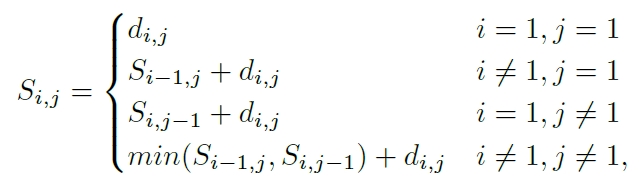旷视的AlignedReID,很有意思。
The end-to-end learning with structure prior is more powerful than a “blind” end-to-end learning.
reid难点:
目前triplet loss等用的比较多。Combining softmax loss with metric learning loss to speed up the convergence is also a popular method. 还有一些考虑局部特征如pose和part的方法,具体见论文。
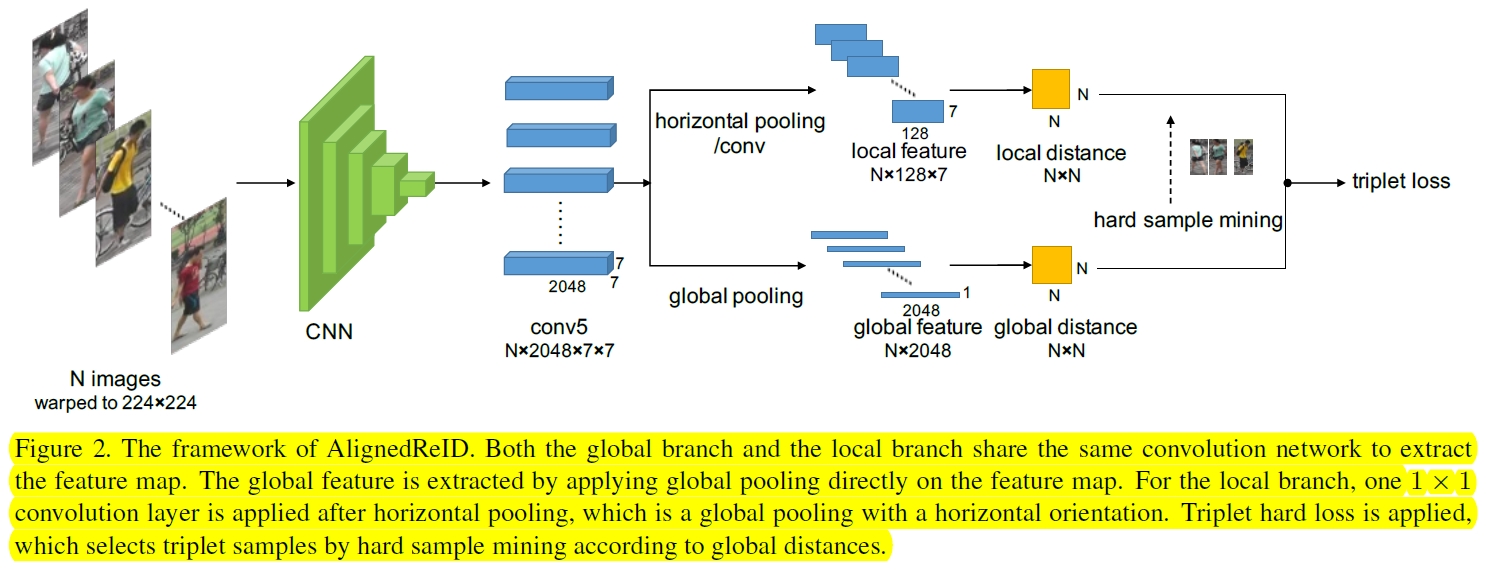
AlignedReID
注意local feature就是先做一个方向的global pooling(垂直纸面方向),然后用1*1卷积降低通道数到128,这样就把图片中水平的信息在图片的宽度方向上进行了叠加。global feature用L2计算距离,local feature采用:
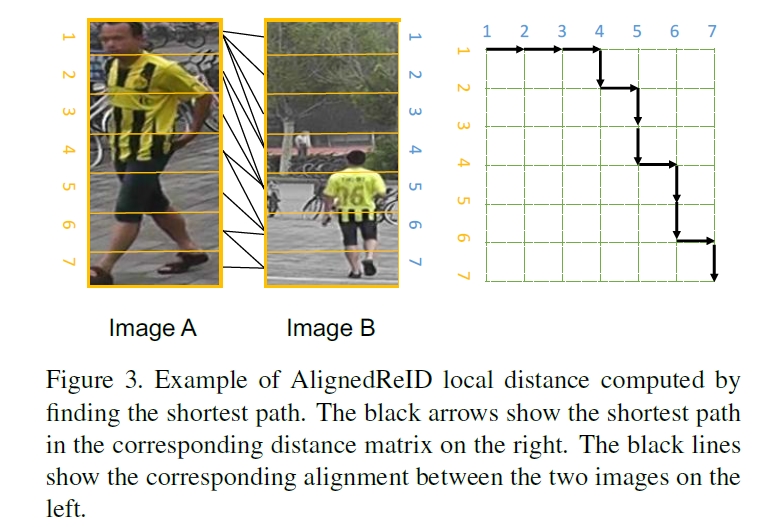
