概述
最近一直研究Matrix框架,也找了很多相关博客,发现大多都是说了大致框架流程,细节不够深入,或者是基于较早的版本,所以决定对照最新的版本自己撸一篇。建议不太了解Matrix Trace Canary的同学先看一下官方文档,有助于本文理解。话不多说开始吧。
框架解析
Trace是基于ASM字节码插桩,在编译期对所有class文件中的函数字节码修改,在函数执行前后打点。
自定义MatrixTraceTransform
Transform可在class文件打包成dex文件之前对class字节码进行编辑。 插桩部分不是本文重点,网上也有很多相关文章,不做过度介绍。看一下关键代码
@Override
protected void onMethodEnter() {
TraceMethod traceMethod = collectedMethodMap.get(methodName);
if (traceMethod != null) {
traceMethodCount.incrementAndGet();
mv.visitLdcInsn(traceMethod.id);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, TraceBuildConstants.MATRIX_TRACE_CLASS, "i", "(I)V", false);
}
}
在需要插桩的函数执行前插入AppMethodBeat.i()方法
@Override
protected void onMethodExit(int opcode) {
TraceMethod traceMethod = collectedMethodMap.get(methodName);
if (traceMethod != null) {
if (hasWindowFocusMethod && isActivityOrSubClass && isNeedTrace) {
TraceMethod windowFocusChangeMethod = TraceMethod.create(-1, Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC, className,
TraceBuildConstants.MATRIX_TRACE_ON_WINDOW_FOCUS_METHOD, TraceBuildConstants.MATRIX_TRACE_ON_WINDOW_FOCUS_METHOD_ARGS);
if (windowFocusChangeMethod.equals(traceMethod)) {
traceWindowFocusChangeMethod(mv, className);
}
}
traceMethodCount.incrementAndGet();
mv.visitLdcInsn(traceMethod.id);
mv.visitMethodInsn(INVOKESTATIC, TraceBuildConstants.MATRIX_TRACE_CLASS, "o", "(I)V", false);
}
}
}
在需要插桩的函数执行后插入AppMethodBeat.o()方法
private void traceWindowFocusChangeMethod(MethodVisitor mv, String classname) {
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 0);
mv.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ILOAD, 1);
mv.visitMethodInsn(Opcodes.INVOKESTATIC, TraceBuildConstants.MATRIX_TRACE_CLASS, "at", "(Landroid/app/Activity;Z)V", false);
}
private void insertWindowFocusChangeMethod(ClassVisitor cv, String classname) {
MethodVisitor methodVisitor = cv.visitMethod(Opcodes.ACC_PUBLIC, TraceBuildConstants.MATRIX_TRACE_ON_WINDOW_FOCUS_METHOD,
TraceBuildConstants.MATRIX_TRACE_ON_WINDOW_FOCUS_METHOD_ARGS, null, null);
methodVisitor.visitCode();
methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ALOAD, 0);
methodVisitor.visitVarInsn(Opcodes.ILOAD, 1);
methodVisitor.visitMethodInsn(Opcodes.INVOKESPECIAL, TraceBuildConstants.MATRIX_TRACE_ACTIVITY_CLASS, TraceBuildConstants.MATRIX_TRACE_ON_WINDOW_FOCUS_METHOD,
TraceBuildConstants.MATRIX_TRACE_ON_WINDOW_FOCUS_METHOD_ARGS, false);
traceWindowFocusChangeMethod(methodVisitor, classname);
methodVisitor.visitInsn(Opcodes.RETURN);
methodVisitor.visitMaxs(2, 2);
methodVisitor.visitEnd();
}
在 Activity 的 onWindowFocusChanged函数中插入AppMethodBeat.at()方法
TracePlugin
TracePlugin 的start()方法是整个project的起始位置
@Override
public void start() {
super.start();
if (!isSupported()) {
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "[start] Plugin is unSupported!");
return;
}
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "start!");
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (!UIThreadMonitor.getMonitor().isInit()) {
try {
UIThreadMonitor.getMonitor().init(traceConfig);
} catch (java.lang.RuntimeException e) {
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "[start] RuntimeException:%s", e);
return;
}
}
AppMethodBeat.getInstance().onStart();
UIThreadMonitor.getMonitor().onStart();
anrTracer.onStartTrace();
frameTracer.onStartTrace();
evilMethodTracer.onStartTrace();
startupTracer.onStartTrace();
}
};
if (Thread.currentThread() == Looper.getMainLooper().getThread()) {
runnable.run();
} else {
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "start TracePlugin in Thread[%s] but not in mainThread!", Thread.currentThread().getId());
MatrixHandlerThread.getDefaultMainHandler().post(runnable);
}
}
AppMethodBeat
hook的函数的相关逻辑都在AppMethodBeat里面
AppMethodBeat.i()/AppMethodBeat.o()
之前插桩的函数运行开始时调用i(),结束调用o();
public static void i(int methodId) {
if (status <= STATUS_STOPPED) {
return;
}
if (methodId >= METHOD_ID_MAX) { //1
return;
}
if (status == STATUS_DEFAULT) {
synchronized (statusLock) {
if (status == STATUS_DEFAULT) {
realExecute();//2
