一个表达式可以分为两种:
- 有二元运算符的表达式
- 没有二元运算符的表达式
没有二元运算符的表达式很简单,只要遍历分解成上述词法单元的集合即可,而如果有二元运算符且大于1个的时候,这时候就比较复杂了,因为我们解析的顺序是从左到右,而运算符的顺序是不确定的。
那么如何解决呢?下面用一个例子的处理流程解释核心的优先级计算思想:
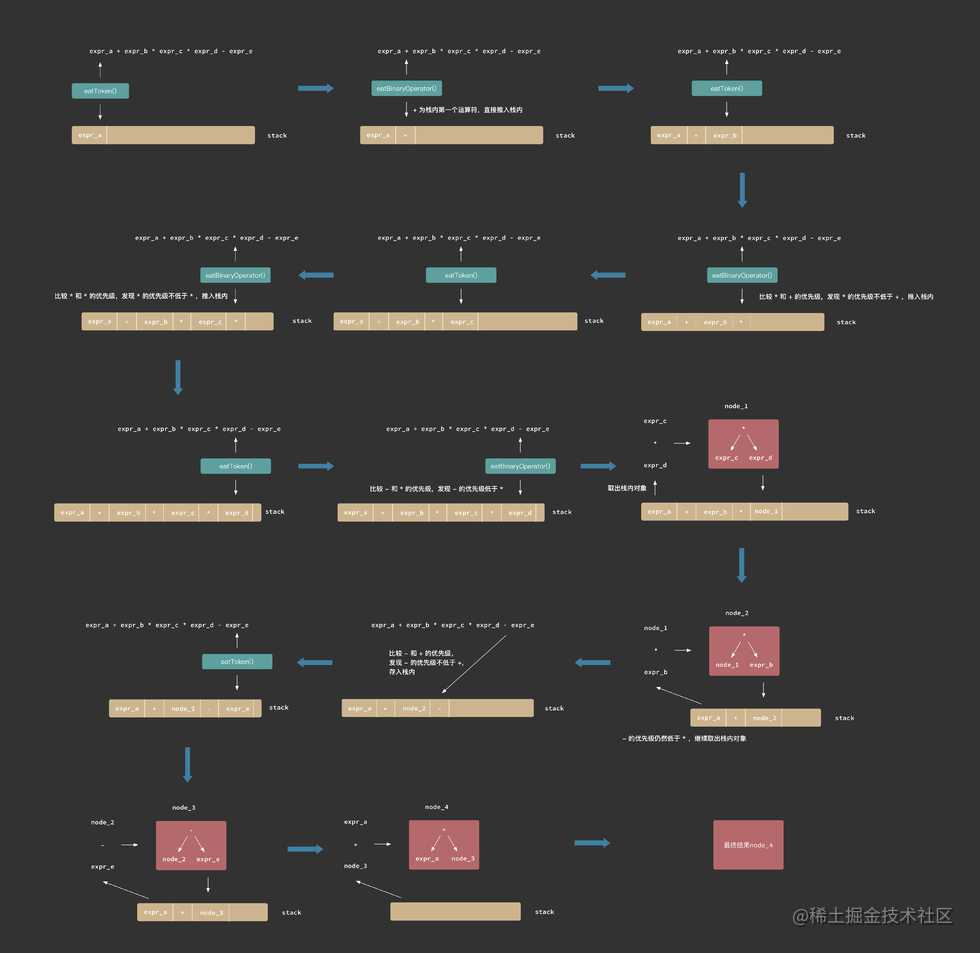
主要的思想就是利用一个堆栈,把解析的token存进堆栈,当解析到运算符(一元运算符解析成token,这里指二元运算符)的时候,对比栈中最靠近顶部的运算符,如果发现新解析的运算符优先级更高,直接推进栈内。所以,在栈中,运算符的优先级保证是从低到高的,一旦新解析的运算符优先级更低,说明栈内的token可以合成一个node直到栈内的运算符优先级全部都是从低到高。最后,再从右向左依次合成node,得到一个完整的表达式二叉树。
最核心的思想就是保证栈内优先级从低到高,下面贴代码让大家再巩固理解:
eatExpression() {
let left = this.eatToken();
let operator = this.eatBinaryOperator();
// 说明这个运算树只有左侧
if (!operator) {
return left;
}
let operatorInfo = {
precedence: this.getOperatorPrecedence(operator), // 获取运算符优先级
value: operator,
};
let right = this.eatToken();
if (!right) {
this.throwError(`"${operator}"运算符后应该为表达式`);
}
const stack = [left, operatorInfo, right];
// 获取下一个运算符
while (operator = this.eatBinaryOperator()) {
const precedence = this.getOperatorPrecedence(operator);
// 如果遇到了非法的yuan fa
if (precedence === 0) {
break;
}
operatorInfo = {
precedence,
value: operator,
};
while (stack.length > 2 && precedence < stack[stack.length - 2].precedence) {
right = stack.pop();
operator = stack.pop().value;
left = stack.pop();
const node = this.createNode(operator, left, right);
stack.push(node);
}
const node = this.eatToken();
if (!node) {
this.throwError(`"${operator}"运算符后应该为表达式`);
}
stack.push(operatorInfo, node);
}
let i = stack.length - 1;
let node = stack[i];
while (i > 1) {
node = this.createNode(stack[i - 1].value, stack[i - 2], node);
i -= 2;
}
return node;
}
createNode:
const LOGICAL_OPERATORS = ['||', '&&', '===', '!==', '>', '<', '>=', '<=', 'include'];
...
createNode(operator, left, right) {
const type = LOGICAL_OPERATORS.indexOf(operator) !== -1 ? 'LOGICAL_EXP' : 'BINARY_EXP';
return {
type,
operator,
left,
right,
};
}
getOperatorPrecedence:
const BINARY_OPERATORS = {
'||': 1,
'&&': 2,
'===': 6, '!==': 6,
'<': 7, '>': 7, '<=': 7, '>=': 7,
'+': 9, '-': 9,
'*': 10, '/': 10, '%': 10,
include: 11,
};
...
getOperatorPrecedence(operator) {
return BINARY_OPERATORS[operator] || 0;
}
相信现在你对于整体的思路已经很清晰了,接下来还有一个比较重要的需要讲一下,这就是token的解析
Token解析
token解析的过程,可以想象成有个下标一个字符一个字符地从左到右移动,遇到可以辨识的token开头标志,就解析token,然后继续移动下标直到整个字符串结束或者无法遇到可辨识的标志。
