篇章一:入口篇
我们学习Mybatis时知道其核心是SqlSessionFactory,它是mybatis的核心类,也是Mybatis运行的入口,spring集成mybatis时需要配置SqlSessionFactoryBean和扫描mapper的MapperScannerConfigurer,spring-mybatis集成主要的配置就这么点,从这理解也就不难理解mybatis入口问题了,但是<bean>节点只是指明了该类的路径和一些属性信息,并没有指明先运行哪个方法呀?我们带着问题【SqlSessionFactoryBean是入口,那入口方法是哪个?】继续研究下去,
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory"
class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="mapperLocations"
value="classpath:com/jianlejun/mapper/*.xml" />
<property name="configuration">
<bean class="org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration">
<property name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
<!--扫描dao -->
<bean class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<property name="basePackage" value="com.jianlejun.dao" />
<property name="sqlSessionFactoryBeanName"
value="sqlSessionFactory"></property>
</bean>我们点进去看看SqlSessionFactoryBean.
public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<SqlSessionFactory>, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (failFast && event instanceof ContextRefreshedEvent) {
// fail-fast -> check all statements are completed
this.sqlSessionFactory.getConfiguration().getMappedStatementNames();
}
}
}可以看到SqlSessionFactoryBean实现了三个接口:
1.ApplicationListener接口:里面只有一个onApplicationEvent方法,有什么用呢?看官方的注释,它是基于观察者模式创建的,当上下文ApplicationContext加载完实现了该接口的bean后,负责通知该bean,bean接收到通知后(onApplicationEvent方法),可以在方法内做自己的逻辑处理,简单点理解就是容器你好,我收到你加载我完毕的通知了,接下里就交给我吧,不用你操心了。
很显然这不是我们要找的方法入口,因为bean都加载完了,说明mybatis配置文件什么都处理完了,那我们再来看看InitializingBean接口
2.InitializingBean接口:接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是继承该接口的类,在初始化bean的时候都会执行该方法(如果bean配置了init-method属性,afterPropertiesSet优先级高于init-method)。
由上可知,这就是我们要找的入口了,spring在初始化bean时,会先调用afterPropertiesSet()方法,从上面代码可知,它在里面调用了buildSqlSessionFactory()方法,哎,最上面我们是不是说了mybatis的核心是SqlSessionFactory,可想而知,这个构造SqlSessionFactory的方法buildSqlSessionFactory()是最核心的方法了。
入口篇完。
篇章二:配置篇
1.配置文件加载
Mybatis配置bean时注入了一个mapperLocations属性,指明项目xml mapper文件的路径,SqlSessionfactoryBean内定义了一个Resource数组接收mapperLocations的位置
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory"
class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<property name="mapperLocations"
value="classpath:com/jianlejun/com/mapper/*.xml" />
<property name="configuration">
<bean class="org.apache.ibatis.session.Configuration">
<property name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true" />
</bean>
</property>
</bean>public class SqlSessionFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<SqlSessionFactory>, InitializingBean, ApplicationListener<ApplicationEvent> {
private Resource configLocation;
private Configuration configuration;
private Resource[] mapperLocations;
/**
* Set locations of MyBatis mapper files that are going to be merged into the {@code SqlSessionFactory}
* configuration at runtime.
*
* This is an alternative to specifying "<sqlmapper>" entries in an MyBatis config file.
* This property being based on Spring's resource abstraction also allows for specifying
* resource patterns here: e.g. "classpath*:sqlmap/*-mapper.xml".
