一、简介
虽然单向链表能够100%解决逻辑关系为“一对一”数据的存储问题,但在解决那些需要大量查找前趋节点的问题是,单向链表无疑是不能用了,因为单向链表适合“从前往后”查找,并不适合“从后往前”查找。
如果要提高链表的查找效率,那双向链表(双链表)无疑是首选。
双向链表字面上的意思是“双向”的链表,如图1所示。
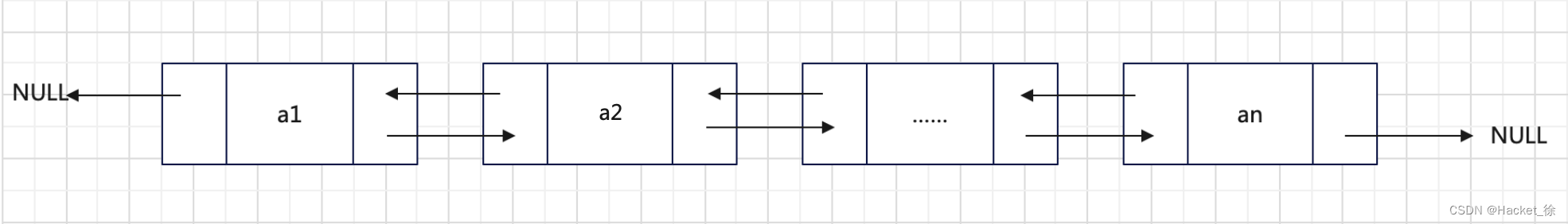
双向指各个节点之间的逻辑关系是双向的,该链表通常只有一个头节点。
从图1还可以看出,双向链表中每个节点包括一下3个部分,分别是指针域(用于指向当前节点的直接前驱节点)、数据域(用于存储数据元素)和指针域(用于指向当前节点的后继节点)。
二、创建
1、声明
typedef struct line{
struct line *prior;//指向直接前趋
int data;
struct line *next;//指向直接后继
}line;2、创建
line* initLine(line *head){
head=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));//创建链表第一个结点(首元结点)
head->prior=NULL;
head->next=NULL;
head->data=1;
line *list=head;
for(int i=2; i<=3; i++)
{
//创建并初始化一个新结点
line *body=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
body->prior=NULL;
body->next=NULL;
body->data=i;
list->next=body;//直接前趋结点的next指针指向新结点
body->prior=list;//新结点指向直接前趋结点
list=list->next;
}
return head;
}三、基本操作
1、添加节点
添加节点可以分为三种,分别是:添加至表头、添加至链表的中间位置和添加至链表尾。
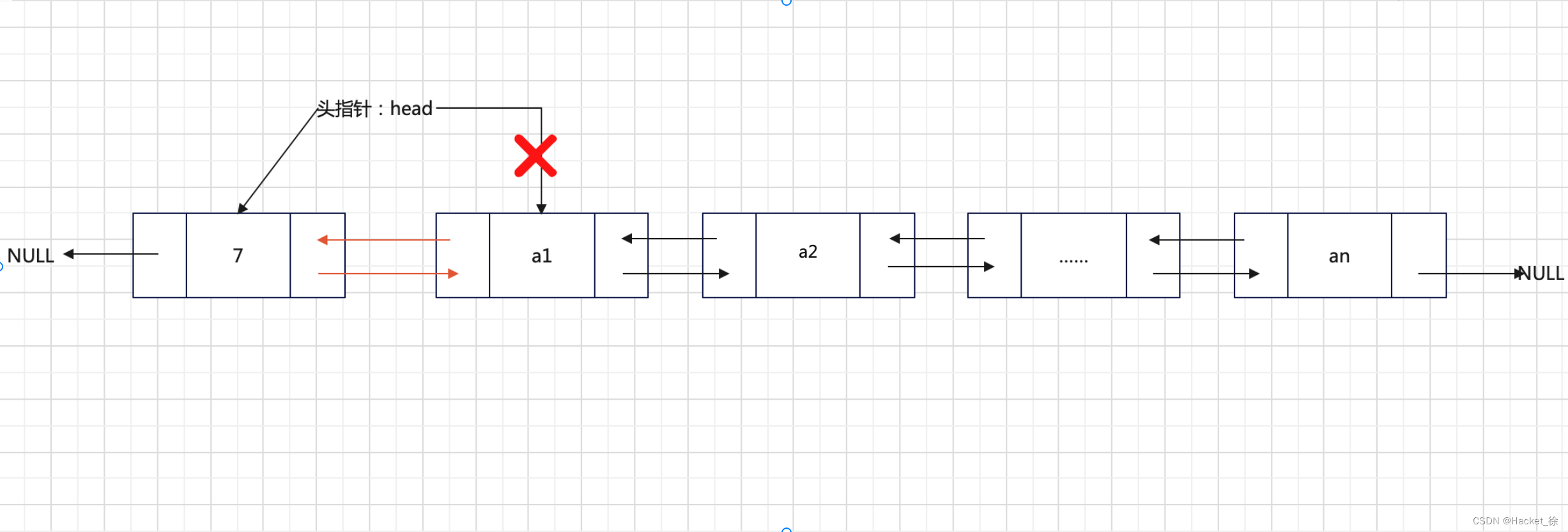
添加至表头
将新元素添加到表头,只需要将其与表头元素建立双层逻辑关系即可。
假设定义新元素节点为tmp,表头节点为head,则只需要执行下面两个步骤和即可:
- tmp的next变成head,head的prior编程tmp;
- 将head移至tmp,重新指向新的表头。
比如将元素7天添加到双向链表的表头,则实现过程如图2所示。
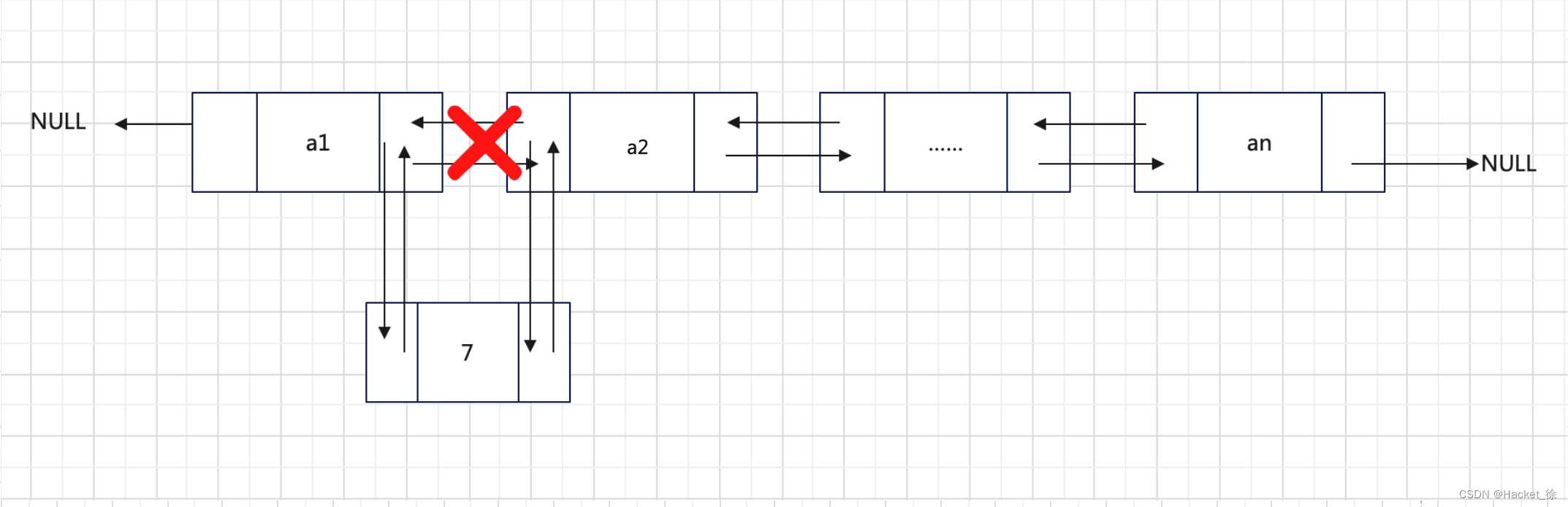
添加至链表的中间位置
添加至表的中间位置主要分为两个步骤:
- 新节点先与其后继节点建立双层逻辑关系;
- 新节点的前驱与之建立双层逻辑关系。
此过程如图3所示。
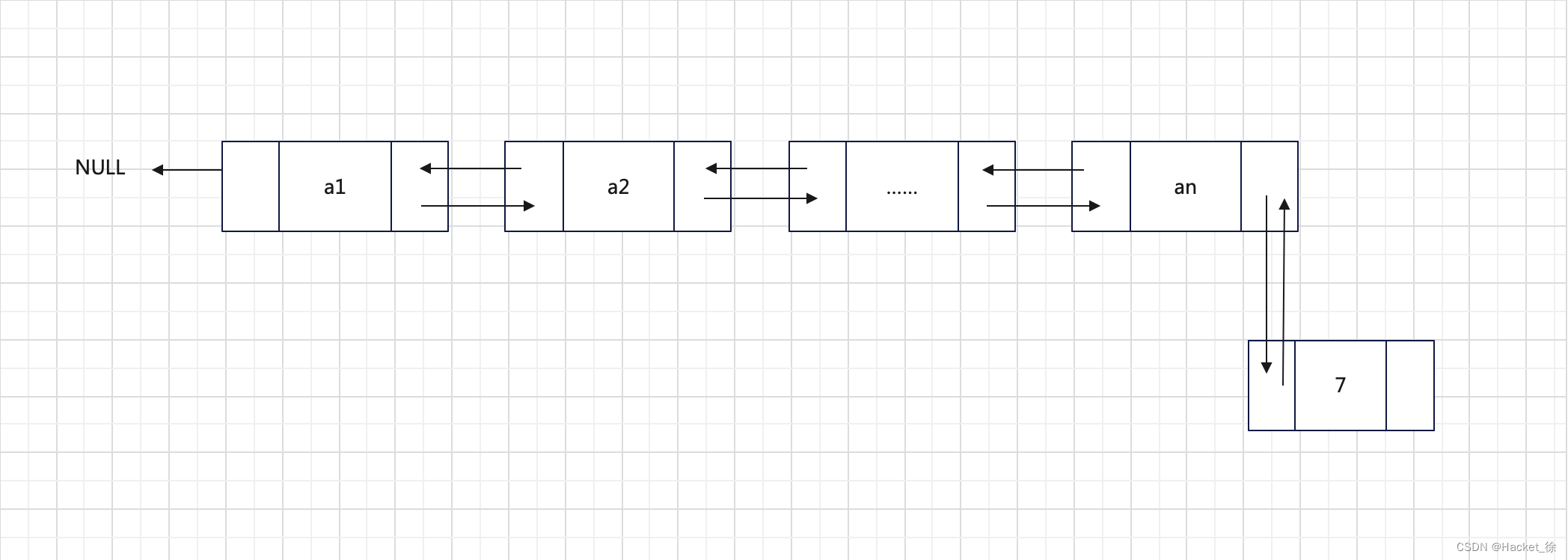
添加至表尾
与添加至表头很相似,其过程如下:
- 找到双向链表的最后一个节点;
- 让新节点与其进行双层逻辑关系建立。
此过程如图4所示。
代码
经过上述内容,我们可以试着编写代码了。
line *insertLine(line *head,int data,int add){
