哈希算法在判定树同构方面的应用(上)
(一)需要掌握的前置知识:
(1)素数筛法:埃氏筛或者欧拉筛均可以。
以下为欧拉筛:
const int maxn=100100;
int p[maxn],cnt=0;
bool ha[maxn];
void Prime(void)
{
ha[1]=true;
for(int i=2;i<maxn;i++)
{
if(!ha[i]) p[++cnt]=i;
for(int j=1;j<=cnt&&i*p[j]<maxn;j++)
{
ha[i*p[j]]=true;
if(i%p[j]==0) break;
}
}
}
(2)一般的哈希知识。
(3)基本的树上 d f s dfs dfs 遍历整棵树。
(4)树上重心的求解:
树的重心: 找到一个点 x x x, 以点 x x x 为根时,其所有的子树中最大的子树节点数最少,那么这个点 x x x 就是这棵树的重心。(以重心为根时,最大子树最小)
性质:
(1)树中所有点到某个点的距离和中,到重心的距离和是最小的,如果有两个重心,他们的距离和一样。(这里树的边权都定义为 1 1 1)
(2)把两棵树通过一条边相连,新的树的重心在原来两棵树重心的连线上。
(3)一棵树添加或者删除一个节点,树的重心最多只移动一条边的位置。
(4)一棵树最多有两个重心,且相邻。
(5)删除重心后所得的所有子树,节点数不超过原树的1/2。
其他说明:判定树同构有多种方法,且树同构的哈希也有多种方法,接下来仅介绍一种常用的哈希方法,其他的哈希方法类推即可。
(二)例题一:洛谷–P5043 【模板】树同构([BJOI2015]树的同构)
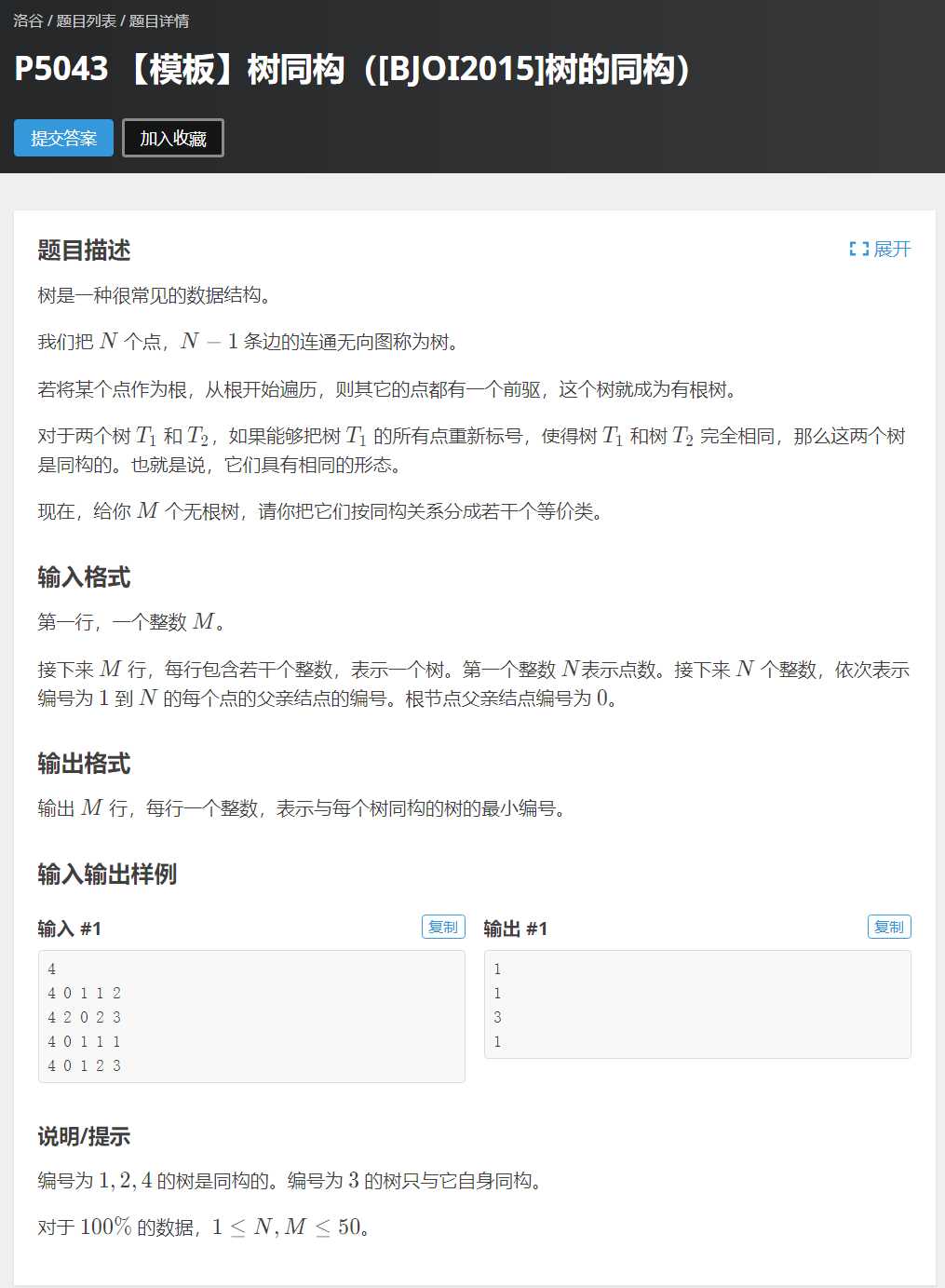
题面截图:
题意:
给定 M M M 棵无根树,对于第 i i i 棵无根树寻找 1 − i 1-i 1−i 中与第 i i i 棵无根树同构的最小的无根树的编号。
题解:
根据题意,我们很容易写出伪代码:
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
if(第 i 棵树与第 j 棵树同构) //找到与第 i 棵树同构的树
{
printf("%d\n",j);
break;
}
}
}
现在问题的关键转化为判断两棵无根树是否同构。
先来考虑问题的简化版:两个有根树如何判定是否同构。
类似于字符串的哈希,我们给树的每个节点附一个权值,记为 f [ x ] f[x] f[x]
我们设 f [ x ] = 1 + ∑ y ∈ s o n x f [ y ] ∗ p [ s i [ y ] ] f[x]=1+\sum\limits_{y\in son_x}f[y]*p[si[y]] f[x]=1+y∈sonx∑f[y]∗p[si[y]]。这里 f [ x ] f[x] f[x] 取自然溢出,即对 2 64 2^{64} 264 取模。
其中 y ∈ s o n x y\in son_x y∈sonx 表示在有根树中 y y y 是 x x x 的儿子节点。 f [ y ] f[y] f[y] 是 y y y 的 f f f 函数。
p p p 数组是我们取前 k k k ( k > = s i [ r o o t ] k>=si[root] k>=si[root])个质数,再随机打乱后的数组。
随机打乱 p p p 数组。
random_shuffle(p+1,p+k+1);//k可以自己选定
s i [ x ] si[x] si[x] 表示 x x x 子树的大小。
那么如果判定两个有根树同构呢,我们认为 如果 f [ r o o t 1 ] = f [ r o o t 2 ] f[root1]=f[root2] f[root1]=f[root2],那么就可以认为两棵树同构。事实上虽然 f [ r o o t 1 ] = f [ r o o t 2 ] f[root1]=f[root2] f[root1]=f[root2] 有可能两棵树不一定同构,如果在确认算法正确且时间允许的情况下,我们可以多哈希来判定树的同构。事实上多哈希来判定同构,冲突的概率就极低了,数据一般也不容易构造。