*/
public void setMapperLocations(Resource[] mapperLocations) {
this.mapperLocations = mapperLocations;
}
}2.读取配置文件
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
//省略了前面次要代码
if (!isEmpty(this.mapperLocations)) {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
configuration, mapperLocation.toString(), configuration.getSqlFragments());
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
if (LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOGGER.debug("Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified or no matching resources found");
}
}
}这段代码主要根据mapperLocation的文件流构造XMLMapperBuilder(解析xml文件的核心类),然后调用XMLMapperBuilder的parse()方法进行xml文件解析,点进去看看parse()方法体
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
public void parse() {
//判断资源文件是否被加载过
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));//解析mapper文件
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);//加载解析完毕放入Set容器中
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
}
public class Configuration{
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<String>();
public boolean isResourceLoaded(String resource) {
return loadedResources.contains(resource);
}
public void addLoadedResource(String resource) {
loadedResources.add(resource);
}
}来看看ConfigurationElement()方法
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
//获取mapper文件命名空间
//即<mapper namespace="com.jianlejun.dao.ProductDao">节点的namespace属性值
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));//解析<parameterMap>
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));//解析<resultMap>节点
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));//解析<sql>节点
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));//解析CRUD节点
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}这里mybatis是将mapper.xml文件分为几个部分来单独解析的,主要关注解析<parameterMap>/<resultMap>/<sql>/<select|..|..>几个步骤
①<resultMap>节点
先上一波源码
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private ResultMap resultMapElement(XNode resultMapNode, List<ResultMapping> additionalResultMappings) throws Exception {
ErrorContext.instance().activity("processing " + resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
//获取<resultMap>标签id属性的值,下面也是解析标签很多属性的值,就不一一注释了
String id = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("id",
resultMapNode.getValueBasedIdentifier());
//需要映射的实体类(String)
String type = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("type",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("ofType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("resultType",
resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("javaType"))));
String extend = resultMapNode.getStringAttribute("extends");
Boolean autoMapping = resultMapNode.getBooleanAttribute("autoMapping");
Class<?> typeClass = resolveClass(type);//根据全限定名加载类
Discriminator discriminator = null;
List<ResultMapping> resultMappings = new ArrayList<ResultMapping>();
resultMappings.addAll(additionalResultMappings);
List<XNode> resultChildren = resultMapNode.getChildren();
//解析<resultMap>标签的子节点
for (XNode resultChild : resultChildren) {
if ("constructor".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
processConstructorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else if ("discriminator".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
discriminator = processDiscriminatorElement(resultChild, typeClass, resultMappings);
} else {
List<ResultFlag> flags = new ArrayList<ResultFlag>();
if ("id".equals(resultChild.getName())) {
flags.add(ResultFlag.ID);
}
resultMappings.add(buildResultMappingFromContext(resultChild, typeClass, flags));
}
}
ResultMapResolver resultMapResolver = new ResultMapResolver(builderAssistant, id, typeClass, extend, discriminator, resultMappings, autoMapping);
try {
return resultMapResolver.resolve();//该方法会调用MapperBuilderAssistant的addResultMap()方法,然后方法内部再调用 configuration.addResultMap(resultMap);将解析好的文件对象存到Configuration