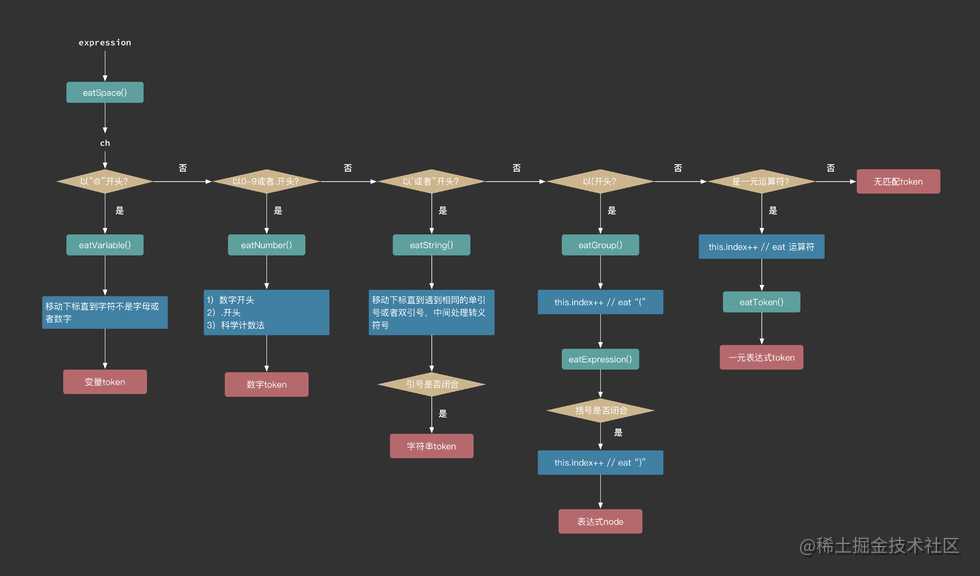
具体每种类型的token如何去匹配,可以查看完整的代码。
计算结果值
token解析好后,我们是需要计算表达式值的,由于变量的存在,所以我们需要提供一个context来供变量获取值,形如:
const expr = new ExpressionParser('@load > 5');
console.log(expr.valueOf({ load: 8 })); // true
因为我们已经把表达式生成一个二叉树了,所以只要递归遍历计算每个二叉树的值即可,由于是递归计算,越底下的树越早计算,与我们开始设计优先级的思路一致。
完整代码:
const OPEN_PAREN_CODE = 40; // (
const CLOSE_PAREN_CODE = 41; // )
const VARIABLE_BEGIN_CODE = 64; // @,变量开头
const PERIOD_CODE = 46; // '.'
const SINGLE_QUOTE_CODE = 39; // single quote
const DOUBLE_QUOTE_CODE = 34; // double quotes
const SPACE_CODES = [32, 9, 10, 13]; // space
// 一元运算符
const UNARY_OPERATORS = { '-': true, '!': true, '+': true };
// 二元运算符
const LOGICAL_OPERATORS = ['||', '&&', '===', '!==', '>', '<', '>=', '<=', 'include'];
const BINARY_OPERATORS = {
'||': 1,
'&&': 2,
'===': 6, '!==': 6,
'<': 7, '>': 7, '<=': 7, '>=': 7,
'+': 9, '-': 9,
'*': 10, '/': 10, '%': 10,
include: 11,
};
// 获取对象键的最大长度
const getMaxKeyLen = function getMaxKeyLen(obj) {
let max = 0;
Object.keys(obj).forEach((key) => {
if (key.length > max && obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
max = key.length;
}
});
return max;
};
const maxBinaryOperatorLength = getMaxKeyLen(BINARY_OPERATORS);
const maxUnaryOperatorLength = getMaxKeyLen(UNARY_OPERATORS);
class ExpressionParser {
constructor(expr) {
if (typeof expr !== 'string') {
throw new Error(`[expression-parser] constructor need a string parameter, but get [${typeof expr}]`);
}
this.expr = expr;
}
parse() {
this.index = 0;
try {
this.tokens = this.eatExpression();
if (this.index < this.expr.length) {
throw new Error(`非法字符"${this.charAt()}"`);
}
} catch (error) {
this.tokens = undefined;
if (typeof this.onErrorCallback === 'function') {
this.onErrorCallback(error.message, this.index, this.charAt());
} else {
throw new Error(error.message);
}
}
return this;
}
eatExpression() {
let left = this.eatToken();
let operator = this.eatBinaryOperator();
// 说明这个运算树只有左侧
if (!operator) {
return left;
}
let operatorInfo = {
precedence: this.getOperatorPrecedence(operator), // 获取运算符优先级
value: operator,
};
let right = this.eatToken();
if (!right) {
throw new Error(`"${operator}"运算符后应该为表达式`);
}
const stack = [left, operatorInfo, right];
// 获取下一个运算符
