一、简介
Lz4压缩算法是由Yann Collet在2011年设计实现的,lz4属于lz77系列的压缩算法。lz77严格意义上来说不是一种算法,而是一种编码理论,它只定义了原理,并没有定义如何实现。基于lz77理论衍生的算法除lz4以外,还有lzss、lzb、lzh等。
lz4是目前基于综合来看效率最高的压缩算法,更加侧重于压缩解压缩速度,压缩比并不突出,本质上就是时间换空间。
对于github上给出的lz4性能介绍:每核压缩速度大于500MB/s,多核CPU可叠加;它所提供的解码器也是极其快速的,每核可达GB/s量级。
二、算法思想
lz77编码思想:它是一种基于字典的算法,它将长字符串(也可以称为匹配项或者短语)编码成短小的标记,用小标记代替字典中的短语,也就是说,它通过用小的标记来代替数据中多次重复出现的长字符串来达到数据压缩的目的。其处理的符号不一定是文本字符,也可以是其他任意大小的符号。
短语字典维护:lz77使用的是一个前向缓冲区和一个滑动窗口。它首先将数据载入到前向缓冲区,形成一批短语,再由滑动窗口滑动时,变成字典的一部分。
三、算法实现
作者没有看过lz4的源码,c语言看起来太费劲了😭,对压缩过程、解压过程是通过一些比较好博客进行了学习,并简单总结了一些。
有兴趣的同学可以看下:lz4 GitHub链接
1、lz4数据格式
lz4实现了两种格式,分别是lz4_block_format和lz4_frame_format。
lz4_frame_format用于特殊场景,如file压缩、pipe压缩和流式压缩;这里主要介绍lz4_block_format(一般场景使用格式)
压缩块有多个序列组成,一个序列是由一组字面量(非压缩字节),后跟一个匹配副本。每个序列以token开始,字面量和匹配副本的长度是有token以及offset决定的。
literals指没有重复、首次出现的字节流,即不可压缩的部分
literals length指不可压缩部分的长度
match length指重复项(可以压缩的部分)长度
下图为单个序列的数据格式,一个完整的lz4压缩块是由多个序列组成的。
2、lz4压缩过程
lz4遵循上面说到的lz77思想理论,通过滑动窗口、hash表、数据编码等操作实现数据压缩。压缩过程以至少4字节为扫描窗口查找匹配,每次移动1字节进行扫描,遇到重复的就进行压缩。
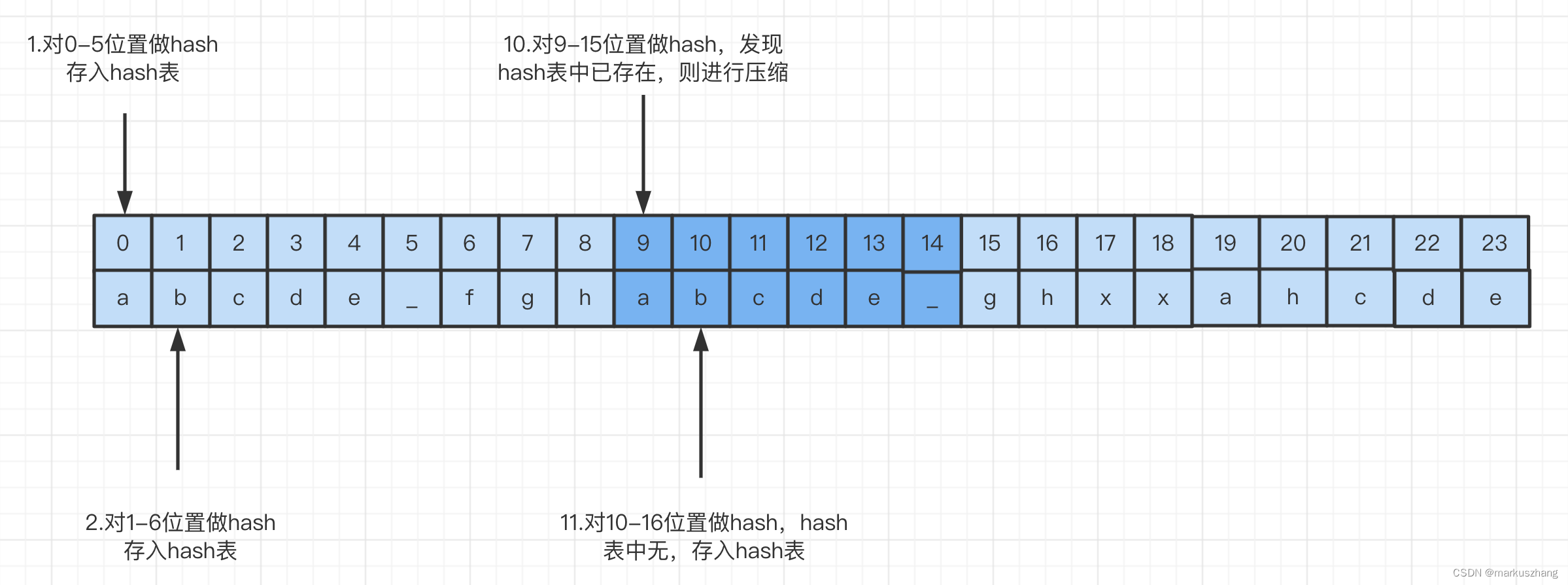
举个例子:给出一个字符串:
abcde_fghabcde_ghxxahcde,描述出此字符串的压缩过程ps:我们按照6字节扫描窗口,每次1字节来进行扫描
- 假设lz4的滑动窗口大小为6字节,扫描窗口为1字节;
- lz4开始扫描,首先对0-5位置做hash运算,hash表中无该值,所以存入hash表;
- 向后扫描,开始计算1-6位置hash值,hash表中依然无此值,所以继续将hash值存入hash表;
- 扫描过程依次类推,直到图中例子,在计算9-15位置的hash值时,发现hash表中已经存在,则进行压缩,偏移量offset值置为9,重复长度为6,该值存入token值的低4位中;
- 匹配压缩项后开始尝试扩大匹配,当窗口扫描到10-16时,发现并没有匹配到,则将此值存入hash表;如果发现hash表中有值,如果符合匹配条件(例如10-15符合1-6)则扩大匹配项,重复长度设为7,调整相应的token值
- 这样滑动窗口扫描完所有的字符串之后,结束操作
最终,这样压缩过程就结束了,得到这样一个字节串[-110, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 95, 102, 103, 104, 9, 0, -112, 103, 104, 120, 120, 97, 104, 99, 100, 101]。大家可能在看到这段内容可能有些懵逼,我在解压过程解释一下。
3、lz4解压过程
lz4压缩串: [-110, 97, 98, 99, 100, 101, 95, 102, 103, 104, 9, 0, -112, 103, 104, 120, 120, 97, 104, 99, 100, 101]
二进制是字符串经过utf-8编码后的值
下图是对上面压缩串的解释:
这里简单记录下解压的过程:
- 当lz4解压从0开始遍历时,先判断token值(-110),-110转换为计算机二进制为10010010,高四位1001代表字面量长度为9,低四位0010代表重复项匹配的长度2+4(minimum repeated bytes)
- 向后遍历9位,得到长度为9的字符串(abcde_fgh),偏移量为9,从当前位置向前移动9位则是重复位起始位置,低四位说明重复项长度为6字节,则继续生成长度为6的字符串(abcde_)
- 此时生成(abcde_fghabcde_),接着开始判断下一sequence token起始位,最终生成abcde_fghabcde_ghxxahcde(压缩前的字符串)
四、Lz4-Java
lz4/lz4-java是由Rei Odaira等人写的一套使用lz4压缩的Java类库。
1、简介
该类库提供了对两种压缩方法的访问,他们都能生成有效的lz4流:
- 快速扫描(lz4)
- 内存占用少(16KB)
- 非常快
- 合理的压缩比(取决于输入的冗余度)
- 高压缩(lz4hc)
- 内存占用中等(256KB)
- 相当慢(比lz4慢10倍)
- 良好的压缩比(取决于输入的大小和冗余度)
- 这两种压缩算法产生的流使用相同的压缩格式,解压缩速度非常快,可以由相同的解压缩实例解压缩
2、类库
该类库提供了几个关键类,这里简单介绍一下
LZ4Factory
Lz4 API的入口点,该类有3个实例
- 一个native实例,它是与原始LZ4 C实现的JNI绑定
- 一个safe Java实例,它是原始C库的纯Java端口(Java 官方编写的API)
- 一个unsafe Java实例,它是使用非官方sun.misc.Unsafe API的Java端口(Unsafe类可用来直接访问系统内存资源并进行自主管理,其在提升Java运行效率,增强Java语言底层操作能力方面起到很大的作用,Unsafe可认为是Java中留下的后门,提供了一些低层次操作,如直接内存访问、线程调度等)
只有safe Java实例才能保证在JVM上工作,因此建议使用fastestInstance()或fastestJavaInstance()来拉取LZ4Factory实例。
LZ4Compressor
压缩器有两种,一种是fastCompressor,也就是lz4简介中说的快速扫描压缩器;另一种是highCompressor,是实现高压缩率压缩器(lz4hc)。
LZ4Decompressor
lz4-java提供了两个解压器:LZ4FastDecompressor;LZ4SafeDecompressor
