#TensorFlow实现写诗机器人
##概述
在这篇博客中,我们要使用RNN生成藏头诗,你给它输入一些古诗词,它会学着生成和前面相关联的字词。同样的如果你把训练数据换成一堆姓名,它也会学着生成姓名;给它训练一堆音乐,它会学着生成音乐,甚至可以给它训练源代码。
我们使用文本文件做为输入、训练RNN模型,然后使用它生成和训练数据类似的文本。
项目地址:[GitHub](https://github.com/Quanfita/TensorFlow-Poems)使用的数据集:全唐诗(43030首):https://pan.baidu.com/s/1o7QlUhO
环境介绍:
- python 3.6
- TensorFlow 1.2
- i5-6200U(笔记本)
##代码分析:
首先,对使用的神经网络进行简单的介绍:
RNN:
RNN这种网络的内部状态可以展示动态时序行为。不同于前馈神经网络的是,RNN让我们可以利用它内部的记忆来处理任意时序的输入序列。简言之,RNN是为了对序列数据进行建模而产生的。
**什么是样本序列性?**
如果样本间存在顺序关系,每个样本和它之前的样本存在关联,那么我们就可以说这些样本具有序列性。比如说,在文本中,一个词和它前面的词是有关联的;在气象数据中,一天的气温和前几天的气温是有关联的。
在实现过程中我们将整个程序分成5个文件,分别是main.py、poems.py、tangpoems.py、model.py、cleancn.py
– main.py:定义了参数和接口,可以训练或作诗 – poems.py:导入训练文件开始训练 – tang_poems.py:主要功能函数,包括了数据训练,和作诗过程 – model.py:保存训练好的模型 – cleancn.py:这里对中文字符进行处理
这里我们来看一下main.py中 的参数和接口:
import argparse
def parse_args():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Intelligence Poem Writer.')
help_ = 'choose to train or generate.'
#参数--train可以训练--no-train可以让机器人作诗
parser.add_argument('--train', dest='train', action='store_true', help=help_)
parser.add_argument('--no-train', dest='train', action='store_false', help=help_)
parser.set_defaults(train=True)
args_ = parser.parse_args()
return args_
if __name__ == '__main__':
args = parse_args()
import tang_poems
if args.train:
tang_poems.main(True)
else:
tang_poems.main(False)
接下来是主要的文件tangpoems.py:
import collections
import os
import sys
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from model import rnn_model
from poems import process_poems, generate_batch
import heapq
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('batch_size', 64, 'batch size.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_float('learning_rate', 0.01, 'learning rate.')
# set this to 'main.py' relative path
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('checkpoints_dir', os.path.abspath('./checkpoints/'), 'checkpoints save path.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('file_path', os.path.abspath('./poems.txt'), 'file name of poems.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_string('model_prefix', 'poems', 'model save prefix.')
tf.app.flags.DEFINE_integer('epochs', 50, 'train how many epochs.')
FLAGS = tf.app.flags.FLAGS
start_token = 'G'
end_token = 'E'
#开始训练
def run_training():
if not os.path.exists(os.path.dirname(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir)):
os.mkdir(os.path.dirname(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir))
if not os.path.exists(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir):
os.mkdir(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir)
poems_vector, word_to_int, vocabularies = process_poems(FLAGS.file_path)
batches_inputs, batches_outputs = generate_batch(FLAGS.batch_size, poems_vector, word_to_int)
input_data = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [FLAGS.batch_size, None])
output_targets = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [FLAGS.batch_size, None])
end_points = rnn_model(model='lstm', input_data=input_data, output_data=output_targets, vocab_size=len(
vocabularies), rnn_size=128, num_layers=2, batch_size=64, learning_rate=FLAGS.learning_rate)
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables())
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer())
with tf.Session() as sess:
# sess = tf_debug.LocalCLIDebugWrapperSession(sess=sess)
# sess.add_tensor_filter("has_inf_or_nan", tf_debug.has_inf_or_nan)
sess.run(init_op)
start_epoch = 0
checkpoint = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir)
if checkpoint:
saver.restore(sess, checkpoint)
print("[INFO] restore from the checkpoint {0}".format(checkpoint))
start_epoch += int(checkpoint.split('-')[-1])
print('[INFO] start training...')
