因为要做这个知识图谱,对这方面完全是小白
D3js和这个Neo4j是啥咱也不清楚,学呗!
1前置知识
1.1D3.jshttps://www.d3js.org.cn/
据说,不同版本之间的坑很多(怎么办,我也很绝望)
D3js 是一个可以基于数据来操作文档的 JavaScript 库。可以帮助你使用 HTML, CSS, SVG 以及 Canvas 来展示数据。D3 遵循现有的 Web 标准,可以不需要其他任何框架独立运行在现代浏览器中,它结合强大的可视化组件来驱动 DOM 操作。
最新发行版或者插入如下代码来在线使用:
1.1.1力图
https://observablehq.com/@d3/force-directed-graph
miserable.json存放一些测试数据文件
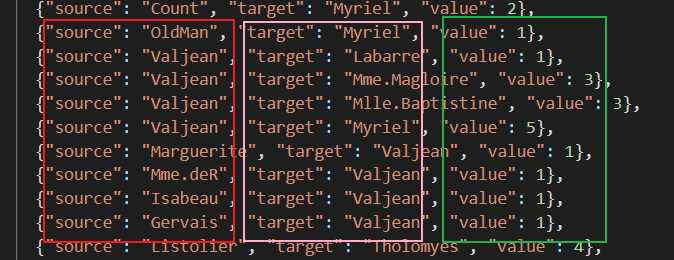
1.1.2分析一下这些数据
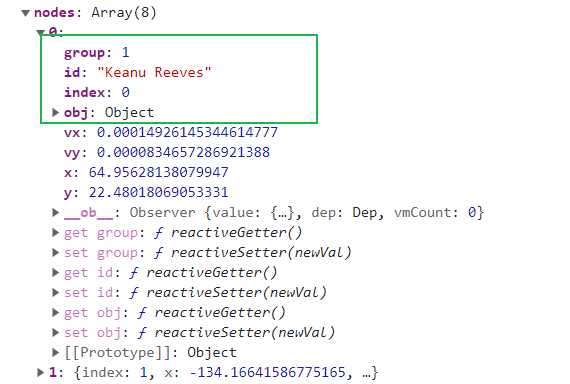
node(节点)节点的对象里有两个属性,一个是id,一个是group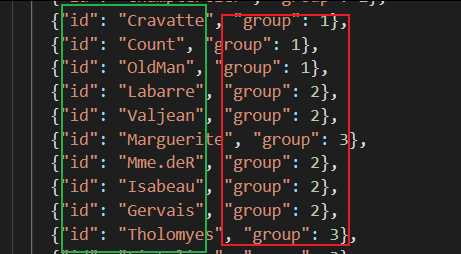
1.1.3项目中安装d3
应该要全局安装吧,我现在也整不明白,就这吧
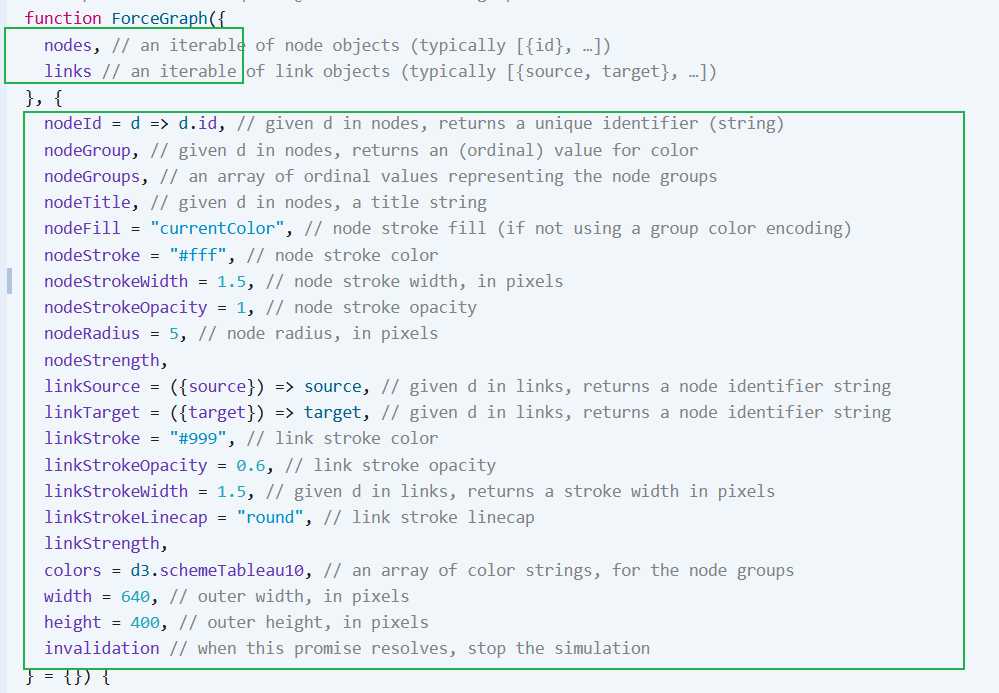
1.1.4认识初始化函数
可以看出,官网给的则个函数有两个参数,其中第一个参数是这个提供的数据,第二个参数(为啥可以这样写呢?是指定默认值吗)
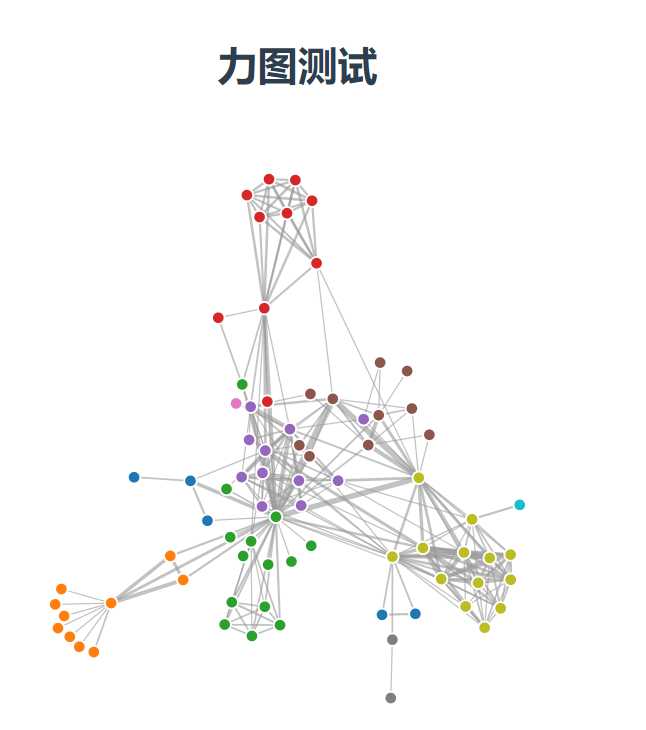
1.1.5效果
代码
<template>
<div class="hello">
<h1>力图测试</h1>
<div class="container">
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import * as d3 from 'd3'
export default {
name: 'HelloWorld',
props: {
},
data() {
return {
testGraph : {
"nodes": [
{
"id": "Myriel", "group": 1},
。。。。。此处省略
],
"links": [
{
"source": "Napoleon", "target": "Myriel", "value": 1},
。。。。。此处省略
]
}
}
},
mounted() {
this.initGraph(this.testGraph,{
nodeId: d => d.id,
nodeGroup: d => d.group,
nodeTitle: d => `${
d.id}\n${
d.group}`,
linkStrokeWidth: l => Math.sqrt(l.value),
width :640,
height: 600,
// invalidation // a promise to stop the simulation when the cell is re-run
})
},
methods: {
initGraph({
nodes, // an iterable of node objects (typically [{id}, …])
links // an iterable of link objects (typically [{source, target}, …])
}, {
nodeId = d => d.id, // given d in nodes, returns a unique identifier (string)
nodeGroup, // given d in nodes, returns an (ordinal) value for color
nodeGroups, // an array of ordinal values representing the node groups
nodeTitle, // given d in nodes, a title string
nodeFill = "currentColor", // node stroke fill (if not using a group color encoding)
