预备知识:线段树,DFS序
DFS序
DFS序,字面意思,就是DFS到的顺序
我们只需要在搜到节点的时候记录一下就可以了
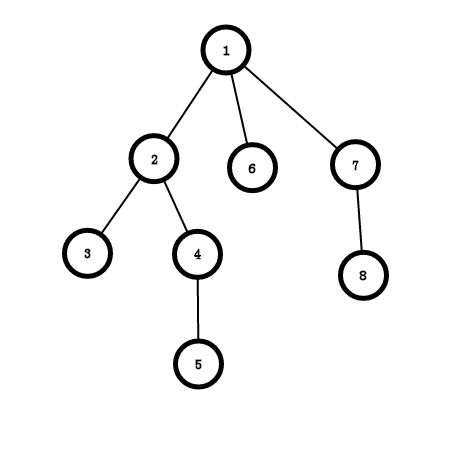
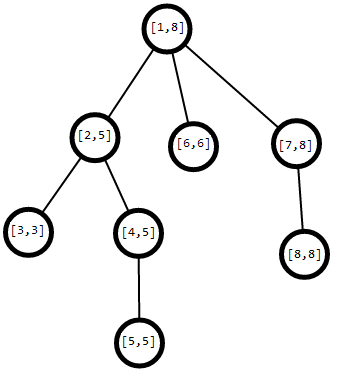
比如这样可能是一个树的DFS序
那知道了DFS序又有什么用呢
我们可以发现一颗子树在DFS序上是连续的一段
那么它就有了一个区间的性质,每个节点对应一段区间,那么我们在进行一些操作像什么:将以某节点为根的子树节点都加上x时,就可以转化为在线段树内的区间加了
树链剖分
首先我们要清楚一些概念:
重儿子(节点):子树结点数目最多的结点
轻儿子(节点):除了重儿子以外的结点
重边:父亲结点和重儿子连成的边
轻边:父亲节点和轻儿子连成的边
重链:由多条重边连接而成的路径
轻链:由多条轻边连接而成的路径
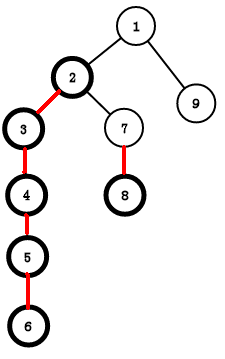
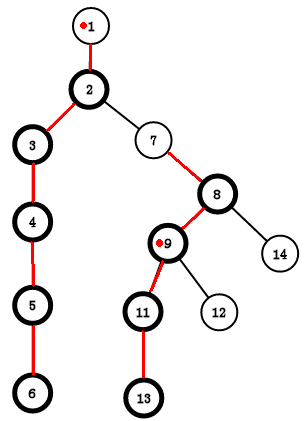
看图感受一下,
可以看到:对于1节点4的子树的节点比2,3的多,所以4是重儿子
对于4节点9的子树的节点比8,9的多,所以9是重儿子
以此类推
所以结果是:图中黑色的节点是重儿子,其余的节点是轻儿子
红边是重边,黑边是轻边
1 – 4 – 9 – 13 – 14;3 – 7;2 – 6 – 11是重链
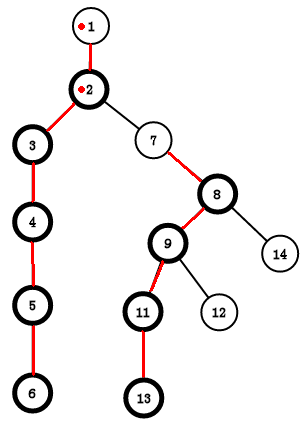
我们发现:叶节点没有重儿子,非叶节点有且只有1个重儿子
并不是轻儿子之后全是轻儿子,比如3后面就有6和11两个重儿子
我们就可以这样理解:
当一个节点选了他的重儿子之后,我们并不能保证它的轻儿子就是叶节点,所以我们就以这个轻儿子为根,再去选这个轻儿子的轻重儿子
也就是一个DFS的过程,这样我们就会得到很多重链
有如下两个性质:
1.轻边(u,v)中, size(u)≤ size(u/2)
2.从根到某一点的路径上,不超过logn条轻链和不超过logn条重链。
那我们要怎么求出轻重儿子呢
这里我们定义几个数组:
son[u]:表示u的重儿子
size[u]:表示以u为根的树的节点个数,如上图的size[1] = 13
在这里,我们还可以顺带的求出
f[u]:节点的父节点
dep[u]:节点的深度
//u是当前节点 //fa是当前节点的父节点
void dfs1(int u, int fa) { size[u] = 1;//表示刚搜到u的时候以u为根的子树里只有u一个节点
for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v;//连向的节点
if (v != fa) {//因为连的是无相边,而且是树,不能往上搜,所以我们要判断u是不是从fa搜过来,也就是判断v是不是u的子节点,也可以写作!dep[v](没有被搜到过)
dep[v] = dep[u] + 1;//v的深度是当前节点的深度+1
f[v] = u;//记录一下父亲