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteResultMap(resultMapResolver);
throw e;
}
}
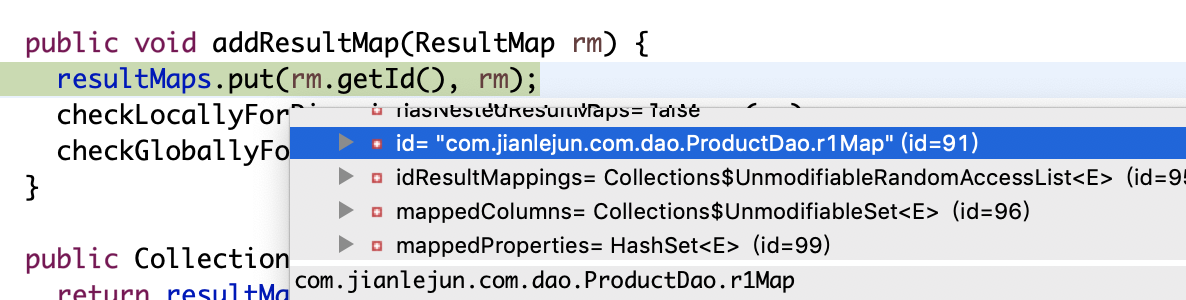
}解析<resultMap>节点时,解析完该节点数据会存储在ResultMap类中,<resultMap>节点是通过id来区分的,那么mybatis底层是如何区分的呢?看源码最终定位到Configuration类的这段代码,当mybatis解析完<resultMap>节点并转换成实体对象ResultMap后,会调用Configuration类的addResultMap方法将解析成功的<resultMap>节点加入到Configuration类,类中定义了一个StrictMap来存储解析成功节点,键为<resultMap>的id(dao类全限定名+id),值为ResultMap对象。但是这个StrictMap比较特殊,它是mybatis自实现的HashMap,并且是Configuration的内部类,map里不能存在相同的key。(这里面试时经常会被问道为什么标签的id为什么不能相同,现在知道怎么回答了吧,其他标签也是如何,最终解析完的结果都是放入都是StrictMap中)
package org.apache.ibatis.session;
public class Configuration {
protected final Map<String, ResultMap> resultMaps = new StrictMap<ResultMap>("Result Maps collection");
public void addResultMap(ResultMap rm) {
resultMaps.put(rm.getId(), rm);
checkLocallyForDiscriminatedNestedResultMaps(rm);
checkGloballyForDiscriminatedNestedResultMaps(rm);
}
}
StrictMap源码:
package org.apache.ibatis.session;
public class Configuration {
protected static class StrictMap<V> extends HashMap<String, V> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -4950446264854982944L;
private final String name;
public StrictMap(String name, int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
super(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
this.name = name;
}
public StrictMap(String name, int initialCapacity) {
super(initialCapacity);
this.name = name;
}
public StrictMap(String name) {
super();
this.name = name;
}
public StrictMap(String name, Map<String, ? extends V> m) {
super(m);
this.name = name;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public V put(String key, V value) {
if (containsKey(key)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " already contains value for " + key);
}
if (key.contains(".")) {
final String shortKey = getShortName(key);
if (super.get(shortKey) == null) {
super.put(shortKey, value);
} else {
super.put(shortKey, (V) new Ambiguity(shortKey));
}
}
return super.put(key, value);
}
public V get(Object key) {
V value = super.get(key);
if (value == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(name + " does not contain value for " + key);
}
if (value instanceof Ambiguity) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(((Ambiguity) value).getSubject() + " is ambiguous in " + name
+ " (try using the full name including the namespace, or rename one of the entries)");
}
return value;
}
private String getShortName(String key) {
final String[] keyParts = key.split("\\.");
return keyParts[keyParts.length - 1];
}
protected static class Ambiguity {
final private String subject;
public Ambiguity(String subject) {
this.subject = subject;
}
public String getSubject() {
return subject;
}
}
}
}至此<resultMap>节点加载解析完毕。
②<select|update|insert|delete>节点
继续来看看ConfigurationElement()方法内部调用的buildStatementFromContext()方法,主要负责解析<select>等CURD标签
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
}里面创建了个XMLStatementBuilder来负责mapper文件<select|update|insert|delete>节点的解析工作,并且调用了其statementParser.parseStatementNode()方法。
具体解析节点xml文件代码如下:
public class XMLStatementBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, this.requiredDatabaseId)) {
return;
}
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
LanguageDriver langDriver = getLanguageDriver(lang);
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
StatementType statementType = StatementType.valueOf(context.getStringAttribute("statementType", StatementType.PREPARED.toString()));
ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
boolean resultOrdered = context.getBooleanAttribute("resultOrdered", false);
// Include Fragments before parsing
XMLIncludeTransformer includeParser = new XMLIncludeTransformer(configuration, builderAssistant);
//解析前先解析<include>引用的sql片段
includeParser.applyIncludes(context.getNode());
// Parse selectKey after includes and remove them.
