%% Find Green Object
% This script reads in an image file and then attempts to find a green
% object in the image. It is designed to find one green ball and highlight
% that ball on the original image
% Copyright 2013 The MathWorks, Inc.
%% Housekeeping
clear all; close all; clc;
%% Step 1: Read image into MATLAB
% First we read the specified image from the file and bring it into MATLAB
% as a variable. We also display the image to ensure it is correct.
greenBall1 = imread(‘greenBall1.jpg’);
t = imtool(greenBall1);
%%
close(t);
%% Step 2: Identify Unique Characteristics of Object of Interest
%%
% Extract each color
% Next we using indexing to extract three 2D matrices from the 3D image
% data corresponding to the red, green, and blue components of the image.
r = greenBall1(:, :, 1);
g = greenBall1(:, :, 2);
b = greenBall1(:, :, 3);
%%
% View different color planes
figure, colormap gray
subplot(2,2,1),imagesc(r)
subplot(2,2,2),imagesc(g)
subplot(2,2,3),imagesc(b)
%%
% Calculate Green
% Then we perform an arithmetic operation on the matrices as a whole to try
% to create one matrix that represents an intensity of green.
justGreen = g – r/2 – b/2;
colorPlanesPlot(r,g,b,justGreen);
%%
close all
%% Step 3: Isolate Object of Interest
%%
% Threshold the image
% Now we can set a threshold to separate the parts of the image that we
% consider to be green from the rest.
bw = justGreen > 50;
figure;
imagesc(bw);
colormap(gray);
%%
% Remove small unwanted objects
% We can use special functions provided by the Image Processing toolbox to
% quickly perform common image processing tasks. Here we are using
% BWAREAOPEN to remove groups of pixels less than 30.
ball1 = bwareaopen(bw, 30);
figure;
imagesc(ball1);
%% Step 4: Find center of green object
% Now we are using REGIONPROPS to extract the centroid of the group of
% pixels representing the ball.
figure;
s = regionprops(ball1, {‘centroid’,’area’});
if isempty(s)
error(‘No ball found!’);
else
[~, id] = max([s.Area]);
hold on, plot(s(id).Centroid(1),s(id).Centroid(2),’wp’,’MarkerSize’,20,’MarkerFaceColor’,’r’), hold off
disp([‘Center location is (‘,num2str(s(id).Centroid(1),4),’, ‘,num2str(s(id).Centroid(2),4),’)’])
end
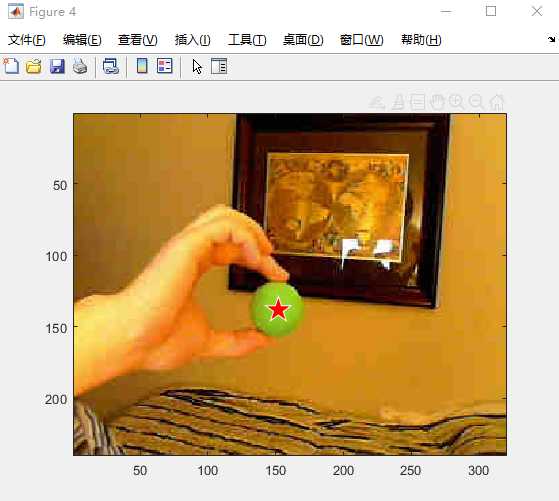
%% Step 5: Verify estimated location
% Finally we will plot the center on the original image to clearly evaluate
% how well we have found the center.
figure;
imagesc(greenBall1);
hold on, plot(s(id).Centroid(1),s(id).Centroid(2),’wp’,’MarkerSize’,20,’MarkerFaceColor’,’r’), hold off
B168
今天的文章模版匹配定位跟踪分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读,如果确实帮到您,您可以动动手指转发给其他人。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/33002.html