dfs1(v, u);//继续往下搜,一直搜到叶节点为止
size[u] += size[v];//往上回溯,更新以u为根的子树的size
if (size[v] > size[son[u]]) son[u] = v;//重儿子是节点个数更多的子树,如果以u的子树中,以v为根的子树节点多,那就更新一下u的重儿子为v
} } }
这样我们就求出了这棵树的所有重儿子,所有点的深度,和所有点的父亲。
既然我们已经求出来重儿子,轻儿子那么我们就要把他们连成链
因为我们要把轻重儿子连城链,所以我们就一定要让链上的点连续,方便我们的操作
那该怎么办呢,这就用到了我们之前提到的DFS序了
我们从根开始一遍DFS,如果有重儿子就先走重儿子(将一条重链放到一个区间内),搜到叶子节点后回溯回去再去搜轻儿子(轻链)
这一遍DFS里,我们又引入了几个数组:
top[u]:节点u所在链的顶端
id[u]:节点u的新编号(DFS序)
a[cnt]:在新编号(DFS序)下的当前点的点值
w[u]:题目中给出的节点u的点值
//u是当前节点 //t是所在链的顶端
void dfs2(int u, int t) { id[u] = ++cnt;//给这个点一个新的编号
a[cnt] = w[u];//记录这个编号下点的值
top[u] = t;//记录u所在链的顶端为t
if (son[u]) dfs2(son[u], t);//u的重儿子和u在同一条链里
for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v;//搜轻儿子
if (v != f[u] && v != son[u])//判断是否是轻儿子
dfs2(v, v);//以轻儿子为顶的链
} }
为什么是dfs2(v,v)呢,因为当v是重儿子的时候,它不可能为一条链的顶,因为根据重边的定义,一定有一条边连向重儿子,若重儿子为顶,还会有一条边连向它,所以重儿子不会为顶端。
树链剖分求LCA
为什么要先讲树剖求LCA呢
因为树剖的很多题是要求要在链上进行操作的,而链上操作其实就是LCA
树剖求LCA其实也是往上跳,但这里的往上跳不是倍增的往上跳
我们这里只要把两个点跳到同一条链里就好了
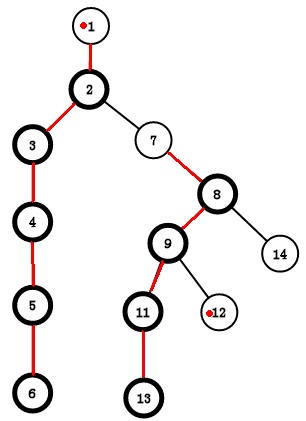
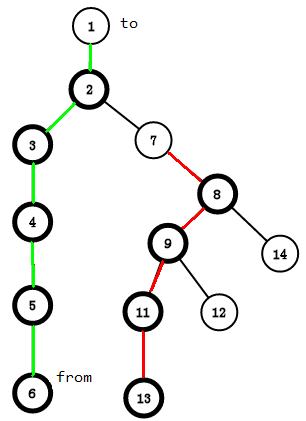
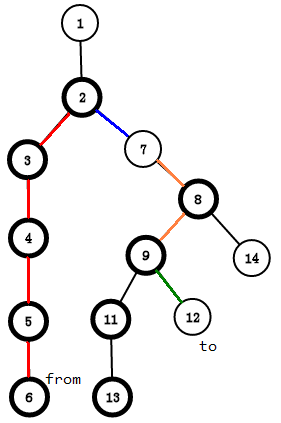
如图:我们要求LCA的话,有两种情况
1、在同一条链内,如3和5。这时直接输出深度较小的那个节点就好了
2、不再同一条链内,如6和8。因为他们不再一条链内,所以我们让其中一个点 x 直接跳到链的顶端也是没有问题的。这时我们就让那个深度深的 x 一直往上跳,这把 x 更新 x 的顶端的父亲节点,也就是到了另一条链上,记录一下它在这条新链上的顶端是谁,用来判断和另一个点 y 是否在同一条链内。当 x 跳到它所在的链的顶端时,深度可能就小于 y 的顶端了,也就是在另一条链的上面(这时 x 不会再往上跳,y 也不会再往上跳,但没有找到LCA),这时我们就要交换他们(其实只是换了个名字,管原来的 y 叫 x ,管原来的 x 叫 y,原来的树并没有变,想了很久),保证 x , y 会更新到同一条链内