两者不同点在于:LZ4FastDecompressor在解压缩时是已知源字符串长度,而LZ4SafeDecompressor在解压缩时是已知压缩字段的长度
使用
上面说到的两个压缩器和两个解压缩器,在压缩和解压缩的时候,是可以互换的,比如说FastCompressor可以和LZ4SafeDecompressor搭配使用这样,因为两种压缩算法生成的流格式是一样的,无论用哪个解压缩器都能解压。
在说完上面基本的类之后,再来看下lz4-Java类库给我们提供流式传输类:LZ4BlockOutputStream(输出流-编码)、LZ4BlockInputStream(输入流-解码)
下面这段代码是使用示例:
package com.markus.compress.utils;
import net.jpountz.lz4.*;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/** * @author: markus * @date: 2022/5/22 4:54 下午 * @Description: Lz4压缩工具 * @Blog: http://markuszhang.com/ */
public class Lz4Utils {
private static final int ARRAY_SIZE = 4096;
private static LZ4Factory factory = LZ4Factory.fastestInstance();
private static LZ4Compressor compressor = factory.fastCompressor();
private static LZ4FastDecompressor decompressor = factory.fastDecompressor();
private static LZ4SafeDecompressor safeDecompressor = factory.safeDecompressor();
public static byte[] compress(byte[] bytes) {
if (bytes == null || bytes.length == 0) {
return null;
}
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
LZ4BlockOutputStream lz4BlockOutputStream = new LZ4BlockOutputStream(outputStream, ARRAY_SIZE, compressor);
lz4BlockOutputStream.write(bytes);
lz4BlockOutputStream.finish();
return outputStream.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Lz4压缩失败");
}
return null;
}
public static byte[] uncompress(byte[] bytes) {
if (bytes == null || bytes.length == 0) {
return null;
}
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(ARRAY_SIZE);
ByteArrayInputStream inputStream = new ByteArrayInputStream(bytes);
LZ4BlockInputStream decompressedInputStream = new LZ4BlockInputStream(inputStream, decompressor);
int count;
byte[] buffer = new byte[ARRAY_SIZE];
while ((count = decompressedInputStream.read(buffer)) != -1) {
outputStream.write(buffer, 0, count);
}
return outputStream.toByteArray();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("lz4解压缩失败");
}
return null;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte[] bytes = "abcde_fghabcde_ghxxahcde".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
byte[] compress = compress(bytes);
byte[] decompress = uncompress(compress);
}
}
3、性能对比
在了解完lz4的算法思想、实现思路以及Java类库后,我们可以使用它来和其他压缩类进行一个性能对比
测试源代码:(相关源码可以去我github仓库下载仓库链接)
package com.markus.compress.test;
import com.markus.compress.domain.User;
import com.markus.compress.service.UserService;
import com.markus.compress.utils.*;
import org.openjdk.jmh.annotations.*;
import org.openjdk.jmh.results.format.ResultFormatType;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.Runner;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.RunnerException;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.Options;
import org.openjdk.jmh.runner.options.OptionsBuilder;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/** * @author: markus * @date: 2022/5/22 5:08 下午 * @Description: 压缩工具的性能测试 * @Blog: http://markuszhang.com/ */
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.Throughput)