nodeStroke = "#fff", // node stroke color
nodeStrokeWidth = 1.5, // node stroke width, in pixels
nodeStrokeOpacity = 1, // node stroke opacity
nodeRadius = 5, // node radius, in pixels
nodeStrength,
linkSource = ({
source}) => source, // given d in links, returns a node identifier string
linkTarget = ({
target}) => target, // given d in links, returns a node identifier string
linkStroke = "#999", // link stroke color
linkStrokeOpacity = 0.6, // link stroke opacity
linkStrokeWidth = 1.5, // given d in links, returns a stroke width in pixels
linkStrokeLinecap = "round", // link stroke linecap
linkStrength,
// colors = d3.schemeTableau10, // an array of color strings, for the node groups
colors = d3.schemeCategory10,// -十个分类颜色的数组,表示为 RGB 十六进制字符串。
width = 640, // outer width, in pixels
height = 400, // outer height, in pixels
//invalidation(失效)
// invalidation // when this promise resolves, stop the simulation
} = {
}) {
// Compute values.
const N = d3.map(nodes, nodeId).map(intern);//生成一个map对象
const LS = d3.map(links, linkSource).map(intern);
const LT = d3.map(links, linkTarget).map(intern);
if (nodeTitle === undefined) nodeTitle = (_, i) => N[i];
const T = nodeTitle == null ? null : d3.map(nodes, nodeTitle);
const G = nodeGroup == null ? null : d3.map(nodes, nodeGroup).map(intern);
const W = typeof linkStrokeWidth !== "function" ? null : d3.map(links, linkStrokeWidth);
const L = typeof linkStroke !== "function" ? null : d3.map(links, linkStroke);
// Replace the input nodes and links with mutable(可变的) objects for the simulation.
nodes = d3.map(nodes, (_, i) => ({
id: N[i]}));
links = d3.map(links, (_, i) => ({
source: LS[i], target: LT[i]}));
// Compute default domains.
if (G && nodeGroups === undefined) nodeGroups = d3.sort(G);
// Construct the scales(规模,等级,尺寸).序数比例尺,将一组命名类别映射到一组颜色
const color = nodeGroup == null ? null : d3.scaleOrdinal(nodeGroups, colors);
// Construct the forces.