稍微模拟一下
如图:
如果我们要求6和12的LCA
设x = 12,y = 1
这时我们先比较一下两者的top,fx = top[x] = 12,fy = top[y] = 1
发现他们的top不一样
那就往上跳呗,dep[fx] > dep[fy],所以 x = f[fx] = 9,fx = top[x] = 7
12往上跳跳到了9
变成了这样
找到9所在链的顶为7
发现7 != 1说明9和1不再同一个链里
继续往上跳
x = top[fx] = 2,fx = top[2] = 1
发现1 == 1
说明我们现在的 x 和 y 在同一条链里了
这时我们就返回深度小的那个就可以了
//fx表示x所在链的顶,fy表示y所在链的顶
int LCA(int x, int y) { int fx = top[x], fy = top[y]; while (fx != fy) { if (dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy); x = f[fx], fx = top[x]; } return dep[x] < dep[y] ? x : y;//最后返回深度小的那个
}
如果还有边权的话,只要在dfs1里加1句话就可以了
void dfs1(int u, int fa) { size[u] = 1; for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != fa) { dep[v] = dep[u] + 1; f[v] = u; dis[v] = dis[u] + e[i].w;//here
dfs1(v, u); size[u] += size[v]; if (size[v] > size[son[u]]) son[u] = v; } } }
dis[u]表示从根到u的距离,其实倍增,tarjan都是这么着
查询距离的时候还是
dis[x] + dis[y] - 2 * dis[LCA(x, y)]
路径上的修改/查询
讲完了LCA,剩下的路径上修改和查询就和LCA差不多了,只是加了几句话而已
这里要结合我们上面的DFS序和LCA
那对于路径上的操作,我们先想LCA,在求LCA的时候,我们每次都往上跳一条链,直到这两个点在一个路径上为止
就像我们刚开始的找6的top一样
一次就经过了这么一条链(绿边)
我们再回想一下DFS序的性质,会得到在这一条链上,新的编号是连续的,我们要对这一条链进行修改和查询操作,这让我们想到了什么
线段树!!
线段树最支持的不就是区间修改和查询吗
那么我们就可以用线段树维护这一条路径了。
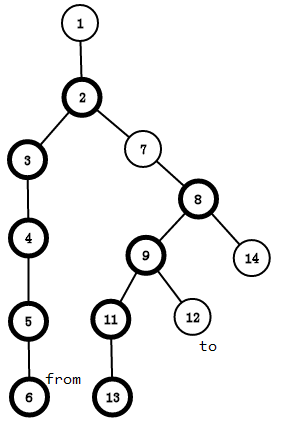
那如果我们要维护6到12这样一条路径呢?