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)
public class PerformanceTest {
/** * 用来序列化的用户对象 */
@State(Scope.Benchmark)
public static class CommonState {
User user;
byte[] originBytes;
byte[] lz4CompressBytes;
byte[] snappyCompressBytes;
byte[] gzipCompressBytes;
byte[] bzipCompressBytes;
byte[] deflateCompressBytes;
@Setup(Level.Trial)
public void prepare() {
UserService userService = new UserService();
user = userService.get();
originBytes = ProtostuffUtils.serialize(user);
lz4CompressBytes = Lz4Utils.compress(originBytes);
snappyCompressBytes = SnappyUtils.compress(originBytes);
gzipCompressBytes = GzipUtils.compress(originBytes);
bzipCompressBytes = Bzip2Utils.compress(originBytes);
deflateCompressBytes = DeflateUtils.compress(originBytes);
}
}
/** * Lz4压缩 * * @param commonState * @return */
@Benchmark
public byte[] lz4Compress(CommonState commonState) {
return Lz4Utils.compress(commonState.originBytes);
}
/** * lz4解压缩 * * @param commonState */
@Benchmark
public byte[] lz4Uncompress(CommonState commonState) {
return Lz4Utils.uncompress(commonState.lz4CompressBytes);
}
/** * snappy压缩 * * @param commonState * @return */
@Benchmark
public byte[] snappyCompress(CommonState commonState) {
return SnappyUtils.compress(commonState.originBytes);
}
/** * snappy解压缩 * * @param commonState * @return */
@Benchmark
public byte[] snappyUncompress(CommonState commonState) {
return SnappyUtils.uncompress(commonState.snappyCompressBytes);
}
/** * Gzip压缩 * * @param commonState * @return */
@Benchmark
public byte[] gzipCompress(CommonState commonState) {
return GzipUtils.compress(commonState.originBytes);
}
/** * Gzip解压缩 * * @param commonState * @return */
@Benchmark
public byte[] gzipUncompress(CommonState commonState) {
return GzipUtils.uncompress(commonState.gzipCompressBytes);
}
/** * bzip2压缩 * * @param commonState * @return */
@Benchmark
public byte[] bzip2Compress(CommonState commonState) {
return Bzip2Utils.compress(commonState.originBytes);
}
/** * bzip2压缩 * * @param commonState * @return */
@Benchmark
public byte[] bzip2Uncompress(CommonState commonState) {
return Bzip2Utils.uncompress(commonState.bzipCompressBytes);
}
/** * bzip2压缩 * * @param commonState * @return */
@Benchmark
public byte[] deflateCompress(CommonState commonState) {
return DeflateUtils.compress(commonState.originBytes);
}
/** * bzip2压缩 * * @param commonState * @return */
@Benchmark
public byte[] deflateUncompress(CommonState commonState) {
return DeflateUtils.uncompress(commonState.deflateCompressBytes);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws RunnerException {
Options opt = new OptionsBuilder()
.include(PerformanceTest.class.getSimpleName())
.forks(1)
.threads(1)
.warmupIterations(10)
.measurementIterations(10)
.result("PerformanceTest.json")
.resultFormat(ResultFormatType.JSON).build();
new Runner(opt).run();
}
}
性能测试图:
附上lz4官网给出的性能测试图和自己测试的性能图,有些差异,有可能对于压缩数据的不同导致的差异。
官网给的:
自己测得:
