Abstract:
其实我以前觉得写这种文章的分享很耗费时间,不过现在觉得看过的文章不做整理实在是记不住,也很浪费,不如把精读的文章整理一下,比如这篇文章属于自带代码的单细胞文章,还是一篇cell,理应精读学习一波。数据比较大,边跑边整理好了。
CODE:
代码在github,但是数据存在google drive里面,而且几十个G,我自然下载不了。画了半个小时探索后,我用五毛钱在某二手平台找了个大哥帮我,花了一天时间拿到了数据,这里就分享出来。
github:All code used to generate the results of this study can be found on github at czbiohub/scell_lung_adenocarcinoma and czbiohub/cerebra.
数据在data:https://pan.baidu.com/s/10wc6BHZjNfNl2cVUr-jgJw
提取码:rp93
里面的object应该是在script中间保留的Rdata,属于是超级大了几十个G,就没让大哥帮我下载,咱自己跑出来吧
文章:Therapy-Induced Evolution of Human Lung CancerRevealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing
Summary:机翻加自己校正了一下
肺癌是导致癌症死亡的主要原因,它表现出高度异质性,这使得疾病的适应性更强,限制了治疗的成功,并且仍不完全被人了解。49份临床活检样本的单细胞RNA测序(scRNA-seq)来自进行靶向治疗之前或正处于靶向治疗的30个病人。超过20000个肿瘤和肿瘤微环境(TME)单细胞图谱反映了丰富而动态变化的肿瘤生态系统(ecosystem)。肿瘤细胞的scRNA序列照亮了(高亮了;原文是illuminated,可能翻译成highlight?)超出临床检测范围的靶向癌基因。治疗后的疾病状态分为RD和PD。作为Residual disease (RD)而从治疗中存活的癌细胞表达肺泡再生细胞(alveolar-regenerative cell)signature,表明治疗诱导下,细胞状态向原始细胞状态的转变;而在治疗后Progressive disease(PD)中存在的癌细胞,则上调了犬尿氨酸、纤溶酶原和缝隙连接通路(kynurenine, plasminogen, and gap-junction pathway)。RD时存在活跃的T淋巴细胞和减少的巨噬细胞;PD则表现出免疫抑制细胞的状态。scRNA-seq揭示的生物学特征是独立队列中临床结果的生物标志物。这项研究强调了转移癌在治疗诱导后,产生的多细胞生态系统的适应性是如何影响临床结果的。
Introduction:
1.强调异质性:细胞和TME之间的相互作用也是肿瘤微环境的重要组成In addition to cancercell intrinsic heterogeneity, cells within the tumor microenvironment(TME) further contribute to tumor heterogeneity in a cancer cell extrinsicmanner
2.longitudinally美: [ˌlɒndʒɪ’tjudɪnəlɪ]英: [ˌlɒndʒɪ’tju:dɪnəlɪ]adv. 纵向;orthogonally正交的;应该都是指互不干扰的两个东西的结合;比如两种方法。our understanding of how these properties evolve and interact longitudinally in response to systemic treatment remains incomplete, particularly in metastatic tumors。
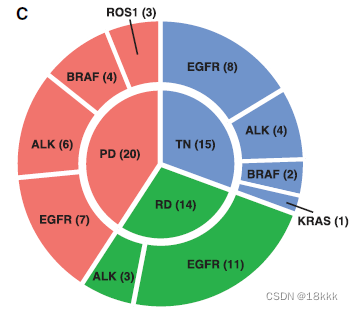
3.提到四种突变:临床上根据他们展开靶向治疗。但是治疗反应常不完全,并且在治疗后出现耐药复发等问题,bulk测序提示治疗后肿瘤的分子异质性增强。