//新建数据域为data的结点
line *temp=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
temp->data=data;
temp->prior=NULL;
temp->next=NULL;
//插入到链表头,要特殊考虑
if(add==1)
{
temp->next=head;
head->prior=temp;
head=temp;
}
else
{
line *body=head;
//找到要插入位置的前一个结点
for(int i=1; i<add-1; i++)
{
body=body->next;
}
//判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾
if(body->next==NULL)
{
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}
else
{
body->next->prior=temp;
temp->next=body->next;
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}
}
return head;
}2、删除节点
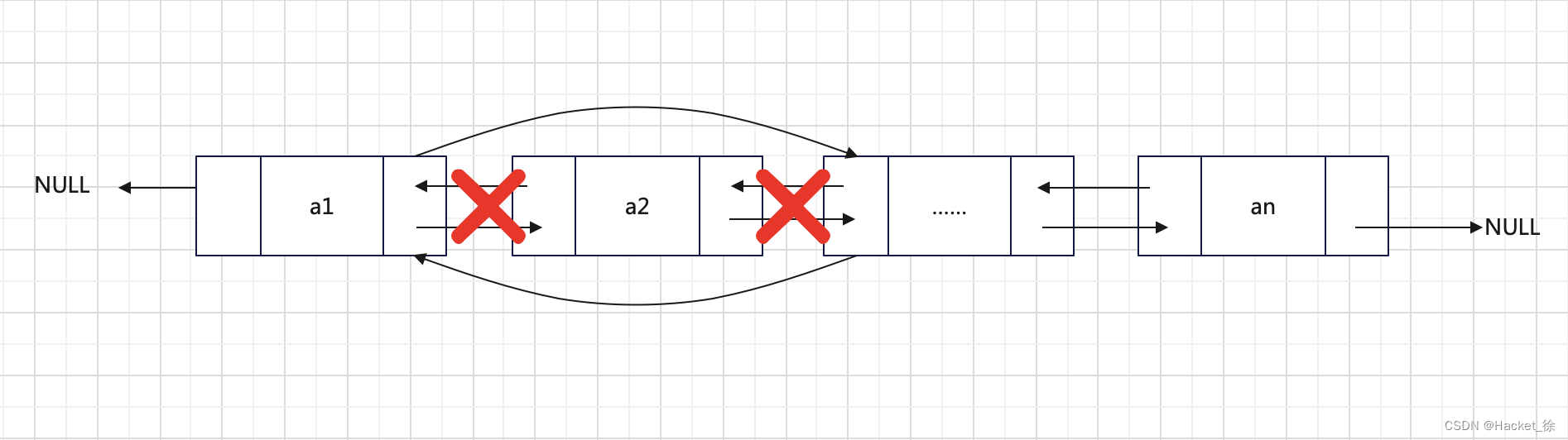
双向链表删除节点时,只需要遍历到要删除的节点,然后将其删除即可。
例如,从删除2的过程如图5所示。
代码
//删除结点的函数,data为要删除结点的数据域的值
line *delLine(line *head,int data)
{
line *temp=head;
//遍历链表
while(temp)
{
//判断当前结点中数据域和data是否相等,若相等,摘除该结点
if (temp->data==data)
{
temp->prior->next=temp->next;
temp->next->prior=temp->prior;
free(temp);
return head;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("链表中无该数据元素");
return head;
}3、查找节点
依次遍历表中数据,直到找到为止。
代码
//head为原双链表,elem表示被查找元素
int selectElem(line * head,int elem){
//新建一个指针t,初始化为头指针 head
line * t=head;
int i=1;
while(t)
{
if(t->data==elem)
{
return i;
}
i++;
t=t->next;
}
//程序执行至此处,表示查找失败
return -1;
}4、更改节点
在查找的基础上完成。过程是通过遍历找到的节点,直接将数据域修改即可。
代码
//更新函数,其中,add 表示更改结点在双链表中的位置,newElem 为新数据的值
line *amendElem(line *p,int add,int newElem){
line *temp=p;
//遍历到被删除结点
for (int i=1; i<add; i++)
{
