解析java中的clone方法
1 是什么
clone方法是Object类中的一个被protected和native修饰的方法,被native就代表它的实现源码是用c++实现的,只不过是我们无法去修改它的代码罢了。
2 作用
为子类提供可以重写的clone()方法,目的是实现对象的浅克隆和深克隆
3 如何用
3.1 前提
3.1.1 克隆的原理
在堆内存中新开辟一段空间,然后把被克隆对象的属性和方法赋值一份到新开辟的空间里面(副本)。
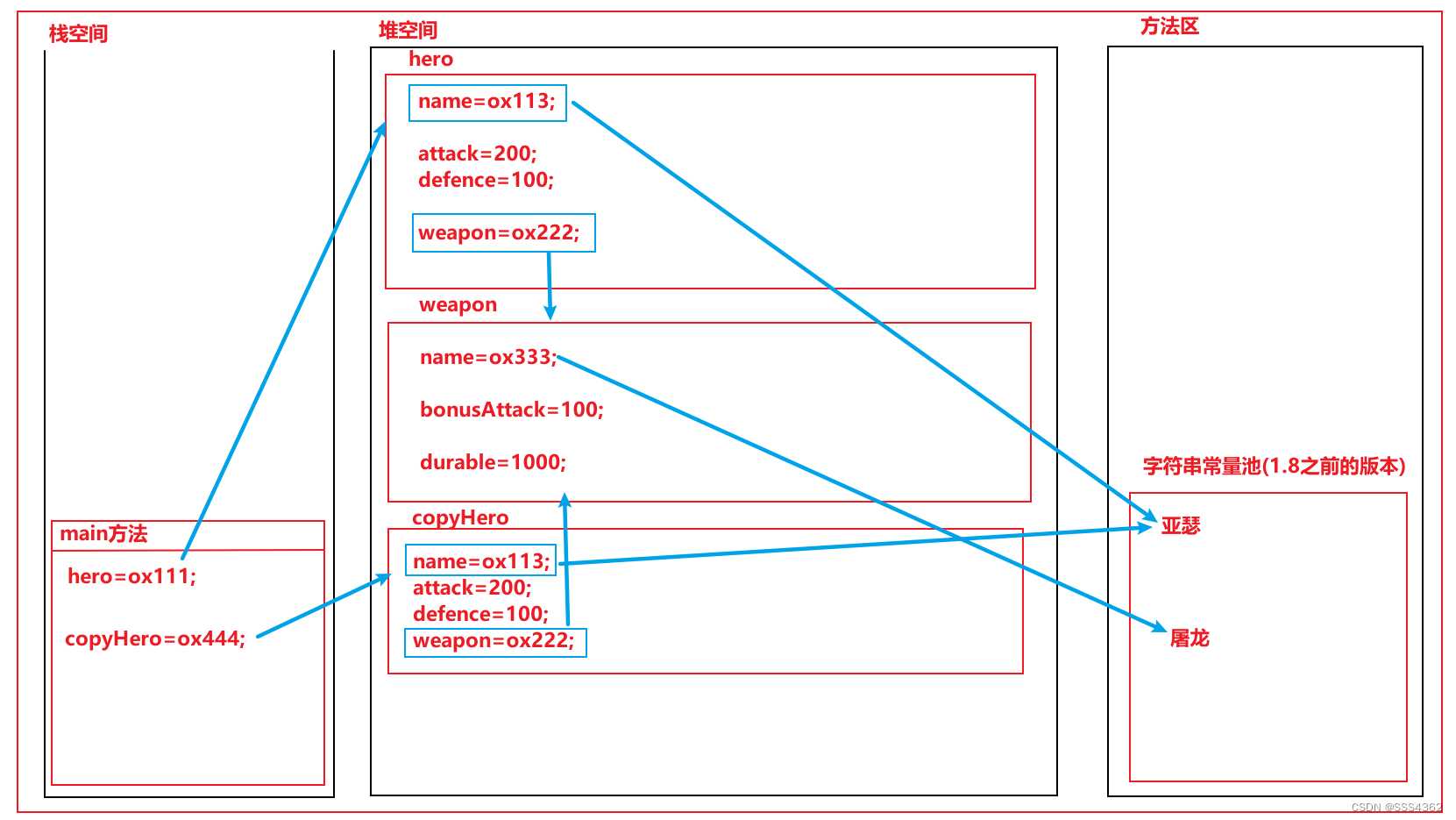
3.2 浅克隆
3.2.1 原理
对于基本数据类型而言,是复制其的副本到新开辟的空间里面
对于引用数据类型而言,只是复制了引用的地址,并没有开辟新的空间,新的空间里面的引用和被克隆的里面的引用都指向于同一个空间
3.2.2 浅克隆的实现步骤
a 实现cloneable接口,这个是判断能否克隆的条件
b 重写Clone方法,建议采用如下所示的写法
public 被克隆对象的类型 clone(){
//不要上抛异常,在方法体里面处理异常以及进行向下转型
被克隆对象的类型 对象名=null;
try {
对象名=(被克隆对象的类型)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 对象名;
}
3.2.3 示例代码
Hero
package Work;
//英雄类,因为需要用克隆,需要实现Cloneable接口
public class Hero implements Cloneable {
private String name;
//名字
private int attack;
//攻击力
private int defence;
//防御力
private Weapon weapon;
//武器
public Hero() {
}
public Hero(String name, int attack, int defence, Weapon weapon) {
this.name = name;
this.attack = attack;
this.defence = defence;