左上角到右下角的最短路径长度就是local feature的长度,可以用动态规划法求解:
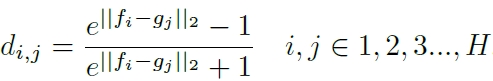
注意fig 3中有的边是没用的,如A的1连B的1,其实是不匹配的。但是在设计dij的公式时,使得不匹配的地方L2差别大,梯度小,这样在训练时还是主要在缩小匹配部分的距离,不匹配的地方不太起作用。使用TriHard loss进行训练。而测试时只使用global feature来计算距离,因为local feature和global feature的联合训练实际上也优化了global feature,使得它almost as good as the combined features(当然也有可能是local的距离中包含了不匹配的部分,这部分在训练时可能影响不大,但是测试时对总的loss计算有干扰?)。
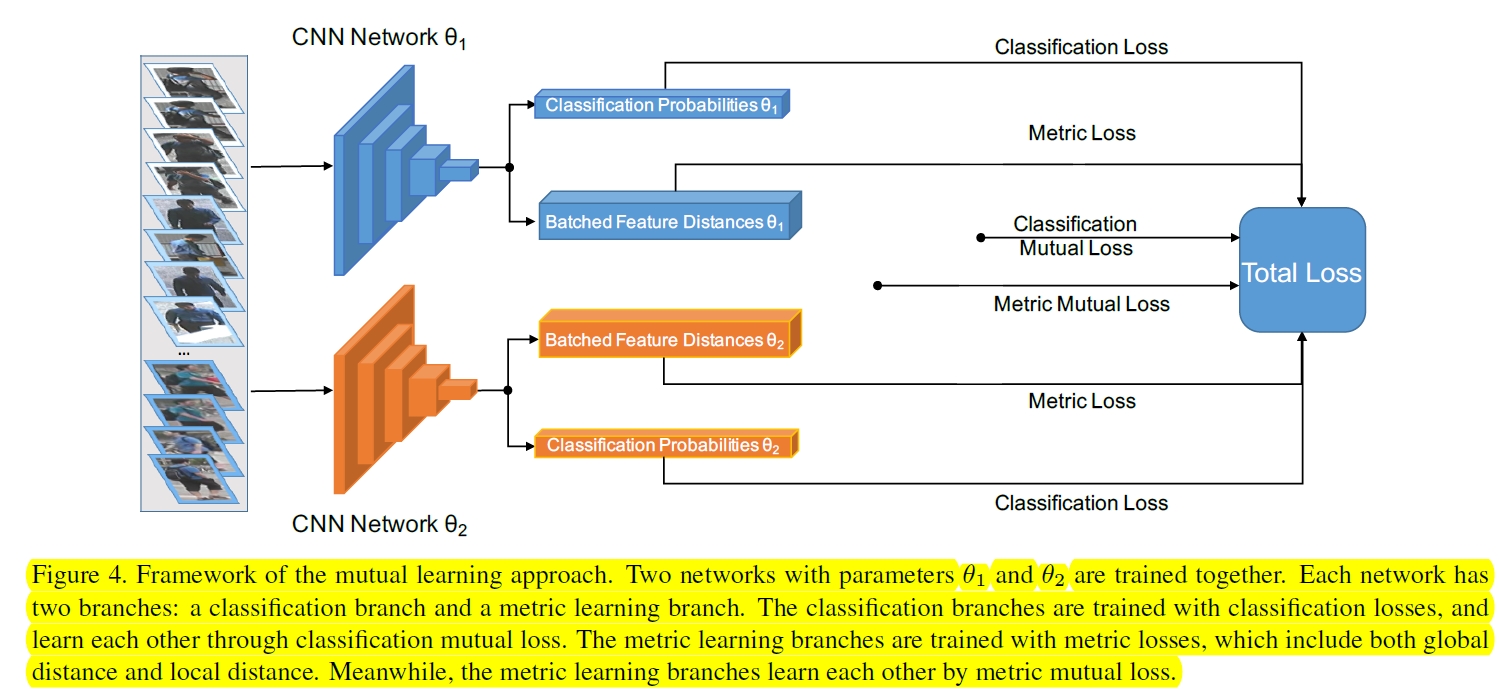
mutual learning
metric loss: both the global distances and the local distances
metric mutual loss: only the global distances.