EGFR,EGFR(英语:epidermal growth factor receptor,简称为EGFR、ErbB-1或HER1)是表皮生长因子受体(HER)家族成员之一。 研究表明在许多实体肿瘤中存在EGFR的高表达或异常表达。
ALK,ALK是anaplastic lymphoma kinase的缩写,翻译过来是间变性淋巴瘤激酶。这个基因与它表达的产物最早是在淋巴瘤中发现的。间变性大细胞淋巴瘤中就有一种亚型,拥有ALK阳性表达。后来在肺腺癌中也发现了这个基因有变异。那么怎么确定ALK基因突变呢? 一般是从病理组织中去检测,比如免疫组织化学,RT-PCR, Fish法,高通量测序。什么检测最好呢,测序法。
ROS1,ROS1位于第6号染色体上,编码1个受体酪氨酸激酶,由富含糖蛋白的胞外结构域、跨膜结构域及胞内酪氨酸激酶组成。ROS1重排最初在胶质母细胞瘤细胞系中被发现,产生新的融合基因,ROS1融合是潜在的致癌因素。最近,在其他几种恶性肿瘤中也发现ROS1重排,包括胆管癌、卵巢癌和胃癌。ROS1重排的NSCLC是一种具有独特临床病理特征的分子亚型。非小细胞肺癌中ROS1融合基因阳性的约占1%~2%。其好发于年轻、不吸烟的亚裔肺腺癌女性和表皮生长因子受体( epidermal growth factor receptor,EGFR) 及间变性淋巴瘤激酶( anaplastic lymphoma kinase,ALK) 野生型的肺腺癌患者中。
BRAF,该基因位于人类7号染色体上(NC_000007.14 (140719327..140924928, complement)),编码RAF家族丝氨酸/苏氨酸蛋白激酶。该蛋白在调节MAPK/ERK信号通路中起作用,影响细胞分裂,分化和分泌。该基因的突变,最常见的突变为V600E,最常在黑色素瘤,非霍奇金淋巴瘤,大肠癌,甲状腺癌,非小细胞肺癌,多毛细胞白血病和腺肺癌中发生突变。
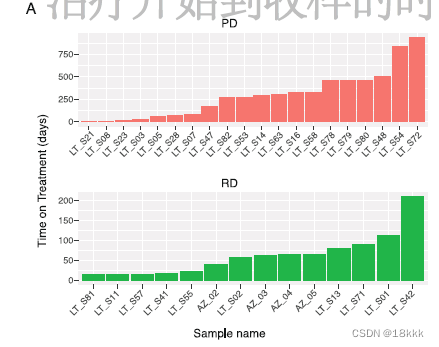
4.创新性:首次关注了三个治疗时间点的转移性 advanced-stage NSCLC 患者,即TN;RD;PD。同时,样本的采样时间也有所不同。
patients before initiating systemic targeted therapy(TKI naive [TN]),治疗前TN
at the residual disease (RD) state, which includes samples taken at any time during treatment with targeted therapy while the tumor was regressing or stable by clinical imaging(RD), 治疗后肿瘤消减或者稳定RD
and upon subsequent progressive disease as determined by clinical imaging, at which point the tumors showed acquired drug resistance (progression [PD]).治疗后肿瘤进展PD
5.方法:
smart_seq2测序。比起10x的3’测序count数据,这种测序使用的是TPM transcripts per kilobase million计数,属于全基因长度测序。一般基于96-plate,但本文好像用的是384plate。它可以detect more genes,适合寻找低丰度的基因,研究它们的功能,也可以发现可变剪接。一个样本的细胞数大约在几百个,所以本文近50个样,最后有20000个细胞,一个样大概400个细胞,和10X的几千细胞一个样还是有很多差距。reads在1-10M;对比10X在5000-10000。smart_seq2依赖更深的测序深度可以发现更多的细胞互作,与bulk的测序结果可能更加相似。而相对来讲发现新亚群的能力差于10X.
文章之所以用smart_seq2后文也写清楚了,NSCLC的转移患者一般也不需要切除治疗,获得样本比较困难,所以就用需要细胞量少一点的方法
6.样本:
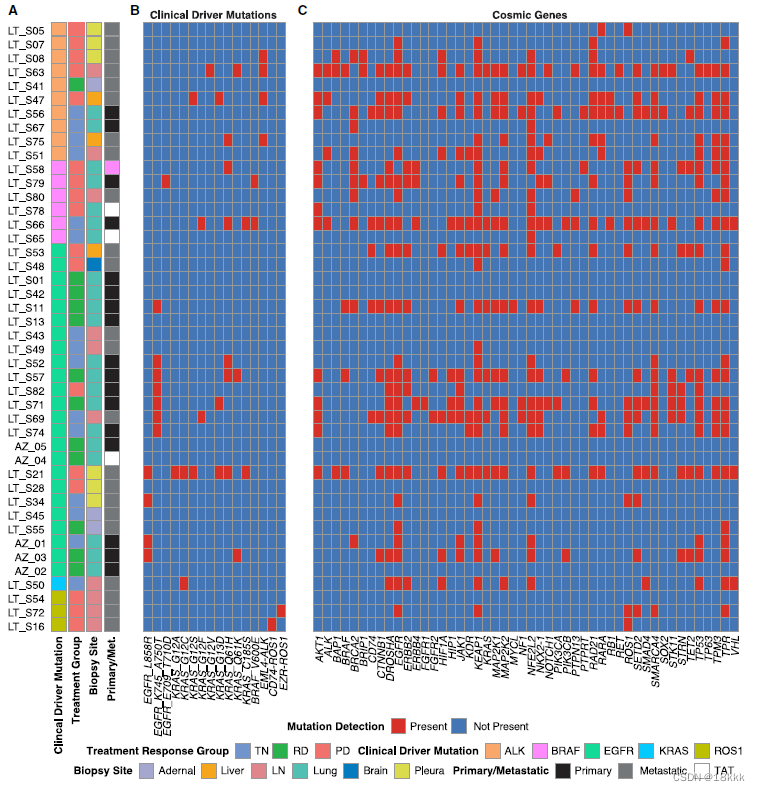
49 samples; corresponding to 30 individual patients.