this.weapon = weapon;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAttack() {
return attack;
}
public void setAttack(int attack) {
this.attack = attack;
}
public int getDefence() {
return defence;
}
public void setDefence(int defence) {
this.defence = defence;
}
public Weapon getWeapon() {
return weapon;
}
public void setWeapon(Weapon weapon) {
this.weapon = weapon;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hero{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", attack=" + attack +
", defence=" + defence +
", weapon=" + weapon +
'}';
}
@Override
public Hero clone(){
Hero hero=null;
try {
hero=(Hero)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return hero;
}
}
Weapon
package Work;
public class Weapon implements Cloneable{
private String name;
//名字
private int bonusAttack;
//攻击力加成
private int durable;
//耐久值
public Weapon() {
}
public Weapon(String name, int bonusAttack, int durable) {
this.name = name;
this.bonusAttack = bonusAttack;
this.durable = durable;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getBonusAttack() {
return bonusAttack;
}
public void setBonusAttack(int bonusAttack) {
this.bonusAttack = bonusAttack;
}
public int getDurable() {
return durable;
}
public void setDurable(int durable) {
this.durable = durable;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Weapon{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", bonusAttack=" + bonusAttack +
", durable=" + durable +
'}';
}
@Override
public Weapon clone() {
Weapon weapon=null;
try {
weapon=(Weapon)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return weapon;
}
}
TestHero
package Work;
public class TestHero {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hero hero=new Hero("亚瑟",200,100,new Weapon("屠龙",100,1000));
Hero copyHero=hero.clone();
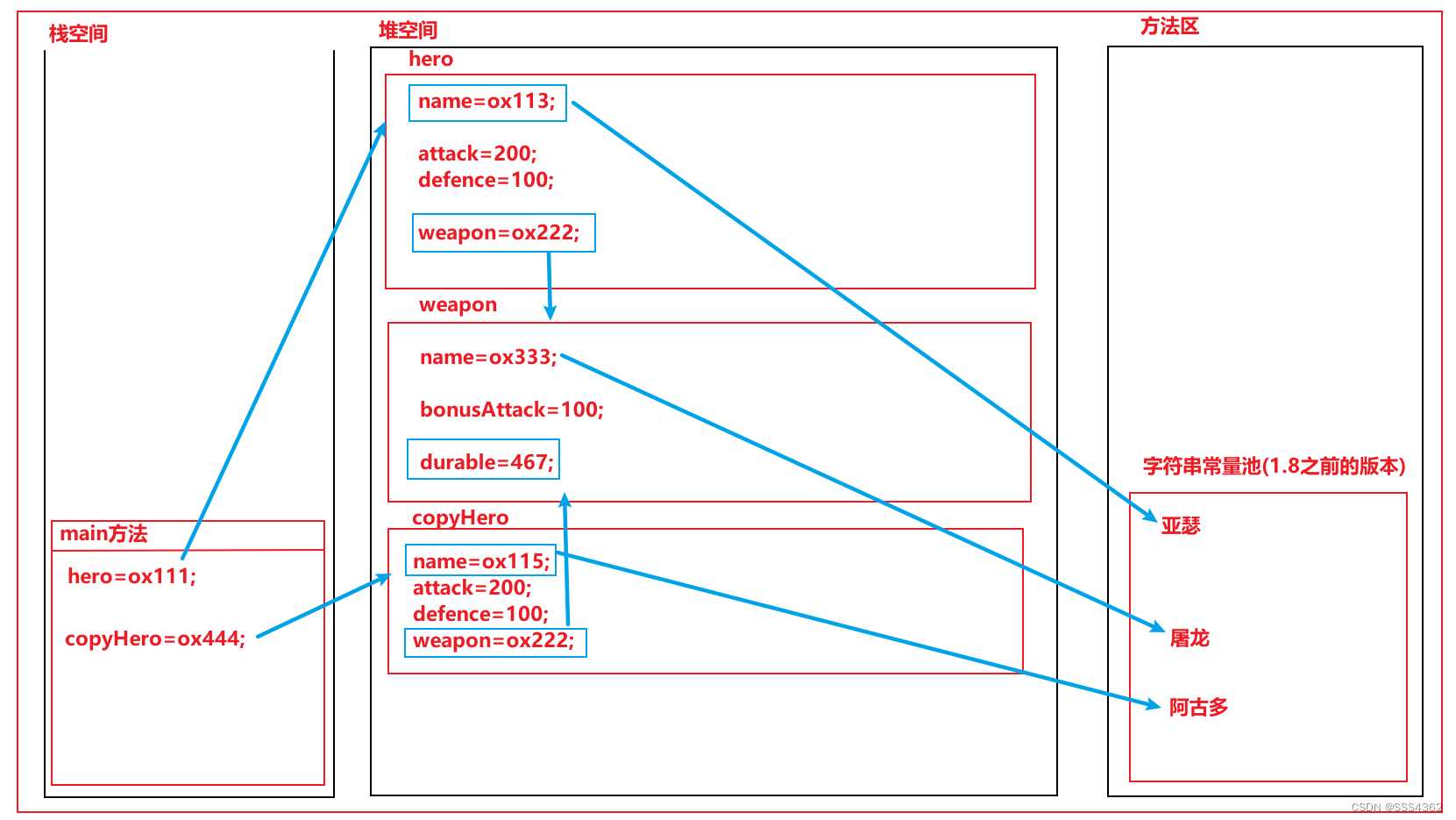
copyHero.getWeapon().setDurable(467);
copyHero.setName("阿古多");
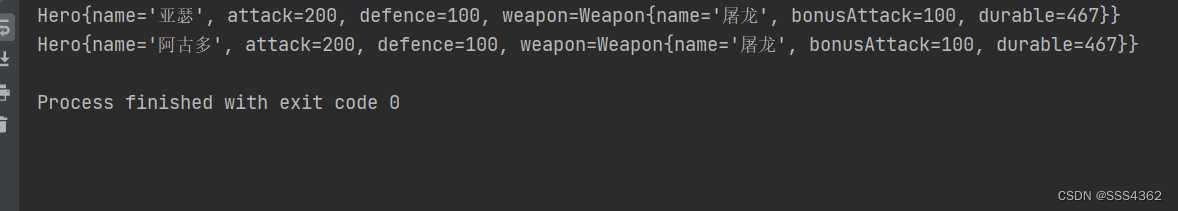
System.out.println(hero);