const forceNode = d3.forceManyBody();
const forceLink = d3.forceLink(links).id(({
index: i}) => N[i]);
if (nodeStrength !== undefined) forceNode.strength(nodeStrength);
if (linkStrength !== undefined) forceLink.strength(linkStrength);
const simulation = d3.forceSimulation(nodes)
.force("link", forceLink)
.force("charge", forceNode)
.force("center", d3.forceCenter())
.on("tick", ticked);
// const svg = d3.create("svg")
// .attr("width", width)
// .attr("height", height)
// .attr("viewBox", [-width / 2, -height / 2, width, height])
// .attr("style", "max-width: 100%; height: auto; height: intrinsic;");
//重写,node和link的容器
const svg = d3.select(".container")
.append("svg")
.attr("width", width)
.attr("height", height)
.attr("viewBox", [-width / 2, -height / 2, width, height])
.attr("style", "max-width: 100%; height: auto; height: intrinsic;");
const link = svg.append("g")
.attr("stroke", typeof linkStroke !== "function" ? linkStroke : null)
.attr("stroke-opacity", linkStrokeOpacity)
.attr("stroke-width", typeof linkStrokeWidth !== "function" ? linkStrokeWidth : null)
.attr("stroke-linecap", linkStrokeLinecap)
.selectAll("line")
.data(links)
.join("line");
const node = svg.append("g")
.attr("fill", nodeFill)
.attr("stroke", nodeStroke)
.attr("stroke-opacity", nodeStrokeOpacity)
.attr("stroke-width", nodeStrokeWidth)
.selectAll("circle")
.data(nodes)
.join("circle")
.attr("r", nodeRadius)
// .call(drag(simulation)
.call(drag(simulation));
if (W) link.attr("stroke-width", ({
index: i}) => W[i]);
if (L) link.attr("stroke", ({
index: i}) => L[i]);
if (G) node.attr("fill", ({
index: i}) => color(G[i]));
if (T) node.append("title").text(({
index: i}) => T[i]);//鼠标悬浮时,节点显示的信息
// node.append('title').text(d => d.id);
// if (invalidation != null) invalidation.then(() => simulation.stop());
//intern(实习生,扣留)
//传给迭代器函数map的函数,用来筛选值
function intern(value) {
return value !== null && typeof value === "object" ? value.valueOf() : value;
}
//tick 给……打勾
function ticked() {
link
.attr("x1", d => d.source.x)
.attr("y1", d => d.source.y)
.attr("x2", d => d.target.x)
.attr("y2", d => d.target.y);
node
.attr("cx", d => d.x)
.attr("cy", d => d.y);
}
function drag(simulation) {
//拖动开始
function dragstarted(event) {
if (!event.active) simulation.alphaTarget(0.3).restart();
event.subject.fx = event.subject.x;
event.subject.fy = event.subject.y;
}
//拖动
function dragged(event) {
event.subject.fx = event.x;
event.subject.fy = event.y;
}
//拖动结束
function dragended(event) {
if (!event.active) simulation.alphaTarget(0);
event.subject.fx = null;
event.subject.fy = null;
}
//绑定返回
return d3.drag()
.on("start", dragstarted)
.on("drag", dragged)
.on("end", dragended);
}
//Object.assign()合并两个对象