status = STATUS_READY;
}
}
}
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
if (sMethodEnterListener != null) {
sMethodEnterListener.enter(methodId, threadId);
}
if (threadId == sMainThreadId) {
if (assertIn) {
android.util.Log.e(TAG, "ERROR!!! AppMethodBeat.i Recursive calls!!!");
return;
}
assertIn = true;
if (sIndex < Constants.BUFFER_SIZE) {
mergeData(methodId, sIndex, true);//3
} else {
sIndex = 0;
mergeData(methodId, sIndex, true);
}
++sIndex;
assertIn = false;
}
}
注释1处先对methodId做了校验,methodId有以下两种
- AppMethodBeat.i(AppMethodBeat.METHOD_ID_DISPATCH); 先买个坑,后面解释
- traceMethod.id = methodId.incrementAndGet(); 插桩过程中的AtomicInteger的自增
注释2处状态的判断,主要看执行的realExecute()方法
private static void realExecute() {
MatrixLog.i(TAG, "[realExecute] timestamp:%s", System.currentTimeMillis());
sCurrentDiffTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - sDiffTime;
sHandler.removeCallbacksAndMessages(null);
//2.1 sHandler.postDelayed(sUpdateDiffTimeRunnable, Constants.TIME_UPDATE_CYCLE_MS);
sHandler.postDelayed(checkStartExpiredRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (statusLock) {
MatrixLog.i(TAG, "[startExpired] timestamp:%s status:%s", System.currentTimeMillis(), status);
if (status == STATUS_DEFAULT || status == STATUS_READY) {
status = STATUS_EXPIRED_START;
}
}
}
}, Constants.DEFAULT_RELEASE_BUFFER_DELAY);
//2.2 ActivityThreadHacker.hackSysHandlerCallback();
LooperMonitor.register(looperMonitorListener);
}
private static Runnable sUpdateDiffTimeRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
while (!isPauseUpdateTime && status > STATUS_STOPPED) {
sCurrentDiffTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - sDiffTime;
SystemClock.sleep(Constants.TIME_UPDATE_CYCLE_MS);
}
synchronized (updateTimeLock) {
updateTimeLock.wait();
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "" + e.toString());
}
}
};
注释2.1处这里主要看sUpdateDiffTimeRunnable 这里通过开辟线程的方式每隔5ms更新sCurrentDiffTime的值,官方的解释是插桩函数每次获取时间加大性能开销,毕竟是在主线程,至于低于5ms的时间间隔可以忽略。直呼666啊 注释2.2处这里是跟Activity的启动相关的检测,先挖个坑,后面说 注释3处再说mergeData之前 先说一下 sBuffer,sIndex
private static long[] sBuffer = new long[Constants.BUFFER_SIZE];
private static int sIndex = 0;
函数的运行记录都被记录在sBuffer中,sIndexr就是sBuffe当前的索引记录
private static void mergeData(int methodId, int index, boolean isIn) {
if (methodId == AppMethodBeat.METHOD_ID_DISPATCH) {
sCurrentDiffTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - sDiffTime;
}
long trueId = 0L;
if (isIn) {
trueId |= 1L << 63;
}
trueId |= (long) methodId << 43;
trueId |= sCurrentDiffTime & 0x7FFFFFFFFFFL;
sBuffer[index] = trueId;
checkPileup(index);//3.1
sLastIndex = index;
}
private static void checkPileup(int index) {
IndexRecord indexRecord = sIndexRecordHead;
while (indexRecord != null) {
if (indexRecord.index == index || (indexRecord.index == -1 && sLastIndex == Constants.BUFFER_SIZE - 1)) {
indexRecord.isValid = false;
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "[checkPileup] %s", indexRecord.toString());
sIndexRecordHead = indexRecord = indexRecord.next;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
注释3.1主要是对于数据做了校验 IndexRecord是一个链表,这里为什么这么操作我也有疑问,条件满足的情况下先设置了头节点的isValid属性但是又删除了头节点。
AppMethodBeat.at()
AppMethodBeat.at() 也是个插桩函数,不过是监测Activity启动的,后面放在StartupTracer一起说
OK 到这里主要的数据格式大致有些了解了,下面开始结合代码流程
EvilMethodTracer
EvilMethodTracer先关注的api
@Override
public void onAlive() {
super.onAlive();
if (isEvilMethodTraceEnable) {
UIThreadMonitor.getMonitor().addObserver(this);
}
}
public void addObserver(LooperObserver observer) {
if (!isAlive) {
onStart();
}
synchronized (observers) {
observers.add(observer);
}
}
这里设置了监听,可以看出来实际上是设置了LooperObserver的监听,跟进看看EvilMethodTracer里的实现函数是什么时候回调,最终在LooperPrinter中找到dispatch(x.charAt(0) == ‘>’, x);方法
class LooperPrinter implements Printer {
public Printer origin;
boolean isHasChecked = false;
boolean isValid = false;
LooperPrinter(Printer printer) {
this.origin = printer;
}
@Override public void println(String x) {
if (null != origin) {
origin.println(x);
if (origin == this) {