classification mutual loss: KL divergence
就是说使得不同网络的分类loss和metric loss之间的差别变小,使得这些网络共同进步。the weight of classification mutual loss (KL) is set to 0.01, and the weight of metric mutual loss is set to 0.001.
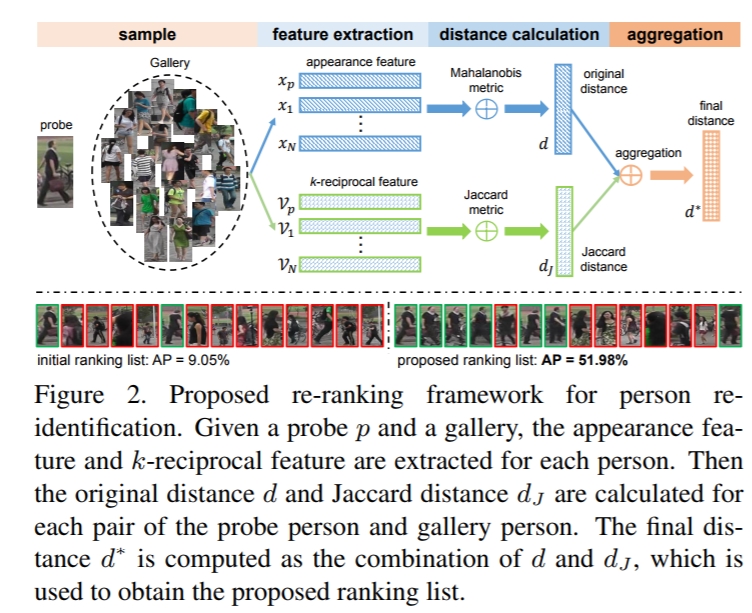
re-ranking
Re-ranking Person Re-identification with k-reciprocal Encoding
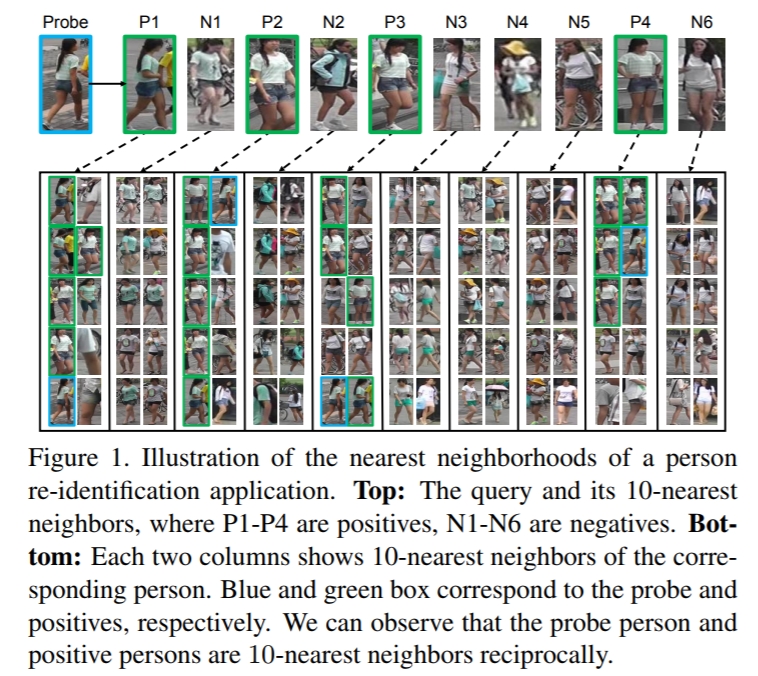
第一行: directly using the top-k ranked images may introduce noise.
第二行:the probe is a reciprocal neighbor to the true matched images, but not to the false matches.
When two images are called k-reciprocal nearest neighbors, they are both ranked top-k when the other image is taken as the probe. Therefore, the k-reciprocal nearest neighbor serves as a stricter rule whether two images are true matches or not.
具体怎么计算呢:
然后就是一堆算法设计了,不赘述。
今天的文章AlignedReID分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/4678.html