temp=temp->next;
}
temp->data=newElem;
return p;
}四、完整代码
给出的所有代码的整合代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
typedef struct line{
struct line *prior;
int data;
struct line *next;
}line;
//双链表的创建
line* initLine(line * head);
//双链表插入元素,add表示插入位置
line * insertLine(line * head,int data,int add);
//双链表删除指定元素
line * delLine(line * head,int data);
//双链表中查找指定元素
int selectElem(line * head,int elem);
//双链表中更改指定位置节点中存储的数据,add表示更改位置
line *amendElem(line * p,int add,int newElem);
//输出双链表的实现函数
void display(line * head);
int main(){
line *head=NULL;
//创建双链表
head=initLine(head);
display(head);
//在表中第 3 的位置插入元素 7
head=insertLine(head,7,3);
display(head);
//表中删除元素 2
head=delLine(head,2);
display(head);
printf("元素 3 的位置是:%d\n",selectElem(head,3));
//表中第 3 个节点中的数据改为存储 6
head=amendElem(head,3,6);
display(head);
return 0;
}
line* initLine(line * head){
head=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
head->prior=NULL;
head->next=NULL;
head->data=1;
line *list=head;
for(int i=2; i<=5; i++)
{
line*body=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
body->prior=NULL;
body->next=NULL;
body->data=i;
list->next=body;
body->prior=list;
list=list->next;
}
return head;
}
line *insertLine(line *head,int data,int add){
//新建数据域为data的结点
line *temp=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
temp->data=data;
temp->prior=NULL;
temp->next=NULL;
//插入到链表头,要特殊考虑
if(add==1)
{
temp->next=head;