try:
for epoch in range(start_epoch, FLAGS.epochs):
n = 0
n_chunk = len(poems_vector) // FLAGS.batch_size
for batch in range(n_chunk):
loss, _, _ = sess.run([
end_points['total_loss'],
end_points['last_state'],
end_points['train_op']
], feed_dict={
input_data: batches_inputs[n], output_targets: batches_outputs[n]})
n += 1
print('[INFO] Epoch: %d , batch: %d , training loss: %.6f' % (epoch, batch, loss))
if epoch % 6 == 0:
saver.save(sess, os.path.join(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir, FLAGS.model_prefix), global_step=epoch)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
print('[INFO] Interrupt manually, try saving checkpoint for now...')
saver.save(sess, os.path.join(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir, FLAGS.model_prefix), global_step=epoch)
print('[INFO] Last epoch were saved, next time will start from epoch {}.'.format(epoch))
def to_word(predict, vocabs):
t = np.cumsum(predict)
s = np.sum(predict)
sample = int(np.searchsorted(t, np.random.rand(1) * s))
if sample > len(vocabs):
sample = len(vocabs) - 1
return vocabs[sample]
#调用模型生成诗句
def gen_poem(begin_word):
batch_size = 1
print('[INFO] loading corpus from %s' % FLAGS.file_path)
poems_vector, word_int_map, vocabularies = process_poems(FLAGS.file_path)
input_data = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, [batch_size, None])
end_points = rnn_model(model='lstm', input_data=input_data, output_data=None, vocab_size=len(
vocabularies), rnn_size=128, num_layers=2, batch_size=64, learning_rate=FLAGS.learning_rate)
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables())
init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(), tf.local_variables_initializer())
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
checkpoint = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(FLAGS.checkpoints_dir)
saver.restore(sess, checkpoint)
x = np.array([list(map(word_int_map.get, start_token))])
[predict, last_state] = sess.run([end_points['prediction'], end_points['last_state']],
feed_dict={
input_data: x})
if begin_word:
word = begin_word
else:
word = to_word(predict, vocabularies)
poem = ''
while word != end_token:
poem += word
x = np.zeros((1, 1))
x[0, 0] = word_int_map[word]
[predict, last_state] = sess.run([end_points['prediction'], end_points['last_state']],
feed_dict={
input_data: x, end_points['initial_state']: last_state})
word = to_word(predict, vocabularies)
# word = words[np.argmax(probs_)]
return poem
#这里将生成的诗句,按照中文诗词的格式输出
#同时方便接入应用
def pretty_print_poem(poem):
poem_sentences = poem.split('。')
for s in poem_sentences:
if s != '' and len(s) > 10:
print(s + '。')
def main(is_train):
if is_train:
print('[INFO] train tang poem...')
run_training()
else:
print('[INFO] write tang poem...')