return Object.assign(svg.node(), {
scales: {
color}});
}
},
}
</script>
<!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only -->
<style scoped>
</style>
1.2Neo4j
-
Install Neo4j
oh,no, 删了重新下吧
-
Open Neo4j Browser
Start Up the Neo4j Browser Visit: http://localhost:7474/
Default login is username ‘neo4j’ and password ‘neo4j’ (full installation instructions below)
然后可以重设用户名密码
-
Explore Sample Datasets
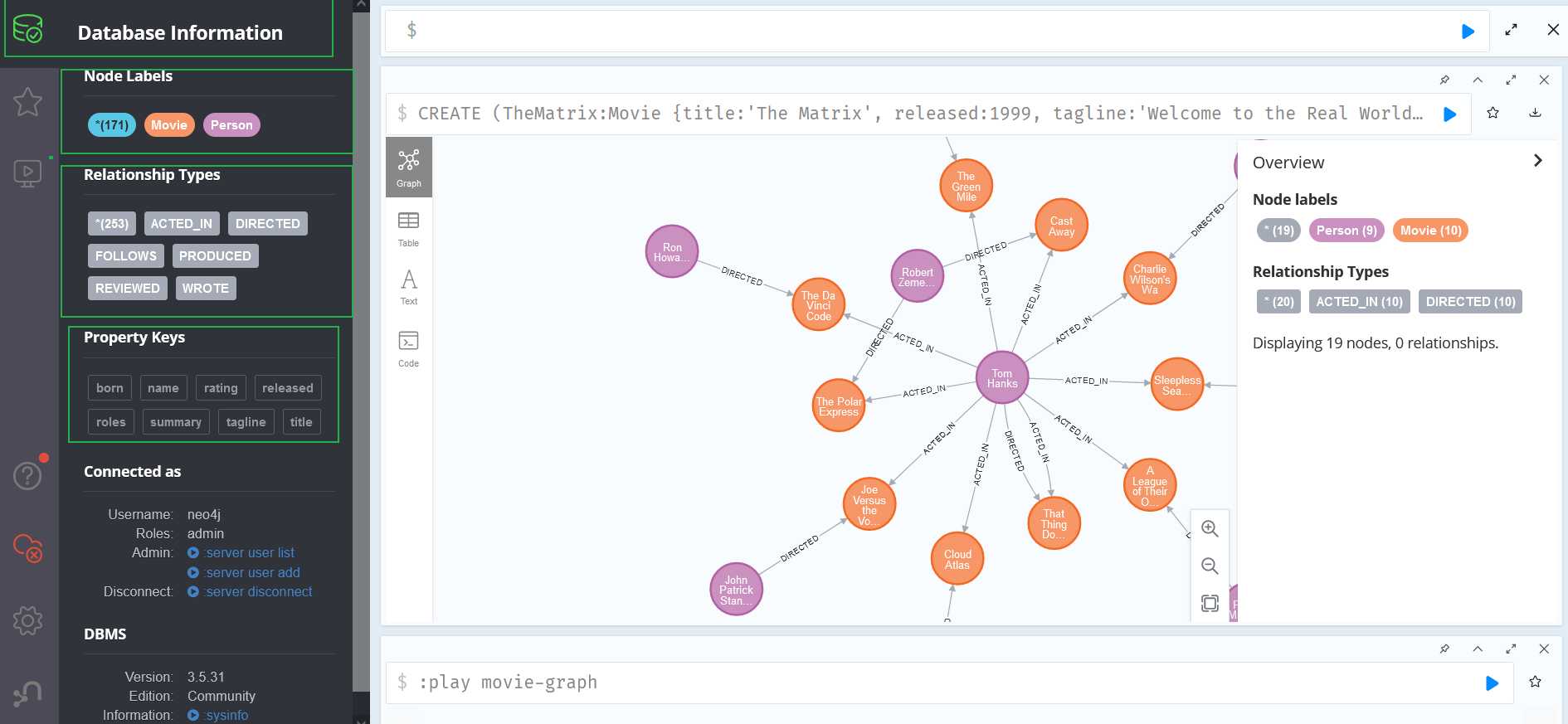
点击第二页的Create就可以看到如下效果
SpringBoot连接Neo4j
https://spring.io/guides/gs/accessing-data-neo4j/文档
做的时候和文档不太一样
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-neo4j
spring.neo4j.uri=bolt://localhost:7687
spring.data.neo4j.username=neo4j
spring.data.neo4j.password=secret
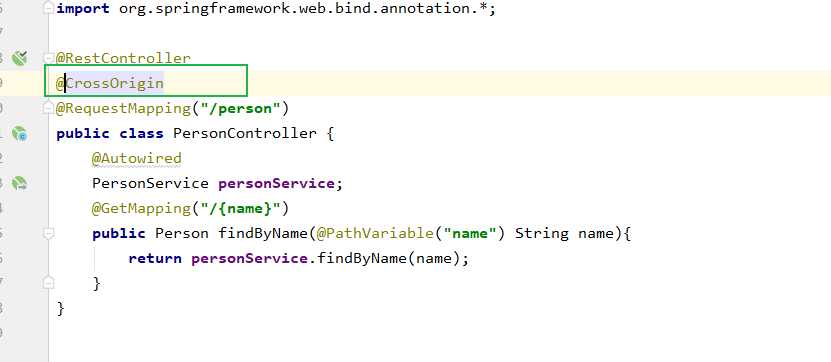
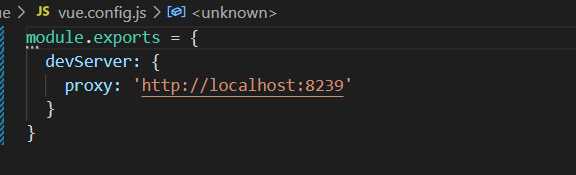
跨域
后端
前端
默认写的不清楚是啥,覆盖就行
测试
前端
this.axios.get('http://localhost:8329/person/'+'Kiefer Sutherland')
.then((relove)=>{
console.log(relove)
})
.catch((error)=>{
console.log(error)
})
后端
@GetMapping("/{name}")
public Person findByName(@PathVariable("name") String name){
return personServiindByName(name);
}
1.3其他
vue咱学过了,咱会哈
VSCODE搭建vue脚手架
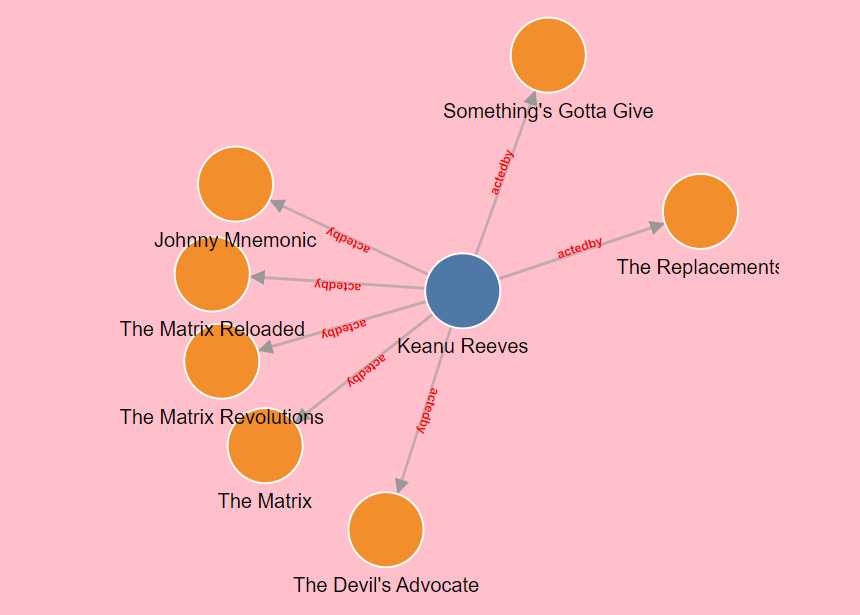
2 一个实践
前后端分离,从数据库中获得人物与电影之间的关系,生成力图
just be like:
2.1从后端获取节点和连接线的数据,并初始化svg
mounted(){
var _this = this
console.log(this.testGraph)
this.axios.get('http://localhost:8329/person/queryNodes/'+'actedby'+'/'+'Keanu Reeves')
.then((resolve)=>{
console.log(resolve)
_this.testGraph["nodes"] = resolve.data;
_this.axios.get('http://localhost:8329/person/queryLinks/'+'actedby'+'/'+'Keanu Reeves')
.then((resolve)=>{
console.log(resolve)
_this.testGraph["links"] = resolve.data;
this.ForceGraph(_this.testGraph, {
nodeId: d => d.id,
nodeGroup: d => d.group,
nodeTitle: d => `${
d.id}\n${
d.group}`,
linkStrokeWidth: l => Math.sqrt(l.value),
width: 640,
height: 600,
// invalidation // a promise to stop the simulation when the cell is re-run
})
})
.catch((error)=>{
console.log(error);
})
})
.catch((error)=>{
console.log(error);
})
},
本来想把异步函数(获取数据的axios)写在created里,但是不知道为什么初始化时获得的数据为空,可能是。。。还不清楚是什么问题,如果有人解答,感激不尽
看一眼前端数据的格式
2.2生成节点和节点内容
const node = svg.append("g")
.attr("fill", nodeFill)
.attr("stroke", nodeStroke)
.attr("stroke-opacity", nodeStrokeOpacity)
.attr("stroke-width", nodeStrokeWidth)
.selectAll("circle")
.data(nodes)
.join("circle")
.attr("r", nodeRadius)
.call(drag(simulation));
const nodeText = svg.append("g")
.selectAll("text")
.data(nodes)
.join("text")
.text(d => d.id)//填充的内容
.attr("dx",function () {
//水平方向上偏移,是文本内容宽度的一半
return this.getBoundingClientRect().width/2*(-1)
})
.attr("dy",50)
.attr("class","nodeText")
ticked函数
node
.attr("cx", d => d.x)
.attr("cy", d => d.y);
nodeText
.attr("x",d => d.x)