head->prior=temp;
head=temp;
}
else
{
line * body=head;
//找到要插入位置的前一个结点
for(int i=1; i<add-1; i++)
{
body=body->next;
}
//判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾
if(body->next==NULL)
{
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}
else
{
body->next->prior=temp;
temp->next=body->next;
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}
}
return head;
}
line *delLine(line *head,int data)
{
line *temp=head;
//遍历链表
while(temp)
{
//判断当前结点中数据域和data是否相等,若相等,摘除该结点
if(temp->data==data)
{
temp->prior->next=temp->next;
temp->next->prior=temp->prior;
free(temp);
return head;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("链表中无该数据元素");
return head;
}
//head为原双链表,elem表示被查找元素
int selectElem(line *head,int elem){
//新建一个指针t,初始化为头指针 head
line *t=head;
int i=1;
while(t)
{
if(t->data==elem)
{
return i;
}
i++;
t=t->next;
}
//程序执行至此处,表示查找失败
return -1;
}
//更新函数,其中,add 表示更改结点在双链表中的位置,newElem 为新数据的值
line *amendElem(line *p,int add,int newElem){
line * temp=p;
//遍历到被删除结点
for(int i=1; i<add; i++)
{
temp=temp->next;
}
temp->data=newElem;
return p;
}
//输出链表的功能函数
void display(line *head)
{
line *temp=head;
while(temp)
{
if(temp->next==NULL)
{
printf("%d\n",temp->data);
}
else
{
printf("%d->",temp->data);
}
temp=temp->next;
}
}参考文献:http://c.biancheng.net/view/3343.html
好啦,以上就是本文的全部内容啦!创作不易,点个赞再走呗~
今天的文章双向链表是线性结构吗_什么是双向链表分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/78739.html
