1 编写该文章的起因
博主是一枚小新,经常挖坑填坑。最近在工作中遇到了这样一种情况。某天小伙伴说博主写得一个方法有问题,并且相应的测试类也跑不通。博主一直秉着磨刀不误砍柴工的思想,测试类都是写得好好地并且能杠杠运行的!怀着好奇,经过一番debug,发现某句代码抛出了空指针,如下
String url = linkedService.getUrlById(id);
getUrlById是通过id去查询数据库中的某条数据。问题到这里已经暴露无遗了,博主在测试该方法时将id写死,并且在数据库中能查出该条数据。而小伙伴的数据库中并没有这条数据,就导致了这个bug。最终,博主将sql语句发给小伙伴,测试通过了,问题似乎得到了**“解决”**,大家也皆大欢喜地继续做其他任务了。
然而,过了几天,博主在又遇到了相同的问题。
UserInfo user = userInfoService.getUser(id);
okok,这次博主一下子就定位到了问题的关键处,添加了相应的数据就解决了问题。但此时博主心里已经产生了一个疑问,并且在第二天例会时提了出来。
博主:“因为环境的改变(数据不同:每个同事维护自己的数据库,并没有使用共同的数据库),造成测试用例有时通过,有时不通过,这应该怎么有效的解决?”
孙大大:(博主的同事,喜欢专研问题并解决问题):“环境改变可能包括数据库,网络等其他因素,而你们遇到的这个问题,是测试用例写得不够自动化、专业化,在自己电脑上能测试并且通过,换到其他电脑上不能运行,这就是测试用例写得不够好。”
博主的好奇心一下子被吸引住了,如何解决这种问题,什么才能叫做写得好的测试用例?于是博主专门花了三天的时间阅读了 David Thomas 和Andrew Hunt 写的《单元测试之道Java版:使用JUnit》。这本书总共只有170多页,内容不多,没有啃大部头的那种挫败感,算是一本入门书籍,让我在短时间内了解如何使用JUnit编写单元测试。
2 如何编写好的测试类
2.1 运用好断言
一个单元测试是程序员写的一段代码,用于执行另一段代码并判断代码的行为是否与期望值一致。在实际中,为了验证行为和期望值是否一致,需要使用到assertion(断言)。它是一种非常简单的方法调用,用于判断某个语句是否为真。使用的时候需要在测试类中引入相应的方法
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
比如方法assertTrue将会检查给定的二元条件是否为真,如果条件非真,则该断言将会失败。具体的实现如下面所示:
public void assertTrue(boolean condition){
if(!condition){
abort();
}
}
我们可以利用该断言来检查两个数字是否相等:
assertTrue(a == 2);
如果由于某种原因,当调用assertTrue()的时候,a并不等于2,那么上面的程序将会中止并报错。
2.2 少用输出语句
输出语句大家用的都不少,譬如现在要看一个pojo,在重写了它的toString()方法后,利用如下方式输出
System.out.println(pojo);
logger.info("pojo={}",pojo);
接着就在满是日志的控制台里查找我们需要的信息。这种方法并不是不可取,但是效率低。如果你已经知道了期望值,那么最好使用断言来判断结果。
2.3 注重有效的单元测试
本小节内容引用自《单元测试之道Java版:使用JUnit》
2.3.1 明确测试目的
我如何知道代码运行是否正确呢?
我要如何对它进行测试?
还有哪些方面可能会发生错误?
这个问题是否会在其他的地方出现呢?
2.3.2 一般原则
测试任务可能失败的地方。
测试任何已经失败的地方。
对于新加的代码,在被证明正确之前,都可能是有问题的。
至少编写和产品代码一样多的测试代码。
针对每次编译都做局部测试。
签入代码之前做全局测试。
2.3.3 使用你的RIGHT-BICEP
结果是否正确(Right)?
边界(boundary)条件是否正确?
是否可以检查反向(inverse)关联?
是否可以使用其他方法来跨检查(cross-check)结果?
错误条件(error condition)是否可以重新?
性能方面是否满足条件?
