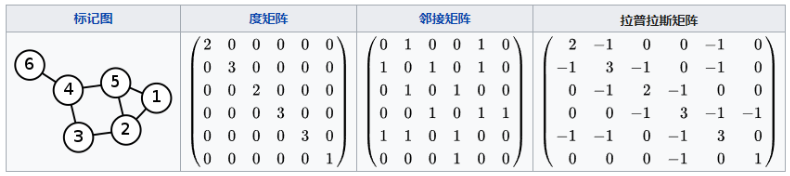
拉普拉斯矩阵(Combinatorial Laplacian)
拉普拉斯矩阵(Laplacian matrix)也叫做导纳矩阵、基尔霍夫矩阵或离散拉普拉斯算子,主要应用在图论中,作为一个图的矩阵表示。
给定一个有 $n$ 个顶点的图 $G$,它的拉普拉斯矩阵:
$L=D-A$
其中 $D$ 为图的度矩阵,$A$ 为图的邻接矩阵。度矩阵在有向图中,只需要考虑出度或者入度中的一个。
性质
-
拉普拉斯矩阵是半正定矩阵;
-
特征值中 0 出现的次数就是图连通区域的个数;
-
最小特征值是 0,因为拉普拉斯矩阵每一行的和均为0;
-
最小非零特征值是图的代数连通度。
Symmetric normalized Laplacian
L 左乘 度矩阵 的 $-1/2$ 次,再右乘度矩阵的 $-1/2$ 次,展开得到单位矩阵 $I$ 减去 $A$ 左乘度矩阵的 $-1/2$ 次,再右乘度矩阵的 $-1/2$ 次。
$L^{\text {sym }}:=D^{-1 / 2} L D^{-1 / 2}=I-D^{-1 / 2} A D^{-1 / 2}$
该矩阵中的元素由下面的式子给出:
$L_{i, j}^{s y m}:=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} 1 & \text { if } i=j \text { and } \operatorname{deg}\left(v_{i}\right) \neq 0 \\ -\frac{1}{\sqrt{\operatorname{deg}\left(v_{i}\right) \operatorname{deg}\left(v_{j}\right)}} & \text { if } i \neq j \text { and } v_{i} \text { is adjacent to } v_{j} \\ 0 & \text { otherwise. } \end{array}\right.$
上图例子:
$A=\left\{\begin{array}{llllll}0 & 1 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\1 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 \\0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 1 \\1 & 1 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 & 0\end{array}\right\} \quad D=\left\{\begin{array}{llllll}2 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 3 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 2 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 & 3 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 3 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\end{array}\right\}$
$L=D-A=\left\{\begin{array}{cccccc}2 & -1 & 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 \\-1 & 3 & -1 & 0 & -1 & 0 \\0 & -1 & 2 & -1 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & -1 & 3 & -1 & -1 \\-1 & -1 & 0 & -1 & 3 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 & -1 & 0 & 1\end{array}\right\} \quad D^{-1 / 2}=\left\{\begin{array}{cccccc}\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 & \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} & 0 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & \frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 0 & 1\end{array}\right\}$
$L^{\text {sys }}=D^{-1 / 2} L D^{-1 / 2}=I-D^{-1 / 2} A D^{-1 / 2}=\left\{\begin{array}{cccccc}1 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}} & 0 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}} & 0 & 0 \\-\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}} & 1 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}} & 0 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{9}} & 0 \\0 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}} & 1 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}} & 0 & 0 \\-\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}} & 0 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{6}} & 1 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{9}} & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} \\0 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{9}} & 0 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{9}} & 1 & 0 \\0 & 0 & 0 & -\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}} & 0 & 1\end{array}\right\}$
Random walk normalized Laplacian
$L^{r w}=D^{-1} L=I-D^{-1} A$
$L_{i j}^{r w}=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} 1 & \text { if } i=j \text { and } D_{i i} \neq 0 \\ -\frac{1}{D_{i i}} & \text { if } i \neq j \text { and } v_{i} \text { is adjacent to } v_{j} \\ 0 & \text { otherwise } \end{array}\right.$