目录
定义一个整型的长度为3 x 4的二维数组k[3] [4],并将数组中元素k[i] [j] 值初始化为值ixj。然后,将元素k[2] [3]打印出来。(可以直接赋值)
从命令行出入几个字符串,统计并打印出输入字符串的个数、以及各字符串的字符个数。(提示:args.length/args[k].length())。
从命令行输入一个数字,判断它是奇数还是偶数。(提示:利用%;三元条件或if/else;int a=Integer.parseInt(args[0]))//数据输入)。
从命令行输入两个数字,判断两个数谁大谁小。(提示:读输入参数args[];三元条件 或 if/else )
编写一个模拟同时掷骰子的程序。要用Math.random()模拟产生两个骰子,将两个结果相加,相加的和等于7的可能性最大,等于2和12的可能性最小。程序模投掷3600次,判断求和的结果是否合理。
首先定义一个计算长方形面积的类rectangleClass,要求类中有一个定义长方形左上角和右下角坐标的构造函数,以及一个通过长方形右下角坐标与左上角坐标计算长方形面积,并实例化两个长方形进行测试。
请创建一个银行账户类,要求如下:1)类包括账户名、账户号、存款余额等属性;2)可实现余额查询,存款和取款的操作。3)创建该类的对象,验证以上两点。
编写程序统计一个字符子串在一个字符串中出现的次数和位置。如子字符串”nba”在字符串”asfasfnabasdfnbasdnbasnbasdnbadfasdf”中出现的次数和出现的位置。
对字符串”23 10 -8 0 3 7 108″中的数值进行升序排序,生成一个数值有序的字符串”-8 0 3 7 10 23 208″。
请使用Map实现获取字符串“bwaerbctyxbacecrtdcvr”
利用Swing包创建一个窗口,窗口位置为(220,160)、大小为320×240,并在窗口(20,80)、(120,80)、(220,80)处各安置一个按钮,按钮大小为80×40
设计出如图所示Windows操作系统附带的小应用-计算器样式的简单计算器。(只需要实现简单的加减乘除功能。菜单内容和样式如同系统自带计算器,但功能只需实现退出系统功能。)
定义一个整型的长度为3*4的二维数组k[3][4],并将数组中元素k[i][j]值初始化为i*j。然后,将元素k[2][3]打印出来。(可以直接赋值)。:定义一个整型的长度为3*4的二维数组k[3][4],并将数组中元素k[i][j]值初始化为i*j。然后,将元素k[2][3]打印出来。(可以直接赋值)。
public class test1{
public static void main(String[] args){
int k[] = new int[6];
for(int i = 0;i < k.length;i++)
k[i] = i;
System.out.println("k[3]=" + k[3]);
}
}
定义一个整型的长度为3 x 4的二维数组k[3] [4],并将数组中元素k[i] [j] 值初始化为值ixj。然后,将元素k[2] [3]打印出来。(可以直接赋值)
public class test2{
public static void main(String[] args){
int k[][] = new int[3][4];
for(int i = 0;i < k.length;i++) {
for(int j = 0;j < k[i].length;j++)
k[i][j] = i * j;
}
System.out.println("k[2][3]="+k[2][3]);
}
}
从命令行出入几个字符串,统计并打印出输入字符串的个数、以及各字符串的字符个数。(提示:args.length/args[k].length())。
public class test3{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("字符串的个数"+args.length);
for(int i = 0;i < args.length;i++)
System.out.println("第"+(i + 1)+"个字符串的字符数"+args[i].length());
}
}
从命令行输入一个数字,判断它是奇数还是偶数。(提示:利用%;三元条件或if/else;int a=Integer.parseInt(args[0]))//数据输入)。
class test4{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
if(a%2==0)
System.out.println("这是一个偶数");
else
System.out.println("这是一个奇数");
}
}
从命令行输入两个数字,判断两个数谁大谁小。(提示:读输入参数args[];三元条件 或 if/else )
public class test5{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
int b = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
if(a > b) System.out.println(a+">"+b);
else if(a == b) System.out.println(a+"="+b);
else System.out.println(a+"<"+b);
}
}
角谷猜想:任何一个正整数n,如果它是偶数则除以2,如果是奇数则乘3加1,这样得到一个新的整数,如此继续进行上述处理,则最后得到的数一定是1。编写应用程序证明:在3~10000之间的所有正整数都符合上述规则。
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args){
for(int i=3;i<=10000;i++){
int n=i;
while(n!=1){
if(n%2==0){
n=n/2;
}else{
n=n*3+1;
}
}
System.out.println(i+"符合角谷猜想");
}
}
}
编写一个模拟同时掷骰子的程序。要用Math.random()模拟产生两个骰子,将两个结果相加,相加的和等于7的可能性最大,等于2和12的可能性最小。程序模投掷3600次,判断求和的结果是否合理。
public class test{
public static void main(String[] args){
int sum[] = new int [13]; //定义一个数组,用来放和
for(int i=1;i<=3600;i++){
int a = (int)(Math.random()*6)+1; //第一个骰子,随机产生[1-6]
int b = (int)(Math.random()*6)+1;
int c = a + b;
sum[c] ++;
}
for (int i=1;i<=12;i++) {
System.out.println("出现和为"+i+"的次数:"+sum[i]);
}
}
编程:读取一个星号的长度,采用循环语句打印
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您需要打印的三角形的行数:");
int length = in.nextInt();
for(int i=0;i<=length;i++){
for(int j=length-1;j>=i;j--)
System.out.print(" "); //打印每行的空格
for(int n=1;n<=i;n++)
System.out.print("*");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你需要打印的三角形的行数:");