begin_word = input('开始作诗,请输入起始字:')
poem2 = gen_poem(begin_word)
pretty_print_poem(poem2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
tf.app.run()
在poems.py中有两部分:process_poems()和generate_batch(),其中process_poems()对数据进行了导入、排序等操作,generate_batch()将数据分块,为训练做准备:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import collections
import os
import sys
import numpy as np
start_token = 'G'
end_token = 'E'
def process_poems(file_name):
# 诗集
poems = []
with open(file_name, "r", encoding='utf-8', ) as f:
for line in f.readlines():
try:
title, content = line.strip().split(':')
content = content.replace(' ', '')
if '_' in content or '(' in content or '(' in content or '《' in content or '[' in content or \
start_token in content or end_token in content:
continue
if len(content) < 5 or len(content) > 79:
continue
content = start_token + content + end_token
poems.append(content)
except ValueError as e:
pass
# 按诗的字数排序
poems = sorted(poems, key=lambda l: len(line))
# 统计每个字出现次数
all_words = []
for poem in poems:
all_words += [word for word in poem]
# 这里根据包含了每个字对应的频率
counter = collections.Counter(all_words)
count_pairs = sorted(counter.items(), key=lambda x: -x[1])
words, _ = zip(*count_pairs)
# 取前多少个常用字
words = words[:len(words)] + (' ',)
# 每个字映射为一个数字ID
word_int_map = dict(zip(words, range(len(words))))
poems_vector = [list(map(lambda word: word_int_map.get(word, len(words)), poem)) for poem in poems]
return poems_vector, word_int_map, words
def generate_batch(batch_size, poems_vec, word_to_int):
# 每次取64首诗进行训练
n_chunk = len(poems_vec) // batch_size
x_batches = []
y_batches = []
for i in range(n_chunk):
start_index = i * batch_size
end_index = start_index + batch_size
batches = poems_vec[start_index:end_index]
# 找到这个batch的所有poem中最长的poem的长度
length = max(map(len, batches))
# 填充一个这么大小的空batch,空的地方放空格对应的index标号
x_data = np.full((batch_size, length), word_to_int[' '], np.int32)
for row in range(batch_size):
# 每一行就是一首诗,在原本的长度上把诗还原上去
x_data[row, :len(batches[row])] = batches[row]
y_data = np.copy(x_data)
# y的话就是x向左边也就是前面移动一个
y_data[:, :-1] = x_data[:, 1:]