throw new RuntimeException(TAG + " origin == this");
}
}
if (!isHasChecked) {
isValid = x.charAt(0) == '>' || x.charAt(0) == '<';
isHasChecked = true;
if (!isValid) {
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "[println] Printer is inValid! x:%s", x);
}
}
if (isValid) {
dispatch(x.charAt(0) == '>', x);//
}
}
}
在LooperMonitor初始化的时候调用了resetPrinter()
private synchronized void resetPrinter() {
Printer originPrinter = null;
try {
if (!isReflectLoggingError) {
originPrinter = ReflectUtils.get(looper.getClass(), "mLogging", looper);
if (originPrinter == printer && null != printer) {
return;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
isReflectLoggingError = true;
Log.e(TAG, "[resetPrinter] %s", e);
}
if (null != printer) {
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "maybe thread:%s printer[%s] was replace other[%s]!",
looper.getThread().getName(), printer, originPrinter);
}
looper.setMessageLogging(printer = new LooperPrinter(originPrinter));
if (null != originPrinter) {
MatrixLog.i(TAG, "reset printer, originPrinter[%s] in %s", originPrinter, looper.getThread().getName());
}
}
可以看到该方法通过反射获取Looper中的mLogging属性,下面看下Looper中的代码
for (;;) {
Message msg = queue.next(); // might block
final Printer logging = me.mLogging;
if (logging != null) {
logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +
msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);
}
...//省略了无关代码
if (logging != null) {
logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);
}
}
可以发现 Looper在处理message开始和结束时会打印相关日志,LooperMonitor正是基于这个实现了主线程处理message时是否出现了超时情况;
让我们再回到EvilMethodTracer和UIThreadMonitor中,当主线程的一个message开始dispatch时会调用它们的dispatchBegin(),dispatch结束后调用它们的dispatchEnd()
UIThreadMonitor中
private void dispatchBegin() {
token = dispatchTimeMs[0] = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
dispatchTimeMs[2] = SystemClock.currentThreadTimeMillis();
AppMethodBeat.i(AppMethodBeat.METHOD_ID_DISPATCH);//1
synchronized (observers) {
for (LooperObserver observer : observers) {
if (!observer.isDispatchBegin()) {
observer.dispatchBegin(dispatchTimeMs[0], dispatchTimeMs[2], token);
}
}
}
}
之前methodId埋的坑这里可以填了,这里主线程的message 的dispatch开始和结束方法用AppMethodBeat.METHOD_ID_DISPATCH来标记,同样添加到sBuffer数组中,dispatchEnd()方法类似,就不介绍了
@Override
public void dispatchBegin(long beginMs, long cpuBeginMs, long token) {
super.dispatchBegin(beginMs, cpuBeginMs, token);
indexRecord = AppMethodBeat.getInstance().maskIndex("EvilMethodTracer#dispatchBegin");
}
public IndexRecord maskIndex(String source) {
if (sIndexRecordHead == null) {//1
sIndexRecordHead = new IndexRecord(sIndex - 1);
sIndexRecordHead.source = source;
return sIndexRecordHead;
} else {
IndexRecord indexRecord = new IndexRecord(sIndex - 1);
indexRecord.source = source;
IndexRecord record = sIndexRecordHead;
IndexRecord last = null;
while (record != null) {
if (indexRecord.index <= record.index) {
if (null == last) {
IndexRecord tmp = sIndexRecordHead;
sIndexRecordHead = indexRecord;
indexRecord.next = tmp;
} else {
IndexRecord tmp = last.next;
if (null != last.next) {
last.next = indexRecord;
}
indexRecord.next = tmp;
}
return indexRecord;//2
}
last = record;
record = record.next;
}
last.next = indexRecord;
return indexRecord;//3
}
}
maskIndex方法用于生成一个IndexRecord节点,这里主要是对单链表增加节点的操作。 IndexRecord中的index属性的值根据当前sBuffer的索引sIndex决定的,也是相当于插桩方法在sBuffer的索引,这个是重点。
- 注释1处直接设置为头节点
- 注释2处,如果last==null 则在当前sIndexRecordHead之前插入,last!=null在sIndexRecordHead中间插入,具体位置根据节点的index大小来确定
- 注释3处 直接在尾节点新增 接着回到EvilMethodTracer中 刚刚介绍了dispatchBegin,接下来肯定要说dispatchEnd,和dispatchBegin一样是主线次
@Override
public void dispatchEnd(long beginMs, long cpuBeginMs, long endMs, long cpuEndMs, long token, boolean isBelongFrame) {
super.dispatchEnd(beginMs, cpuBeginMs, endMs, cpuEndMs, token, isBelongFrame);
long start = config.isDevEnv() ? System.currentTimeMillis() : 0;
try {
long dispatchCost = endMs - beginMs;
if (dispatchCost >= evilThresholdMs) {
long[] data = AppMethodBeat.getInstance().copyData(indexRecord);
long[] queueCosts = new long[3];