int length = in.nextInt();
length=length/2;
//打印上半部分
for(int i=1;i<=length;i++){
for(int k=1;k<=i;k++)
System.out.print("*");
System.out.println();
}
//打印下半部分
for(int i=length+1;i>=0;i--){
for(int k=1;k<=i;k++)
System.out.print("*");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入你需要打印的三角形的行数:");
int length = in.nextInt();
//length=length/2;
//打印上半部分
for(int i=1;i<=length;i++){
for(int k=1;k<=i;k++)
System.out.print("*");
System.out.println();
}
//打印下半部分
for(int i=length;i>0;i--){
for(int j=length;j>=i;j--)
System.out.print(" ");
for(int k=1;k<=i;k++)
System.out.print("*");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
编程:读取一个星号的长度,采用循环语句打印:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test4 {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您需要打印的三角形的行数:");
int length = in.nextInt();
for(int i=1;i<=length;i++){
for(int j=length;j>=i;j--)
System.out.print(" "); //打印每行中左边的空格
for(int k=1;k<=i;k++)
System.out.print("*"); //打印每行左边三角形的*
for(int j=1; j<=i-1; j++) //打印每行右边三角形的*
System.out.print("*");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test5{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入您需要打印的棱形的行数:");
int length = in.nextInt();
//打印上半部分的菱形
for(int i=1;i<=length/2+1;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=(length-(2*i-1))/2;j++)
System.out.print(" ");
for(int k=1;k<=2*i-1;k++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
//打印下半部分的菱形
for(int i=1;i<=length/2;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++)
System.out.print(" ");
for(int k=1;k<=length-i*2;k++)
{
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
读取一个矩形的长度,然后输出一个空心矩形。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入矩形的宽:");
int length = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入矩形的长:");
int height = in.nextInt();
for (int i=0;i<height;i++) {
for (int j=0;j<length;j++) {
if ( i == 0 ) {
System.out.print("*");//第一行
}
else if (i == height-1) {
System.out.print("*");//最后一行
}
else if (j == 0 || j == length-1) {//每行的第一个和最后一个
System.out.print("*");
}
else {
System.out.print(" ");//其余空格
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
读取一个矩形外边和内边的长度,然后输出一个空心矩形。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入外框的值:");
int wk = in.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入内框的值:");
int nk = in.nextInt();
int x=wk-nk;
for (int i=0;i<wk;i++) {
for (int j=0;j<wk;j++) {
if ( i<=x-1) {
System.out.print("*");
}else if (i >= nk ) {
System.out.print("*");
}else if (j <= x-1 || j >= nk) {
System.out.print("*");
}else {
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
定义一个复数类complex,它的内部具有两个实例变量:realPart和imagPart,分别代表复数的实部和虚部,编程实现要求的数学运算:1)实现两个复数相加;2)实现两个复数相减;3)输出运算的结果。然后,调用上述方法实现两个复数(18+2i、19-13i的相加、相减,并打印出结果)
class Complex{
int realPart,imagPart;
Complex(){
}
public
Complex(int realPart,int imagPart){
this.realPart = realPart;
this.imagPart = imagPart;
}
static public void add(Complex c1,Complex c2){
Complex sum = new Complex();
sum.realPart = c1.realPart + c2.realPart;
sum.imagPart = c1.imagPart + c2.imagPart;
System.out.println("(" + c1.realPart + "+" + c1.imagPart + "i)" + "+" + "(" + c2.realPart + "+" + c2.imagPart + "i)" + "=" +"(" + sum.realPart + "+" + sum.imagPart + "i)");
}
static public void sub(Complex c1,Complex c2){
Complex sum = new Complex();
sum.realPart = c1.realPart - c2.realPart;
sum.imagPart = c1.imagPart - c2.imagPart;