现在我们来总结一下怎样判定两棵根分别为 r o o t 1 , r o o t 2 root1,root2 root1,root2 的树的同构的方法:
(1)求解 p p p 数组,利用埃氏筛或者欧拉筛。
(2)在树上进行 d f s dfs dfs 求解 f f f 数组
(3)比较 f [ r o o t 1 ] f[root1] f[root1] 与 f [ r o o t 2 ] f[root2] f[root2]
现在来考虑如何判定两棵无根树是否同构:
假设我们现在有两棵无根树 A , B A,B A,B 同构,那么我们在 A A A 树中选一点 x x x 作为 A A A 树的根,那么在 B B B 树中一定存在一点 y y y,使得 B B B 树以 y y y 为根与 A A A 树以 x x x 为根同构。
相反的,如果我们在 A A A 树中选一点 x x x 作为 A A A 树的根,那么在 B B B 树中如果存在一点 y y y,使得 B B B 树以 y y y 为根与 A A A 树以 x x x 为根同构,那么两棵 无根树 A , B A,B A,B 同构。
我们对 A A A 树中的某一点 x x x ,去找在 B B B 树中是否能存在一个点 y y y ,使得 B B B 树中以点 y y y 为根的树与 A A A 树中以点 x x x 为根的树同构。
那么我们能得到判定无根树同构的算法:
对于 A A A 树中的某一点 x x x,求出 A A A 树中以 x x x 为根的 f [ x ] f[x] f[x],然后在 B B B 树中寻找,是否存在一点 y y y,使得 B B B 树中以 y y y 为根的 f [ y ] f[y] f[y] 等于 A A A 树中以 x x x 为根的 f [ x ] f[x] f[x]。若存在,则说明 A , B A,B A,B同构,否则不同构。
为了方便判别,我们可以有以下处理:
对于 A A A 树的每个节点 x x x ,求出 A A A 树中以 x x x 为根的 f [ x ] f[x] f[x],将这些 f [ x ] f[x] f[x] 保存至 a a a 数组。
对于 B B B 树的每个节点 y y y ,求出 B B B 树中以 y y y 为根的 f [ y ] f[y] f[y],将这些 f [ y ] f[y] f[y] 保存至 b b b 数组。
将 a , b a,b a,b 两数组按照相同的排序规则排序 (都升序或者都降序),那么如果最终 A , B A,B A,B两棵树的节点数相同且 a , b a,b a,b 两数组对应位置相同,那么认为 A , B A,B A,B 两棵树同构。
回到本题:
我们对 M M M 棵树,对于第 i i i 棵树,我们保存下以 x x x 为根的 f [ x ] f[x] f[x] 值,记为 h a [ i ] [ x ] = f [ x ] ha[i][x]=f[x] ha[i][x]=f[x],然后再对 h a [ i ] ha[i] ha[i] 数组进行排序。
判定两棵树是否同构的时候只需要比较两棵树的大小和 h a [ i ] , h a [ j ] ha[i],ha[j] ha[i],ha[j] 两个数组即可。
空间复杂度 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2) ,时间复杂度 O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O(n3)。(因为 n n n 和 m m m 同级别,就都当作 n n n 来计算)