还记得我们求LCA的时候是怎么往上跳的吗
左半部分的12往上跳,每次都跳到所在链的顶端(只记录初末位置),我们可以得到12跳到的当前点 u 所处的链的顶的新编号(跳到9,顶为7),我们又知道当前点 u 的新编号,那我们就可以用线段树对从顶段到当前点 u 这条路径进行操作了,这样我们每次修改一条链(可能是一部分),就完成了路径的操作;
跳到2的时候,fx == fy,两点在同一条链内,x = 2,y = 6,然后我们操作 id[2] 到 id[6] ,这样我们就一条链一条链的完成了对这条路径的操作
全程我们操作的区间是[id[2],id[6]],[id[7],id[9]],[id[12],id[12]]
我们不对蓝边上的点和绿边上的点操作,因为他们不是重链,只是注明一下点经过的路径,若对它们操作的话会算重复
我刚写完这句话的时候想到了一个error
如果图长这样
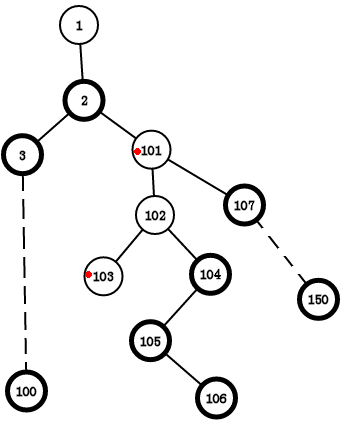
如果我们要查询 103 到 101 呢,它们之间没有重链啊,那只好就一个一个的往上跳了,103->102->101.(退化成单点操作)
//修改
void update_chain(int x, int y, int z) { int fx = top[x], fy = top[y]; while (fx != fy) { if (dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy); update(id[fx], id[x], z, 1, cnt, 1);//每往上跳一次,就修改以次经过路径上的值,因为DFS序中id[fx] < id[x],所以是区间[id[fx],id[x]];
x = f[fx], fx = top[x]; } if (id[x] > id[y]) swap(x, y);//要保证区间是从小到大的
update(id[x], id[y], z, 1, cnt, 1); }
//查询
int query_chain(int x, int y) { int ans = 0, fx = top[x], fy = top[y]; while (fx != fy) { if (dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy); ans += query(id[fx], id[x], 1, cnt, 1); x = f[fx], fx = top[x]; } if (id[x] > id[y]) swap(x, y); ans += query(id[x], id[y], 1, cnt, 1); return ans; }
到此为止,我们就完成了树链剖分的基本操作
完整代码:


#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int N = 1e6 + 10; int n, m, num, cnt, rt, cntt, k, s, mod; int head[N], size[N], top[N], f[N], son[N], dep[N], a[N], id[N], w[N]; struct node { int v, nx; } e[N]; struct tree { int sum, lazy; int len; } t[N]; #define lson rt << 1
#define rson rt << 1 | 1 template<class T>inline void read(T &x) { x = 0; int f = 0; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) f |= (ch == '-'), ch = getchar(); while (isdigit(ch)) x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); x = f ? -x : x; return ; } inline void add(int u, int v) { e[++num].nx = head[u], e[num].v = v, head[u] = num; } void dfs1(int u, int fa) { size[u] = 1; for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != fa) { dep[v] = dep[u] + 1; f[v] = u; dfs1(v, u); size[u] += size[v]; if (size[v] > size[son[u]]) son[u] = v; } } } void dfs2(int u, int t) { id[u] = ++ cnt; a[cnt] = w[u]; top[u] = t; if (son[u]) dfs2(son[u], t); for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != f[u] && v != son[u]) dfs2(v, v); } } inline void pushup(int rt) { t[rt].sum = t[lson].sum + t[rson].sum; } void build(int l, int r, int rt) { t[rt].len = r - l + 1; if (l == r) { t[rt].sum = a[l]; return; } int m = (l + r) >> 1; build(l, m, lson); build(m + 1, r, rson); pushup(rt); } inline void pushdown(int rt) { if (t[rt].lazy) { t[lson].lazy += t[rt].lazy, t[lson].lazy %= mod; t[rson].lazy += t[rt].lazy, t[rson].lazy %= mod; t[lson].sum += t[rt].lazy * t[lson].len, t[lson].sum %= mod; t[rson].sum += t[rt].lazy * t[rson].len, t[rson].sum %= mod; t[rt].lazy = 0; } } void update(int L, int R, int c, int l, int r, int rt) { if (L <= l && r <= R) { t[rt].sum += (t[rt].len * c) % mod; t[rt].lazy += c; return ; } pushdown(rt); int m = (l + r) >> 1; if (L <= m) update(L, R, c, l, m, lson); if (R > m) update(L, R, c, m + 1, r, rson); pushup(rt); } int query(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt) { if (L <= l && r <= R) return t[rt].sum; pushdown(rt); int m = (l + r) >> 1, ans = 0; if (L <= m) ans += query(L, R, l, m, lson) % mod; if (R > m) ans += query(L, R, m + 1, r, rson) % mod; return ans % mod; } void update_chain(int x, int y, int z) { int fx = top[x], fy = top[y]; while (fx != fy) { if (dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy); update(id[fx], id[x], z, 1, cnt, 1); x = f[fx], fx = top[x]; } if (id[x] > id[y]) swap(x, y); update(id[x], id[y], z, 1, cnt, 1); } int query_chain(int x, int y) { int ans = 0, fx = top[x], fy = top[y]; while (fx != fy) { if (dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy); ans += query(id[fx], id[x], 1, cnt, 1); x = f[fx], fx = top[x]; } if (id[x] > id[y]) swap(x, y); ans += query(id[x], id[y], 1, cnt, 1); return ans % mod; } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); read(n), read(m), read(s), read(mod); for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) read(w[i]); for (int i = 1, x, y; i < n; ++ i) { read(x), read(y); add(x, y), add(y, x); } f[s] = 1, dep[s] = 0; dfs1(s, 0); dfs2(s, s); build(1, n, 1); for (int i = 1, x, y, z; i <= m; ++i) { read(k), read(x); if (k == 1) {read(y), read(z); update_chain(x, y, z);} if (k == 2) {read(y); printf("%d\n", query_chain(x, y));} if (k == 3) {read(z); update(id[x], id[x] + size[x] - 1, z, 1, n, 1);} if (k == 4) printf("%d\n", query(id[x], id[x] + size[x] - 1, 1, n, 1) % mod); } return 0; }
树链剖分
例题:


#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
using namespace std; const int N = 5e6 + 10; int n, m, num, cnt, cntt, rt; int head[N], dep[N], f[N], id[N], size[N], w[N], son[N], a[N], top[N]; struct node { int v, nx; } e[N]; struct tree { ll sum, lazy; int len; } t[N]; #define lson rt << 1
#define rson rt << 1 | 1 template<class T>inline void read(T &x) { x = 0; int f = 0; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) f |= (ch == '-'), ch = getchar(); while (isdigit(ch)) x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); x = f ? -x : x; return; } inline void add(int u, int v) { e[++num].nx = head[u], e[num].v = v, head[u] = num; } void dfs1(int u, int fa) { size[u] = 1; for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != fa) { dep[v] = dep[u] + 1; f[v] = u; dfs1(v, u); size[u] += size[v]; if (size[v] > size[son[u]]) son[u] = v; } } } void dfs2(int u, int t) { id[u] = ++ cnt; a[cnt] = w[u]; top[u] = t; if (son[u]) dfs2(son[u], t); for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != f[u] && v != son[u]) dfs2(v, v); } } inline void pushup(int rt) { t[rt].sum = t[lson].sum + t[rson].sum; } void build(int l, int r, int rt) { t[rt].len = r - l + 1; if (l == r) { t[rt].sum = a[l]; return; } int m = l + r >> 1; build(l, m, lson); build(m + 1, r, rson); pushup(rt); } inline void pushdown(int rt) { if (t[rt].lazy) { t[lson].lazy += t[rt].lazy; t[rson].lazy += t[rt].lazy; t[lson].sum += t[rt].lazy * t[lson].len; t[rson].sum += t[rt].lazy * t[rson].len; t[rt].lazy = 0; } } void update(int L, int R, ll c, int l, int r, int rt) { if (L <= l && r <= R) { t[rt].sum += c * t[rt].len; t[rt].lazy += c; return ; } int m = l + r >> 1; pushdown(rt); if (L <= m) update(L, R, c, l, m, lson); if (R > m) update(L, R, c, m + 1, r, rson); pushup(rt); } ll query(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt) { if (L <= l && r <= R) return t[rt].sum; pushdown(rt); int m = l + r >> 1; ll ans = 0; if (L <= m) ans += query(L, R, l, m, lson); if (R > m) ans += query(L, R, m + 1, r, rson); return ans; } ll query_chain(int x, int y) { ll ans = 0; int fx = top[x], fy = top[y]; while (fx != fy) { if (dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy); ans += query(id[fx], id[x], 1, cnt, 1); x = f[fx], fx = top[x]; } if (id[x] > id[y]) swap(x, y); ans += query(id[x], id[y], 1, cnt, 1); return ans; } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); read(n), read(m); for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) read(w[i]); for (int i = 1, x, y; i < n; ++ i) { read(x), read(y); add(x, y), add(y, x); } dep[1] = 1; dfs1(1, 0), dfs2(1, 1); build(1, n, 1); for (int i = 1, x, y, z; i <= m; ++ i) { read(x), read(y); if (x == 1) read(z), update(id[y], id[y], z, 1, n, 1); if (x == 2) read(z), update(id[y], id[y] + size[y] - 1, z, 1, n, 1); if (x == 3) printf("%lld\n",query_chain(1,y)); } return 0; }
P3178


