由于公司需求,所以需要做数据可视化。看了很多库,觉的D3.js库很强大,于是决定用D3.js库。 在使用树状图时,看到固定的树形图,在想能不能做了思维导图了,于是便开始了探索。。。
//先进行NPM安装
npm i vued3tree
// 在页面中引用
import * as d3 from 'd3'
import {tree} from 'vued3tree'
html:
// 用的是ELEMENT-UI
<template>
<div class="main">
<div class="tb-menu" ref="main" :style="menuPos" v-show="isMenuShow" style="z-index: 1">
<div v-show="menuInfo.move" @click="menuClick('move')">删除节点</div>
<div v-show="menuInfo.inNextNode" @click="menuClick('inNextNode')">插入下一级节点</div>
<div v-show="menuInfo.inSameNode" @click="menuClick('inSameNode')">插入同级节点</div>
<div v-show="menuInfo.reName" @click="menuClick('reName')">重命名</div>
</div>
<div class="context">
<tree :data="tree" node-text="name" @clicked="addNode" @mouseup.stop="rClick($event,idx)" type="cluster" layoutType="euclidean">
</tree>
</div>
// 点击节点出现的弹窗
<el-dialog
:visible.sync="dialogVisible"
width="30%"
:before-close="handleClose">
<div class="dialog" style="line-height: 50px">
<div style="margin-top: 20px;">
<span style="margin-right: 20px;">输入新节点名称</span>
<el-input v-model="newVal" placeholder="请输入内容"></el-input>
</div>
<span slot="footer" class="dialog-footer">
<el-button @click="dialogVisible = false">取 消</el-button>
<el-button type="primary" @click="handleExport">确 定</el-button>
</span>
</div>
</el-dialog>
<div>
</div>
</template>
JS:
export default {
components: {
tree,SoltTemp
},
data() {
return {
getNode: {},
showTree: false,
habit: '',
workHabit: '',
lifeHabit: '',
tree: {
name: "habit",
children:[{
name: "work",
children:[ {name: "watch skill's page", id: 1}, {name: "doing some new test", id: 2}]
},{
name: "life",
children:[ {name: "watch movie", id: 3}, {name: "run", id: 4},{name: "cookie", id: 4}]
}]
},
treeTwo: {},
menuPos: {
left: 500,
top: 500
},
isMenuShow: false,
menuInfo: {
move: true, // 移除
inNextNode: true, // 插入下一个节点
inSameNode: true, // 插入相同的节点
reName: true,
},
dialogVisible: false,
newVal: '',
type: ''
}
},
watch: {
'this.tree' (val) {
this.tree = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.tree))
}
},
methods: {
yes() {
this.showTree = true
},
addHabit() {
this.tree.children.push({name: this.habit, id: this.tree.children[0].length + 1})
},
addWorkHabit() {
this.tree.children[0].children.push({name: this.workHabit, id: this.tree.children[0].children.length + 1})
this.tree = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.tree))
},
addFileHabit() {
this.tree.children[1].children.push({name: this.lifeHabit, id: this.tree.children[1].children.length + 1})
},
addNode(type) {
this.getNode = type
// 对于点击事件进行取反操作
this.isMenuShow = !this.isMenuShow
this.menuPos.left = type.element.x + 1200 + 'px'
this.menuPos.top = type.element.y + 200 + 'px'
// 得到节点,就可以知道如何去插入
// 对插数据进行操作
},
menuClick(type) {
this.isMenuShow = false
this.type = type
if(type !== 'move') {
this.newVal = ''
this.dialogVisible = true
}
if(this.type == 'move') {
this.math(this.tree)
}
},
math(arr){
if(this.tree.name == this.getNode.data.name && this.type == 'inNextNode') {
this.tree.children.push({name: this.newVal, id: this.tree.children.length +1 })
} else {
arr.children.forEach((element, index) => {
if(element.name == this.getNode.data.name){
if(this.type == 'move') this.tree = Object.assign({}, this.tree, arr.children.splice(index,1))
if(this.type == 'reName') element.name = this.newVal
// 当选择下一条有没有孩子节点时所做的操作
if(this.type == 'inNextNode' && element.children) element.children.push({name: this.newVal, id: element.children.length + 1})
if(this.type == 'inNextNode' && !element.children) {
element.children = []
element.children.push({name: this.newVal, id:0})
this.$nextTick(() => {
//否则数据没有办法立即更新
this.tree = Object.assign({}, this.tree,element.children )
})
}
if(this.type == 'inSameNode') {
arr.children.push({name: this.newVal, id: arr.children.length + 1})
this.tree = Object.assign({}, this.tree,arr.children)
}
} else if(element.children){
this.math(element)
}
})
}
},
handleExport() {
this.dialogVisible = false
// 相同节点所作操作 常规的for循环 ---- 改进则使用递归
this.math(this.tree)
},
handleClose(done) {
this.$confirm('确认关闭?')
.then(_ => {
done();
})
.catch(_ => {});
}
},
mounted() {
// 取消右键的点击事件
this.$el.querySelector('.context').oncontextmenu = () => { return false }
}
}
</script>
CSS
<style <style lang="scss" scoped> .context { display: flex; justify-content: center; margin: 0 auto; width:500px; height: 200px; } .tb-menu { width: 180px; padding: 8px 0; position: absolute; line-height: 30px; top: 0; left: 0; background: #fff; border: 1px solid #eee; border-radius: 4px; box-shadow: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.12) 0px 2px 4px, rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.04) 0px 0px 6px; div { cursor: pointer; padding: 6px 12px; height:50px; &:hover { background: #eee; } span { font-size: 12px; color: #ccc; } } el-dialog .dialog{ // height: 60vh; line-height: 30px; } } </style>
于是,便实现了简易的思维导图
截图:
进行节点操作:
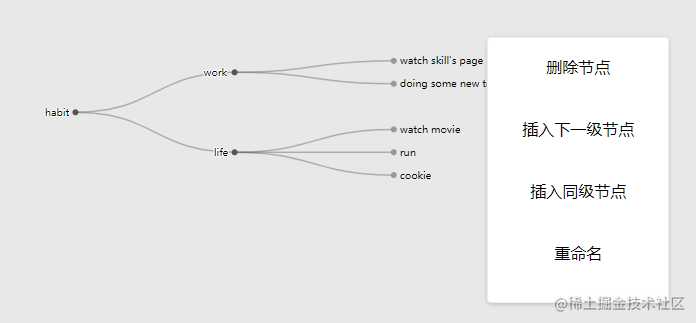
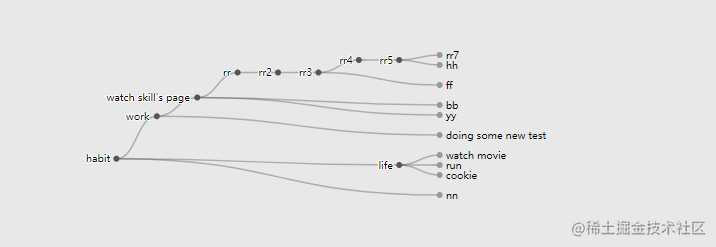
于是简易的思维导图就可以实现啦~~
后续继续完善~

今天的文章利用D3.js实现思维导图分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/22962.html