""" x_data y_data [6,2,4,6,9] [2,4,6,9,9] [1,4,2,8,5] [4,2,8,5,5] """
x_batches.append(x_data)
y_batches.append(y_data)
return x_batches, y_batches
model.py进行了RNN模型的定义,代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
def rnn_model(model, input_data, output_data, vocab_size, rnn_size=128, num_layers=2, batch_size=64,
learning_rate=0.01):
""" construct rnn seq2seq model. :param model: model class 模型种类 :param input_data: input data placeholder 输入 :param output_data: output data placeholder 输出 :param vocab_size: 词长度 :param rnn_size: 一个RNN单元的大小 :param num_layers: RNN层数 :param batch_size: 步长 :param learning_rate: 学习速率 :return: """
end_points = {
}
def rnn_cell():
if model == 'rnn':
cell_fun = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicRNNCell
elif model == 'gru':
cell_fun = tf.contrib.rnn.GRUCell
elif model == 'lstm':
cell_fun = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell
cell = cell_fun(rnn_size, state_is_tuple=True)
return cell
cell = tf.contrib.rnn.MultiRNNCell([rnn_cell() for _ in range(num_layers)], state_is_tuple=True)
if output_data is not None:
initial_state = cell.zero_state(batch_size, tf.float32)
else:
initial_state = cell.zero_state(1, tf.float32)
with tf.device("/cpu:0"):
embedding = tf.get_variable('embedding', initializer=tf.random_uniform(
[vocab_size + 1, rnn_size], -1.0, 1.0))
inputs = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(embedding, input_data)
# [batch_size, ?, rnn_size] = [64, ?, 128]
outputs, last_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(cell, inputs, initial_state=initial_state)
output = tf.reshape(outputs, [-1, rnn_size])
weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([rnn_size, vocab_size + 1]))
bias = tf.Variable(tf.zeros(shape=[vocab_size + 1]))
logits = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(output, weights), bias=bias)
# [?, vocab_size+1]
if output_data is not None:
# output_data must be one-hot encode
labels = tf.one_hot(tf.reshape(output_data, [-1]), depth=vocab_size + 1)