System.arraycopy(queueTypeCosts, 0, queueCosts, 0, 3);
String scene = AppMethodBeat.getVisibleScene();
MatrixHandlerThread.getDefaultHandler().post(new AnalyseTask(isForeground(), scene, data, queueCosts, cpuEndMs - cpuBeginMs, endMs - beginMs, endMs));
}
} finally {
indexRecord.release();
if (config.isDevEnv()) {
String usage = Utils.calculateCpuUsage(cpuEndMs - cpuBeginMs, endMs - beginMs);
MatrixLog.v(TAG, "[dispatchEnd] token:%s cost:%sms cpu:%sms usage:%s innerCost:%s",
token, endMs - beginMs, cpuEndMs - cpuBeginMs, usage, System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
}
}
}
当dispatchCost超过阀值即为出现耗时方法, long[] data = AppMethodBeat.getInstance().copyData(indexRecord);获取sBuffer中的耗时方法记录
public long[] copyData(IndexRecord startRecord) {
return copyData(startRecord, new IndexRecord(sIndex - 1));
}
private long[] copyData(IndexRecord startRecord, IndexRecord endRecord) {
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long[] data = new long[0];
try {
if (startRecord.isValid && endRecord.isValid) {
int length;
int start = Math.max(0, startRecord.index);
int end = Math.max(0, endRecord.index);
if (end > start) {
length = end - start + 1;
data = new long[length];
System.arraycopy(sBuffer, start, data, 0, length);
} else if (end < start) {
length = 1 + end + (sBuffer.length - start);
data = new long[length];
System.arraycopy(sBuffer, start, data, 0, sBuffer.length - start);
System.arraycopy(sBuffer, 0, data, sBuffer.length - start, end + 1);
}
return data;
}
return data;
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
MatrixLog.e(TAG, e.toString());
return data;
} finally {
MatrixLog.i(TAG, "[copyData] [%s:%s] length:%s cost:%sms", Math.max(0, startRecord.index), endRecord.index, data.length, System.currentTimeMillis() - current);
}
}
这里的startRecord就是之前在dispatchBegin中生成的IndexRecord节点,endRecord中index对应的是sBuffer中当前索引。这样就能截取一个message在dispatch过程中所有执行的函数。
因为默认sBuffer数组的长度是1000000,当达到最大值之后sIndex会被置为0,所以存在end< start 的情况,如下代码所示
if (sIndex < Constants.BUFFER_SIZE) {
mergeData(methodId, sIndex, true);
} else {
sIndex = 0;
mergeData(methodId, sIndex, true);
}
回到dispatchEnd()方法中
String scene = AppMethodBeat.getVisibleScene(); scene其实是当前所在activity
private void updateScene(Activity activity) {
visibleScene = activity.getClass().getName();
}
最后在AnalyseTask中处理和上报数据 先看analyse()中的
TraceDataUtils.structuredDataToStack(data, stack, true, endMs);
public static void structuredDataToStack(long[] buffer, LinkedList<MethodItem> result, boolean isStrict, long endTime) {
long lastInId = 0L;
int depth = 0;
LinkedList<Long> rawData = new LinkedList<>();
boolean isBegin = !isStrict;
for (long trueId : buffer) {// 1
if (0 == trueId) {
continue;
}
if (isStrict) {
if (isIn(trueId) && AppMethodBeat.METHOD_ID_DISPATCH == getMethodId(trueId)) {
isBegin = true;
}
if (!isBegin) {
MatrixLog.d(TAG, "never begin! pass this method[%s]", getMethodId(trueId));
continue;
}
}
if (isIn(trueId)) {
lastInId = getMethodId(trueId);
if (lastInId == AppMethodBeat.METHOD_ID_DISPATCH) {
depth = 0;
}
depth++;
rawData.push(trueId);
} else {
int outMethodId = getMethodId(trueId);
if (!rawData.isEmpty()) {
long in = rawData.pop();
depth--;
int inMethodId;
LinkedList<Long> tmp = new LinkedList<>();
tmp.add(in);
while ((inMethodId = getMethodId(in)) != outMethodId && !rawData.isEmpty()) {
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "pop inMethodId[%s] to continue match ouMethodId[%s]", inMethodId, outMethodId);
in = rawData.pop();
depth--;
tmp.add(in);
}
if (inMethodId != outMethodId && inMethodId == AppMethodBeat.METHOD_ID_DISPATCH) {
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "inMethodId[%s] != outMethodId[%s] throw this outMethodId!", inMethodId, outMethodId);
rawData.addAll(tmp);
depth += rawData.size();
continue;
}
long outTime = getTime(trueId);
long inTime = getTime(in);
long during = outTime - inTime;
if (during < 0) {
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "[structuredDataToStack] trace during invalid:%d", during);
rawData.clear();
result.clear();