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// Parse the SQL (pre: <selectKey> and <include> were parsed and removed)
#获得sql语句
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");
String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");
String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = context.getBooleanAttribute("useGeneratedKeys",
configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType))
? Jdbc3KeyGenerator.INSTANCE : NoKeyGenerator.INSTANCE;
}
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType,
fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,
resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,
keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}
}mybatis在做CURD解析前会调用XMLIncludeTransformer的applyIncludes()方法,将标签内<include>元素解析。
<select>等元素内部的SQL语句会被放入到SqlSource对象中。
最终解析完后会调用MapperBuilderAssistant的addMappedStatement()方法,将<select|insert>等解析完的东东统一封装到MappedStatement中,然后将对象放到Configuration的StrictMap中。
MapperBuilderAssistant类
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
StatementType statementType,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Integer fetchSize,
Integer timeout,
String parameterMap,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
ResultSetType resultSetType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
boolean resultOrdered,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
String keyColumn,
String databaseId,
LanguageDriver lang,
String resultSets) {
if (unresolvedCacheRef) {
throw new IncompleteElementException("Cache-ref not yet resolved");
}
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType)
.resource(resource)
.fetchSize(fetchSize)
.timeout(timeout)
.statementType(statementType)
.keyGenerator(keyGenerator)
.keyProperty(keyProperty)
.keyColumn(keyColumn)
.databaseId(databaseId)
.lang(lang)
.resultOrdered(resultOrdered)
.resultSets(resultSets)
.resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id))
.resultSetType(resultSetType)
.flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect))
.useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect))
.cache(currentCache);
ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);
if (statementParameterMap != null) {
statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);
}
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);//最终将解析好的节点信息放入configuration,如果存在相同id的节点则抛出异常
return statement;
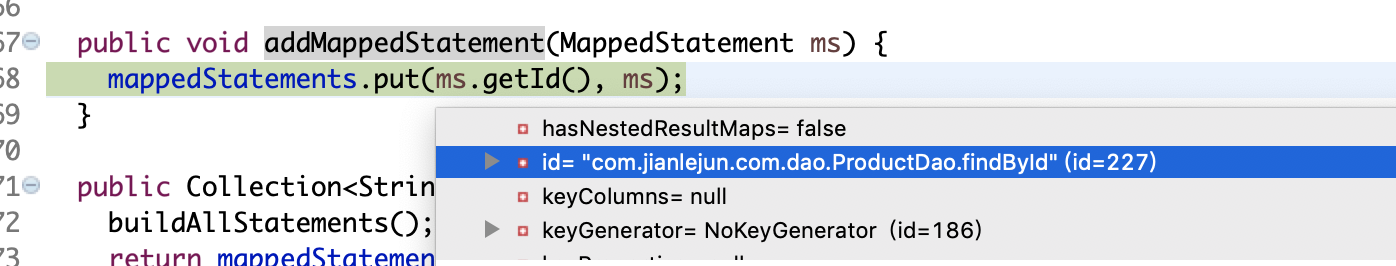
}这里关键的是调用configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);跟resultMap节点一样,节点信息也是存入一个StrictMap中
,key为sql语句的id,value为构造好的MapperStatement对象,由于StrictMap是不允许存在相同key的,所以sql的id相同是回抛出一样
Configuration类
package org.apache.ibatis.session;
public class Configuration {
protected final Map<String, KeyGenerator> keyGenerators = new StrictMap<KeyGenerator>("Key Generators collection");
//存储解析好的<select|update|insert|delete>节点信息
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements = new StrictMap<MappedStatement>("Mapped Statements collection");
public boolean hasKeyGenerator(String id) {
return keyGenerators.containsKey(id);
}
public void addMappedStatement(MappedStatement ms) {
mappedStatements.put(ms.getId(), ms);
}
}由下图可以看到key为dao(mapper)全限定名+sql节点的id,value为MappedStatement对象
其他<parameterMap><sql>节点就不一一赘述了,原理都差不多,<parameterMap>节点最终被封装成ParameterMap对象中,然后放入到StrictMap,<sql>节点主要应用在解析<include>时。
至此<select|insert|update|delete>节点解析完毕。
篇章三:应用篇
通过上面的章节,我们来思考些问题,mapper文件已经解析完了,那mybatis调用dao的方法时,如何通过dao的方法名找到对应的sql,并最终执行?执行后怎么映射到mapper文件配置的实体上?
