质量声明:原创文章,内容质量问题请评论吐槽。如对您产生干扰,可私信删除。
主要参考:Active Contour Model — skimage v0.16.dev0 docs – scikit-image
skimage实现
函数声明
Active contours by fitting snakes to features of images. Supports single and multichannel 2D images. Snakes can be periodic (for segmentation) or have fixed and/or free ends. The output snake has the same length as the input boundary. As the number of points is constant, make sure that the initial snake has enough points to capture the details of the final contour.
active_contour(image, snake, alpha=0.01, beta=0.1, w_line=0, w_edge=1, gamma=0.01,
bc='periodic', max_px_move=1.0, max_iterations=2500, convergence=0.1)
Parameters
----------
image : (N, M) or (N, M, 3) ndarray
Input image.
snake : (N, 2) ndarray
Initial snake coordinates. For periodic boundary conditions, endpoints
must not be duplicated.
alpha : float, optional
Snake length shape parameter. Higher values makes snake contract
faster.
beta : float, optional
Snake smoothness shape parameter. Higher values makes snake smoother.
w_line : float, optional
Controls attraction to brightness. Use negative values to attract toward
dark regions.
w_edge : float, optional
Controls attraction to edges. Use negative values to repel snake from
edges.
gamma : float, optional
Explicit time stepping parameter.
bc : {'periodic', 'free', 'fixed'}, optional
Boundary conditions for worm. 'periodic' attaches the two ends of the
snake, 'fixed' holds the end-points in place, and 'free' allows free
movement of the ends. 'fixed' and 'free' can be combined by parsing
'fixed-free', 'free-fixed'. Parsing 'fixed-fixed' or 'free-free'
yields same behaviour as 'fixed' and 'free', respectively.
max_px_move : float, optional
Maximum pixel distance to move per iteration.
max_iterations : int, optional
Maximum iterations to optimize snake shape.
convergence: float, optional
Convergence criteria.
Returns
-------
snake : (N, 2) ndarray
Optimised snake, same shape as input parameter.
References
----------
.. [1] Kass, M.; Witkin, A.; Terzopoulos, D. "Snakes: Active contour
models". International Journal of Computer Vision 1 (4): 321
(1988). DOI:`10.1007/BF00133570`
代码示例
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from skimage.color import rgb2gray
from skimage import data
from skimage.filters import gaussian
from skimage.segmentation import active_contour
img = data.astronaut() # 读入图像
img = rgb2gray(img) # 灰度化
# 圆的参数方程:(220, 100) r=100
t = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, 400) # 参数t, [0,2π]
x = 220 + 100*np.cos(t)
y = 100 + 100*np.sin(t)
# 构造初始Snake
init = np.array([x, y]).T # shape=(400, 2)
# Snake模型迭代输出
snake = active_contour(gaussian(img,3), snake=init, alpha=0.1, beta=1, gamma=0.01, w_line=0, w_edge=10)
# 绘图显示
plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
plt.imshow(img, cmap="gray")
plt.plot(init[:, 0], init[:, 1], '--r', lw=3)
plt.plot(snake[:, 0], snake[:, 1], '-b', lw=3)
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]), plt.axis("off")
plt.show()
结果显示
Numpy实现
代码示例
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def getGaussianPE(src):
""" 描述:计算负高斯势能(Negative Gaussian Potential Energy, NGPE) 输入:单通道灰度图src 输出:无符号的浮点型单通道,取值0.0 ~ 255.0 """