System.out.println("(" + c1.realPart + "+" + c1.imagPart + "i)" + "-" + "(" + c2.realPart + "+" + c2.imagPart + "i)" + "=" +"(" + sum.realPart + "+" + sum.imagPart + "i)");
}
}
public class Fushu{
public static void main(String[] args){
Complex c1 = new Complex(18,2);
Complex c2 = new Complex(19,-13);
c2.add(c1,c2);
c2.sub(c1,c2);
}
}
首先定义一个计算二维坐标系中圆面积的类circleClass,要求类中有一个定义圆心坐标,圆上一点坐标的构造函数,以及一个通过圆上一点坐标与圆心坐标计算圆面积的方法area。然后,通过上述类生成两个圆circle1、circle2进行测试;一个圆心、圆上一点坐标分别为(0,0)、(8.5,9),另有一个圆心、圆上一点坐标分别为(2,3.5)、(9,6),并分别显示各自面积。
class dianClass{
double x,y;
public dianClass(double x,double y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
void getSpot(){
System.out.print("(" + this.x + "," + this.y + ")");
}
}
class CircleClass{
final static double PI = 3.14;
dianClass x,y;
double area,r;
CircleClass(dianClass x,dianClass y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.r = ((x.x-y.x)*(x.x-y.x)+(x.y-y.y)*(x.y-y.y));
this.area = PI*r;
}
void getArea(){
System.out.println("圆的面积为:"+area);
}
}
public class Yuanmianji{
public static void main(String[] args){
CircleClass circle1 = new CircleClass(new dianClass(0,0),new dianClass(8.5,9));
CircleClass circle2 = new CircleClass(new dianClass(2,3.5),new dianClass(9,6));
circle1.getArea();
circle2.getArea();
}
}
首先定义一个计算长方形面积的类rectangleClass,要求类中有一个定义长方形左上角和右下角坐标的构造函数,以及一个通过长方形右下角坐标与左上角坐标计算长方形面积,并实例化两个长方形进行测试。
public class RectangleClass {
double x1;
double x2;
double y1;
double y2;
public RectangleClass(double x1,double x2,double y1,double y2) {
this.x1=x1;
this.x2=x2;
this.y1=y1;
this.y2=y2;
}
public double getArea() {
double width = Math.abs(y2-y1);
double length = Math.abs(x2-x1);
double area = width * length;
return area;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RectangleClass r1 = new RectangleClass(23,21,12,34);
RectangleClass r2 = new RectangleClass(25,17,23,24);
System.out.println("r1长方形的面积是:"+r1.getArea());
System.out.println("r2长方形的面积是:"+r2.getArea());
}
}
将笛卡尔坐标系上的点定义为一个类Point,该类要求提供求得坐标系上两个间距离的功能、获取和设置坐标的功能、获取极坐标的功能,以及完成对已创建的Point类对象进行个数统计的功能。设计测试Point类的应用程序主类,测试并显示输出提供所有功能的结果。
class Point{
private int x,y;
final double PI = 3.14;
static int count = 0;
public Point(){
}
public Point(int x,int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void getPoint(int x,int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
System.out.println("("+this.x+","+this.y+")");
}
public void setPoint(int x,int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double angle(){
return (180/PI)*Math.atan2(y,x);
}
public double radius(){
return Math.sqrt(x*x+y*y);}
public double distance(Point a){
double r;
r = Math.sqrt((double)((x-a.x)*(x-a.x)+(y-a.y)*(y-a.y)));
return r;
}
static void setCount(){
count+=1;
}
static int getCount(){
return count;
}
}
public class Dikaer{
public static void main(String[] args){
Point a = new Point();
a.setCount();a.getCount();
System.out.println("当前点的个数:"+a.getCount());
Point b = new Point(2,3);
b.setCount();
b.getCount();
System.out.println("当前点的个数:"+b.getCount());
Point c = new Point(3,9);
c.setCount();c.getCount();
System.out.println("当前点的个数:"+c.getCount());
a.distance(b);
a.distance(c);
System.out.println("a,b两点的距离:"+a.distance(b));
System.out.println("a,c两点的距离:"+a.distance(c));
System.out.println("c点的极坐标为:angle="+c.angle()+" radius="+c.radius());
}
}
设计一个表示图书的Book类,它包含图书的书名、作者、月销售量等属性,另有两个构造方法(一个不带参数,另一个带参数),成员方法setBook(),printBook()分别用于设置和输出书名、作者、月销售量等数据。并设计相应的测试Book类的应用程序主类,测试并显示输出提供所有功能的结果。