先来看看我的service
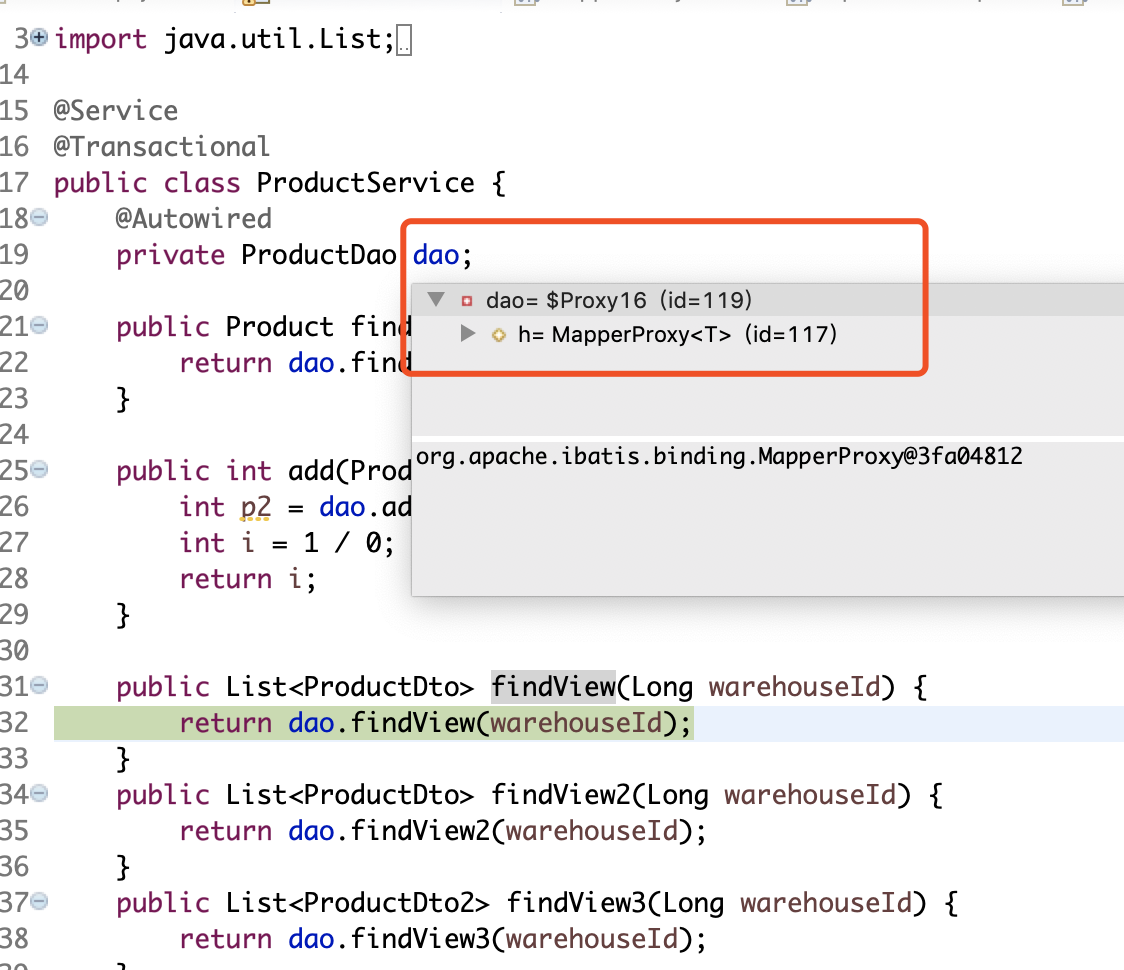
@Service
@Transactional
public class ProductService {
@Autowired
private ProductDao dao;
public Product findById(Long id) {
return dao.findById(id);
}
public List<ProductDto> findView(Long warehouseId) {
return dao.findView(warehouseId);
}
public List<ProductDto> findView2(Long warehouseId) {
return dao.findView2(warehouseId);
}
public List<ProductDto2> findView3(Long warehouseId) {
return dao.findView3(warehouseId);
}
public List<ProductDto2> findView4(Long warehouseId) {
return dao.findView4(warehouseId);
}
}假设执行的是findView方法
由上图可以看到这这里注入的dao其实是一个MapperProxy代理,代理最终调用的都是invoke方法(不知道为什么的话请找找谷哥/度娘这对模范夫妻,请教他们是什么代理模式),点进去看看