(45 lung adenocarcinomas,1 squamous cell carcinoma, and 3 tumor adjacent tissues[TATs]),这些病人进一步依据oncogenic driver;时间点,进一步分组
Results:
scRNA-seq Analysis of Advanced-Stage NSCLCs during Targeted Therapy:
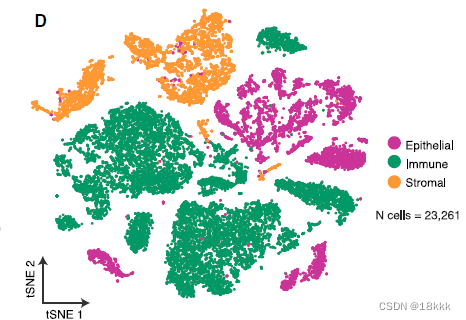
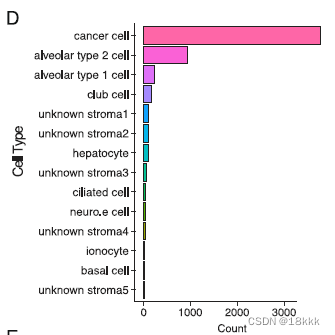
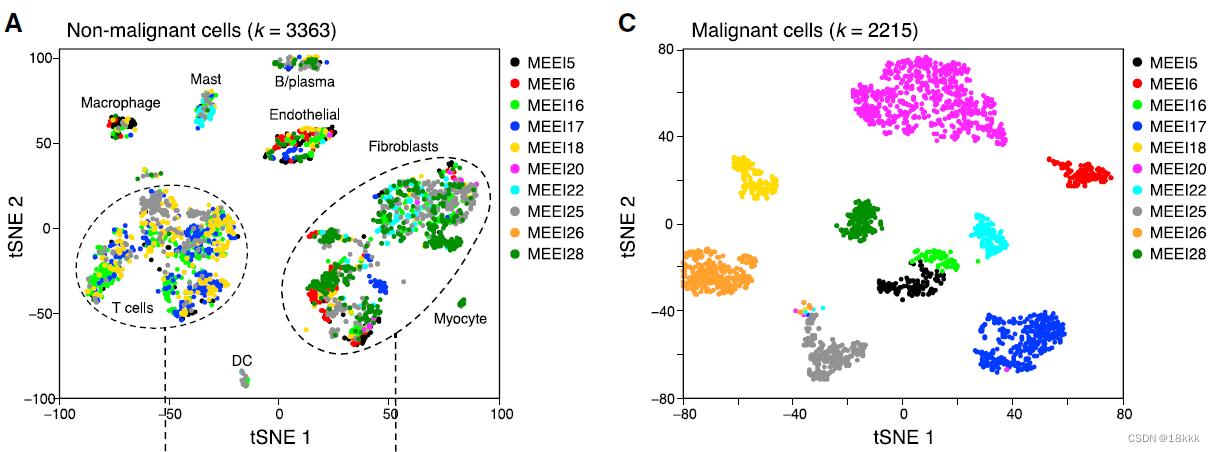
23261个细胞在质控后被保留,初步分群为三群:code中检查的基因如下
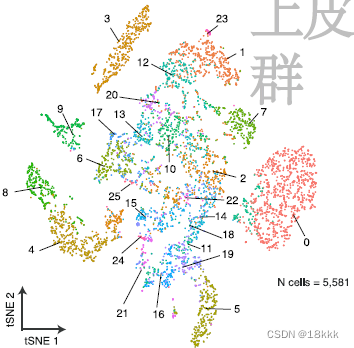
genes_to_check = c("PTPRC","EPCAM","CD3G","CD3E", "CD79A", "BLNK","MS4A1", "CD68", "CSF1R", "MARCO", "CD207", "PMEL", "ALB", "C1QB", "CLDN5", "FCGR3B", "COL1A1")上皮的5581个细胞进一步提取,再分群为26个上皮群Res = 0.5, Kparam = 30
Clustering-Based Copy-Number Variation Resolves Cancer from Non-cancer Epithelial Cells
CNV的检查来确定epithelial cells as either cancer or non-cancer
ref选择了fibroblasts and endothelial cells (controls)
三个癌旁TAT也参与了CNV推断,并且主要被分为了non-cancer
平均CNV得分在三个治疗时间点是有一致性的
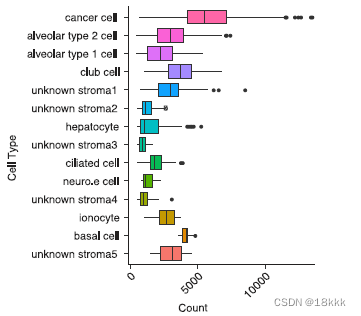
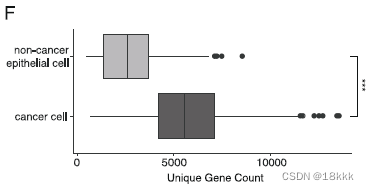
在CNV推断的同时,作者强调肿瘤细胞相较于非肿瘤细胞更倾向于表达显著增加的unique gene,并且这种unique gene的增加不能被解释为测序深度(Pearson correlation = 0.19)的不同。这再次有了一种可以鉴别良恶性细胞的方法。
下图上方的是count,下方是unique gene数,可以看到cancer cell的unique gene明显的多。应该是这两个图的数据做correlation得出unique gene的增加不能被解释为测序深度的不同所致。
或许cor是用这个算出来的?