2.3.4 好的测试是一个TRIP
Automatic(自动的)。
Thorough(全面的)。
Repetable(可重复的)。
Independent(独立的)。
Professional(专业的)。
2.3.5 CORRECT边界条件
一致性(Conformance)——值是否符合预期的格式?
有序性(Ordering)——一组值是该有序的,还是无序的?
区间性(Range)——值是否在一个合理的最大值和最小值的范围之内?
引用、耦合性(Reference)——代码是否引用了一些不受代码本身直接控制的外部因素?
存在性(Existence)——值是否存在(例如,非null,非零,包含于某个集合等)
基数性(Cardinality)——是否恰好有足够的值?
时间性,绝对的或者相对的(Time)——所有事情是否都是按顺序发生的?是否在正确的时间?是否及时?
3 快速入门
本章的主要目标是在Spring+SpringMVC+MyBatis的基础架构上,从传统的Dao、Service、Controller,由下往上针对这三层完成一次完整的测试。通过这个例子,希望大家能够更加了解测试如何编写。
3.1 环境要求
本文采用JAVA 1.8.0_92、Spring Framework 4.3.9.RELEASE、 Junit 4.12、mysql-5.6.32通过测试,使用maven构建项目、idea作为编译器。
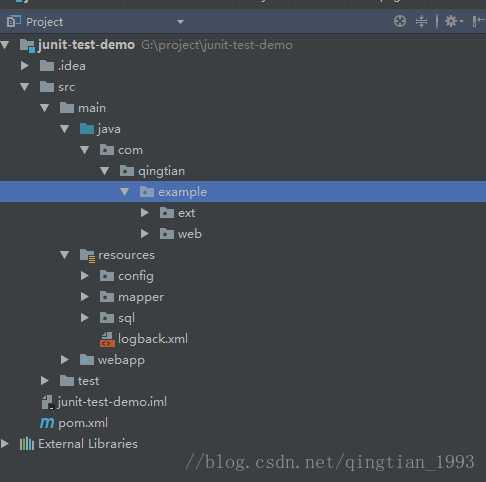
3.2 项目结构解析
src/main/java/qingtian/example程序的主要代码src/main/resourcesconfig配置文件mappermybatis映射文件sql数据库脚本logback.xml日志配置文件
src/test测试类
3.3 代码解析
BaseTest
在src/test/下创建一个测试的基类,在这里设置了事务回滚,测试数据不会污染数据库。当然,并不是完全不对数据库造成影响。如果主键被设置为自动增长时,会发现ID是不连续的,且在不断增长,所以这并不是真正意义上的无污染。
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration({"classpath:config/spring/spring-dao.xml",
"classpath:config/spring/spring-service.xml",
"classpath:config/spring/spring-web.xml"})
@Transactional
@Rollback
public class BaseTest{
}
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)让测试在Spring容器环境下执行ContextConfiguration加载所需的配置文件(可以以字符数组的形式加载)@Transactional开启事务:已经配置了注解式事务@Rollback设置测试后回滚,默认属性为true,即回滚
PeopleDao
在src/main/java/下创建dao层,实现了最简单的增删查改分页操作。
package com.qingtian.example.web.dao;
import com.qingtian.example.web.entity.People;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author qingtian
* @Description
* @Date Created in 2018/3/15
*/
public interface PeopleDao {
/**
* 返回people全部数据(分页)
* @param offset
* @param limit
* @return
*/
List<People> listAll(@Param("offset") int offset, @Param("limit") int limit );
/**
* 查找
* @param id
* @return
*/
People getPeople(long id);
/**
* 插入一条数据
* @param people
* @return
*/
long insertPeople(People people);
/**
* 更新一条数据
* @param people
* @return
*/
long updatePeople(People people);
/**
* 删除一条数据
* @param id
* @return
*/
long deletePeople(long id);
}
People
People实体类非常简单,只有两个字段,id和name
private long id ;
private String name;
//省略get、set方法
Peolple-mapper
people类的映射文件,注意一点,调用insertPeople时通过设置属性useGeneratedKeys="true"、keyProperty="id"可以返回新增数据的主键。
useGeneratedKeys="true"设置是否使用JDBC的getGenereatedKeys方法获取主键并赋值到keyProperty设置的领域模型属性中keyProperty="id"设置绑定返回的属性为id
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.qingtian.example.web.dao.PeopleDao">
<select id="listAll" resultType="People">
select id,name from people limit #{offset},#{limit}
</select>
<select id="getPeople" resultType="People">
select id,name from people where id = #{id}
</select>
<insert id="insertPeople" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id">
insert ignore into people(name) VALUES (#{name})
</insert>
<update id="updatePeople" parameterType="People">
update people set name = #{name} where id = #{id}
</update>
<delete id="deletePeople" >
delete from people where id = #{id}
</delete>
</mapper>
PeopleDaoTest
在src/test/下创建PeopleDaoTest测试类。该测试类要验证(有序)
- 插入十条数据,测试
listAll()方法能否查到十条数据 - 测试
getPeople()方法查到数据是否刚插入的数据 - 调用
updatePeople()修改name属性,查询刚修改的数据并验证是否修改 - 调用
deletePeople()删除最后一条数据,查询数据库判断数据是否已经不存在
以上测试均使用Assert断言的方式来验证方法的正确性
package com.qingtian.example.web.dao;
import com.qingtian.example.core.BaseTest;
import com.qingtian.example.web.entity.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertNull;
/**
* @Author qingtian
* @Description
* @Date Created in 2018/3/15
*/
public class PeopleDaoTest extends BaseTest{
@Autowired
private PeopleDao peopleDao;
@Test