.attr("y",d => d.y);
2.3 生成线
将线的类型从line改为path,更为灵活
const link = svg.append("g")
.attr("stroke", typeof linkStroke !== "function" ? linkStroke : null)
.attr("stroke-opacity", linkStrokeOpacity)
.attr("stroke-width", typeof linkStrokeWidth !== "function" ? linkStrokeWidth : null)
.attr("stroke-linecap", linkStrokeLinecap)
.attr("marker-end", "url(#positiveMarker)")//在末尾处进行标记,url指明标记的内容,这个用于生成连接线末尾的标记,具体看2.4
.selectAll("path")//path 比line更加灵活
.data(links)
.join("path")
//给path增加一个属性id,使得文字能够依附在线上,这个用于将连接线上的内容与连接线绑定,具体看2.5
.attr("id",d => d.source.id+"_"+d.relationship+"_"+d.target.id);
ticked函数
link
//意为起点的(x1,y1)到终点的(x2,y2)之间的连线
// .attr("x1", d => d.source.x)
// .attr("y1", d => d.source.y)
// .attr("x2", d => d.target.x)
// .attr("y2", d => d.target.y);
//path和line指明路径的方式不一样
//意为画笔移动到(Move)(d.source.x,d.source.y)画一条线(Line)到点(d.target.x,d.target.y)
.attr("d",d=>'M'+d.source.x+" "+d.source.y+"L"+d.target.x+" "+d.target.y)
2.4 生成末尾箭头
const marker = svg.append("marker")
.attr("id","positiveMarker")//给一个id属性,link就能获得这个id
.attr("orient","auto")//自动调整方向
.attr("stroke-width",2)//箭头粗细
.attr("markerUnits", "strokeWidth")//匹配调整粗细的问题
.attr("markerUnits", "userSpaceOnUse")//匹配调整粗细的问题
.attr("viewBox", "0 -5 10 10")//箭头所在的可视范围
.attr("refX", 35)//偏移
.attr("refY", 0)//
.attr("markerWidth", 12)
.attr("markerHeight", 12)
.append("path")
.attr("d", "M 0 -5 L 10 0 L 0 5")//path的形状
.attr('fill', '#999')
.attr("stroke-opacity", 0.6);
2.5 生成连接线上的内容
const linksName = svg.append("g")
.selectAll("text")
.data(links)
.join("text")
.attr('x',100)
.attr('y',80)
.style('text-anchor','middle')
.style('fill', 'red')
.style('font-size', '10px')
.style('font-weight', 'bold')
.append('textPath')//将textpath的g标签放在text下
//path的id
.attr(
'xlink:href',d =>"#"+d.source.id+"_"+d.relationship+"_"+d.target.id
)
.text(d => d.relationship);
2.6 完整代码
注释没有删,而且没有搞明白为什么在
<template>
<div>
<div class="container">
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import * as d3 from 'd3'
export default {
name: 'Test01',
props: {
},
data() {
return {
nodes: [],
links: [],
testGraph : {
"nodes": [],
"links": []
}
// testGraph : {
// }
}
},
mounted(){
var _this = this
console.log(this.testGraph)
this.axios.get('http://localhost:8329/person/queryNodes/'+'actedby'+'/'+'Keanu Reeves')
.then((resolve)=>{
console.log(resolve)
_this.testGraph["nodes"] = resolve.data;
_this.axios.get('http://localhost:8329/person/queryLinks/'+'actedby'+'/'+'Keanu Reeves')
.then((resolve)=>{
console.log(resolve)
_this.testGraph["links"] = resolve.data;
this.ForceGraph(_this.testGraph, {
nodeId: d => d.id,
nodeGroup: d => d.group,
nodeTitle: d => `${
d.id}\n${
d.group}`,
linkStrokeWidth: l => Math.sqrt(l.value),
width: 640,