while (operator = this.eatBinaryOperator()) {
const precedence = this.getOperatorPrecedence(operator);
// 如果遇到了非法的yuan fa
if (precedence === 0) {
break;
}
operatorInfo = {
precedence,
value: operator,
};
while (stack.length > 2 && precedence < stack[stack.length - 2].precedence) {
right = stack.pop();
operator = stack.pop().value;
left = stack.pop();
const node = this.createNode(operator, left, right);
stack.push(node);
}
const node = this.eatToken();
if (!node) {
throw new Error(`"${operator}"运算符后应该为表达式`);
}
stack.push(operatorInfo, node);
}
let i = stack.length - 1;
let node = stack[i];
while (i > 1) {
node = this.createNode(stack[i - 1].value, stack[i - 2], node);
i -= 2;
}
return node;
}
eatToken() {
this.eatSpaces();
const ch = this.charCodeAt();
if (ch === VARIABLE_BEGIN_CODE) {
// 变量
return this.eatVariable();
} else if (this.isDigit(ch) || ch === PERIOD_CODE) {
// 数字
return this.eatNumber();
} else if (ch === SINGLE_QUOTE_CODE || ch === DOUBLE_QUOTE_CODE) {
// 字符串
return this.eatString();
} else if (ch === OPEN_PAREN_CODE) {
// 括号
return this.eatGroup();
} else {
// 检查单操作符 !+ -
let toCheck = this.expr.substr(this.index, maxUnaryOperatorLength);
let toCheckLength;
while (toCheckLength = toCheck.length) {
if (
UNARY_OPERATORS.hasOwnProperty(toCheck) &&
this.index + toCheckLength <= this.expr.length
) {
this.index += toCheckLength;
return {
type: 'UNARY_EXP',
operator: toCheck,
argument: this.eatToken(),
};
}
toCheck = toCheck.substr(0, --toCheckLength);
}
}
}
eatGroup() {
this.index++; // eat "("
const node = this.eatExpression();
this.eatSpaces();
const ch = this.charCodeAt();
if (ch !== CLOSE_PAREN_CODE) {
throw new Error('括号没有闭合');
} else {
this.index++; // eat ")"
return node;
}
}
eatVariable() {
const ch = this.charAt();
this.index++; // eat "@"
const start = this.index;
while (this.index < this.expr.length) {
const ch = this.charCodeAt();
if (this.isVariablePart(ch)) {
this.index++;
} else {
break;
}
}
const identifier = this.expr.slice(start, this.index);
return {
type: 'VARIABLE',
value: identifier,
raw: ch + identifier,
};
}
eatNumber() {
let number = '';
// 数字开头
while (this.isDigit(this.charCodeAt())) {
number += this.charAt(this.index++);
}
// '.'开头
if (this.charCodeAt() === PERIOD_CODE) {