imblur = cv.GaussianBlur(src, ksize=(5, 5), sigmaX=3)
dx = cv.Sobel(imblur, cv.CV_16S, 1, 0) # X方向上取一阶导数,16位有符号数,卷积核3x3
dy = cv.Sobel(imblur, cv.CV_16S, 0, 1)
E = dx**2 + dy**2
return E
def getDiagCycleMat(alpha, beta, n):
""" 计算5对角循环矩阵 """
a = 2 * alpha + 6 * beta
b = -(alpha + 4 * beta)
c = beta
diag_mat_a = a * np.eye(n)
diag_mat_b = b * np.roll(np.eye(n), 1, 0) + b * np.roll(np.eye(n), -1, 0)
diag_mat_c = c * np.roll(np.eye(n), 2, 0) + c * np.roll(np.eye(n), -2, 0)
return diag_mat_a + diag_mat_b + diag_mat_c
def getCircleContour(centre=(0, 0), radius=(1, 1), N=200):
""" 以参数方程的形式,获取n个离散点围成的圆形/椭圆形轮廓 输入:中心centre=(x0, y0), 半轴长radius=(a, b), 离散点数N 输出:由离散点坐标(x, y)组成的2xN矩阵 """
t = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, N)
x = centre[0] + radius[0] * np.cos(t)
y = centre[1] + radius[1] * np.sin(t)
return np.array([x, y])
def getRectContour(pt1=(0, 0), pt2=(50, 50)):
""" 根据左上、右下两个顶点来计算矩形初始轮廓坐标 由于Snake模型适用于光滑曲线,故这里用不到该函数 """
pt1, pt2 = np.array(pt1), np.array(pt2)
r1, c1, r2, c2 = pt1[0], pt1[1], pt2[0], pt2[1]
a, b = r2 - r1, c2 - c1
length = (a + b) * 2 + 1
x = np.ones((length), np.float)
x[:b] = r1
x[b:a + b] = np.arange(r1, r2)
x[a + b:a + b + b] = r2
x[a + b + b:] = np.arange(r2, r1 - 1, -1)
y = np.ones((length), np.float)
y[:b] = np.arange(c1, c2)
y[b:a + b] = c2
y[a + b:a + b + b] = np.arange(c2, c1, -1)
y[a + b + b:] = c1
return np.array([x, y])
def snake(img, snake, alpha=0.5, beta=0.1, gamma=0.1, max_iter=2500, convergence=0.01):
""" 根据Snake模型的隐式格式进行迭代 输入:弹力系数alpha,刚性系数beta,迭代步长gamma,最大迭代次数max_iter,收敛阈值convergence 输出:由收敛轮廓坐标(x, y)组成的2xN矩阵, 历次迭代误差list """
x, y, errs = snake[0].copy(), snake[1].copy(), []
n = len(x)
# 计算5对角循环矩阵A,及其相关逆阵
A = getDiagCycleMat(alpha, beta, n)
inv = np.linalg.inv(A + gamma * np.eye(n))
# 初始化
y_max, x_max = img.shape
max_px_move = 1.0
# 计算负高斯势能矩阵,及其梯度
E_ext = -getGaussianPE(img)
fx = cv.Sobel(E_ext, cv.CV_16S, 1, 0)
fy = cv.Sobel(E_ext, cv.CV_16S, 0, 1)
T = np.max([abs(fx), abs(fy)])
fx, fy = fx / T, fy / T
for g in range(max_iter):
x_pre, y_pre = x.copy(), y.copy()
i, j = np.uint8(y), np.uint8(x)
try:
xn = inv @ (gamma * x + fx[i, j])
yn = inv @ (gamma * y + fy[i, j])
except Exception as e:
print("索引超出范围")
# 判断收敛
x, y = xn, yn
err = np.mean(0.5 * np.abs(x_pre - x) + 0.5 * np.abs(y_pre - y))
errs.append(err)
if err < convergence:
print(f"Snake迭代{g}次后,趋于收敛。\t err = {err:.3f}")
break
return x, y, errs
def main():
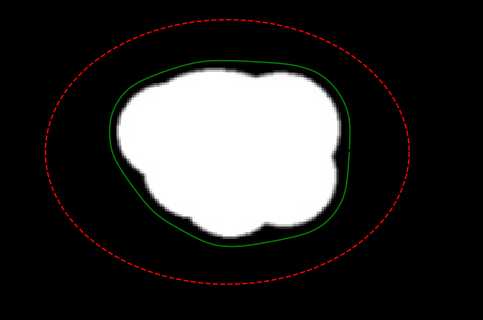
src = cv.imread("circle.jpg", 0)
img = cv.GaussianBlur(src, (3, 3), 5)
# 构造初始轮廓线
init = getCircleContour((140, 95), (110, 80), N=200)
# Snake Model
x, y, errs = snake(img, snake=init, alpha=0.1, beta=1, gamma=0.1)
plt.figure() # 绘制轮廓图
plt.imshow(img, cmap="gray")
plt.plot(init[0], init[1], '--r', lw=1)
plt.plot(x, y, 'g', lw=1)
plt.xticks([]), plt.yticks([]), plt.axis("off")
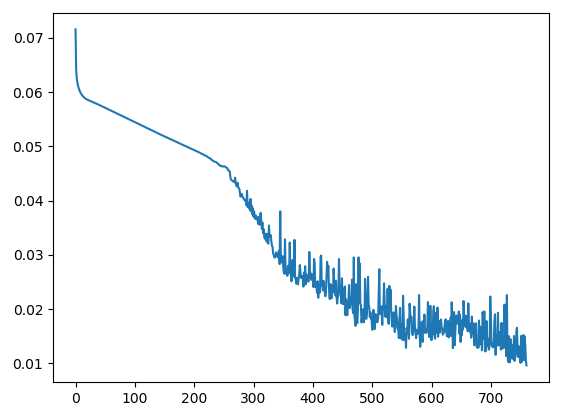
plt.figure() # 绘制收敛趋势图
plt.plot(range(len(errs)), errs)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
结果显示
Snake迭代760次后,趋于收敛。 err = 0.010
 |
 |
今天的文章主动轮廓模型:Snake模型的python实现分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读,如果确实帮到您,您可以动动手指转发给其他人。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/27490.html