height: 600,
// invalidation // a promise to stop the simulation when the cell is re-run
})
})
.catch((error)=>{
console.log(error);
})
})
.catch((error)=>{
console.log(error);
})
},
methods: {
ForceGraph({
nodes, // an iterable of node objects (typically [{id}, …])
links // an iterable of link objects (typically [{source, target}, …])
}, {
nodeId = d => d.id, // given d in nodes, returns a unique identifier (string)
nodeGroup, // given d in nodes, returns an (ordinal) value for color
nodeGroups, // an array of ordinal values representing the node groups
nodeTitle, // given d in nodes, a title string
nodeFill = "currentColor", // node stroke fill (if not using a group color encoding)
nodeStroke = "#fff", // node stroke color
nodeStrokeWidth = 1.5, // node stroke width, in pixels
nodeStrokeOpacity = 1, // node stroke opacity
nodeRadius = 30, // node radius, in pixels
nodeStrength,
linkSource = ({
source}) => source, // given d in links, returns a node identifier string
linkTarget = ({
target}) => target, // given d in links, returns a node identifier string
linkStroke = "#999", // link stroke color
linkStrokeOpacity = 0.6, // link stroke opacity
linkStrokeWidth = 1.5, // given d in links, returns a stroke width in pixels
linkStrokeLinecap = "round", // link stroke linecap
linkStrength,
colors = d3.schemeTableau10, // an array of color strings, for the node groups
width = 640, // outer width, in pixels
height = 400, // outer height, in pixels
// invalidation // when this promise resolves, stop the simulation
} = {
}) {
// Compute values.
const N = d3.map(nodes, nodeId).map(intern);
const LS = d3.map(links, linkSource).map(intern);
const LT = d3.map(links, linkTarget).map(intern);
if (nodeTitle === undefined) nodeTitle = (_, i) => N[i];
const T = nodeTitle == null ? null : d3.map(nodes, nodeTitle);
const G = nodeGroup == null ? null : d3.map(nodes, nodeGroup).map(intern);
const W = typeof linkStrokeWidth !== "function" ? null : d3.map(links, linkStrokeWidth);
const L = typeof linkStroke !== "function" ? null : d3.map(links, linkStroke);
// Replace the input nodes and links with mutable objects for the simulation.
// nodes = d3.map(nodes, (_, i) => ({id: N[i]}));
// links = d3.map(links, (_, i) => ({source: LS[i], target: LT[i]}));
// Compute default domains.
if (G && nodeGroups === undefined) nodeGroups = d3.sort(G);
// Construct the scales.
const color = nodeGroup == null ? null : d3.scaleOrdinal(nodeGroups, colors);
// Construct the forces.
const forceNode = d3.forceManyBody();
const forceLink = d3.forceLink(links).id(({
index: i}) => N[i]).distance(200);
if (nodeStrength !== undefined) forceNode.strength(nodeStrength);
