今天在公司又学习到了一个新的知识点:委托!
它相当于C/C++中的函数指针。也就是间接调用!
其实它的作用还是挺大的,但是也是挺难学习的,花了好大的时间才搞懂一点点,但是还是不知道它在项目中该用在什么地方。
算了,先不管,先用博客记录下来,也许以后就知道了,就用得上了!!!
委托有两种方式:系统封装好的,自定义的。
系统封装好的委托
系统封装好的委托有很多,这里就主要讲常用的两种:Action 和 Func.
其实这两个很好区别的:
Action是没有返回值类型的,所以它只适合0至n个参数的void返回值的方法。Func是固定要有一个返回值的,所以它只适合0至n个参数的和带返回值的方法。
Action
定义:Action action = new Action(对象.方法名);
下面我们写一个类来测试一下:
class ActionFuncDelegate {
public void ADelegate() {
Console.WriteLine("这是一个返回值为空,参数也为空的函数!");
}
}
Mian函数:
static void Main(string[] args) {
ActionFuncDelegate actionDelegate = new ActionFuncDelegate();
Console.WriteLine("---系统自带委托:Action---");
// 定义系统的委托:Action
// 对象.方法名
Action action = new Action(actionDelegate.ADelegate);
// 间接调用
action.Invoke(); // 等效于: action();
// 直接调用
actionDelegate.ADelegate();
}
运行截图:
其他例子:
Action:void返回值,带两个不同的参数。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _Action {
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Action<int, string> action = new Action<int, string>(OutName);
action.Invoke(5, "Mir.Yang");
Console.ReadKey();
}
static void OutName(int count, string name) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Console.WriteLine("Hello {0}.", name);
}
}
}
}
Func
定义:Func<返回类型, 参数类型1, 参数类型2, 参数类n> func1 = new Func<返回类型, 参数类型1, 参数类型2, 参数类型n>(对象名.方法名);
下面我们写一个类来测试一下:
class ActionFuncDelegate {
public int Add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
public int Minus(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
}
Main函数:
static void Main(string[] args) {
ActionFuncDelegate actionDelegate = new ActionFuncDelegate();
Console.WriteLine("\n");
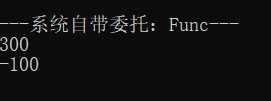
Console.WriteLine("---系统自带委托:Func---");
// 定义系统的委托:Func
Func<int, int, int> func1 = new Func<int, int, int>(actionDelegate.Add);
Func<int, int, int> func2 = new Func<int, int, int>(actionDelegate.Minus);
int x = 100;
int y = 200;
int z = 0;
// 间接调用
z = func1.Invoke(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
z = func2.Invoke(x, y);
Console.WriteLine(z);
运行截图:
自定义委托(delegate)
自定义委托,使用的关键字是:delegate
声明:public delegate 返回类型 委托名(参数1, 参数2,参数n);
例::public delegate double UserD(double x, double y);
当我们需要使用到它时,需要new实例化它才可以使用!
下面我们写一个类来测试一下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Delegate_委托 {
/************************************************/
// 声明自定义委托
public delegate double UserD(double x, double y);
class UserDelegate {
// 下面方法返回值都是double类型,且参数都是两个double类型
public double Add(double x, double y) {
return x + y;
}
public double Min(double x, double y) {
return x - y;
}
public double Mul(double x, double y) {
return x * y;
}
public double Div(double x, double y) {
return x / y;
}
}
}
Main函数:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Delegate_委托 {
class Mains {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("---自定义委托---");
UserDelegate userDelegate = new UserDelegate();
// ***自定义委托***
// 实例化委托
UserD userD1 = new UserD(userDelegate.Add);
UserD userD2 = new UserD(userDelegate.Min);
UserD userD3 = new UserD(userDelegate.Mul);
UserD userD4 = new UserD(userDelegate.Div);
double a = 100;
double b = 200;
double c = 0;
// 间接调用