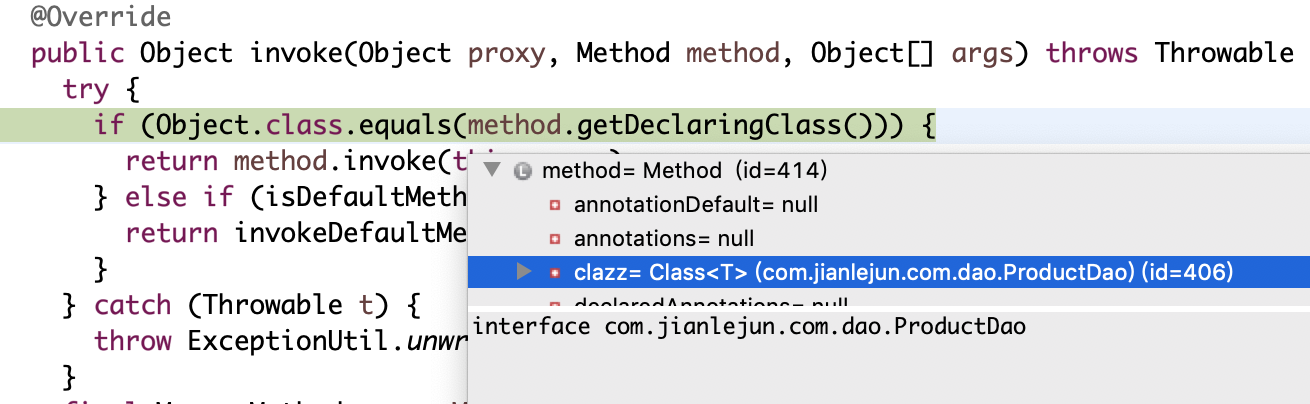
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {
return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
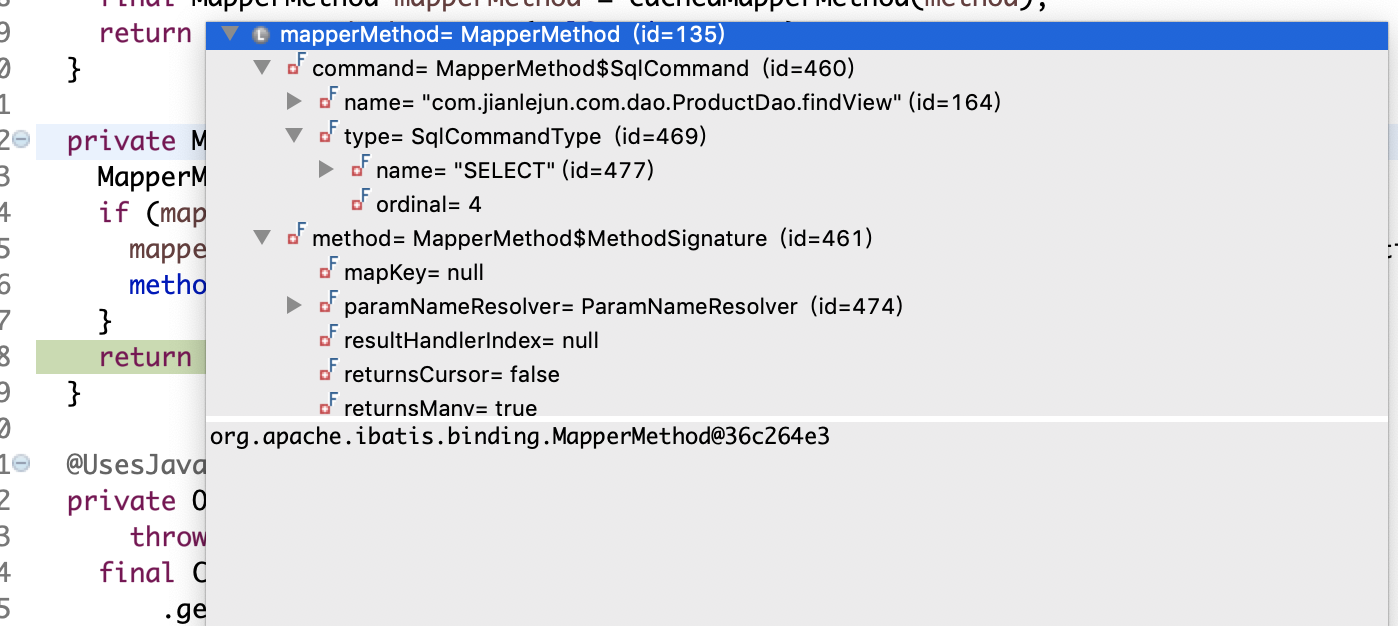
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
}这里先判断代理方法的声明类是否是Object,很显然我这里是ProductDao,不执行if语句块,会转到cachedMapperMethod(),从缓存中获取MapperMethod
接着执行MapperMethod的execute()
package org.apache.ibatis.binding;
public class MapperMethod {
private final SqlCommand command;
private final MethodSignature method;
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
//方法参数转换成SQL执行所需要的参数
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