49个样本中有44个鉴定出了恶性细胞,包括TAT组织,这可能因为TAT本身处于交界区,有一部分肿瘤细胞(0.57%–1.8% of total TAT obtained cells)并不令人吃惊。
所有的肿瘤细胞,3754个,再次重新分群为25个群。计算分群的病人特异性occupancy。由于肿瘤细胞的高度异质性,大部分cancer cluster应该主要由1-2种病人组成,而非肿瘤的epi cluster则应该不具有病人特异性,由多种病人组成。也是鉴别良恶性细胞的方法,但主要用来作证。
明显可以看出肿瘤细胞和非肿瘤细胞病人组成上的差异,计算occupancy
在文章Single-Cell Transcriptomic Analysis of Primary and Metastatic Tumor Ecosystems in Head and Neck Cancer也能看到良恶性细胞不同的病人组成情况
scRNA-seq Analysis Reveals a Rich Complexity of Expressed Gene Alterations in Cancer Cells计算突变
在一开始的突变后oncogenic ‘‘driver’’ alteration (e.g., oncogenic EGFR, ALK, KRAS),还可能出现别的突变导致肿瘤进一步进展和治疗抵抗。由于所有的病人都有clinical的突变数据,作者想根据测序结果观察这些病人是否有进一步的突变情况,即somatic alterations。clinical数据来自clinical-grade bulk DNA analysis。
研究结果发现看20个病人有着与clinial一致的突变结果,这符合测序的drop-out发生率(drop out是一种常见的现象,10X的droplet技术受影响更大。
在这20个病人种,有11个发现了额外的突变。
突变有利于靶向药物的使用,但多数据证实(Zehir et al., 2017),突变多的患者OS下降。
结论:临床的突变检查结果可能低估了肿瘤的异质性。
Transcriptional Differences between TN and RD Cancer Cells Detected by scRNA-Seq Analysis Reveal Cell-State-Specific Biological Programs:探究TN和RD在转录水平的差异,个人觉得这一个小结是比较有意思的地方。标红注意下。
对这两个组别进行比较,寻找差异基因。
629 significantly(p < 0.05) upregulated genes in RD cancer cells –许多基因associated with cancer-associated pathways,其实就是对这些基因进行通路的富集。
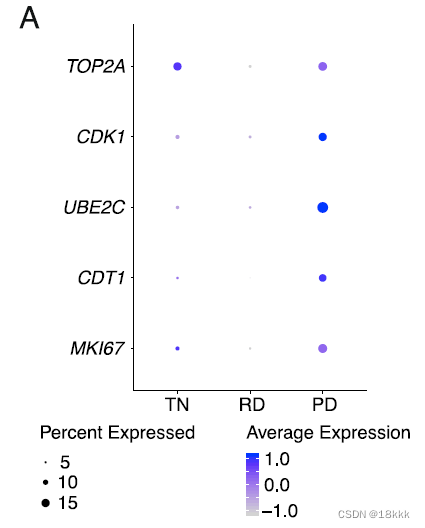
结果发现:RD cancer cells expressed decreased proliferation marker genes compared to TN and PD,这与靶向治疗后肿瘤细胞的低活性相一致。
此外,发现肺泡细胞基因表达signature(17个gene),与TN相比在RD的cancer cell中显著增加。alveolar分为alveolar1和alveolar2,其中alveolar1可以转变为alveolar2。大体的意思是这两种肺泡上皮的signature与干细胞、损伤修复相关,这两型均在上皮中被检测到相应的signature。绿色代表RD。
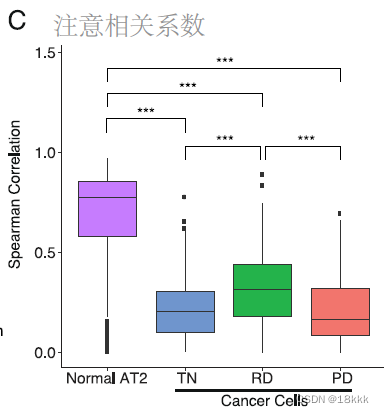
有趣的地方在于作者希望证明这种signature是真正存在于RD的肿瘤细胞,而不是混入了正常的细胞,将三种治疗状态的癌细胞和正常的AT2细胞与外部数据集的健康AT2细胞做相关,结果显示只有正常的AT2细胞与外部数据集有显著的相关,而肿瘤细胞均低相关,说明这些signature来自肿瘤细胞而非正常细胞。
同时使用orthogonal approaches 也就是正交的,相互独立的方法去做验证。比如先用pre-clinical model这里就是细胞系实验。
细胞系:patient-derived EGFR mutant NSCLCs (PC9)
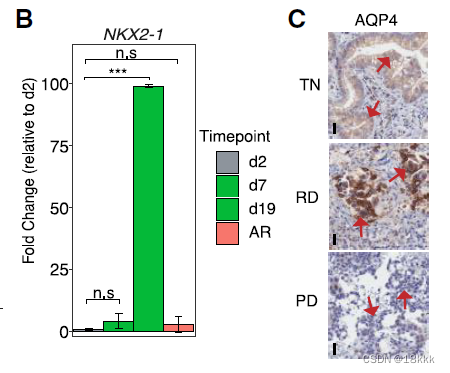
方法:B图,RT-PCR,发现肺泡signaturer在RD模拟样本中显著上调(相较于control和resistance)
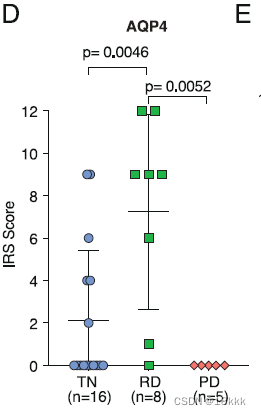
方法:进一步,在转录层面证实了,希望在翻译层面证实。用IHC去看AQP4,同时给出典型视野和IMC score得分统计图。放图一定要有统计结果。
再用TCGA数据库验证,按照表达量的高低,以四分位间距分了四组,发现与预后显著相关该signature表达越多,预后越好。作者的解释是表达量高者,与修复损伤相关
这种损伤修复的机制是什么?细节是什么?注意力转移到了WNT/β-catenin通路及相关基因SUSD2和CAV1。
In NSCLCs, the WNT/β-catenin signaling pathway contributes to tumorigenesisrepair, and regeneration after cell injury。
discussion中的一段总结:we found the alveolar cell signature was enriched at RD and was associated with improved survival. This signature exhibited features consistent with cellular plasticity and injury response, perhaps indicating a treatment-inducedadaptive phenotype that permits the survival of cancer cells, albeit in a less aggressive state (Wang et al., 2018). Our data also highlight a connection from the alveolar cell signature to the WNT/b-catenin pathway as a mechanism of injury response and regeneration. Though the WNT/b-catenin pathway is potentially therapeutically targetable, (Krishnamurthy and Kurzrock, 2018), it will be critical to determine how to best modulate this pathway to impact residual cancer cell survival for clinical benefit.
