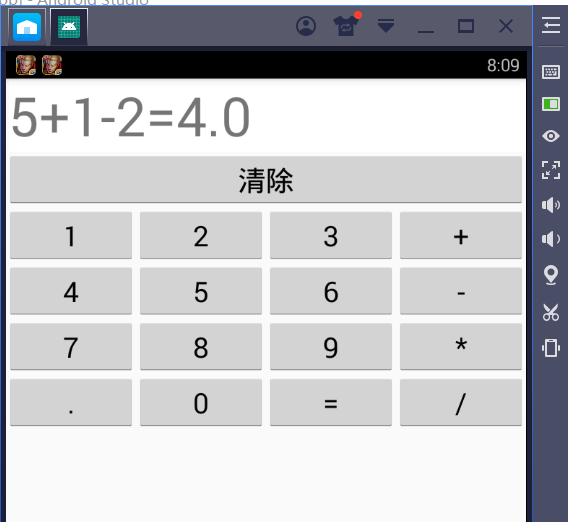
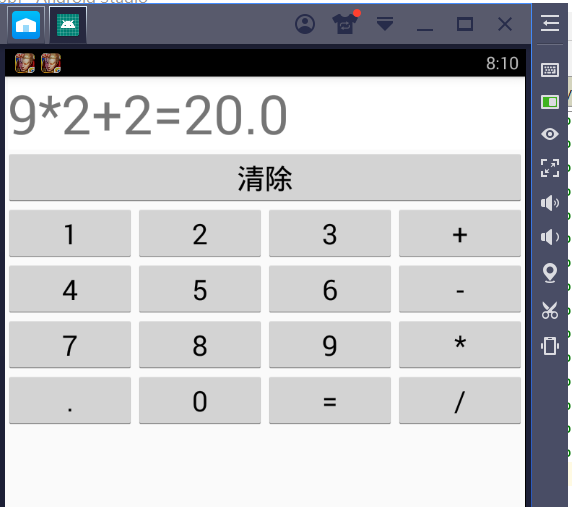
一、让我们先来看一下运行结果,方便我们清楚实验需求
二、源码分析(见注释)
2.1 布局文件(这里不用@string封装数据了,方便读者阅读)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:rowCount="6"
android:columnCount="4">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_columnSpan="4"
android:layout_gravity="left"
android:layout_marginLeft="4px"
android:text=""
android:textSize="50dip"
android:background="@android:drawable/screen_background_light"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_clear"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_columnSpan="4"
android:text="清除"
android:textSize="26sp"/>
<Button android:text="1" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_1"/>
<Button android:text="2" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_2"/>
<Button android:text="3" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_3"/>
<Button android:text="+" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_plus"/>
<Button android:text="4" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_4"/>
<Button android:text="5" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_5"/>
<Button android:text="6" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_6"/>
<Button android:text="-" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_minus"/>
<Button android:text="7" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_7"/>
<Button android:text="8" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_8"/>
<Button android:text="9" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_9"/>
<Button android:text="*" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_multipy"/>
<Button android:text="." android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_point"/>
<Button android:text="0" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_0"/>
<Button android:text="=" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_equal"/>
<Button android:text="/" android:textSize="26sp" android:id="@+id/btn_divide"/>
</GridLayout>2.2控制文件
package hp480.example.calculator;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
import android.util.Log;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
//声明变量
Button btn_plus,btn_minus,btn_multipy,btn_divide,btn_clear,btn_equal;
TextView tv;
int[] buttons;
Float result;
Float result0;
Float result1;
String str1;
String str2;
int flag = 0;
Button temp;
//构造函数
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); // 跳转到activity_main界面
initButton(); //初始化变量
// 监听“清空按钮”
btn_clear.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener(){
public void onClick(View v) {
str1 = "";
str2 = ""; // 清空记录
result=null;
tv.setText(str1);
flag = 0;
}
});
// 监听每一个“数字button”
for (int i = 0; i < buttons.length; i++) {
temp = (Button) findViewById(buttons[i]);
temp.setOnClickListener( // 为Button添加监听器
new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
str2 = ((Button) v).getText().toString();// 获得新输入的值
tv.setText(tv.getText().toString().trim()+str2);
str1=str1+ str2;
Log.d("myTag", "str1" + ":::" + str1);
}
});
}
// 为“计算符号”绑定事件,以标记
buttonListener(btn_plus, 1);
buttonListener(btn_minus, 2);
buttonListener(btn_multipy, 3);
buttonListener(btn_divide, 4);
// 为“等于号”添加事件,得出结果
btn_equal.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if(result==null){
String str = tv.getText().toString().trim();
String h[] =str.split("\\+|\\-|\\*|\\/");