return;
}
MethodItem methodItem = new MethodItem(outMethodId, (int) during, depth);
addMethodItem(result, methodItem);//2
} else {
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "[structuredDataToStack] method[%s] not found in! ", outMethodId);
}
}
}
while (!rawData.isEmpty() && isStrict) {//3
long trueId = rawData.pop();
int methodId = getMethodId(trueId);
boolean isIn = isIn(trueId);
long inTime = getTime(trueId) + AppMethodBeat.getDiffTime();
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "[structuredDataToStack] has never out method[%s], isIn:%s, inTime:%s, endTime:%s,rawData size:%s",
methodId, isIn, inTime, endTime, rawData.size());
if (!isIn) {
MatrixLog.e(TAG, "[structuredDataToStack] why has out Method[%s]? is wrong! ", methodId);
continue;
}
MethodItem methodItem = new MethodItem(methodId, (int) (endTime - inTime), rawData.size());
addMethodItem(result, methodItem);
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(null, null);
stackToTree(result, root);//4
result.clear();
treeToStack(root, result);//5
}
先看注释1的数组遍历 这里主要是将数组中记录的方法转变成带有层级的属性depth的MethodItem链表
例如
fun1(){//depth=0
fun2(){//depth=1
fun3(){ //depth=2
}
fun4(){// depth=2
}
}
}
MethodItemd的属性也比较简单 层级depth,耗时,方法id
public MethodItem(int methodId, int durTime, int depth) {
this.methodId = methodId;
this.durTime = durTime;
this.depth = depth;
}
注释2 将生成的methodItem添加到链表头结点,如果有下相同的methodId节点则更新该节点
private static int addMethodItem(LinkedList<MethodItem> resultStack, MethodItem item) {
if (AppMethodBeat.isDev) {
Log.v(TAG, "method:" + item);
}
MethodItem last = null;
if (!resultStack.isEmpty()) {
last = resultStack.peek();
}
if (null != last && last.methodId == item.methodId && last.depth == item.depth && 0 != item.depth) {
item.durTime = item.durTime == Constants.DEFAULT_ANR ? last.durTime : item.durTime;
last.mergeMore(item.durTime);
return last.durTime;
} else {
resultStack.push(item);
return item.durTime;
}
}
注释3处主要是对不正常的数据的校验操作,通常截取的sBuffer数据i o函数都是一一对应的。
注释4处是将链表数据转化成树结构,注意这指的不是二叉树,可以理解为省市区多级的树状数据格式
public static final class TreeNode {
MethodItem item;
TreeNode father;
LinkedList<TreeNode> children = new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode(MethodItem item, TreeNode father) {
this.item = item;
this.father = father;
}
private int depth() {
return null == item ? 0 : item.depth;
}
private void add(TreeNode node) {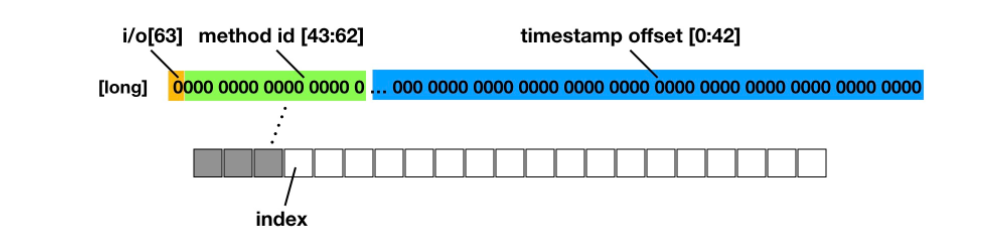
children.addFirst(node);
}
private boolean isLeaf() {
return children.isEmpty();
}
}
回到AnalyseTask的analyse()中
TraceDataUtils.trimStack(stack, Constants.TARGET_EVIL_METHOD_STACK, new TraceDataUtils.IStructuredDataFilter() {
@Override
public boolean isFilter(long during, int filterCount) {
return during < filterCount * Constants.TIME_UPDATE_CYCLE_MS;
}
@Override
public int getFilterMaxCount() {
return Constants.FILTER_STACK_MAX_COUNT;
}
@Override
public void fallback(List<MethodItem> stack, int size) {
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "[fallback] size:%s targetSize:%s stack:%s", size, Constants.TARGET_EVIL_METHOD_STACK, stack);
Iterator iterator = stack.listIterator(Math.min(size, Constants.TARGET_EVIL_METHOD_STACK));
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
iterator.next();
iterator.remove();
}
}
});
这里主要是对收集的数据进行过滤
public static void trimStack(List<MethodItem> stack, int targetCount, IStructuredDataFilter filter) {
if (0 > targetCount) {
stack.clear();
return;
}
int filterCount = 1;
int curStackSize = stack.size();
while (curStackSize > targetCount) {//1
ListIterator<MethodItem> iterator = stack.listIterator(stack.size());
while (iterator.hasPrevious()) {
MethodItem item = iterator.previous();
if (filter.isFilter(item.durTime, filterCount)) {//2
iterator.remove();
curStackSize--;
if (curStackSize <= targetCount) {
return;
}
}
}
curStackSize = stack.size();
filterCount++;
if (filter.getFilterMaxCount() < filterCount) {
break;
}
}
int size = stack.size();
if (size > targetCount) {
filter.fallback(stack, size);
}
}
注释1处设置了超过30个节点的阀值才会出发过滤 注释2处是对具体的耗时判断是否需要过滤;