因为这里节点数 n n n 比较小,所以我们直接打质数表即可。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#define ll long long
#define pr make_pair
#define pb push_back
#define lc (cnt<<1)
#define rc (cnt<<1|1)
using namespace std;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll lnf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double dnf=1e15;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const int maxn=55;
int head[maxn],ver[maxn<<1],nt[maxn<<1];
int n[maxn],si[maxn],tot=1;
unsigned ll ha[maxn][maxn],f[maxn];
int p[]={
0,2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31,37,
41,43,47,53,59,61,67,71,73,79,83,89,97,
101,103,107,109,113,127,131,137,139,149,
151,157,163,167,173,179,181,191,193,197,
199,211,223,227,229};
void init(void)
{
memset(head,0,sizeof(head));
tot=1;
}
void add(int x,int y)
{
ver[++tot]=y,nt[tot]=head[x],head[x]=tot;
}
void dfs(int x,int fa)
{
f[x]=si[x]=1;
for(int i=head[x];i;i=nt[i])
{
int y=ver[i];
if(y==fa) continue;
dfs(y,x);
f[x]+=f[y]*p[si[y]];
si[x]+=si[y];
}
}
bool check(int i,int j)
{
for(int k=1;k<=n[i];k++)
{
if(ha[i][k]!=ha[j][k]) return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(void)
{
random_shuffle(p+1,p+50+1);
int m,fa;
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
init();
scanf("%d",&n[i]);
for(int j=1;j<=n[i];j++)
{
scanf("%d",&fa);
if(fa) add(fa,j),add(j,fa);
}
for(int j=1;j<=n[i];j++)
{
dfs(j,0);
ha[i][j]=f[j];
}
sort(ha[i]+1,ha[i]+n[i]+1);
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
if(n[i]==n[j]&&check(i,j))
{
printf("%d\n",j);
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
虽然 O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O(n3) 的算法足够通过本题,但是如果 n = 5 e 3 n=5e3 n=5e3 级别的就不能再处理了,考虑优化。
思考:我们为什么要求第 i i i 棵无根树分别以每个节点 x x x 为根的 f [ x ] f[x] f[x] ?