#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int N = 1e5 + 10; int n, m, num, cnt, cntt, rt; int head[N], size[N], dep[N], f[N], id[N], w[N], a[N], top[N], son[N]; string s; struct node { int v, nx; } e[N]; struct tree { int sum, lazy, mx; int len; } t[N]; #define lson rt << 1
#define rson rt << 1 | 1 template<class T> inline void read(T &x) { x = 0; int f = 0; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) f |= (ch == '-'), ch = getchar(); while (isdigit(ch)) x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); x = f ? -x : x; return; } inline void add(int u, int v) { e[++num].nx = head[u], e[num].v = v, head[u] = num; } void dfs1(int u, int fa) { size[u] = 1; for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != fa) { f[v] = u; dep[v] = dep[u] + 1; dfs1(v, u); size[u] += size[v]; if (size[v] > size[son[u]]) son[u] = v; } } } void dfs2(int u, int t) { id[u] = ++ cnt; a[cnt] = w[u]; top[u] = t; if (son[u]) dfs2(son[u],t); for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != f[u] && v != son[u]) dfs2(v, v); } } inline void pushup(int rt) { t[rt].sum = t[lson].sum + t[rson].sum; t[rt].mx = max(t[lson].mx, t[rson].mx); } void build(int l, int r, int rt) { t[rt].len = r - l + 1; if (l == r) { t[rt].sum = t[rt].mx = a[l]; return; } int m = l + r >> 1; build(l, m, lson); build(m + 1, r, rson); pushup(rt); } void update(int L, int c, int l, int r, int rt) { if (l == r) { t[rt].sum = c; t[rt].mx = c; return; } int m = l + r >> 1; if (L <= m) update(L, c, l, m, lson); else update(L, c, m + 1, r, rson); pushup(rt); } int query_sum(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt) { if (L <= l && r <= R) return t[rt].sum; int m = l + r >> 1, ans = 0; if (L <= m) ans += query_sum(L, R, l, m, lson); if (R > m) ans += query_sum(L, R, m + 1, r, rson); return ans; } int query_max(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt) { if (L <= l && r <= R) return t[rt].mx; int m = l + r >> 1, ans = -0x3f3f3f3f; if (L <= m) ans = max(ans, query_max(L, R, l, m, lson)); if (R > m) ans = max(ans, query_max(L, R, m + 1, r, rson)); return ans; } int query_chain_sum(int x, int y) { int ans = 0, fx = top[x], fy = top[y]; while (fx != fy) { if (dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy); ans += query_sum(id[fx], id[x], 1, cnt, 1); x = f[fx], fx = top[x]; } if (id[x] > id[y]) swap(x, y); ans += query_sum(id[x], id[y], 1, cnt, 1); return ans; } int query_chain_max(int x, int y) { int ans = -0x3f3f3f3f, fx = top[x], fy = top[y]; while (fx != fy) { if (dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy); ans = max(ans, query_max(id[fx], id[x], 1, cnt, 1)); x = f[fx], fx = top[x]; } if (id[x] > id[y]) swap(x, y); ans = max(ans, query_max(id[x], id[y], 1, cnt, 1)); return ans; } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); read(n); for (int i = 1, x, y; i < n; ++ i) { read(x), read(y); add(x, y), add(y, x); } for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++ i) read(w[i]); f[1] = 0, dep[1] = 1; dfs1(1, 0), dfs2(1, 1); build(1, n, 1); read(m); for (int i = 1, x, y; i <= m; ++ i) { cin >> s; if (s == "CHANGE") read(x), read(y), update(id[x], y, 1, n, 1); if (s == "QMAX") read(x), read(y), printf("%d\n", query_chain_max(x, y)); if (s == "QSUM") read(x), read(y), printf("%d\n", query_chain_sum(x, y)); } return 0; }
P2590


//路径最值
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int N = 2e5 + 10; int n, m, num, cnt; int head[N], f[N], top[N], son[N], size[N], dep[N], id[N]; struct node { int v, nx; } e[N]; struct tree { int mx; int lazy; } t[N]; #define lson rt << 1