class Book{
String BookName;
String BookWriter;
int MonthSales;
public Book(){
BookName = "无";
BookWriter = "无";
MonthSales = 0;
}
public Book(String BookName,String BookWriter,int MonthSales){
this.BookName = BookName;
this.BookWriter = BookWriter;
this.MonthSales = MonthSales;
}
public void setBook(String BookName,String BookWriter,int MonthSales){
this.BookName = BookName;
this.BookWriter = BookWriter;
this.MonthSales = MonthSales;
}
public void printBook(){
System.out.println("书名:"+ BookName);
System.out.println("作者:"+ BookWriter);
System.out.println("月销售量:"+ MonthSales);
}
}
public class Tushu{
public static void main(String[] args){
Book a = new Book("福尔摩斯探案集","阿瑟·柯南道尔",2020);
a.printBook();
a.setBook("飘","玛格丽特·米切尔",1937);
a.printBook();
Book b = new Book();
b.printBook();
}
}
请创建一个银行账户类,要求如下:1)类包括账户名、账户号、存款余额等属性;2)可实现余额查询,存款和取款的操作。3)创建该类的对象,验证以上两点。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Account {
public int id;
public String name;
public int password;
public int money;
//方法Account(),创建账户的账号、密码、姓名和余额
public Account(int id, String name, int password, int money) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.password = password;
this.money = money;
}
//方法Display(),显示账户的账号、姓名和余额信息
public void Display(){
System.out.println("账户:" + id);
System.out.println("姓名:" + name);
System.out.println("余额:" + money);
}
/*取款方法 takeMoney(),先让用户输入密码验证,
密码正确后输入取款金额,取款成功后余额减除相应的金额*/
public void takeMoney(){
while(true){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入密码进行验证!");
int pass = sc.nextInt();
if(pass == password){
System.out.println("请输入需要取款的金额:");
int withdrawals = sc.nextInt();
if(withdrawals <= money) {
money= money-withdrawals;
System.out.println("账户余额:" + money);
}else {
System.out.println("当前余额不足!");
}
break;
}else {
System.out.println("你输入的密码有误,请重新输入!");
}
sc.close();
}
}
/*存款方法 saveMoney(int moneys),
存款是直接传入存款金额,账户余额增加相应的金额*/
public void saveMoney(int inmoney){
money = money + inmoney;
System.out.println("此次存款为:" + inmoney);
System.out.println("账户余额:" + money);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account acc = new Account(10000,"小明",123456,100000);
/*
acc.id = 10000;
acc.name = "小明";
acc.password = 123456;
acc.money = 100000;
*/
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
System.out.println("---欢迎进入银行账户操作系统---");
System.out.println("---------1银行账户信息--------");
System.out.println("---------2取款操作------------");
System.out.println("---------3存款操作------------");
System.out.println("---------4退出系统------------");
System.out.println("------------------------------");
int choice = sc.nextInt();
switch(choice) {
case 1:
System.out.println("---银行账户信息---");
acc.Display();
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("---取款操作---");
acc.takeMoney();
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("---存款操作---");
acc.saveMoney(1000);
break;
case 4:
System.exit(0);
break;
default:
System.out.println("您的选择有误!");
break;
}
}
}
}
class BankClass{
String bankName;
String bankNumber;
double balance;
public BankClass(){
}
public BankClass(String bankName,String bankNumber,double balance){
this.bankName = bankName;
this.bankNumber = bankNumber;
this.balance = balance;
}
public void require(){
System.out.println(bankName +"的账号为:"+ bankNumber +" 余额为:"+balance);
}
public void cunQian(double money){
balance = balance + money;
System.out.println("存入" + money + "元到该账号,该账号现在的余额为:" + balance);