if (linkStrength !== undefined) forceLink.strength(linkStrength);
const simulation = d3.forceSimulation(nodes)
.force("link", forceLink)
.force("charge", forceNode)
.force("center", d3.forceCenter())
.on("tick", ticked);
// const svg = d3.create("svg")
// .attr("width", width)
// .attr("height", height)
// .attr("viewBox", [-width / 2, -height / 2, width, height])
// .attr("style", "max-width: 100%; height: auto; height: intrinsic;");
//重写,node和link的容器
const svg = d3.select(".container")
.append("svg")
.attr("width", width)
.attr("height", height)
.attr("viewBox", [-width / 2, -height / 2, width, height])
.attr("style", "max-width: 100%; height: auto; height: intrinsic;");
const marker = svg.append("marker")
.attr("id","positiveMarker")//指明方向
.attr("orient","auto")//自动调整方向
.attr("stroke-width",2)//箭头粗细
.attr("markerUnits", "strokeWidth")//匹配调整粗细的问题
.attr("markerUnits", "userSpaceOnUse")//匹配调整粗细的问题
.attr("viewBox", "0 -5 10 10")//箭头所在的可视范围
.attr("refX", 35)//偏移
.attr("refY", 0)//
.attr("markerWidth", 12)
.attr("markerHeight", 12)
.append("path")
.attr("d", "M 0 -5 L 10 0 L 0 5")//path的形状
.attr('fill', '#999')
.attr("stroke-opacity", 0.6);
// const negativeMarker = this.svgArea.append("marker")
// .attr("id","negativeMarker")
// .attr("orient","auto")
// .attr("stroke-width",2)
// .attr("markerUnits", "strokeWidth")
// .attr("markerUnits", "userSpaceOnUse")
// .attr("viewBox", "0 -5 10 10")
// .attr("refX", -25)
// .attr("refY", 0)
// .attr("markerWidth", 12)
// .attr("markerHeight", 12)
// .append("path")
// .attr("d", "M 10 -5 L 0 0 L 10 5")
// .attr('fill', '#999')
// .attr("stroke-opacity", 0.6);
const link = svg.append("g")
.attr("stroke", typeof linkStroke !== "function" ? linkStroke : null)
.attr("stroke-opacity", linkStrokeOpacity)
.attr("stroke-width", typeof linkStrokeWidth !== "function" ? linkStrokeWidth : null)
.attr("stroke-linecap", linkStrokeLinecap)
.attr("marker-end", "url(#positiveMarker)")//在末尾处进行标记,url指明标记的内容
.selectAll("path")//path 比line更加灵活
// .data(links)
.data(links)
.join("path")
//给path增加一个属性id,使得文字能够依附在线上
.attr("id",d => d.source.id+"_"+d.relationship+"_"+d.target.id);
const linksName = svg.append("g")
.selectAll("text")
.data(links)
.join("text")
.attr('x',100)
.attr('y',80)
.style('text-anchor','middle')
.style('fill', 'red')
.style('font-size', '10px')
.style('font-weight', 'bold')
.append('textPath')//将textpath的g标签放在text下
//path的id
.attr(
'xlink:href',d =>"#"+d.source.id+"_"+d.relationship+"_"+d.target.id
)
.text(d => d.relationship);
const node = svg.append("g")
.attr("fill", nodeFill)
.attr("stroke", nodeStroke)
.attr("stroke-opacity", nodeStrokeOpacity)
.attr("stroke-width", nodeStrokeWidth)
.selectAll("circle")
.data(nodes)
.join("circle")