继续回到 analyse()中
long stackCost = Math.max(cost, TraceDataUtils.stackToString(stack, reportBuilder, logcatBuilder));
这里获取最大耗时,逻辑比较简单
String stackKey = TraceDataUtils.getTreeKey(stack, stackCost);
这里是获取本次耗时方法检测数据上报时需要的一个key值,具体看下
public static String getTreeKey(List<MethodItem> stack, long stackCost) {
StringBuilder ss = new StringBuilder();
long allLimit = (long) (stackCost * Constants.FILTER_STACK_KEY_ALL_PERCENT);
LinkedList<MethodItem> sortList = new LinkedList<>();
for (MethodItem item : stack) {
if (item.durTime >= allLimit) {
sortList.add(item);
}
}
Collections.sort(sortList, new Comparator<MethodItem>() {
@Override
public int compare(MethodItem o1, MethodItem o2) {
return Integer.compare((o2.depth + 1) * o2.durTime, (o1.depth + 1) * o1.durTime);
}
});
if (sortList.isEmpty() && !stack.isEmpty()) {
MethodItem root = stack.get(0);
sortList.add(root);
} else if (sortList.size() > 1 && sortList.peek().methodId == AppMethodBeat.METHOD_ID_DISPATCH) {
sortList.removeFirst();
}
for (MethodItem item : sortList) {
ss.append(item.methodId + "|");
break;
}
return ss.toString();
}
逻辑并不复杂,先根据durTime过滤数据,再根据depth和durTime进行排序;这里为什么需要用到depth,应该是考虑到调用栈层级的原因,不能只考虑单个方法的耗时。
analyse中后面就是一些json数据的设置和上报。
至此EvilMethodTracer逻辑基本说完。
AnrTracer
弄清楚了EvilMethodTracer相关逻辑AnrTracer就很简单了,ANR的根本原因就是主线程耗时导致的程序无响应
@Override
public void dispatchBegin(long beginMs, long cpuBeginMs, long token) {
super.dispatchBegin(beginMs, cpuBeginMs, token);
anrTask = new AnrHandleTask(AppMethodBeat.getInstance().maskIndex("AnrTracer#dispatchBegin"), token);
if (traceConfig.isDevEnv()) {
MatrixLog.v(TAG, "* [dispatchBegin] token:%s index:%s", token, anrTask.beginRecord.index);
}
anrHandler.postDelayed(anrTask, Constants.DEFAULT_ANR - (SystemClock.uptimeMillis() - token));
}
@Override
public void dispatchEnd(long beginMs, long cpuBeginMs, long endMs, long cpuEndMs, long token, boolean isBelongFrame) {
super.dispatchEnd(beginMs, cpuBeginMs, endMs, cpuEndMs, token, isBelongFrame);
if (traceConfig.isDevEnv()) {
MatrixLog.v(TAG, "[dispatchEnd] token:%s cost:%sms cpu:%sms usage:%s",
token, endMs - beginMs, cpuEndMs - cpuBeginMs, Utils.calculateCpuUsage(cpuEndMs - cpuBeginMs, endMs - beginMs));
}
if (null != anrTask) {
anrTask.getBeginRecord().release();
anrHandler.removeCallbacks(anrTask);
}
}
- dispatchBegin中延时发送了一个消息
- dispatchEnd中取消这个延时消息,如果没能取消则说明发生了ANR
- 发生了ANR数据上报
StartupTracer
@Override
protected void onAlive() {
super.onAlive();
MatrixLog.i(TAG, "[onAlive] isStartupEnable:%s", isStartupEnable);
if (isStartupEnable) {
AppMethodBeat.getInstance().addListener(this);
Matrix.with().getApplication().registerActivityLifecycleCallbacks(this);
}
}
这里注册了两个监听
- IAppMethodBeatListener
- ActivityLifecycleCallbacks 全局Activity生命周期监听 主要看下IAppMethodBeatListener 发现他的onActivityFocused()方法是在AppMethodBeat中的at()中调用,at跟上文提到的i() o()方法一样 都是编译时期插入的,具体插入位置在Activity子类的onWindowFocusChange方法中
public static void at(Activity activity, boolean isFocus) {
String activityName = activity.getClass().getName();
if (isFocus) {
if (sFocusActivitySet.add(activityName)) {
synchronized (listeners) {
for (IAppMethodBeatListener listener : listeners) {
listener.onActivityFocused(activityName);
}
}
MatrixLog.i(TAG, "[at] visibleScene[%s] has %s focus!", getVisibleScene(), "attach");
}
} else {
if (sFocusActivitySet.remove(activityName)) {
MatrixLog.i(TAG, "[at] visibleScene[%s] has %s focus!", getVisibleScene(), "detach");
}
}
}
StartupTracer中的主要几个回调已经确定,下面具体看一下
@Override
public void onActivityFocused(String activity) {
if (isColdStartup()) {
if (firstScreenCost == 0) {
this.firstScreenCost = uptimeMillis() - ActivityThreadHacker.getEggBrokenTime();
}
if (hasShowSplashActivity) {
coldCost = uptimeMillis() - ActivityThreadHacker.getEggBrokenTime();
} else {
if (splashActivities.contains(activity)) {
hasShowSplashActivity = true;
} else if (splashActivities.isEmpty()) {
MatrixLog.i(TAG, "default splash activity[%s]", activity);
coldCost = firstScreenCost;
} else {