}
public void quQian(double money){
if(balance >= money){
balance = balance - money;
System.out.println("取款"+money+"元,该账号现在的余额为:" + balance);
}
else{
System.out.println("该账号的余额不足");
}
}
}
public class Yinhangzhanghu{
public static void main(String[] args){
BankClass a = new BankClass("zhong","2019014077",666666);
BankClass b = new BankClass("chen","888888888",888888);
a.require();
b.require();
a.cunQian(10000);
b.quQian(2000);
}
}
设计一个学生类student,其数据成员name(姓名)、age(年龄)和degree(学位)。由student类派生出本科生类Undergraduate和研究生类Graduate,本科生类Undergraduate增加成员specialty(专业),研究生类增加成员direction (研究方向)。每个类都有show()方法,用于输出数据成员信息。最后请输出下列信息:
class Student{
String name;
int age;
String degree;
}
class Undergraduate extends Student {
String specialty;
Undergraduate(String name,int age,String degree,String specialty){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.degree = degree;
this.specialty = specialty;
}
void show(){
System.out.print("姓名:"+name);
System.out.print(" 年龄:"+age);
System.out.print(" 学位:"+degree);
System.out.println(" 专业:"+specialty);
}
}
class Graduate extends Student {
String direction;
Graduate(String name,int age,String degree,String direction){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.degree = degree;
this.direction = direction;
}
void show(){
System.out.print("姓名:"+name);
System.out.print(" 年龄:"+age);
System.out.print(" 学位:"+degree);
System.out.println(" 研究方向:"+direction);
}
}
public class Students{
public static void main(String[] args){
Undergraduate a = new Undergraduate("张三",20,"学士","通信工程");
Undergraduate b = new Undergraduate("李四",21,"学士","电子工程");
Graduate c = new Graduate("王五",25,"硕士","软件工程");
Graduate d = new Graduate("刘六",36,"硕士","人机工程");
a.show();
b.show();
c.show();
d.show();
}
}
编程实现有一个电话类phone,它有号码的属性number,是一个12位的字符数组,它有四个功能,设置电话号码setNumber(),显示电话号getNumber(),接电话answer(),拨打电话dial();移动电话mobilePhone和固定电话fixPhone是电话的两个子类,但移动电话号码为11位,并且移动电话和固定电话接听和拨打电话的方式不同,固定电话又有一个子类:无绳电话cordlessPhone无绳电话号码为4位,它相对固定电话还多一个移动功move().实现这几个类,并且测试他们的功能。
class Phone{
char number[] = new char[12];
void setNumber(char[] number){
if(number.length != 12){
System.out.println("号码设置错误");
}
else{
this.number = number;
}
}
void getNumber(){
System.out.print("本机号码:");
for(int i = 0;i<number.length;i++){
System.out.print(number[i]);
}System.out.print("\n");
}
void answer(){
}
void dial(){
}
}
class mobilePhone extends Phone{
void setNumber(char[] number){
if(number.length != 11){
System.out.println("号码设置错误");
}
else{
this.number = number;
}
}
void answer(){
System.out.println("正通过移动网络接听电话....");
}
void dial(){
System.out.println("正通过移动网络拨打电话....");
}
}
class fixPhone extends Phone{
void answer(){
System.out.println("正通过电信固网接听电话....");
}
void dial(){
System.out.println("正通过电信固网拨打电话....");
}
}
class cordlessPhone extends fixPhone{
void setNumber(char[] number){
if(number.length != 4){
System.out.println("号码设置错误");
}
else{
this.number = number;
}
}
void move(){
System.out.println("正在移动通话....");
}
}
public class Phone0{
public static void main(String[] args){
fixPhone fix = new fixPhone();
fix.setNumber(new char[] {'0','5','7','4','8','8','2','2','2','0','9','6'});
fix.getNumber();
fix.dial();
fix.answer();
mobilePhone mobile = new mobilePhone();
mobile.setNumber(new char[] {'1','5','7','8','8','2','2','2','0','9','6'});
mobile.getNumber();
mobile.dial();
mobile.answer();
cordlessPhone cord = new cordlessPhone();