因为 两棵无根树 A , B A,B A,B 同构 等价于 对于 A A A 中以某一点 x x x为根的有根树, B B B 中存在以 y y y 为根的有根树与 A A A 中以 x x x 为根的有根树同构。我们需要在 B B B 中找到 y y y 。
那么我们能不能快速在 A , B A,B A,B中分别找到一点 x , y x,y x,y,使得 x , y x,y x,y 是相对应的,即 让 A , B A,B A,B 是否同构等价于以 x x x为根的有根树与以 y y y为根的有根树是否同构。
能不能找到这样的两点 x , y x,y x,y 呢? 重心!重心!重心!
于是判定同构的条件转化为:
两棵无根树 A , B A,B A,B 是否同构,等价于他们以重心为根的有根树是否同构。
考虑一下为什么?若重心唯一,那么两棵无根树 A , B A,B A,B 同构时的重心必定对应;若重心都不唯一,那么两棵无根树 A , B A,B A,B 同构时两棵树的重心也一一对应。
即,若两棵树同构,那么重心为根的树一定是同构的。如果重心为根的树是同构的,那么两棵树一定是同构的。
那么求解无根树是否同构的方法可以优化为以下做法:
(1)求解树 A , B A,B A,B 的重心,重心至多有两个。
(2)求解树 A , B A,B A,B 以重心为根的 f f f。
(3)判断是否同构。
回到本题:
我们只需要求解第 i i i 棵树的重心,然后求解重心的 f f f 即可。
空间复杂度 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),时间复杂度 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<map>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<set>
#include<ctime>
#define ui unsigned int
#define ll long long
#define llu unsigned ll
#define ld long double
#define pr make_pair
#define pb push_back
#define lc (cnt<<1)
#define rc (cnt<<1|1)
#define len(x) (t[(x)].r-t[(x)].l+1)
#define tmid ((l+r)>>1)
#define fhead(x) for(int i=head[(x)];i;i=nt[i])
#define max(x,y) ((x)>(y)?(x):(y))
#define min(x,y) ((x)>(y)?(y):(x))
using namespace std;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll lnf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
const double dnf=1e18;
const double alpha=0.75;
const int mod=1e9+7;
const double eps=1e-8;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int hp=13331;
const int maxn=55;
const int maxm=100100;
const int maxp=100100;
const int up=1100;
int head[maxn],ver[maxn<<1],nt[maxn<<1];
int n[maxn],si[maxn],dp[maxn],tot=1,rt1,rt2,nown;
llu f[maxn],rt1f[maxn],rt2f[maxn];
int p[]={
0,2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,29,31,37,
41,43,47,53,59,61,67,71,73,79,83,89,97,
101,103,107,109,113,127,131,137,139,149,
151,157,163,167,173,179,181,191,193,197,
199,211,223,227,229};
void init(void)
{
memset(head,0,sizeof(head));
tot=1;
rt1=0,rt2=0;
}
void add(int x,int y)
{
ver[++tot]=y,nt[tot]=head[x],head[x]=tot;
}
void dfs1(int x,int fa)
{
si[x]=1,dp[x]=0;
for(int i=head[x];i;i=nt[i])
{
int y=ver[i];
if(y==fa) continue;
dfs1(y,x);
si[x]+=si[y];
dp[x]=max(dp[x],si[y]);
}
dp[x]=max(dp[x],nown-si[x]);
if(rt1==0||dp[x]<dp[rt1]) rt1=x,rt2=0;
else if(dp[x]==dp[rt1]) rt2=x;
}
void dfs2(int x,int fa)
{
f[x]=si[x]=1;
for(int i=head[x];i;i=nt[i])
{
int y=ver[i];
if(y==fa) continue;
dfs2(y,x);
f[x]+=f[y]*p[si[y]];
si[x]+=si[y];
}
}
bool check(int i,int j)
{
return (rt1f[i]==rt1f[j]&&rt2f[i]==rt2f[j])||(rt1f[i]==rt2f[j]&&rt2f[i]==rt1f[j]);
}
int main(void)
{
random_shuffle(p+1,p+50+1);
int m,fa;
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
init();
scanf("%d",&n[i]);
for(int j=1;j<=n[i];j++)
{
scanf("%d",&fa);
if(fa) add(fa,j),add(j,fa);
}
nown=n[i];
dfs1(1,0);
if(rt1!=0) dfs2(rt1,0),rt1f[i]=f[rt1];
if(rt2!=0) dfs2(rt2,0),rt2f[i]=f[rt2];
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
if(check(i,j))
{
printf("%d\n",j);
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/34994.html