c = userD1.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = userD2.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = userD3.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
c = userD4.Invoke(a, b);
Console.WriteLine(c);
}
}
}
运行截图:
当然也可以时其他的不同类型的组合。
委托小例子
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 委托 {
// 定义委托
public delegate void delSayHi(string name);
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
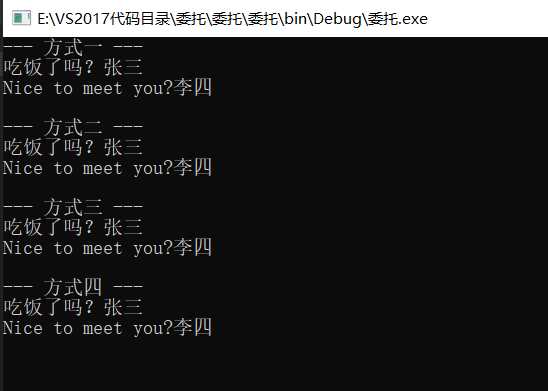
// 方式一 直接调用函数
Console.WriteLine("--- 方式一 ---");
SayHiChinese("张三");
SayHiEnglish("李四");
Console.WriteLine();
// 方式二 通过委托调用函数
Console.WriteLine("--- 方式二 ---");
delSayHi sayHi1 = new delSayHi(SayHiChinese);
delSayHi sayHi2 = new delSayHi(SayHiEnglish);
sayHi1("张三");
sayHi2("李四");
Console.WriteLine();
// 方式三 函数名直接赋值委托调用
Console.WriteLine("--- 方式三 ---");
delSayHi sayHi3 = SayHiChinese;
delSayHi sayHi4 = SayHiEnglish;
sayHi3("张三");
sayHi4("李四");
Console.WriteLine();
// 方式四 直接将函数名当作参数传给委托调用
Console.WriteLine("--- 方式四 ---");
test("张三", SayHiChinese);
test("李四", SayHiEnglish);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.ReadKey();
}
// 带有委托参数的函数
public static void test(string name, delSayHi dsh) {
dsh(name);
}
public static void SayHiChinese(string name) {
Console.WriteLine("吃饭了吗?" + name);
}
public static void SayHiEnglish(string name) {
Console.WriteLine("Nice to meet you?" + name);
}
}
}
运行截图:
泛型委托
泛型就是相当与C++当中的容器,它可以是任何类型。
代码例子:
寻找数组的最大值(任意类型的数组)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 泛型 {
// 定义泛型委托,实现两数相减
public delegate int Delegate<T>(T o1, T o2);
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
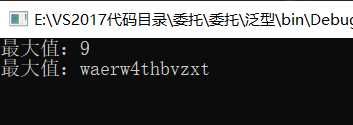
int[] array1 = {
1, 2, 3, 5, 4, 6, 9, 8 };
string[] array2 = {
"asdfasdlg", "xzvcnryt", "waerw4thbvzxt", "asdfgh" };
// 利用匿名函数实现
int result1 = GetMax<int>(array1, delegate (int t1, int t2) {
return t1 - t2;
});
Console.WriteLine("最大值:" + result1);
string result2 = GetMax<string>(array2, delegate (string s1, string s2) {
return s1.Length - s2.Length;
});
Console.WriteLine("最大值:" + result2);
Console.ReadKey();
}
// 定义泛型函数
public static T GetMax<T>(T[] arr, Delegate<T> del) {
T max = arr[0];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) {
// 委托实现max减去arr[i],当小于0,说明max比它小
if (del(max, arr[i]) < 0) {
max = arr[i];
}
}
return max;
}
}
}
运行截图:
其他例子:
实现两个不同类型的变量相加。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 复习委托 {
// 定义泛型委托
public delegate Y MyDeleAdd<T, Y>(T a, Y b);
class 泛型委托 {
static void Main(string[] args) {
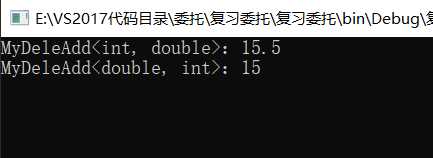
MyDeleAdd<int, double> myDeleAddDouble = new MyDeleAdd<int, double>(DeleAtOne);
double res = myDeleAddDouble.Invoke(10, 5.5);
Console.WriteLine("MyDeleAdd<int, double>:{0}", res);
MyDeleAdd<double, int> myDeleAddInt = new MyDeleAdd<double, int>(DeleteAtTwo);
int ret = myDeleAddInt.Invoke(10.4, 5);
Console.WriteLine("MyDeleAdd<double, int>:{0}", ret);
Console.ReadKey();
}
static double DeleAtOne(int x, double y) {
return x + y;
}
static int DeleteAtTwo(double x, int y) {
return Convert.ToInt32(x + y); // 转换为int类型,按照四舍五入的原则
}
}
}
委托还有两个常用的用法:模板方法 与 回调方法。
模板方法
这个我也不知道该怎么讲,我就把代码放在这里,在讲解一下代码的思路就这样吧!