number += this.charAt(this.index++);
while (this.isDigit(this.charCodeAt())) {
number += this.charAt(this.index++);
}
}
// 科学计数法
let ch = this.charAt();
if (ch === 'e' || ch === 'E') {
number += this.charAt(this.index++);
ch = this.charAt();
if (ch === '+' || ch === '-') {
number += this.charAt(this.index++);
}
while (this.isDigit(this.charCodeAt())) {
number += this.charAt(this.index++);
}
// 如果e + - 后无数字,报错
if (!this.isDigit(this.charCodeAt(this.index - 1))) {
throw new Error(`非法数字(${number}${this.charAt()}),缺少指数`);
}
}
return {
type: 'NUMBER',
value: parseFloat(number),
raw: number,
};
}
eatString() {
let str = '';
const quote = this.charAt(this.index++);
let closed = false;
while (this.index < this.expr.length) {
let ch = this.charAt(this.index++);
if (ch === quote) {
closed = true;
break;
} else if (ch === '\\') {
// Check for all of the common escape codes
ch = this.charAt(this.index++);
switch (ch) {
case 'n':
str += '\n';
break;
case 'r':
str += '\r';
break;
case 't':
str += '\t';
break;
case 'b':
str += '\b';
break;
case 'f':
str += '\f';
break;
case 'v':
str += '\x0B';
break;
default:
str += ch;
}
} else {
str += ch;
}
}
if (!closed) {
throw new Error(`字符"${str}"缺少闭合括号`);
}
return {
type: 'STRING',
value: str,
raw: quote + str + quote,
};
}
eatBinaryOperator() {
this.eatSpaces();
let toCheck = this.expr.substr(this.index, maxBinaryOperatorLength);
let toCheckLength = toCheck.length;
while (toCheckLength) {
if (
BINARY_OPERATORS.hasOwnProperty(toCheck) &&
this.index + toCheckLength <= this.expr.length
) {
this.index += toCheckLength;
return toCheck;
}
toCheck = toCheck.substr(0, --toCheckLength);
}
return false;
}
getOperatorPrecedence(operator) {
return BINARY_OPERATORS[operator] || 0;
}
createNode(operator, left, right) {
const type = LOGICAL_OPERATORS.indexOf(operator) !== -1
? 'LOGICAL_EXP'
: 'BINARY_EXP';
return {
type,
operator,
left,
right,
};
}
isVariablePart(ch) {
return (ch >= 65 && ch <= 90) || // A...Z
(ch >= 97 && ch <= 122) || // a...z
(ch >= 48 && ch <= 57); // 0...9
}
isDigit(ch) {
return ch >= 48 && ch <= 57; // 0...9
}
eatSpaces() {
let ch = this.charCodeAt();
while (SPACE_CODES.indexOf(ch) !== -1) {
ch = this.charCodeAt(++this.index);
}
}
onError(callback) {