#define rson rt << 1 | 1 template<class T>inline void read(T &x) { x = 0; int f = 0; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) f |= (ch == '-'), ch = getchar(); while (isdigit(ch)) x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); x = f ? -x : x; return; } inline void add(int u, int v) { e[++num].nx = head[u], e[num].v = v, head[u] = num; } void dfs1(int u, int fa) { size[u] = 1; for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != fa) { dep[v] = dep[u] + 1; f[v] = u; dfs1(v, u); size[u] += size[v]; if (size[v] > size[son[u]]) son[u] = v; } } } void dfs2(int u, int t) { id[u] = ++cnt; top[u] = t; if (son[u]) dfs2(son[u], t); for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != f[u] && v != son[u]) dfs2(v, v); } } inline void pushup(int rt) { t[rt].mx = max(t[lson].mx, t[rson].mx); } void build(int l, int r, int rt) { if (l == r) return ; int m = (l + r) >> 1; build(l, m, lson); build(m + 1, r, rson); } void pushdown(int rt) { if (t[rt].lazy) { t[lson].lazy += t[rt].lazy; t[rson].lazy += t[rt].lazy; t[lson].mx += t[rt].lazy; t[rson].mx += t[rt].lazy; t[rt].lazy = 0; } } void update(int L, int R, int c, int l, int r, int rt) { if (L <= l && r <= R) { t[rt].lazy += c; t[rt].mx += c; return; } int m = (l + r) >> 1; pushdown(rt); if (L <= m) update(L, R, c, l, m, lson); if (R > m) update(L, R, c, m + 1, r, rson); pushup(rt); } int query(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt) { if (L <= l && r <= R) return t[rt].mx; int m = (l + r) >> 1, ans = -0x3f3f3f3f; if (L <= m) ans = max(ans, query(L, R, l, m, lson)); if (R > m) ans = max(ans, query(L, R, m + 1, r, rson)); return ans; } void update_chain(int x, int y) { int fx = top[x], fy = top[y]; while (fx != fy) { if (dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy); update(id[fx], id[x], 1, 1, cnt, 1); x = f[fx], fx = top[x]; } if (id[x] > id[y]) swap(x, y); update(id[x], id[y], 1, 1, cnt, 1); } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); read(n), read(m); for (int i = 1, x, y; i < n; ++i) { read(x), read(y); add(x, y), add(y, x); } f[1] = 0, dep[1] = 1; dfs1(1, 0), dfs2(1, 1); build(1, n, 1); for (int i = 1, x, y; i <= m; ++i) { read(x), read(y); if (x > y) swap(x, y); update_chain(x, y); } printf("%d\n", query(id[1], id[1] + size[1] - 1, 1, n, 1)); return 0; }
P3128


//树链剖分,但是要转换一下,把边权转化为所连向点的点权,查询的时候要忽略最上面的点
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int N = 1e6 + 10; int n, num, cnt, x, y, z; int dep[N], f[N], top[N], size[N], son[N], a[N], w[N], head[N], mx[N], id[N]; struct node { int v, nx, w; } e[N]; #define lson rt << 1
#define rson rt << 1 | 1 template<class T>inline void read(T &x) { x = 0; int f = 0; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) f |= (ch == '-'), ch = getchar(); while (isdigit(ch)) x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); x = f ? -x : x; return ; } inline void add(int u, int v, int w) { e[++num].nx = head[u], e[num].v = v, e[num].w = w, head[u] = num; } void dfs1(int u, int fa) { size[u] = 1; for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != fa) { dep[v] = dep[u] + 1; f[v] = u; w[v] = e[i].w; dfs1(v, u); size[u] += size[v]; if (size[v] > size[son[u]]) son[u] = v; } } } void dfs2(int u, int t) { id[u] = ++cnt; a[cnt] = w[u]; top[u] = t; if (son[u]) dfs2(son[u], t); for (int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if (v != f[u] && v != son[u]) dfs2(v, v); } } inline void pushup(int rt) { mx[rt] = max(mx[lson], mx[rson]); } void build(int l, int r, int rt) { if (l == r) { mx[rt] = a[l]; return ; } int m = (l + r) >> 1; build(l, m, lson); build(m + 1, r, rson); pushup(rt); } void update(int L, int c, int l, int r, int rt) { if (l == r) { mx[rt] = c; return ; } int m = (l + r) >> 1; if (L <= m) update(L, c, l, m, lson); else update(L, c, m + 1, r, rson); pushup(rt); } int query(int L, int R, int l, int r, int rt) { if (L <= l && r <= R) return mx[rt]; int m = (l + r) >> 1, ans = -0x3f3f3f3f; if (L <= m) ans = max(ans, query(L, R, l, m, lson)); if (R > m) ans = max(ans, query(L, R, m + 1, r, rson)); return