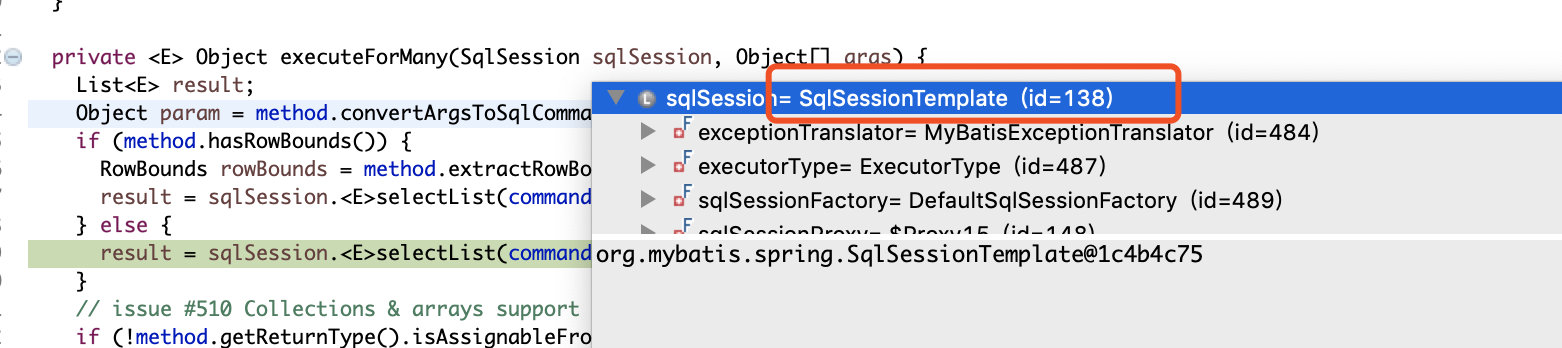
//最终调用的是SqlSessionTemplate模板类的selectList方法
result = sqlSession.<E>selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// issue #510 Collections & arrays support
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}
}execute()方法内部根据带执行的SqlCommand类型匹配switch代码块,我这里的demo是SELECT语句,所以我们直接看 CASE SELECT语句块即可,里面会根据方法放回参数类型类型调用想对应的方法,这里返回的是List,即Many,往下看executeForMany()方法,首先将方法传递的参数转换成执行SQL需要的参数,然后最终会调用SqlSessionTemplate模板的的selectList方法
还没完呢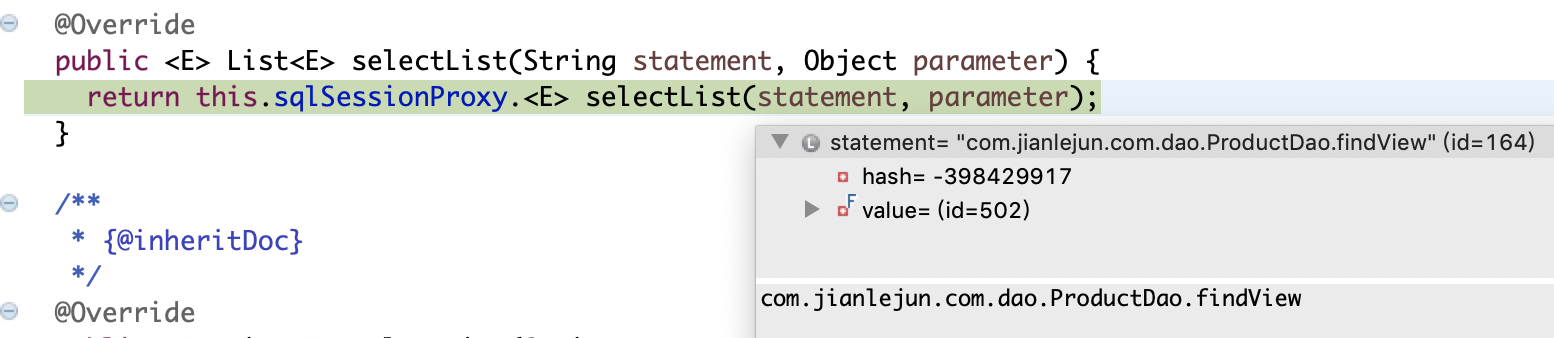
public class SqlSessionTemplate implements SqlSession, DisposableBean {
private final SqlSession sqlSessionProxy;
/**
* {@inheritDoc}