SUSD2 is an activated downstream target of the WNT pathway。
CAV1 can promote nuclear localization of b-catenin (CTNNB1) and transcriptional activation of the WNT/b-catenin pathway 。
老套路,只有转录层面的高表达不行,要有蛋白(免疫组化)的结果。作者认为WNT/βcatenin通路在整个过程中起了重要作用,可以帮助组织修复。
Additionally, in EGFR mutant NSCLC activation of theWNT/b-catenin pathwaymay limit EGFR inhibitor response and may promote survival of a persister cell population duringEGFR inhibitor therapy in vitro。这个通路还会限制靶向治疗的效果。
最后作者提出WNT/βcatein可以作为靶向治疗的一个靶点。并要在两个细胞系中验证。
patient-derived PC9cells as an EGFR mutant NSCLC model and H3122 cells体外实验打药
Transcriptional Differences between TN and PD Cancer Cells Reveal Immune Modulation and Cellular Invasion as Key Features of Cancer Progression视角回到免疫细胞,上一个part比较了TN和RD组,这次比较TN和PD组
When comparing cancer cells from TN and PD samples, we found 901 differentially upregulated genes in PD cancer cells—富集通路kynurenine pathway and multiple genes and pathways associated with oncogenesis and inflammation
瞄准三个显著变化的gene在kynurenine通路,都是些免疫抑制基因,会抑制免疫反应
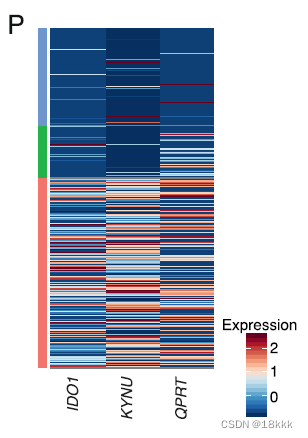
IDO1:吲哚胺2,3-双加氧酶1。IDO1将L-色氨酸(Trp)转化为犬尿氨酸(Kyn),并通过激活芳香烃受体(AhR)发挥多种免疫调节作用。IDO1介导了GCN2激酶的应激反应途径激活,该激酶可以减少蛋白质合成并暂时阻断小鼠CD8+T淋巴细胞功能。
KYNU
QPRT
研究发现这三个基因在多种肿瘤中被广泛报道,
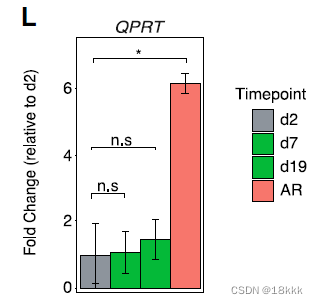
QPRT在体外试验模拟获得性EGFR抗性(after treatment with osimertinib)中,显著增加
再次出现TCGA的生存分析,显示kynurenine与预后的密切关系。
这次比较RD和PD scRNA-seq Profiles of Cancer Cells Change from RD to PD
found a total of 2,182 genes which had significantly(p < 0.001) increased expression in either RD or PD (NRD = 1,121, NPD = 1,061)还是找差异基因