ans; } int query_chain(int x, int y) { int fx = top[x], fy = top[y], ans = -0x3f3f3f3f; while (fx != fy) { if (dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x, y), swap(fx, fy); ans = max(ans, query(id[fx], id[x], 1, cnt, 1)); x = f[fx], fx = top[x]; } if (id[x] > id[y]) swap(x, y); ans = max(ans, query(id[x] + 1, id[y], 1, cnt, 1)); return ans; } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { memset(head, -1, sizeof(head)); read(n); for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) { read(x), read(y), read(z); add(x, y, z), add(y, x, z); } f[1] = 0, dep[1] = 1; dfs1(1, 0), dfs2(1, 1); build(1,n,1); while (1) { string s; cin >> s; if (s == "QUERY") { read(x), read(y); if (x == y) printf("0\n"); else printf("%d\n", query_chain(x, y)); } else if (s == "CHANGE") { read(x), read(y); x = (x << 1) - 1; update(id[e[x].v],y,1,n,1); } else break; } return 0; }
P4114
P3038 [USACO11DEC]牧草种植Grass Planting


#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int N = 4e5 + 10; int n,m,cnt,num; int top[N],f[N],son[N],size[N],id[N],head[N],dep[N]; struct node { int v,nx; }e[N]; struct tree { int sum; int lazy; }t[N]; #define lson rt << 1
#define rson rt << 1 | 1 template<class T>inline void read(T &x) { x = 0;int f = 0;char ch = getchar(); while(!isdigit(ch)) f |= (ch == '-'),ch = getchar(); while(isdigit(ch)) x = x * 10 + ch - '0',ch = getchar(); x = f ? -x : x; return; } inline void add(int u,int v) { e[++num].nx = head[u],e[num].v = v,head[u] = num; } void dfs1(int u,int fa) { size[u] = 1; for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if(v != fa) { dep[v] = dep[u] + 1; f[v] = u; dfs1(v,u); size[u] += size[v]; if(size[v] > size[son[u]]) son[u] = v; } } } void dfs2(int u,int t) { top[u] = t; id[u] = ++cnt; if(son[u]) dfs2(son[u],t); for(int i = head[u]; ~i; i = e[i].nx) { int v = e[i].v; if(v != f[u] && v != son[u]) dfs2(v,v); } } inline void pushup(int rt) { t[rt].sum = t[lson].sum + t[rson].sum; } inline void pushdown(int l,int r,int rt) { if(t[rt].lazy) { t[lson].lazy += t[rt].lazy; t[rson].lazy += t[rt].lazy; t[lson].sum += t[rt].lazy * l; t[rson].sum += t[rt].lazy * r; t[rt].lazy = 0; } } void update(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt) { if(L <= l && r <= R) { t[rt].sum += (r - l + 1); t[rt].lazy += 1; return ; } int m = (l + r) >> 1; pushdown(m - l + 1,r - m,rt); if(L <= m) update(L,R,l,m,lson); if(R > m) update(L,R,m + 1,r,rson); pushup(rt); } int query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int rt) { if(L <= l && r <= R) return t[rt].sum; int m = (l + r) >> 1,ans = 0; pushdown(m - l + 1,r - m,rt); if(L <= m) ans += query(L,R,l,m,lson); if(R > m) ans += query(L,R,m + 1,r,rson); return ans; } void update_chain(int x,int y) { int fx = top[x],fy = top[y]; while(fx != fy) { if(dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x,y),swap(fx,fy); update(id[fx],id[x],1,cnt,1); x = f[fx],fx = top[x]; } if(id[x] > id[y]) swap(x,y); update(id[x] + 1,id[y],1,cnt,1); } int query_chain(int x,int y) { int fx = top[x],fy = top[y],ans = 0; while(fx != fy) { if(dep[fx] < dep[fy]) swap(x,y),swap(fx,fy); ans += query(id[fx],id[x],1,cnt,1); x = f[fx],fx = top[x]; } if(id[x] > id[y]) swap(x,y); ans += query(id[x] + 1,id[y],1,cnt,1); return ans; } int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) { memset(head,-1,sizeof(head)); read(n),read(m); for(int i = 1,x,y; i < n; ++i) { read(x),read(y); add(x,y),add(y,x); } f[1] = 0,dep[1] = 1; dfs1(1,0),dfs2(1,1); for(int i = 1,x,y; i <= m; ++ i) { char c; cin>>c; read(x),read(y); if(c == 'P') update_chain(x,y); else printf("%d\n", query_chain(x,y)); } return 0; }
P3038
今天的文章树链剖分详解_树链分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读,如果确实帮到您,您可以动动手指转发给其他人。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/46265.html