# should be [?, vocab_size+1]
loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=labels, logits=logits)
# loss shape should be [?, vocab_size+1]
total_loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(total_loss)
end_points['initial_state'] = initial_state
end_points['output'] = output
end_points['train_op'] = train_op
end_points['total_loss'] = total_loss
end_points['loss'] = loss
end_points['last_state'] = last_state
else:
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(logits)
end_points['initial_state'] = initial_state
end_points['last_state'] = last_state
end_points['prediction'] = prediction
return end_points
最后cleancn.py实现了初期的数据处理工作:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
""" this script using for clean Chinese corpus. you can set level for clean, i.e.: level='all', will clean all character that not Chinese, include punctuations level='normal', this will generate corpus like normal use, reserve alphabets and numbers level='clean', this will remove all except Chinese and Chinese punctuations besides, if you want remove complex Chinese characters, just set this to be true: simple_only=True """
import numpy as np
import os
import string
cn_punctuation_set = [',', '。', '!', '?', '"', '"', '、']
en_punctuation_set = [',', '.', '?', '!', '"', '"']
def clean_cn_corpus(file_name, clean_level='all', simple_only=True, is_save=True):
""" clean Chinese corpus. :param file_name: :param clean_level: :param simple_only: :param is_save: :return: clean corpus in list type. """
if os.path.dirname(file_name):
base_dir = os.path.dirname(file_name)
else:
print('not set dir. please check')
save_file = os.path.join(base_dir, os.path.basename(file_name).split('.')[0] + '_cleaned.txt')
with open(file_name, 'r+',encoding='utf-8') as f:
clean_content = []
for l in f.readlines():
l = l.strip()
if l == '':
pass
else:
l = list(l)
should_remove_words = []
for w in l:
if not should_reserve(w, clean_level):
should_remove_words.append(w)
clean_line = [c for c in l if c not in should_remove_words]
clean_line = ''.join(clean_line)
if clean_line != '':
clean_content.append(clean_line)