在公司对于特征内容的压缩,观察lz4和snappy的对比,看上去lz4和snappy的压缩和解压缩的性能差不多,但lz4更稳定些,尖刺场景少。由于设计公司内部内容,就不粘图了。
4、压缩率对比
在压缩率上,按照从高到低是:bzip2 > Deflate > Gzip > lz4 > snappy
package com.markus.compress.demo;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.markus.compress.domain.User;
import com.markus.compress.service.UserService;
import com.markus.compress.utils.*;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/** * @author: markus * @date: 2022/5/22 3:52 下午 * @Description: 压缩字节示例 * @Blog: http://markuszhang.com/ */
public class CompressDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User user = new UserService().get();
// json序列化
byte[] origin_json = JSONObject.toJSONBytes(user);
System.out.println("原始json字节数: " + origin_json.length);
// pb序列化
byte[] origin = ProtostuffUtils.serialize(user);
System.out.println("原始pb字节数: " + origin.length);
testGzip(origin, user);
testSnappy(origin, user);
testLz4(origin, user);
testBzip2(origin, user);
testDeflate(origin, user);
}
private static void test(){
System.out.println("--------------------");
String str = getString();
byte[] source = str.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
byte[] compress = Lz4Utils.compress(source);
// 将compress转为字符串
System.out.println(translateString(compress));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--------------------");
String str2 = getString2();
byte[] source2 = str2.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
byte[] compress2 = Lz4Utils.compress(source2);
byte[] uncompress = Lz4Utils.uncompress(compress2);
System.out.println();
}
private static String translateString(byte[] bytes) {
char[] chars = new char[bytes.length];
for (int i = 0; i < chars.length; i++) {
chars[i] = (char) bytes[i];
}
String str = new String(chars);
return str;
}
private static String getString() {
return "fghabcde_bcdefgh_abcdefghxxxxxxx";
}
private static String getString2() {
return "abcde_fghabcde_ghxxahcde";
}
private static void testGzip(byte[] origin, User user) {
System.out.println("---------------GZIP压缩---------------");
// Gzip压缩
byte[] gzipCompress = GzipUtils.compress(origin);
System.out.println("Gzip压缩: " + gzipCompress.length);
byte[] gzipUncompress = GzipUtils.uncompress(gzipCompress);
System.out.println("Gzip解压缩: " + gzipUncompress.length);
User deUser = ProtostuffUtils.deserialize(gzipUncompress, User.class);
System.out.println("对象是否相等: " + user.equals(deUser));
}
private static void testSnappy(byte[] origin, User user) {
System.out.println("---------------Snappy压缩---------------");
// Snappy压缩
byte[] snappyCompress = SnappyUtils.compress(origin);
System.out.println("Snappy压缩: " + snappyCompress.length);
byte[] snappyUncompress = SnappyUtils.uncompress(snappyCompress);
System.out.println("Snappy解压缩: " + snappyUncompress.length);
User deUser = ProtostuffUtils.deserialize(snappyUncompress, User.class);
System.out.println("对象是否相等: " + user.equals(deUser));
}
private static void testLz4(byte[] origin, User user) {