cord.setNumber(new char[] {'2','0','9','6'});
cord.getNumber();
cord.dial();
cord.answer();
cord.move();
}}
有工人、服务员、教师、科学家四种角色,其中服务员、工人只有月固定工资(元/月),教师除月固定工资外,还有深酬(元/节)。科学家除月固定工资外,还有科研激励奖(元/季度)。请通过继承设计出相应的类,将各种类型的员工的全年工资打印出来,并测试(张三、工人、4000元/月)、(李四、服务员、3500/月) (王五、 教师、5000元/月、100元/节,200节1/年),(刘六、科学家、7000元/月、20000元/季度)。
class Person{
int money;
String job;
String name;
Person(String name,String job,int money){
this.name = name;
this.job = job;
this.money = money;
}
void getprint(){
System.out.println(name +": "+job+" " + money);
}
}
class Teacher extends Person {
int classpay;
int classNumber;
Teacher(String name, String job,int money,int classpay,int classNumber) {
super(name,job,money);
this.classpay = classpay;
this.classNumber = classNumber;
}
void getprint() {
System.out.println(name + ": "+ job+" " + money+"/月 "+ classpay+"/节 "+classNumber+"/年 " );
}
}
class Scientist extends Person{
int bonus;
Scientist(String name, String job, int money,int bonus){
super(name,job,money);
this.bonus = bonus;
}
void getprint(){
System.out.println(name + ": "+job+" " + money+"/月 "+bonus+"/季度" );
}
}
public class Gongzi{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person zs = new Person("张三","工人 ",4000);
zs.getprint();
Person ls = new Person("李四","服务员",3500);
ls.getprint();
Teacher ww = new Teacher("王五","教师 ",5000, 100, 200);
ww.getprint();
Scientist ll = new Scientist( "刘六","科学家", 7000, 20000);
ll.getprint();
}
}
在biology包中的animal包中有Human类.它具有name,height,weight的属性,还具有eat(),sleep()和work()的行为,在biology包中的plant包中有Flower类,它具有name,color,smell的属性,还具有drink()和blossom()的行为,现在在一个school包中的garden包中一个张三的人, 他是一个Human类的对象,种植的rose是个Flower类对象,编程实现并测试各自的方法。
package biology.animal;
public class Human {
public String name;
public double height;
public double weight;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("eat");
}
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("sleep");
}
public void work() {
System.out.println("work");
}
}
//二:
package biology.plant;
public class Flower {
public String name;
public String color;
public String smell;
public void drink() {
System.out.println("drink");
}
public void blossom() {
System.out.println("blossom");
}
}
//三:
package school.garden;
import biology.animal.Human;
import biology.plant.Flower;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Human hum = new Human();
hum.name = "张三";
hum.eat();
hum.sleep();
hum.work();
Flower f= new Flower();
f.name="rose";
f.drink();
f.blossom();
}
}
在computer包中的mainbroad包中有一个VGACard的类, 它有一个显示方法show(),显示”VGA checked success”, 在server的包的mainbroad包中的showCard类是继承自VGACard,请测试showCard的show()功能
//一:
package computer.mainbroad;
public class VGACard {
public void show() {
System.out.println("VGA checkd success");
}
}
//二:
package server.mainbroad;
import computer.mainbroad.VGACard;
public class showCard extends VGACard {
public static void main(String[] args) {
showCard sh = new showCard();
sh.show();
}
}
先在在com.graphic包中定义一个圆柱体类Cylinder,并且它有私有属性:private double r;private double h;并构造方法求其体积。再在com.test包中定义一个测试类Test,输入半径为5.34、高为2、半径PI为3.14
package com.graphic;
public class Cylinder {
private double r;
private double h;
public Cylinder(double r, double h) {
this.r = r;
this.h = h;
}
public void volume() {
double PI = 3.14;
System.out.println("圆柱体的体积为:"+PI*r*r*h);
}
}
//二:
package com.test;
import com.graphic.Cylinder;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cylinder cy = new Cylinder(5.34,2);