this.onErrorCallback = callback;
return this;
}
charAt(index = this.index) {
return this.expr.charAt(index);
}
charCodeAt(index = this.index) {
return this.expr.charCodeAt(index);
}
valueOf(scope = {}) {
if (this.tokens == null) {
return undefined;
}
const value = this.getNodeValue(this.tokens, scope);
return !!value;
}
getNodeValue(node, scope = {}) {
const { type, value, left, right, operator } = node;
if (type === 'VARIABLE') {
return scope[value];
} else if (type === 'NUMBER' || type === 'STRING') {
return value;
} else if (type === 'LOGICAL_EXP') {
const leftValue = this.getNodeValue(left, scope);
// 如果是逻辑运算的&&和||,那么可能不需要解析右边的值
if (operator === '&&' && !leftValue) {
return false;
}
if (operator === '||' && !!leftValue) {
return true;
}
const rightValue = this.getNodeValue(right, scope);
switch (node.operator) {
case '&&': return leftValue && rightValue;
case '||': return leftValue || rightValue;
case '>': return leftValue > rightValue;
case '>=': return leftValue >= rightValue;
case '<': return leftValue < rightValue;
case '<=': return leftValue <= rightValue;
case '===': return leftValue === rightValue;
case '!==': return leftValue !== rightValue;
case 'include': return leftValue.toString &&
rightValue.toString &&
leftValue.toString().indexOf(rightValue.toString()) !== -1;
// skip default case
}
} else if (type === 'BINARY_EXP') {
const leftValue = this.getNodeValue(left, scope);
const rightValue = this.getNodeValue(right, scope);
switch (node.operator) {
case '+': return leftValue + rightValue;
case '-': return leftValue - rightValue;
case '*': return leftValue * rightValue;
case '/': return leftValue - rightValue;
case '%': return leftValue % rightValue;
// skip default case
}
} else if (type === 'UNARY_EXP') {
switch (node.operator) {
case '!': return !this.getNodeValue(node.argument, scope);
case '+': return +this.getNodeValue(node.argument, scope);
case '-': return -this.getNodeValue(node.argument, scope);
// skip default case
}
}
}
}
const expression = new ExpressionParser('@load + 3');
expression.onError((message, index, ch) => {
console.log(message, index, ch);
}).parse();
console.log(expression.valueOf({ load: 5 }));
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/21714.html