differentially overexpressed genes at RD were genes associated with the alveolar cell signature, cell growth, differentiation, cell motility, and tumor suppression再次提到了肺泡的signature
SFTPB/C/D and SFTA3:alveolar cell signature属于促进修复的signature,使得RD预后好于PD
NKX2-1 and NFIX:decreased cell motility
Low expression of NKX2-1:loss of differentiation and enhanced tumor seeding ability
PD cancer cells differentially overexpressed genes associated with invasion, cell-to-cell communication, differentiation, and immune modulation
ANXA2, PLAT, PLAUR, PLAU:plasminogen activation pathway纤溶酶原激活途径;
功能:involved in inflammation, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis, via degradation of the extracellular matrix与转移相关的通路
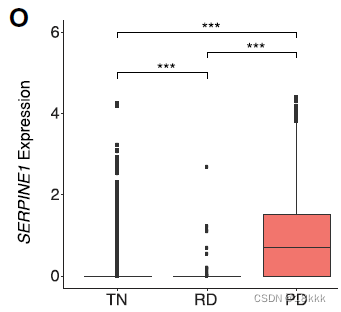
the plasminogen inhibitor SERPINE1 (PAI1)表达也有升高
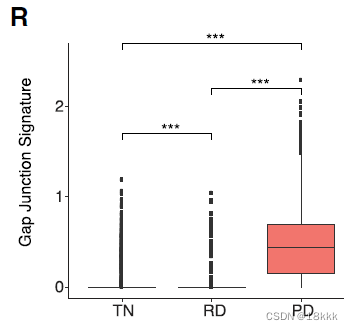
gap-junction proteins differentially overexpressed in PD 升高
功能:cytosolic exchange of ions, metabolites and secondary messengers between cells
再次用TCGA分析plasminogen activation pathway,SERPINE1,gap-junction proteins与OS关系
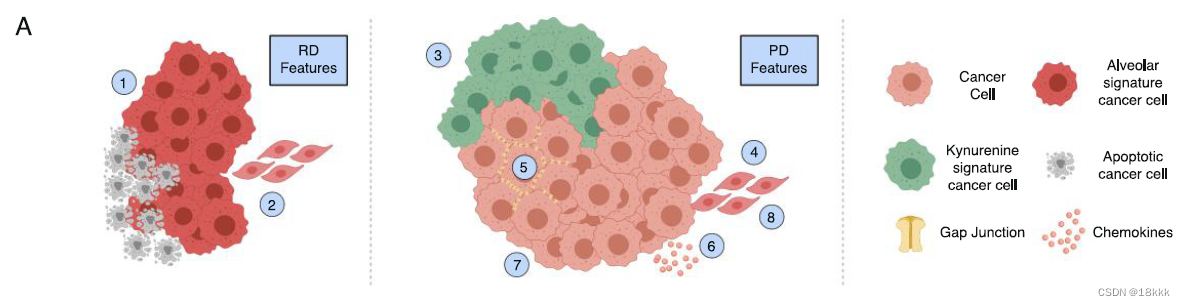
最后在附图里对不同治疗时期,肿瘤细胞周围的环境和几种signature/pathway进行了总结
发现不管是什么突变,这些signatu都是具有保守性的
Longitudinal scRNA-seq Analysis of an Individual Patient’s Tumor during Treatment
这里比较突出的贡献在于找了一个病人,多个时期的标本
we obtained samples from the same primary tumor site from 3 treatment time points from a patient (TH226) whose tumor contained a standard EGFR exon 19 deletion oncogenic mutation and was treated with the EGFR inhibitor osimertinib
这个病人本来是纯纯的肺腺癌,但是在PD中,多出来了很多鳞状细胞的marker,证明了组织学类型的改变,KRT16, KRT14, KRT6A, KRT5, CLCA2, PKP1, ANXA8, DSG3,这可能和EGFR突变患者对EGFR抑制剂的抵抗有关。同时检查几个上文的signature,发现是一致的结果。