cy.volume();
}
}
首先设计一个学生抽象类Student,其数据成员有name(姓名)、age(年龄)和degree(学位),以及一个抽象方法show()。然后由Student类派生出本科生类Undergraduate和研究生类Graduate,本科生类Undergraduate增加成员specialty(专业),研究生类增加成员direction(研究方向)。并且每个类都有show()方法,用于输出数据成员信息。请定义对象,并打印输出下列信息:
abstract class Student{
String name,degree;
int age;
abstract void show();
}
class Undergraduate extends Student{
String specialty;
Undergraduate(String name,int age,String degree,String specialty){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.degree=degree;
this.specialty=specialty;
}
void show(){
System.out.println(name+","+age+","+degree+","+specialty);
}
}
class Graduate extends Student{
String direction;
Graduate(String name,int age,String degree,String direction){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.degree=degree;
this.direction=direction;
}
void show(){
System.out.println(name+","+age+","+degree+","+direction);
}
}
public class t1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graduate g1=new Graduate("张三",20,"本科","通信");
Graduate g2=new Graduate("李四",21,"本科","电子");
Undergraduate u1=new Undergraduate("王五",25,"硕士","通信");
Undergraduate u2=new Undergraduate("刘六",36,"博士","通信");
g1.show();
g2.show();
u1.show();
u2.show();
}
}
首先定义一个接口circleInterface,要求接口中有一个定义PI的常量以及一个计算圆面积的空方法circleArea()。然后设计一个类circleClass实现该接口,通过构造函数circleClass(double r)定义圆半径,并增加一个显示y圆面积的方法。最后,通过上述类生成两个半径分别为3.5和5.0的圆对象circle1,circle2进行测试。
interface circleInterface{
double PI=3.14;
void circleArea();
}
class circleClass implements circleInterface{
double r,area;
circleClass(double r){
this.r=r;
}
public void circleArea(){
area=r*r*PI;
}
void show(){
System.out.println("半径为"+r+"的圆面积为:"+area);
}
}
public class t2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
circleClass circle1=new circleClass(3.5);
circleClass circle2=new circleClass(5.0);
circle1.circleArea();
circle1.show();
circle2.circleArea();
circle2.show();
}
}
先设计一个抽象类Graphics,它具有一个String类型参数name和两个抽象方法parameter()、area(),name用来存储图形的名称,parameter()方法用于输出图形的名称和其它属性特征,area()方法用于输出图形的面积,然后两个子类分别是长方形属性(长宽面积)和圆形属性(颜色半径面积)。
abstract class Graphics{
String name; //储存图形名称
abstract void parameter(); //输出图形的名称和其他属性特征
abstract void area(); //输出图形的面积
}
class Juxing extends Graphics{
int c,k;
Juxing(String name,int c,int k){
this.name=name;
this.c=c;
this.k=k;
}
void parameter(){
System.out.println("形状为:"+name);
System.out.println("长为:"+c+" 宽为:"+k);
}
void area(){
System.out.println("面积为:"+c*k);
}
}
class circle1 extends Graphics{
double r;
final double PI=3.14;
String color;
circle1(String name,String color,double r){
this.name=name;
this.r=r;
this.color=color;
}
void parameter(){
System.out.println("形状为:"+name);
System.out.println("颜色为:"+color+" 半径为:"+r);
}
void area(){
System.out.println("面积为:"+r*r*PI);
}
}
public class t3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Juxing j=new Juxing("长方形",3,2);
circle1 c=new circle1("圆形","红色",4.0);
j.parameter();
j.area();
c.parameter();
c.area();
}
}
设计一个shape接口和它的两个实现类Square和Circle,要求如下:1)shape接口中有一个抽象方法area(),方法接收一个double类型的参数,返回一个double类型的结果。2)Square和Circle实现了shape接口的area()抽象方法,分别求正方形和圆形的面积b并返回。在测试类中创建Square和Circle对象,计算边长为2的正方形面积和半径为3的圆面积。
interface Shape{
void area();
}
class Square implements Shape{
double b;
Square(double b){
this.b=b;
}
public void area(){
System.out.println("正方形面积为:"+b*b);
}
}
class Circle implements Shape{
double r;
final double PI=3.14;
Circle(double r){
this.r=r;