System.out.println(copyHero);
}
}
3.2.4 示例代码的内存原理图
a 克隆后
b 更改String属性和引用数据类型属性后
3.2.5 示例代码运行截图
3.3 深克隆
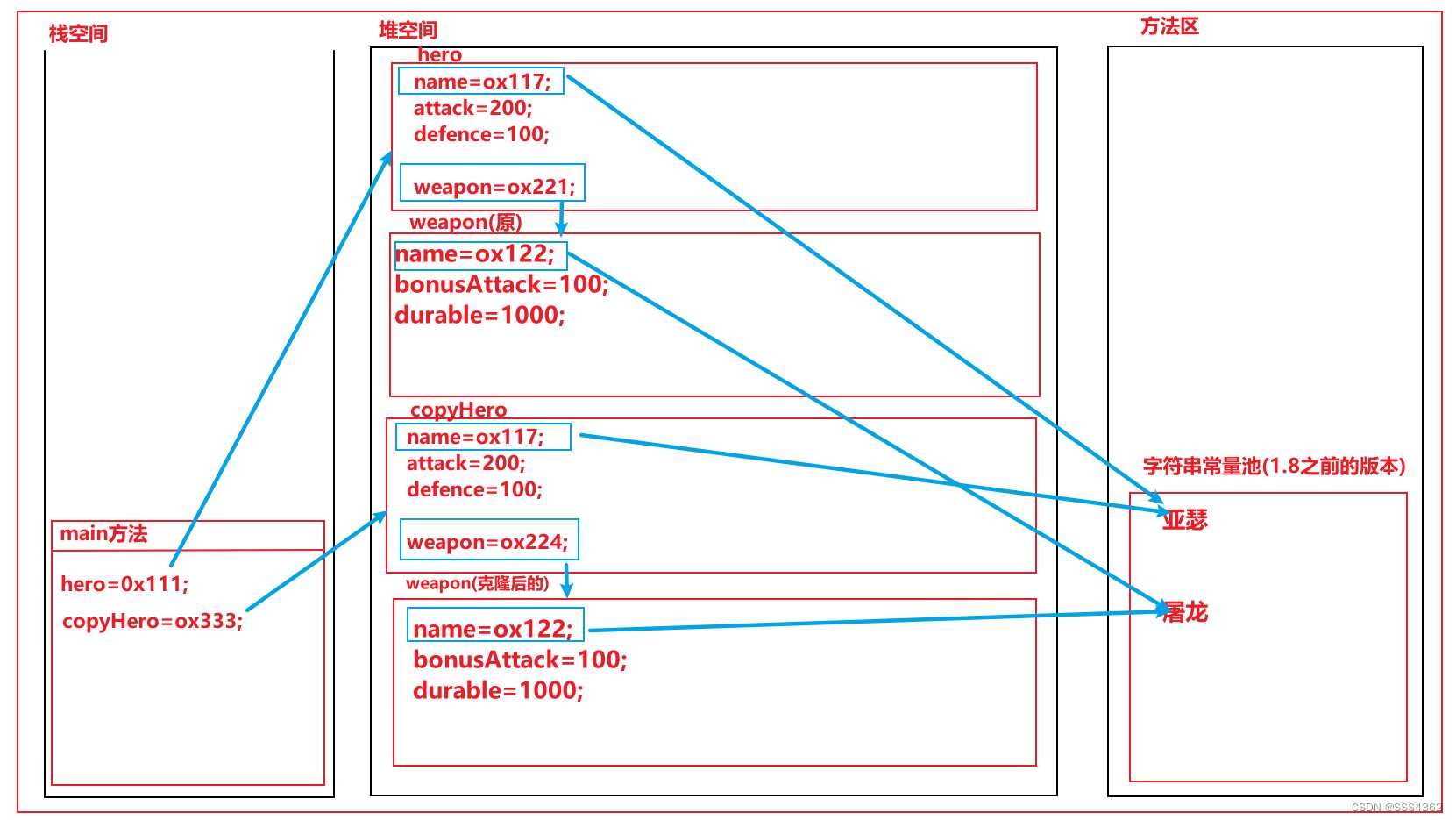
3.3.1 原理
对于基本数据类型而言,是复制其的副本到新开辟的空间里面
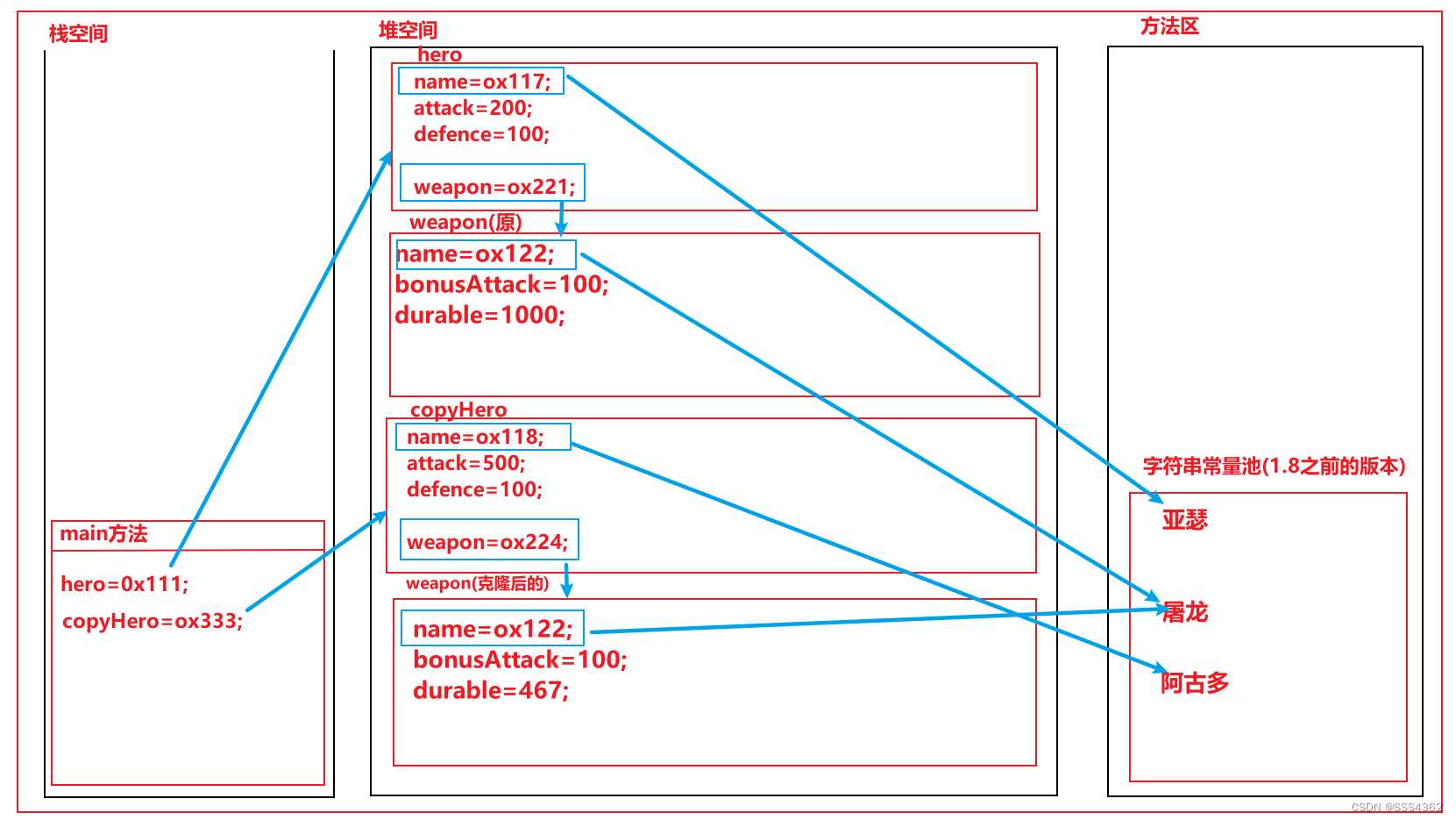
对于引用数据类型而言,并不是复制了引用的地址,而是开辟了一个新的引用对象的空间,并把引用地址里面的属性和方法拷贝一份到新的引用对象的空间中,此时克隆对象里面的引用就指向于这个新的空间
3.3.2 示例代码
Hero类
package Work;
//英雄类,因为需要用克隆,需要实现Cloneable接口
public class Hero implements Cloneable {
private String name;
//名字
private int attack;
//攻击力
private int defence;
//防御力
private Weapon weapon;
//武器
public Hero() {
}
public Hero(String name, int attack, int defence, Weapon weapon) {
this.name = name;
this.attack = attack;
this.defence = defence;
this.weapon = weapon;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAttack() {
return attack;
}
public void setAttack(int attack) {
this.attack = attack;
}
public int getDefence() {
return defence;
}
public void setDefence(int defence) {
this.defence = defence;
}
public Weapon getWeapon() {
return weapon;