if is_save:
with open(save_file, 'w+') as f:
for l in clean_content:
f.write(l + '\n')
print('[INFO] cleaned file have been saved to %s.' % save_file)
return clean_content
def should_reserve(w, clean_level):
if w == ' ':
return True
else:
if clean_level == 'all':
# only reserve Chinese characters
if w in cn_punctuation_set or w in string.punctuation or is_alphabet(w):
return False
else:
return is_chinese(w)
elif clean_level == 'normal':
# reserve Chinese characters, English alphabet, number
if is_chinese(w) or is_alphabet(w) or is_number(w):
return True
elif w in cn_punctuation_set or w in en_punctuation_set:
return True
else:
return False
elif clean_level == 'clean':
if is_chinese(w):
return True
elif w in cn_punctuation_set:
return True
else:
return False
else:
raise "clean_level not support %s, please set for all, normal, clean" % clean_level
def is_chinese(uchar):
"""is chinese"""
if u'\u4e00' <= uchar <= u'\u9fa5':
return True
else:
return False
def is_number(uchar):
"""is number"""
if u'\u0030' <= uchar <= u'\u0039':
return True
else:
return False
def is_alphabet(uchar):
"""is alphabet"""
if (u'\u0041' <= uchar <= u'\u005a') or (u'\u0061' <= uchar <= u'\u007a'):
return True
else:
return False
def semi_angle_to_sbc(uchar):
"""半角转全角"""
inside_code = ord(uchar)
if inside_code < 0x0020 or inside_code > 0x7e:
return uchar
if inside_code == 0x0020:
inside_code = 0x3000
else:
inside_code += 0xfee0
return chr(inside_code)
def sbc_to_semi_angle(uchar):
"""全角转半角"""
inside_code = ord(uchar)
if inside_code == 0x3000:
inside_code = 0x0020
else:
inside_code -= 0xfee0
if inside_code < 0x0020 or inside_code > 0x7e:
return uchar
return chr(inside_code)
##实现效果
我们在命令行中输入:
python main.py –train
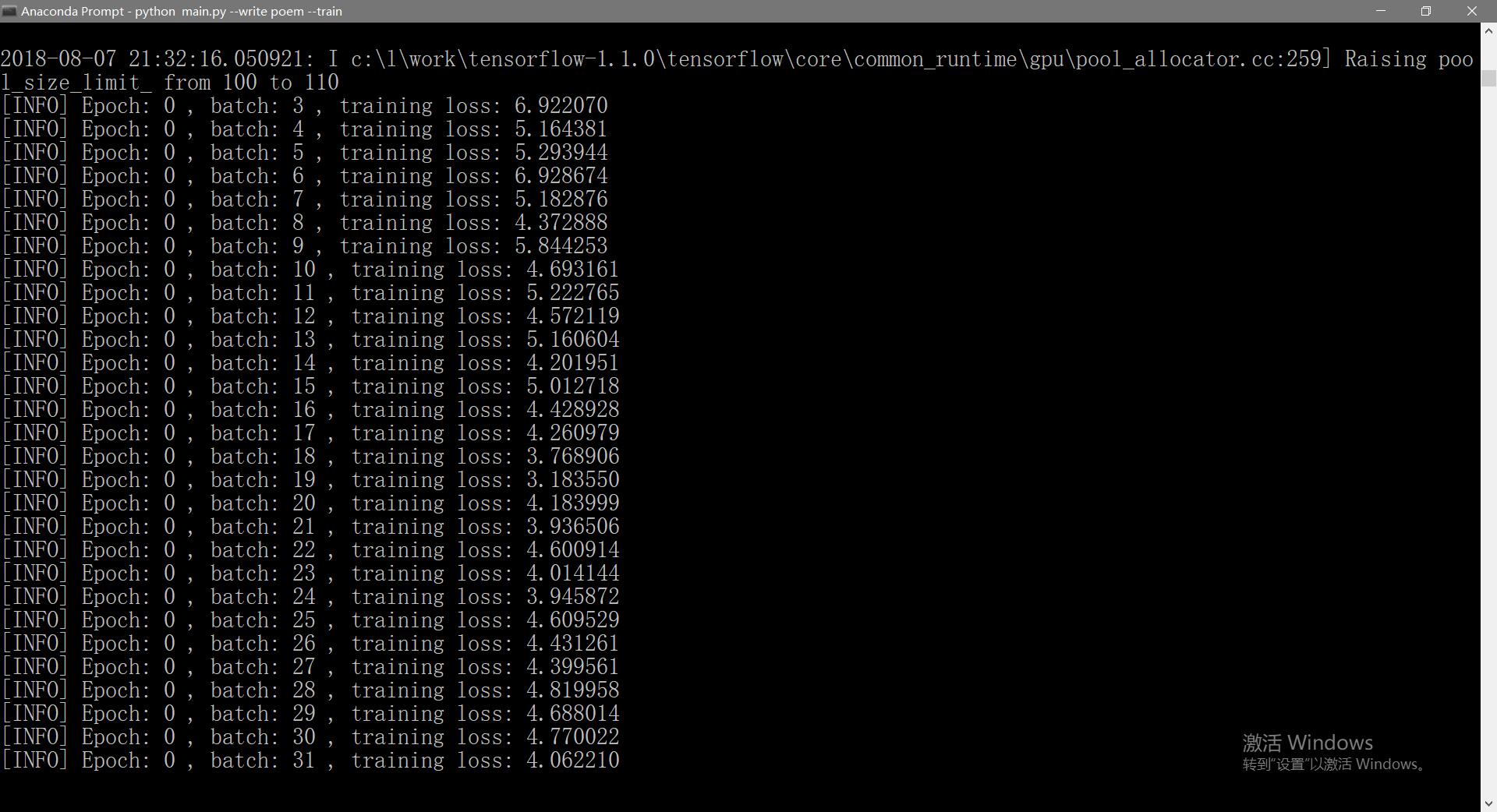
开始训练数据:
训练结束后,我们继续输入命令,让机器人开始作诗:
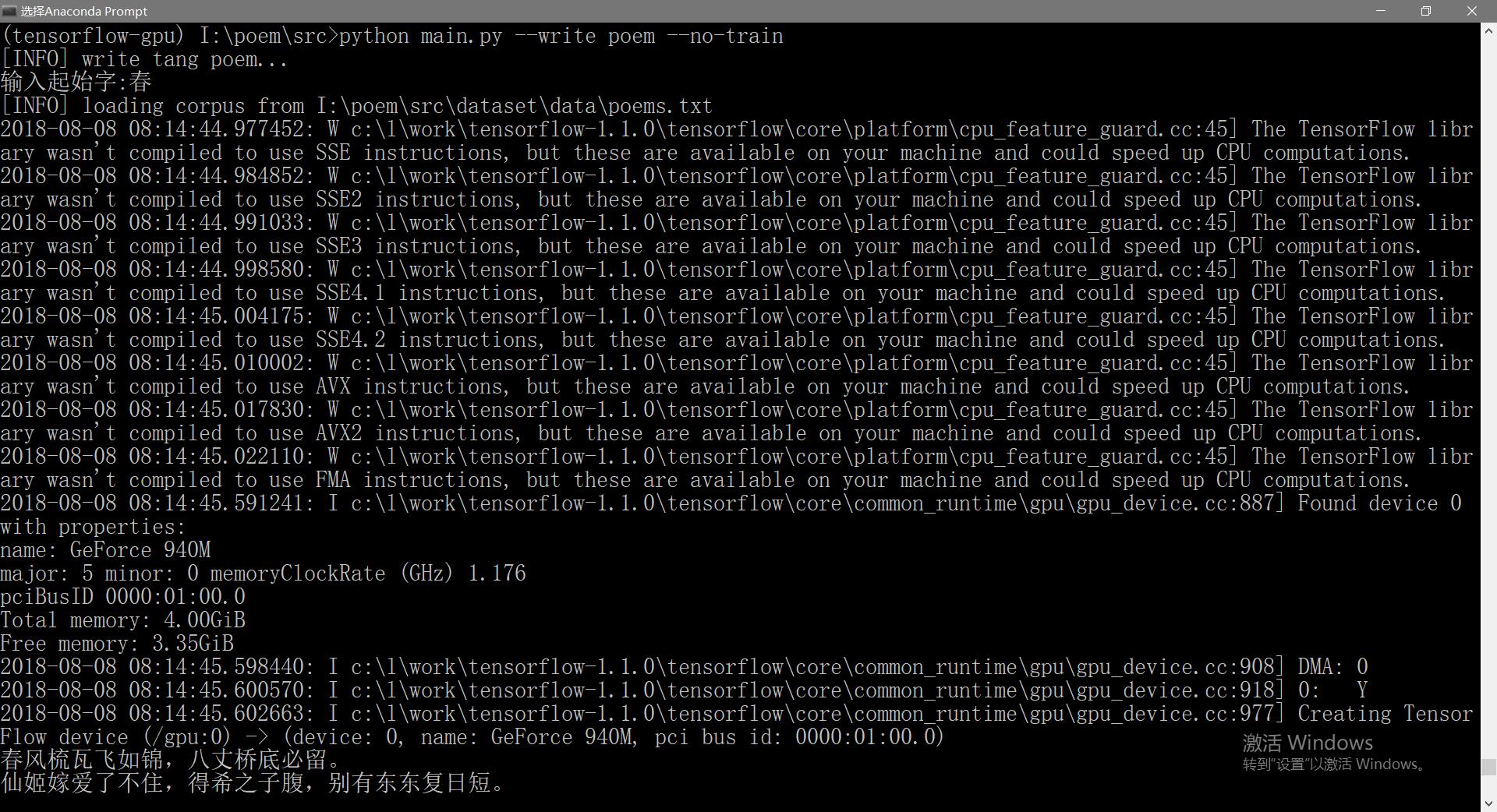
python main.py –no-train
假如我们让机器人作一首以“春”字开头的诗。
我们可以看到机器人为我们写好了一首诗:
##相关文章:
淘宝搜券小助手上线啦,喜欢网购的你赶快来试试吧~!淘宝搜券微信机器人正在开发中,尽情期待!点击链接进入→淘宝搜券小助手
今天的文章TensorFlow实现写诗机器人分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/6192.html