代码思路:
- 我们有一个产品类Product,它包含一个Name属性。
- 还有一个箱子类Box,它包含有产品类的对象属性。
- 紧接着我们编写一个模板方法类TemplateMethod ,它的返回值是Box类型,参数是Func委托类型,该方法的主要作用是将一个产品包装完后,返回包装后Box的类型。
- 我们在定义一个生产产品的工厂类ProductFactory ,里面有生产披萨和玩具卡车的方法。
- 这样定义的作用是:我们以后都不需要去修改Product 类 和 Box 类 和 TemplateMethod 类,只是需要后续还有什么商品需要增加的话,就在ProductFactory 类的增加对应的生产方法。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
/* * 委托:模板方法的使用 */
namespace Delegate_委托 {
// 产品
class Product {
public string Name {
get; set; }
}
// 箱子
class Box {
public Product product {
get; set; }
}
// 模板方法(对产品进行包装)
class TemplateMethod {
public Box Template(Func<Product> func) {
Box box = new Box(); // 找一个箱子
Product product = func.Invoke(); // 找到产品
box.product = product; // 将产品包装到箱子中
return box; // 返回箱子
}
}
// 生产产品的工厂
class ProductFactory {
public Product MakePizza() {
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "Pizza";
return product;
}
public Product MakeToyCar() {
Product product = new Product();
product.Name = "ToyCar";
return product;
}
}
}
Main函数:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Delegate_委托 {
class Mains {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("---委托的常用用法一:模板方法---");
ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory(); // 产品生产工厂
TemplateMethod templateMethod = new TemplateMethod(); // 包装产品
// 定义委托
Func<Product> f1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);
Func<Product> f2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);
// 产品包装
Box box1 = templateMethod.Template(f1);
Box box2 = templateMethod.Template(f2);
Console.WriteLine(box1.product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(box2.product.Name);
Console.WriteLine("\n按任意键继续...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
运行截图:
回调方法
按照我个人的理解就是:当函数在正常执行时遇到一些突发状况而调用一个特定的回调方法!
代码还是和上面差不多的代码,就修改一些部分和添加了一个回调方法类Logger 。
产品Product_2 添加多了一个价格Price属性,当包装类TemplateMethod_2 在包装产品时,判断产品的价格大于50元钱时,出发调用回调方法Logger !
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
/* * 委托:回调方法的使用 */
namespace Delegate_委托 {
// 产品
class Product_2 {
public string Name {
get; set; }
public double Price {
get; set; }
}
// 盒子
class Box_2 {
public Product_2 product {
get; set; }
}
/************/
/* 回调方法 */
class Logger {
public void Log(Product_2 product_2) {
Console.WriteLine("出现价格偏高的产品:产品名字:{0} 产品价格:{1} 出现的时间:{2}",
product_2.Name, product_2.Price, DateTime.Now);
}
}
// 模板方法(对产品进行包装)
class TemplateMethod_2 {
public Box_2 Template(Func<Product_2> func, Action<Product_2> action) {
Box_2 box = new Box_2();
Product_2 product = func.Invoke();
// 调用回调方法
if (product.Price > 50) {
action.Invoke(product);
}
box.product = product;
return box;
}
}
// 生产产品的工厂
class ProductFactory_2 {
public Product_2 MakePizza() {
Product_2 product = new Product_2();
product.Name = "Pizza";
product.Price = 15.5;
return product;
}
public Product_2 MakeToyCar() {
Product_2 product = new Product_2();
product.Name = "ToyCar";
product.Price = 55.6;
return product;
}
}
}
Main函数:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Delegate_委托 {
class Mains {
static void Main(string[] args) {
Console.WriteLine("\n");
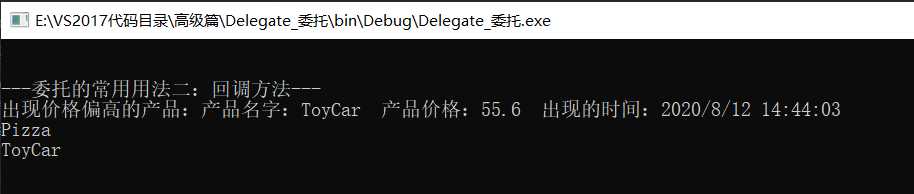
Console.WriteLine("---委托的常用用法二:回调方法---");
ProductFactory_2 productFactory_2 = new ProductFactory_2(); // 产品生产工厂
TemplateMethod_2 templateMethod_2 = new TemplateMethod_2(); // 包装产品
Logger logger = new Logger(); // 定义回调
// 定义委托
Func<Product_2> ff1 = new Func<Product_2>(productFactory_2.MakePizza);
Func<Product_2> ff2 = new Func<Product_2>(productFactory_2.MakeToyCar);
Action<Product_2> action_1 = new Action<Product_2>(logger.Log);
// 产品包装
// 如果有产品价格高于50,则会调用回调方法
Box_2 boxs1 = templateMethod_2.Template(ff1, action_1);
Box_2 boxs2 = templateMethod_2.Template(ff2, action_1);
Console.WriteLine(boxs1.product.Name);
Console.WriteLine(boxs2.product.Name);
Console.WriteLine("\n按任意键继续...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
运行截图:
再讲最后一点:
委托有单播委托和多播委托两种。
上面我们使用的都是单播委托,所以我们这里就演示多播委托的用法!