}
public void setWeapon(Weapon weapon) {
this.weapon = weapon;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Hero{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", attack=" + attack +
", defence=" + defence +
", weapon=" + weapon +
'}';
}
@Override
public Hero clone(){
Hero hero=null;
try {
hero=(Hero)super.clone();
//给weapon属性也给克隆一下
setWeapon(getWeapon().clone());
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return hero;
}
}
Weapon类
package Work;
public class Weapon implements Cloneable{
private String name;
//名字
private int bonusAttack;
//攻击力加成
private int durable;
//耐久值
public Weapon() {
}
public Weapon(String name, int bonusAttack, int durable) {
this.name = name;
this.bonusAttack = bonusAttack;
this.durable = durable;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getBonusAttack() {
return bonusAttack;
}
public void setBonusAttack(int bonusAttack) {
this.bonusAttack = bonusAttack;
}
public int getDurable() {
return durable;
}
public void setDurable(int durable) {
this.durable = durable;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Weapon{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", bonusAttack=" + bonusAttack +
", durable=" + durable +
'}';
}
@Override
public Weapon clone() {
Weapon weapon=null;
try {
weapon=(Weapon)super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return weapon;
}
}
TestHero类
package Work;
public class TestHero {
public static void main(String[] args) {
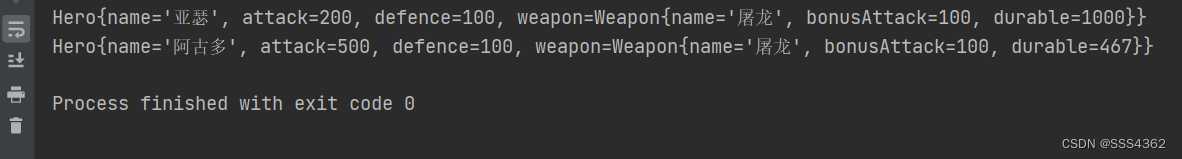
Hero hero=new Hero("亚瑟",200,100,new Weapon("屠龙",100,1000));
Hero copyHero=hero.clone();
copyHero.getWeapon().setDurable(467);
copyHero.setAttack(500);
copyHero.setName("阿古多");
System.out.println(hero);
System.out.println(copyHero);
}
}
3.3.3 示例代码的内存原理图
a 克隆后
b 修改克隆对象的属性和方法
3.3.4 示例代码运行截图
今天的文章解析java中的clone方法分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读,如果确实帮到您,您可以动动手指转发给其他人。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/24473.html