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "pass this activity[%s] at duration of start up! splashActivities=%s", activity, splashActivities);
}
}
if (coldCost > 0) {
analyse(ActivityThreadHacker.getApplicationCost(), firstScreenCost, coldCost, false);
}
} else if (isWarmStartUp()) {
isWarmStartUp = false;
long warmCost = uptimeMillis() - ActivityThreadHacker.getLastLaunchActivityTime();
if (warmCost > 0) {
analyse(ActivityThreadHacker.getApplicationCost(), firstScreenCost, warmCost, true);
}
}
}
这里逻辑不复杂 主要是一些变量的含义
- ActivityThreadHacker.getEggBrokenTime(); 第一次调用AppMethodBeat.i()的时间,看作是程序启动的时间
- ActivityThreadHacker.getLastLaunchActivityTime();这里通过反射ActivityThread中的mH Handler来监听msg.what == LAUNCH_ACTIVITY的消息。 接下来的analyse()方法是数据分析和上报逻辑跟之前的EvilMethodTracer类似
private void analyse(long applicationCost, long firstScreenCost, long allCost, boolean isWarmStartUp) {
MatrixLog.i(TAG, "[report] applicationCost:%s firstScreenCost:%s allCost:%s isWarmStartUp:%s", applicationCost, firstScreenCost, allCost, isWarmStartUp);
long[] data = new long[0];
if (!isWarmStartUp && allCost >= coldStartupThresholdMs) { // for cold startup
data = AppMethodBeat.getInstance().copyData(ActivityThreadHacker.sApplicationCreateBeginMethodIndex);
ActivityThreadHacker.sApplicationCreateBeginMethodIndex.release();
} else if (isWarmStartUp && allCost >= warmStartupThresholdMs) {
data = AppMethodBeat.getInstance().copyData(ActivityThreadHacker.sLastLaunchActivityMethodIndex);
ActivityThreadHacker.sLastLaunchActivityMethodIndex.release();
}
MatrixHandlerThread.getDefaultHandler().post(new AnalyseTask(data, applicationCost, firstScreenCost, allCost, isWarmStartUp, ActivityThreadHacker.sApplicationCreateScene));
}
FrameTracer
FrameTracer模块主要FPSCollector和FrameDecorator, 主要原理是通过Choreographer获取VSync垂直同步相关回调。
choreographer = Choreographer.getInstance();
callbackQueueLock = reflectObject(choreographer, "mLock");
callbackQueues = reflectObject(choreographer, "mCallbackQueues");
addInputQueue = reflectChoreographerMethod(callbackQueues[CALLBACK_INPUT], ADD_CALLBACK, long.class, Object.class, Object.class);
addAnimationQueue = reflectChoreographerMethod(callbackQueues[CALLBACK_ANIMATION], ADD_CALLBACK, long.class, Object.class, Object.class);
addTraversalQueue = reflectChoreographerMethod(callbackQueues[CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL], ADD_CALLBACK, long.class, Object.class, Object.class);
frameIntervalNanos = reflectObject(choreographer, "mFrameIntervalNanos");
通过反射获取Choreographer相关实例
private synchronized void addFrameCallback(int type, Runnable callback, boolean isAddHeader) {
if (callbackExist[type]) {
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "[addFrameCallback] this type %s callback has exist! isAddHeader:%s", type, isAddHeader);
return;
}
if (!isAlive && type == CALLBACK_INPUT) {
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "[addFrameCallback] UIThreadMonitor is not alive!");
return;
}
try {
synchronized (callbackQueueLock) {
Method method = null;
switch (type) {
case CALLBACK_INPUT:
method = addInputQueue;
break;
case CALLBACK_ANIMATION:
method = addAnimationQueue;
break;
case CALLBACK_TRAVERSAL:
method = addTraversalQueue;
break;
}
if (null != method) {//1
method.invoke(callbackQueues[type], !isAddHeader ? SystemClock.uptimeMillis() : -1, callback, null);
callbackExist[type] = true;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
MatrixLog.e(TAG, e.toString());
}
}
注释1:向Choreographer中的mCallbackQueues中添加数据,执行结果会在callback中返回并设置耗时数据
public void addCallbackLocked(long dueTime, Object action, Object token) {
CallbackRecord callback = obtainCallbackLocked(dueTime, action, token);
CallbackRecord entry = mHead;
if (entry == null) {
mHead = callback;
return;
}
if (dueTime < entry.dueTime) {
callback.next = entry;
mHead = callback;
return;
}
while (entry.next != null) {
if (dueTime < entry.next.dueTime) {
callback.next = entry.next;
break;
}
entry = entry.next;
}
entry.next = callback;
}
private void doQueueBegin(int type) {
queueStatus[type] = DO_QUEUE_BEGIN;
queueCost[type] = System.nanoTime();