多播委托
其实也很简单,就将委托相加起来进行了。
或者定义一个委托,然后将委托对象加等于函数名。
看不懂例子一的可以去看例子二。
下面我们写一个类来测试一下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Threading;
/* * 多播委托 */
namespace Delegate_委托 {
class MultiDelegate {
public int ID {
get; set; }
public ConsoleColor penColor {
get; set; } // 设置字体颜色
public void DoHomework() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
// 修改控制台输出字体的颜色
Console.ForegroundColor = this.penColor;
Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing homgwork {1} hour(s)", this.ID, i);
// 睡眠一秒钟
Thread.Sleep(1000);
}
}
}
}
Main函数:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Delegate_委托 {
class Mains {
static void Main(string[] args) {
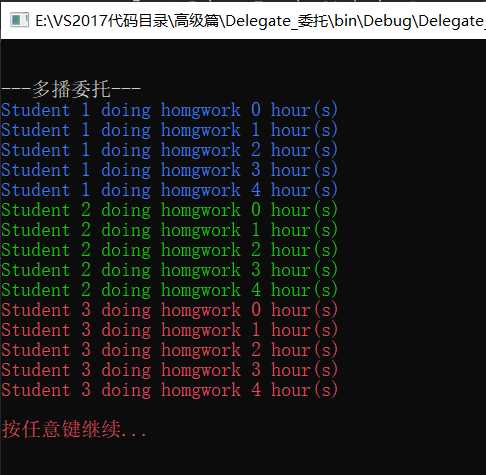
Console.WriteLine("\n");
Console.WriteLine("---多播委托---");
MultiDelegate multicastDelegate1 = new MultiDelegate() {
ID = 1, penColor = ConsoleColor.Blue };
MultiDelegate multicastDelegate2 = new MultiDelegate() {
ID = 2, penColor = ConsoleColor.Green };
MultiDelegate multicastDelegate3 = new MultiDelegate() {
ID = 3, penColor = ConsoleColor.Red };
Action act_1 = new Action(multicastDelegate1.DoHomework);
Action act_2 = new Action(multicastDelegate2.DoHomework);
Action act_3 = new Action(multicastDelegate3.DoHomework);
// 单薄委托测试用例
/* act_1.Invoke(); act_2.Invoke(); act_3.Invoke(); */
// 多播委托测试用例
act_1 += act_2;
act_1 += act_3;
act_1.Invoke();
Console.WriteLine("\n按任意键继续...");
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
运行截图:
多播委托例子二
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 多播委托 {
// 定义委托
public delegate void Del();
class Program {
static void Main(string[] args) {
// 多播委托就是将委托对象+=函数名
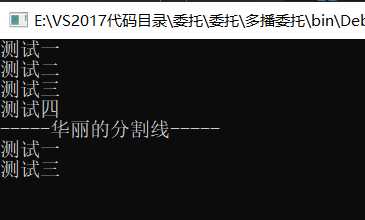
Del del = test1;
del += test2;
del += test3;
del += test4;
del();
Console.WriteLine("-----华丽的分割线-----");
// 有+=,也会有-=
del -= test2;
del -= test4;
del();
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static void test1() {
Console.WriteLine("测试一");
}
public static void test2() {
Console.WriteLine("测试二");
}
public static void test3() {
Console.WriteLine("测试三");
}
public static void test4() {
Console.WriteLine("测试四");
}
}
}
运行截图:
总结:
好了,委托也就讲到这里了,看懂、看不懂也就凑合一下吧,毕竟我也是一名刚入手C#语言的菜鸟!
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/28186.html