System.out.println("---------------Lz4压缩---------------");
// Lz4压缩
byte[] Lz4Compress = Lz4Utils.compress(origin);
System.out.println("Lz4压缩: " + Lz4Compress.length);
byte[] Lz4Uncompress = Lz4Utils.uncompress(Lz4Compress);
System.out.println("Lz4解压缩: " + Lz4Uncompress.length);
User deUser = ProtostuffUtils.deserialize(Lz4Uncompress, User.class);
System.out.println("对象是否相等: " + user.equals(deUser));
}
private static void testBzip2(byte[] origin, User user) {
System.out.println("---------------bzip2压缩---------------");
// bzip2压缩
byte[] bzip2Compress = Bzip2Utils.compress(origin);
System.out.println("bzip2压缩: " + bzip2Compress.length);
byte[] bzip2Uncompress = Bzip2Utils.uncompress(bzip2Compress);
System.out.println("bzip2解压缩: " + bzip2Uncompress.length);
User deUser = ProtostuffUtils.deserialize(bzip2Uncompress, User.class);
System.out.println("对象是否相等: " + user.equals(deUser));
}
private static void testDeflate(byte[] origin, User user) {
System.out.println("---------------Deflate压缩---------------");
// Deflate压缩
byte[] deflateCompress = DeflateUtils.compress(origin);
System.out.println("Deflate压缩: " + deflateCompress.length);
byte[] deflateUncompress = DeflateUtils.uncompress(deflateCompress);
System.out.println("Deflate解压缩: " + deflateUncompress.length);
User deUser = ProtostuffUtils.deserialize(deflateUncompress, User.class);
System.out.println("对象是否相等: " + user.equals(deUser));
}
}
原始json字节数: 5351
原始pb字节数: 3850
---------------GZIP压缩---------------
Gzip压缩: 2170
Gzip解压缩: 3850
对象是否相等: true
---------------Snappy压缩---------------
Snappy压缩: 3396
Snappy解压缩: 3850
对象是否相等: true
---------------Lz4压缩---------------
Lz4压缩: 3358
Lz4解压缩: 3850
对象是否相等: true
---------------bzip2压缩---------------
bzip2压缩: 2119
bzip2解压缩: 3850
对象是否相等: true
---------------Deflate压缩---------------
Deflate压缩: 2167
Deflate解压缩: 3850
对象是否相等: true
Process finished with exit code 0
五、总结
通过上面几节的学习,对lz4有了大致的了解,它的压缩和解压缩效率是非常好的,压缩比相较于其他压缩工具来讲并不是很突出,其压缩比取决于压缩内容的重复率。
在压缩场景中,选择合适的压缩工具,各种压缩工具均有其利弊,扬其长、避其短,才能使得我们的工作更有效。
今天的文章Lz4压缩算法学习「建议收藏」分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/70653.html

![Lz4压缩算法学习「建议收藏」插图1 [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-rfxQ7I9q-1654424611351)()]](https://img.bianchenghao.cn/app/bianchenghao_cn/293047b78c0041ff906705181f185ca5.png)
![Lz4压缩算法学习「建议收藏」插图5 [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-pAz4HBqR-1654424611352)()]](https://img.bianchenghao.cn/app/bianchenghao_cn/bec7406dfe6a4649af10548f89efa788.png)
![Lz4压缩算法学习「建议收藏」插图7 [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EkH9HlDH-1654424611352)(http://cdn.markuszhang.com/img/image-20220605180709948.png)]](https://img.bianchenghao.cn/app/bianchenghao_cn/cdaa593bad354ac8b2eead03354b4c23.png)
![Lz4压缩算法学习「建议收藏」插图9 [外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-m4EQ9VB4-1654424611353)(http://cdn.markuszhang.com/img/image-20220605180406885.png)]](https://img.bianchenghao.cn/app/bianchenghao_cn/77797921eeab420a8951e80cb44bbd53.png)