层次遍历_层次遍历的实现方式此博客链接: 二叉树的层次遍历 题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/ 给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。 示例:二叉树:[3,9,20
此博客链接:
二叉树的层次遍历
题目链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 层序遍历 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例:
二叉树:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其层次遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
题解:
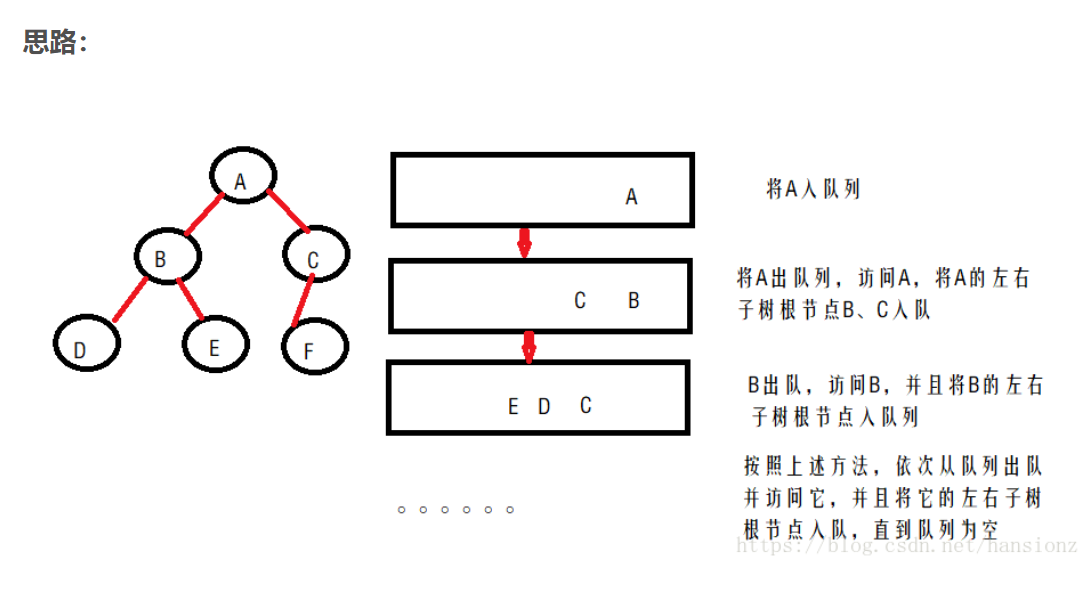
思路:
1.使用队列遍历二叉树。
2.根节点进队列,然后出队列,如果左右孩子不空,则把左右孩子进队列。
3.出队列中的孩子,如果孩子的左右孩子不空,继续进队列,就这样知道队列为空为止,即把二叉树层次遍历完。
这里需要注意:
1.题目中层次遍历的输出结果是一个包含列表的列表,即按二叉树的每层上的节点输出的,所以最后输出的结果需要返回一个列表。
2.每层上的节点也是一个列表,需要把每层上的节点放入一个列表中,再存入最后结果中的列表中,

代码:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Queue <TreeNode> queue=new LinkedList();
List<List<Integer>> result=new ArrayList();
if(root==null)
return result;
if(root!=null)
{
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty())
{
List<Integer> temp=new ArrayList();
int len=queue.size();
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
TreeNode que=queue.poll();
temp.add(que.val);
// temp.add(que.val);
if(que.left!=null)
queue.add(que.left);
if(que.right!=null)
queue.add(que.right);
}
result.add(temp);
}
}
return result;
}
}