接下来是免疫部分,重点关注一下:Inversion of Myeloid and Lymphoid Infiltration within the TME at Progressive Disease Compared to RD 髓系和淋巴系的相反表现
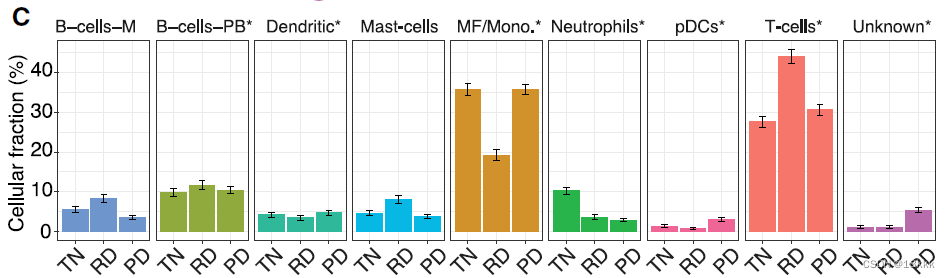
免疫细胞被重新分群n = 13431,没有出现和肿瘤病人一样的病人特异性,显示为low occupancy
在三个时间点查看免疫细胞的组成,发现T细胞和MF/Mono的区别
于是接下来的分析着眼于这三者
相关性分析显示RD的免疫组成与其它两种最不相似
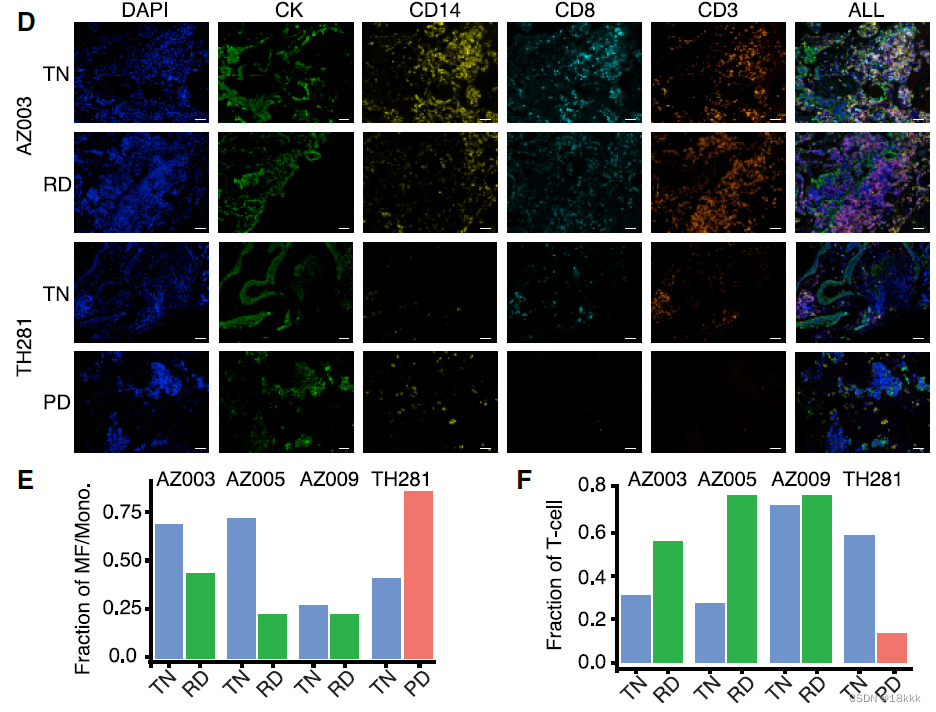
为了验证相关结果,用Immunofluorescence结果对两个病人的组织进行观察
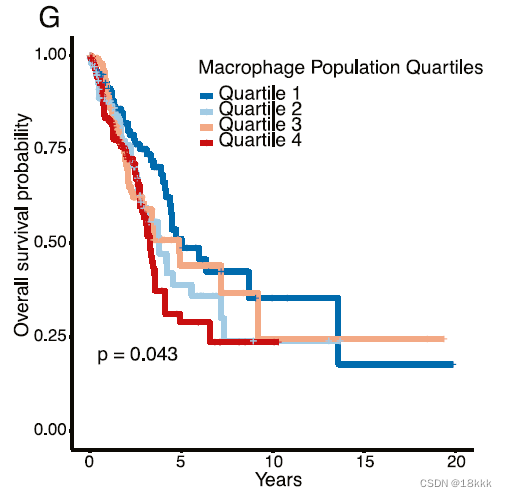
反卷积TCGA,发现巨噬细胞越多,预后越差
同时作者发现,在PD-1靶向治疗后的黑色素瘤中,也出现an increase in the number of CD8+ T cells and natural killer (NK) cells and a decrease in M1macrophages were observed,推测这可能是一种普遍的现象
着眼于巨噬细胞An IDO1-Expressing Macrophage Population Is Enriched at PD
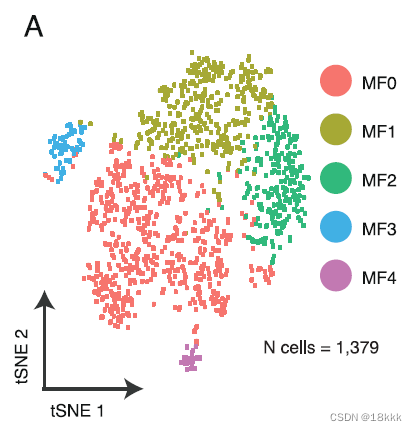
重新聚类分群
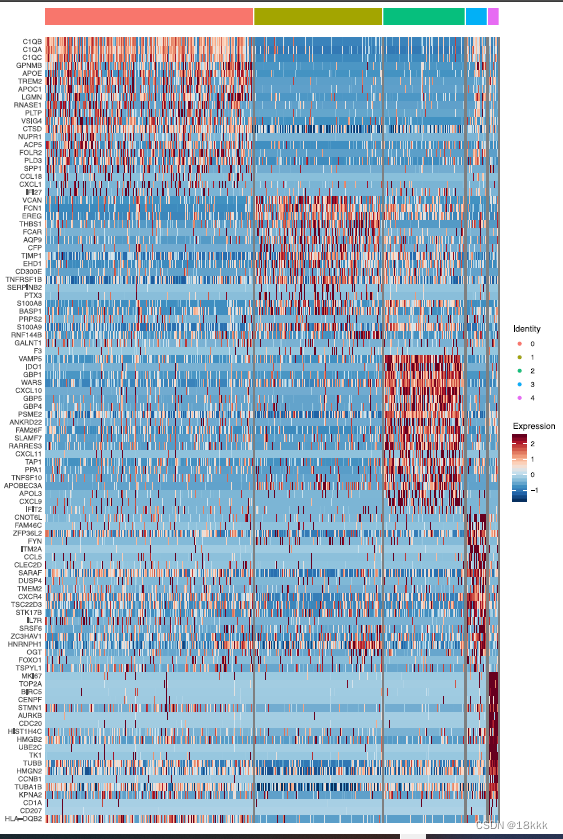
计算这五群在不同时期的分布,每个群都有自己独有的marker基因
MF0:enriched in TN cells, was characterized by expression of genes associated with an immunosuppressive phenotype (C1QC, GPNMB, APOE, TREM2, FOLR2)
MF1,MF3:enriched at RD.
Macrophage cluster MF1 expressed features associated previously with tumor-infiltrating myeloid derived suppressor cells (FCN1, VCAN, S100A8, S100A9) (Zhang et al., 2019) and with THBS1 and PTX3, which are associated with resolution of inflammation, wound healing, and with inhibition of IL-1b
Cluster MF3 expressed genes associated with pro-inflammatory response to tissue damage (CLEC2D, IL7R, OGT)and with promoting inflammatory signaling (FYN, DUSP4, FOXO1)
MF4:consisted of proliferating myeloid cell populations(TOP2A, MKI67) and did not significantly differ between groups.