result=Float.parseFloat(h[0]);
}
// Log.d("111:", String.valueOf(result));
// Log.d("222:", String.valueOf(str1));
if (flag == 1) {
result = result + Float.parseFloat(str1);
Log.d("result:", String.valueOf(result));
} else if (flag == 2) {
result = result - Float.parseFloat(str1);
Log.d("result:", String.valueOf(result));
} else if (flag == 3) {
result = result * Float.parseFloat(str1);
Log.d("result:", String.valueOf(result));
} else if (flag == 4) {
result = (Float) (result / Float.parseFloat(str1));
Log.d("result:", String.valueOf(result));
}
String str = (tv.getText().toString().trim()+String.valueOf(((Button) v).getText())+result).trim();
Log.d("myTag",str);
tv.setText(str);
}
});
}
// 初始化数字按钮
public void initButton() {
tv = (TextView) this.findViewById(R.id.tv); // 获取文本框控件对象
str1 = String.valueOf(tv.getText());
str2 = ""; // 初始化运算输入数值
btn_clear = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btn_clear); // 获得计算按钮的按钮对象
btn_plus = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btn_plus);
btn_minus = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btn_minus);
btn_multipy = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btn_multipy);
btn_divide = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btn_divide);
btn_equal = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.btn_equal);
buttons = new int[] { // 记录数值按钮的id
R.id.btn_0, R.id.btn_1, R.id.btn_2, R.id.btn_3,
R.id.btn_4, R.id.btn_5, R.id.btn_6, R.id.btn_7,
R.id.btn_8, R.id.btn_9 , R.id.btn_point};
}
// 监听计算符号的事件
public void buttonListener(Button button, final int id) {
button.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String str = tv.getText().toString().trim(); //拓展,改成获取每一个运算符前一个数字即可无限运算,还未实现
String h[] =str.split("\\+|\\-|\\*|\\/");
tv.setText(str+String.valueOf(((Button) v).getText()));
if(h.length==1){
flag=id;
}
if(h.length>1){
Log.d("最后一个数字--------",h[h.length-1]);
str=h[h.length-1];
if(h.length==2){
// result=Float.parseFloat(h[h.length-2]);
if (flag == 1) {
result = Float.parseFloat(h[h.length-2]) + Float.parseFloat(str);
Log.d("result:",String.valueOf(result));
} else if (flag == 2) {
result = Float.parseFloat(h[h.length-2]) - Float.parseFloat(str);
Log.d("result:",String.valueOf(result));
} else if (flag == 3) {
result = Float.parseFloat(h[h.length-2]) * Float.parseFloat(str);
Log.d("result:",String.valueOf(result));
} else if (flag == 4) {
result = Float.parseFloat(h[h.length-2]) / Float.parseFloat(str);
Log.d("result:",String.valueOf(result));
}
}else{// result1 = Float.parseFloat(str1);
if (flag == 1) {
Log.d("运算过程:",result + "+" + Float.parseFloat(str));
result = result + Float.parseFloat(str);
Log.d("result:", String.valueOf(result));
} else if (flag == 2) {
Log.d("运算过程:",result + "-" + Float.parseFloat(str));
result = result - Float.parseFloat(str);
Log.d("result:", String.valueOf(result));
} else if (flag == 3) {
Log.d("运算过程:",result + "*" + Float.parseFloat(str));
result = result * Float.parseFloat(str);
Log.d("result:", String.valueOf(result));
} else if (flag == 4) {
Log.d("运算过程:",result + "/" + Float.parseFloat(str));
result = (Float) (result / Float.parseFloat(str));
Log.d("result:", String.valueOf(result));
}
}
flag = id;
}
str1 = "";
str2 = "";
}
});
}
}三、总结与实验不足
1. 未实现运算符优先级判断,本次代码仅是从左到右的执行顺序
2.未作是否是数字的判断,比如输入2.2.2-2忍让不会报错。这个等有时间笔者再修复,最近比较忙。
今天的文章简单计算器–安卓实验一分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/63113.html