.attr("r", nodeRadius)
.call(drag(simulation));
const nodeText = svg.append("g")
.selectAll("text")
.data(nodes)
.join("text")
.text(d => d.id)
.attr("dx",function () {
return this.getBoundingClientRect().width/2*(-1)
})
.attr("dy",50)
.attr("class","nodeText")
if (W) link.attr("stroke-width", ({
index: i}) => W[i]);
if (L) link.attr("stroke", ({
index: i}) => L[i]);
if (G) node.attr("fill", ({
index: i}) => color(G[i]));
if (T) node.append("title").text(({
index: i}) => T[i]);
// if (invalidation != null) invalidation.then(() => simulation.stop());
function intern(value) {
return value !== null && typeof value === "object" ? value.valueOf() : value;
}
function ticked() {
link
//意为起点的(x1,y1)到终点的(x2,y2)之间的连线
// .attr("x1", d => d.source.x)
// .attr("y1", d => d.source.y)
// .attr("x2", d => d.target.x)
// .attr("y2", d => d.target.y);
//path和line指明路径的方式不一样
//意为起点移动到(Move)(d.source.x,d.source.y)画一条线(Line)到点(d.target.x,d.target.y)
.attr("d",d=>'M'+d.source.x+" "+d.source.y+"L"+d.target.x+" "+d.target.y)
node
.attr("cx", d => d.x)
.attr("cy", d => d.y);
nodeText
.attr("x",d => d.x)
.attr("y",d => d.y);
}
function drag(simulation) {
function dragstarted(event) {
if (!event.active) simulation.alphaTarget(0.3).restart();
event.subject.fx = event.subject.x;
event.subject.fy = event.subject.y;
}
function dragged(event) {
event.subject.fx = event.x;
event.subject.fy = event.y;
}
function dragended(event) {
if (!event.active) simulation.alphaTarget(0);
event.subject.fx = null;
event.subject.fy = null;
}
return d3.drag()
.on("start", dragstarted)
.on("drag", dragged)
.on("end", dragended);
}
return Object.assign(svg.node(), {
scales: {
color}});
}
},
}
</script>
<!-- Add "scoped" attribute to limit CSS to this component only -->
<style scoped>
body{
margin: 0px;
}
.container{
background-color : pink;
}
.node{
stroke:#fff;
stroke-width:1;
cursor: pointer;
}
.node:hover{
stroke-width:5;
}
.nodeText{
fill:white;
}
</style>
参考
B站视频地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV11Q4y1M7MS?p=1
D3API:https://www.d3js.org.cn/document/
svg起步:https://www.d3js.org.cn/svg/get_start/
今天的文章基于D3js以及Neo4j的知识图谱系统开发分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读,如果确实帮到您,您可以动动手指转发给其他人。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/26378.html


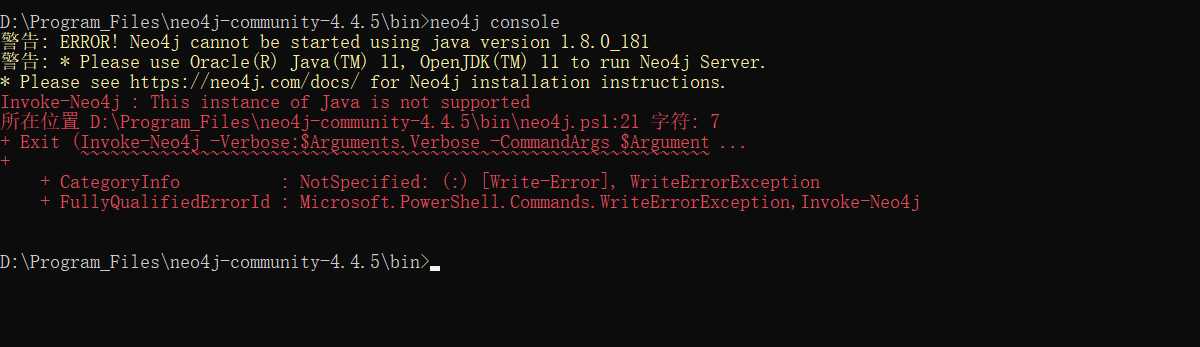 oh,no, 删了重新下吧
oh,no, 删了重新下吧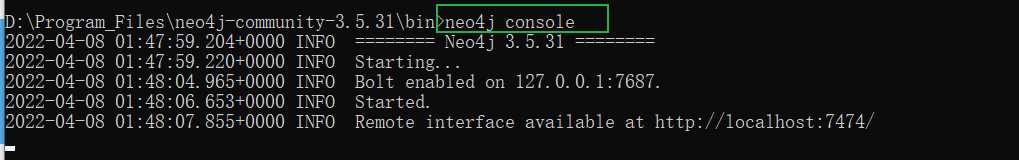
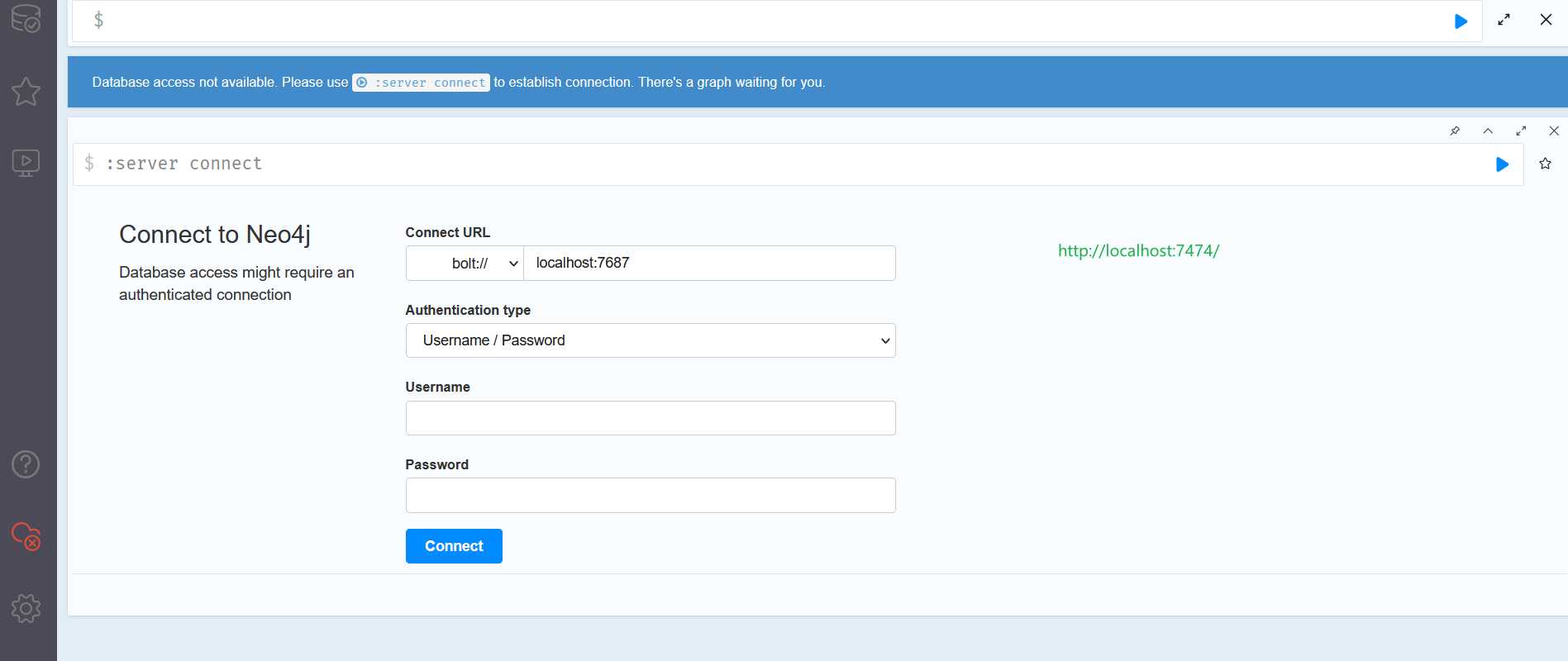 Default login is username ‘neo4j’ and password ‘neo4j’ (full installation instructions below)
Default login is username ‘neo4j’ and password ‘neo4j’ (full installation instructions below)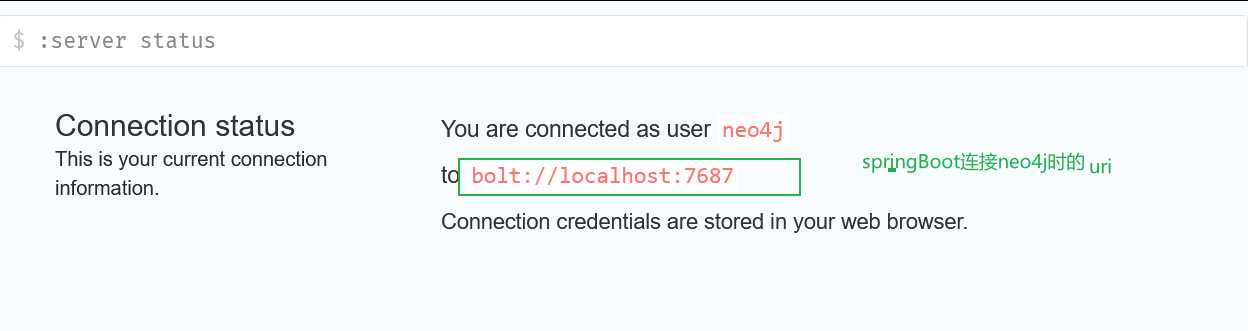
 点击第二页的Create就可以看到如下效果
点击第二页的Create就可以看到如下效果