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.sqlSessionProxy.<E> selectList(statement, parameter);
}
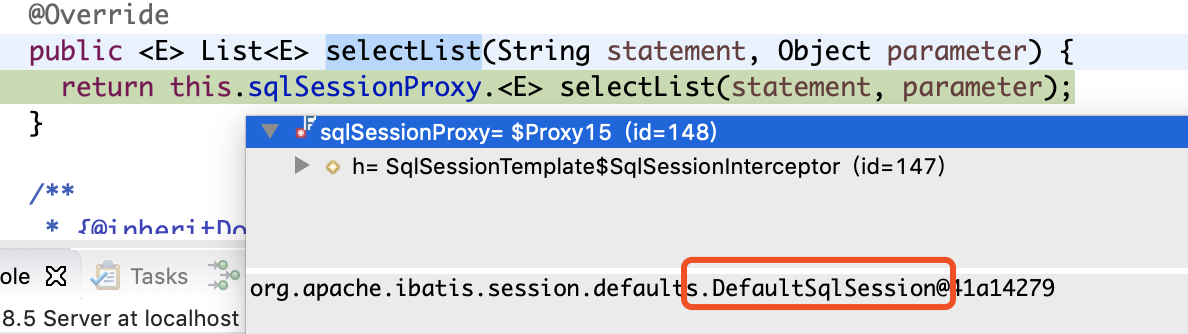
}哎,这里只是调用了SqlSession接口的selectList,不慌,我们来看看这里注入的SqlSession实现类是哪个
哈哈,原来是DefaultSqlSession,继续追踪,要抱着不破楼兰誓不还的决心
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final Executor executor;
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}来到这里,终于真相大白了!!!果不其然,最终是从Configuration中获取封装了<select|update|insert|delete>节点信息的MappedStatement对象,获取到了该对象就说明了获取到了待执行的sql语句信息,剩下的如何执行SQL就不是本文该研究的主题了。
完结撒花?????????????????
喜欢请轻轻点击下方小拇指
今天的文章MyBatis源码分析分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/6177.html