MF2:at PD,expressed pro-inflammatory cytokines CXCL9, CXCL10, and CXCL11 (Figure 5B; Figure S7B), which favor lymphocyte recruitment into the TME。其中最特异的是IDO1,双加氧酶1,induced by inflammation within the TME and promotes a tolerogenic environment through immunosuppressive myeloid cell populations, regulatory T cell (Treg) differentiation, and an immunosuppressive cytokine milieu由TME内的炎症诱导,并通过免疫抑制骨髓细胞群、调节性T细胞(Treg)分化和免疫抑制细胞因子环境促进耐受性环境
着眼于T细胞An Immunosuppressive T Cell Phenotype Is Predominant within the TME at PD
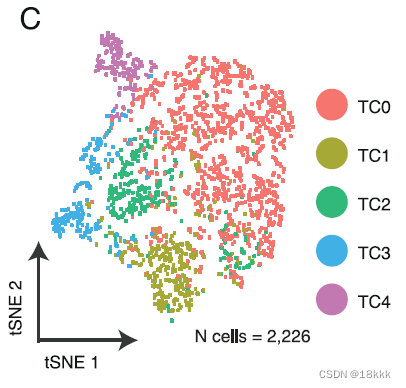
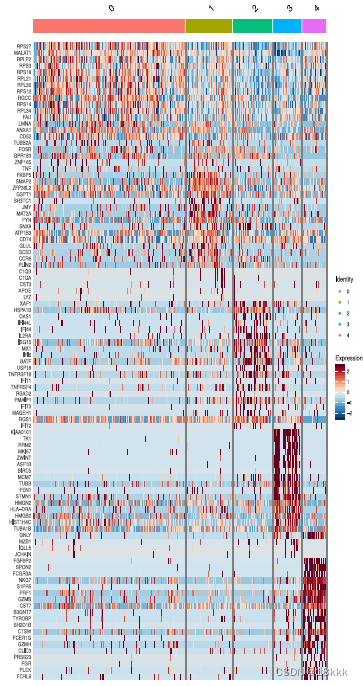
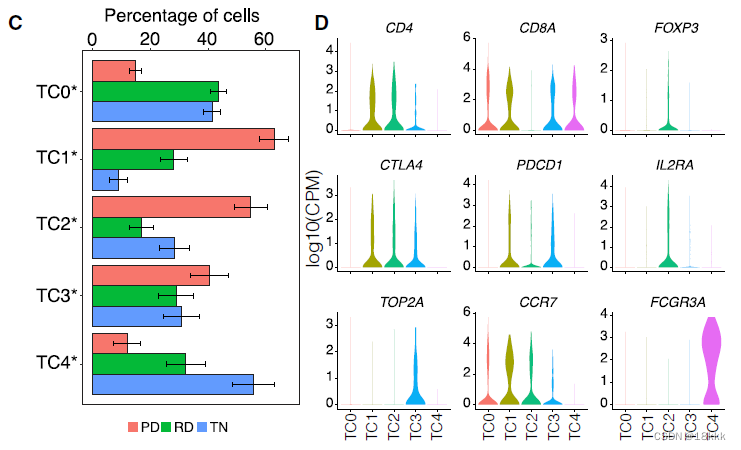
重新聚类分群
计算这五群在不同时期的分布,每个群都有自己独有的marker基因
TC0有CCR7 naive的标志,也可以是naive CD8
CTLA4 PDCD1这样的marker体现TC1是耗竭T细胞
TC2很明显是Treg,异质性的微环境
模式图反应随着时间的变化,巨噬细胞和T细胞组成的变化
代码实操:
作者的代码习惯真好,希望我可以早日学会
读取数据
这里原代码给的是read.csv,读取数据直接爆炸了,还是用fread好啊,高下立判
dir.create("Data_input")
dir.create("rda_yun")
dir.create("plot_yun")
dir.create("data_out_yun")
dir <-paste0(getwd(),"/")
start<-Sys.time()
raw.data <- fread(paste0(dir,"Data_input/csv_files/S01_datafinal.csv"),
header=T)
end<-Sys.time()
runningtime<-end-start
cat(runningtime)
#11.72639
raw.data <- as.data.frame(raw.data)
dim(raw.data)
head(raw.data)[1:5,1:5]
rownames(raw.data) <- raw.data[,1]
raw.data <- raw.data[,-1]
dim(raw.data)
head(raw.data)[1:5,1:5]
##load metadata
metadata <- read.csv(paste(dir,"Data_input/csv_files/S01_metacells.csv", sep=""), row.names=1, header=T)
head(metadata)
##save as rda for quick loading
save(list=c("metadata","raw.data","dir"),
file=paste0(dir,"data_out_yun/Data_and_metadata.rda"))
这里看到metadata的数据还是很多的。每一个细胞的信息都在里面了
准备分析
创建对象
把有ERCC的踢掉了,#ERCC应该是一些有问题的基因名?
##Find ERCC's, compute the percent ERCC, and drop them from the raw data.
erccs <- grep(pattern = "^ERCC-", x = rownames(x = raw.data), value = TRUE)
percent.ercc <- Matrix::colSums(raw.data[erccs, ])/Matrix::colSums(raw.data)
ercc.index <- grep(pattern = "^ERCC-", x = rownames(x = raw.data), value = FALSE)
raw.data <- raw.data[-ercc.index,]把所有的metadata加入,保存好seurat对象以后就可以直接用了
##Create the Seurat object with all the data (unfiltered)
main_tiss <- CreateSeuratObject(counts = raw.data)
# add rownames to metadta
row.names(metadata) <- metadata$cell_id
# add metadata to Seurat object
main_tiss <- AddMetaData(object = main_tiss, metadata = metadata)
main_tiss <- AddMetaData(object = main_tiss, percent.ercc, col.name = "percent.ercc")
# Head to check
head(main_tiss@meta.data)
save(main_tiss, file=paste0(dir,"data_out_yun/Main_Seurat_object_prefilter.rda"))
# 计算核糖体并过滤低质量基因
ribo.genes <- grep(pattern = "^RP[SL][[:digit:]]", x = rownames(x = main_tiss@assays$RNA@data), value = TRUE)
percent.ribo <- Matrix::colSums(main_tiss@assays$RNA@counts[ribo.genes, ])/Matrix::colSums(main_tiss@assays$RNA@data)
main_tiss <- AddMetaData(object = main_tiss, metadata = percent.ribo, col.name = "percent.ribo")
main_tiss_filtered <- subset(x=main_tiss, subset = nCount_RNA > 50000 & nFeature_RNA > 500)
save(main_tiss_filtered, file=paste(dir,"data_out_yun/Main_Seurat_object_filtered.rda", sep=""))随后分析就大片段复制了嘿嘿嘿,还是很详尽的,就不一一展示了,主要学习了一下作者的代码逻辑,真不错。
画了一天断断续续整理,还是有帮助的,系统理解了一下CNS的逻辑。
今天的文章Therapy-Induced Evolution of Human Lung CancerRevealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing 治疗后肺癌单细胞测序文章分享分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/61264.html