public void testPeopleDao(){
//初始化数据
People entity = new People();
entity.setName("peopleDao测试");
//插入10条数据
int count = 10;
while(count != 0){
peopleDao.insertPeople(entity);
count--;
}
//查询db中的列表
int offset = 0;
int limit = 10;
//正常查询
//offset = 0, limit =10
List<People> list = peopleDao.listAll(offset, limit);
//验证是否有10条数据
assertEquals(list.size(),10);
//查询刚才插入的数据
People people = peopleDao.getPeople(entity.getId());
//验证数据是否一致
assertEquals(people.getName(),entity.getName());
//修改插入的数据
String name = "peopleDao测试修改数据";
people.setName(name);
peopleDao.updatePeople(people);
//查询刚才的数据
people = peopleDao.getPeople(people.getId());
assertEquals(name,people.getName());
//删除一条数据
peopleDao.deletePeople(people.getId());
//再查已经不存在了
people = peopleDao.getPeople(people.getId());
assertNull(people);
}
}
测试都是由下而上,遵循dao -> service -> controller,接下来看得是service层的测试。
BaseService
在src/main/java/ 下创建service层的通用接口,定义了增删查改分页5个抽象方法,方便拓展。
package com.qingtian.example.web.service.core;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author qingtian
* @Description
* @Date Created in 2018/3/16
*/
public interface BaseService<T> {
List<T> listAll(int offset,int limit);
T getById(long id);
T update(T entity);
T deleteById(long id);
T add(T entity);
}
PeopleService
在src/main/java 下创建PeopleService接口,并继承BaseService
package com.qingtian.example.web.service;
import com.qingtian.example.web.entity.People;
import com.qingtian.example.web.service.core.BaseService;
/**
* @Author qingtian
* @Description
* @Date Created in 2018/3/16
*/
public interface PeopleService extends BaseService<People> {
}
PeopleServiceImpl
在src/main/java/impl下创建实现类
package com.qingtian.example.web.service.impl;
import com.qingtian.example.web.dao.PeopleDao;
import com.qingtian.example.web.entity.People;
import com.qingtian.example.web.service.PeopleService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author qingtian
* @Description
* @Date Created in 2018/3/15
*/
@Service("peopleService")
public class PeopleServiceImpl implements PeopleService{
@Autowired
private PeopleDao dao;
public List<People> listAll(int offset, int limit) {
return dao.listAll(offset,limit);
}
public People getById(long id) {
return dao.getPeople(id);
}
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public People update(People entity) {
dao.updatePeople(entity);
return dao.getPeople(entity.getId());
}
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public People deleteById(long id) {
People entity = dao.getPeople(id);
dao.deletePeople(id);
return entity;
}
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public People add(People entity) {
dao.insertPeople(entity);
return dao.getPeople(entity.getId());
}
}
PeopleServiceTest
在src/test/下创建peopleService的测试类,测试方案同peopleDao测试类
package com.qingtian.example.web.service;
import com.qingtian.example.core.BaseTest;
import com.qingtian.example.web.entity.People;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import java.util.List;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* @Author qingtian
* @Description
* @Date Created in 2018/3/16
*/
public class PeopleServiceTest extends BaseTest{
@Autowired
private PeopleService peopleService;
@Test
public void testService(){
//初始化数据
People entity = new People();
String name = "peopleService测试";
entity.setName(name);
//循环插入数据
int count = 10;
while(count != 0){
entity = peopleService.add(entity);
count--;
}
//查询数据列表
int offset = 0;
int limit = 10;
List<People> list = peopleService.listAll(offset, limit);
//验证是否有10条数据
assertEquals(list.size(),10);
//获取插入的最后一条数据