}
private void doQueueEnd(int type) {
queueStatus[type] = DO_QUEUE_END;
queueCost[type] = System.nanoTime() - queueCost[type];
synchronized (this) {
callbackExist[type] = false;
}
}
这是回调设置数据的地方,但是queueCost并没有用到。emmm 其实Choreographer一顿操作,FrameTracer并没有用到,仍然用的是主线程message分发的逻辑,跟EvilMethodTracer相同的逻辑
FrameTracer中的核心代码如下
private void notifyListener(final String visibleScene, final long taskCostMs, final long frameCostMs, final boolean isContainsFrame) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
synchronized (listeners) {
for (final IDoFrameListener listener : listeners) {
if (config.isDevEnv()) {
listener.time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
}
final int dropFrame = (int) (taskCostMs / frameIntervalMs);
listener.doFrameSync(visibleScene, taskCostMs, frameCostMs, dropFrame, isContainsFrame);
if (null != listener.getExecutor()) {
listener.getExecutor().execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
listener.doFrameAsync(visibleScene, taskCostMs, frameCostMs, dropFrame, isContainsFrame);//1
}
});
}
}
}
} finally {
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis() - start;
if (config.isDebug() && cost > frameIntervalMs) {
MatrixLog.w(TAG, "[notifyListener] warm! maybe do heavy work in doFrameSync! size:%s cost:%sms", listeners.size(), cost);
}
}
}
注释1在FPSCollector和FrameDecorator有各自的具体实现
FPSCollector中处理的掉帧数据的处理与上报
void collect(int droppedFrames, boolean isContainsFrame) {
long frameIntervalCost = UIThreadMonitor.getMonitor().getFrameIntervalNanos();
sumFrameCost += (droppedFrames + 1) * frameIntervalCost / Constants.TIME_MILLIS_TO_NANO;
sumDroppedFrames += droppedFrames;
sumFrame++;
if (!isContainsFrame) {
sumTaskFrame++;
}
if (droppedFrames >= frozenThreshold) {
dropLevel[DropStatus.DROPPED_FROZEN.index]++;
dropSum[DropStatus.DROPPED_FROZEN.index] += droppedFrames;
} else if (droppedFrames >= highThreshold) {
dropLevel[DropStatus.DROPPED_HIGH.index]++;
dropSum[DropStatus.DROPPED_HIGH.index] += droppedFrames;
} else if (droppedFrames >= middleThreshold) {
dropLevel[DropStatus.DROPPED_MIDDLE.index]++;
dropSum[DropStatus.DROPPED_MIDDLE.index] += droppedFrames;
} else if (droppedFrames >= normalThreshold) {
dropLevel[DropStatus.DROPPED_NORMAL.index]++;
dropSum[DropStatus.DROPPED_NORMAL.index] += droppedFrames;
} else {
dropLevel[DropStatus.DROPPED_BEST.index]++;
dropSum[DropStatus.DROPPED_BEST.index] += (droppedFrames < 0 ? 0 : droppedFrames);
}
}
- 收集掉帧的数主要是通过主线成一个dispatch的时间计算得到的
- 对于掉帧数设置了5个等级
FrameDecorator中主要是根据帧率绘制了一个view,实时展示,更加直观。这部分逻辑比较简单,不做过多介绍。
@Override
public void doFrameAsync(String visibleScene, long taskCost, long frameCostMs, int droppedFrames, boolean isContainsFrame) {
super.doFrameAsync(visibleScene, taskCost, frameCostMs, droppedFrames, isContainsFrame);
sumFrameCost += (droppedFrames + 1) * UIThreadMonitor.getMonitor().getFrameIntervalNanos() / Constants.TIME_MILLIS_TO_NANO;
sumFrames += 1;
long duration = sumFrameCost - lastCost[0];
long collectFrame = sumFrames - lastFrames[0];
if (duration >= 200) {
final float fps = Math.min(60.f, 1000.f * collectFrame / duration);
updateView(view.fpsView, fps);
view.chartView.addFps((int) fps);
lastCost[0] = sumFrameCost;
lastFrames[0] = sumFrames;
mainHandler.removeCallbacks(updateDefaultRunnable);
mainHandler.postDelayed(updateDefaultRunnable, 130);
}
}
private void updateView(final TextView view, final float fps) {
mainHandler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
view.setText(String.format("%.2f FPS", fps));
if (fps >= 50) {
view.setTextColor(view.getResources().getColor(android.R.color.holo_green_dark));
} else if (fps >= 30) {
view.setTextColor(view.getResources().getColor(android.R.color.holo_orange_dark));
} else {
view.setTextColor(view.getResources().getColor(android.R.color.holo_red_dark));
}
}
});
}
总结
matrix Trace—Canary的框架介绍完了,框架结构还是比较清晰,并不复杂,主要是数据处理模块比较繁琐,但这也是trace相对于其他框架的优势之一,能够完整的记录耗时的函数调用栈情况。
今天的文章APM框架Matrix解析-Trace Canary分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/20073.html