People people = peopleService.getById(entity.getId());
//验证name是否一致
assertEquals(people.getName(),name);
//修改最后一条数据
name = "修改测试数据";
people.setName(name);
people = peopleService.update(people);
assertEquals(people.getName(),name);
//删除一条数据
people = peopleService.deleteById(people.getId());
//此时再去查,该条数据已不存在
people = peopleService.getById(people.getId());
assertNull(people);
}
}
controller层的测试比较复杂,使用用了测试框架Mockito,本文重点讲如何编写测试类,Mockito 如何使用请参考官网。
PeopleController
在src/main/java创建 peopleController
JsonUtils将指定数据转换成Json格式@RequestMapping路径规划参照RESTful API
package com.qingtian.example.web.controller;
import com.qingtian.example.ext.common.constant.HttpCode;
import com.qingtian.example.ext.utils.JsonUtils;
import com.qingtian.example.web.entity.People;
import com.qingtian.example.web.service.PeopleService;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author qingtian
* @Description
* @Date Created in 2018/3/15
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/peoples")
public class PeopleController {
public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PeopleController.class);
@Autowired
private PeopleService peopleService;
/**
* 列举所有people的列表
*
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String listAll(@RequestParam(value = "offset", required = false) Integer offset,
@RequestParam(value = "limit", required = false) Integer limit) {
//设置offset参数
if (offset == null || offset < 1) {
offset = 0;
}
//设置limit参数
if (limit == null || limit < 1) {
limit = 10;
}
//查询列表
List<People> peopleList = peopleService.listAll(offset, limit);
return JsonUtils.genInfoJsonStr(HttpCode.HTTP_OK, "获取列表数据成功", peopleList);
}
/**
* 新增一条数据
* @param name
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String save(@RequestParam(value = "name") String name) {
//设置参数
People entity = new People();
entity.setName(name);
//新增数据
try {
entity = peopleService.add(entity);
return JsonUtils.genInfoJsonStr(HttpCode.HTTP_CREATE,"新增数据成功",entity);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("class PeopleController method save execute exception [" + e.getMessage() + "]");
return JsonUtils.genInfoJsonStr(HttpCode.HTTP_INVALID_REQUEST,"新增数据失败",e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 获取单条数据
* @param id
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getPeople(@PathVariable("id")Long id){
People entity = peopleService.getById(id);
return JsonUtils.genInfoJsonStr(HttpCode.HTTP_OK,"获取数据成功",entity);
}
/**
* 更新数据
* @param id
* @param name
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String update(@PathVariable("id")Long id,
@RequestParam(value = "name")String name){
People entity = new People();
entity.setId(id);
entity.setName(name);
try {
entity = peopleService.update(entity);
return JsonUtils.genInfoJsonStr(HttpCode.HTTP_CREATE,"修改信息成功",entity);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("class PeopleController method update execute exception [" + e.getMessage() + "]");
return JsonUtils.genInfoJsonStr(HttpCode.HTTP_INVALID_REQUEST,"修改信息失败",e.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* 删除信息成功
* @param id
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String delete(@PathVariable("id")Long id){
try {
People entity = peopleService.deleteById(id);
return JsonUtils.genInfoJsonStr(HttpCode.HTTP_NO_CONTENT,"删除信息成功",entity);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("class PeopleController method delete execute exception [" + e.getMessage() + "]");
return JsonUtils.genInfoJsonStr(HttpCode.HTTP_INVALID_REQUEST,"删除信息失败",e.getMessage());
}
}
}
PeopleControllerTest
在src/test下创建 PeopleControllerTest测试类,
Mockito一个Mocking测试框架,能够使用简洁的API做测试
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-all</artifactId>
<version>1.9.5</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
JsonPath解析字符类型的Json数据
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId>
<artifactId>json-path</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId>
<artifactId>json-path-assert</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
@WebAppConfiguration:表示测试环境使用的ApplicationContext是WebApplicationContext类型的- 通过
@Autowired WebApplicationContext wac:注入web环境的ApplicationContext容器 - 通过
MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(wac).build()创建一个MockMvc进行测试
测试方案如下(假设数据库中没有任何数据):
- 调用
save()方法新增一条数据,通过JsonPath解析返回的Json数据,获取新增的id、name - 根据
id调用getPeople()方法查询,获得pojo,验证是否为刚插入的数据 - 调用
listAll()方法查询数据,分别测试无分页数据,分页数据为负数以及分页数据存在这三种情况 - 调用
update()方法修改数据,并测试是否修改成功 - 调用
delete()方法删除数据,并测试数据是否已经不存在
package com.qingtian.example.web.controller;
import com.jayway.jsonpath.JsonPath;
import com.qingtian.example.core.BaseTest;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.web.WebAppConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.RequestBuilder;
import org.springframework.test.web.servlet.setup.MockMvcBuilders;
import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext;
import static org.hamcrest.Matchers.is;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.status;
/**
* @Author qingtian
* @Description
* @Date Created in 2018/03/17
*/
@WebAppConfiguration
public class PeopleControllerTest extends BaseTest{
@Autowired
protected WebApplicationContext wac;
private MockMvc mvc;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
mvc = MockMvcBuilders.webAppContextSetup(wac).build(); //初始化MockMvc对象
}
@Test
public void testPeopleController() throws Exception{
RequestBuilder request = null;
String name = "controller测试添加";
//post提交一个people
request = post("/peoples/")
.param("name",name);
String json = mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.data.name",is(name)))
.andReturn().getResponse().getContentAsString();
//获取插入的记录的id和name
Object pId = JsonPath.read(json, "$.data.id");
Object pName = JsonPath.read(json,"$.data.name");
//get方法获取刚插入的数据
request = get("/peoples/" + pId);
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.data.name",is(pName)));
//测试listAll方法
//1:不传offset和limit
request = get("/peoples/");
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(status().isOk());
//2:传负参
request = get("/peoples/")
.param("offset","-1")
.param("limit","-1");
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(status().isOk());
//3:传完整的参数
request = get("/peoples/")
.param("offset","0")
.param("limit","1");
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(status().isOk());
//修改请求
name = "controller测试修改";
request = put("/peoples/" + pId)
.param("name",name);
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.data.name",is(name)));
//删除请求
request = delete("/peoples/" + pId);
mvc.perform(request)
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.data.id",is(pId)));
}
}
以上基本完成了一个测试单元,当然测试覆盖也不够完整,存在很多不足之处,博主会再次完善,谢谢大家观看!
资源下载
- 单元测试之道Java版:使用JUnit:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1QWjXtvQuFY80jzy5mdl3oA 密码:d3g5
- 项目源代码:https://gitee.com/343427276/junit-test-demo
参考资料
- mockito官网:http://site.mockito.org/#how
- mockito中文文档:http://blog.csdn.net/bboyfeiyu/article/details/52127551#2
- SpringMVC 测试 mockMVC:https://www.cnblogs.com/lyy-2016/p/6122144.html
- JsonPath官网:http://goessner.net/articles/JsonPath/
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/34548.html