}
public void area(){
System.out.println("圆的面积为:"+r*r*PI);
}
}
public class t4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Square s=new Square(2.0);
Circle C=new Circle(3.0);
s.area();
C.area();
}
}
通过键盘输入一个int类型的整数,输出其二进制形式(Integer.toBinaryString()).用异常处理语句处理:如果录入得整数过大(BigInteger)、录入的是小数(BigDecimal)或录入的是其他字符,请给予提示。(提示:建议首先键盘录入的结果存储在String类型的字符串中(Scanner.nextLine()),如果直接用(nextInt())将其存入int类型数据中,若有非法字符就会直接报错,无法进行后续判断)
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class t1{
public static void main(String[] args){
while (true) {
System.out.print("请输入一个整数:");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String n = sc.nextLine();
try {
System.out.println(n + "的二进制形式为:" + Integer.toBinaryString(Integer.parseInt(n)));
break;
} catch (Exception e0) {
try {
new BigInteger(n);
System.out.println("录入的整数过大,请重新录入");
} catch (Exception e1) {
try {
new BigDecimal(n);
System.out.println("录入的是小数,请重新录入");
} catch (Exception e2) {
System.out.println("录入其它字符,请重新录入");
}
}
}
}
}
}
设计一个接口circleInterface,要求接口中有一个定义PI的常量以及一个计算圆面积的空方法circleArea()。然后设计一个类circleClass实现该接口,通过构造函数circleClass(double r)定义圆半径,并增加一个显示圆面积的方法。最后,通过上述类生成两个半径分别为3.5、5.0的圆对象circle1、circle2进行测试。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.*;
public class try2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner( System.in);
System.out.println("请输入一个五位整数");
while(true){
String line = sc.nextLine();
try {
int i = line.length();
int num = Integer.parseInt(line);
if (i == 5) {
System.out.println("整数组为" + num);
break;
} else {
System.out.println("请输入5个整数");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
new BigDecimal(line);
System.out.println("录入的是一个小数,请输入整数");
} catch (Exception e1) {
System.out.println("录入的是非法字符数,请输入整数");
}
}
} }
}
编写程序统计一个字符子串在一个字符串中出现的次数和位置。如子字符串”nba”在字符串”asfasfnabasdfnbasdnbasnbasdnbadfasdf”中出现的次数和出现的位置。
public class Practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "asfasfnabaasdfnbasdnbasnbasdnbadfasdf";
String str2 = "nba";
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <= str1.length() - str2.length(); i++) {
if (str2.equals(str1.substring(i, i + 3))) {
count++;
System.out.println(i);
}
}
System.out.print("总共出现了" + count + "次");
}
}
//第二种
public class test1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "asfasfnabaasdfnbasdnbasnbasdnbadfasdf";
int count = 0;
int index = 0;
while (s.indexOf("nba",index)>=0){
index = s.indexOf("nba",index);
count++;
System.out.println("nba位置"+index);
System.out.println(count);
index = index +3;
}
}
}
对字符串”23 10 -8 0 3 7 108″中的数值进行升序排序,生成一个数值有序的字符串”-8 0 3 7 10 23 208″。
import java.util.Arrays;
public class practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="23 10 -8 0 3 7 108";
String[] strArry=str.split(" ");
int[] intArry=new int[strArry.length];
for(int i=0;i<intArry.length;i++){
intArry[i] = Integer.parseInt(strArry[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(intArry);
StringBuilder str2=new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < intArry.length; i++) {
str2.append(intArry[i]);
if(i!=intArry.length-1)
str2.append(" ");
}
System.out.print(str2);
}
}
public class test2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String stringTest="23,10,-8,0,3,7,108";
System.out.println("字符串:"+stringTest);
String[] stringArray=stringTest.split(",");
System.out.println(stringArray.length);
int[] intArray= new int[stringArray.length];
for (int i = 0; i < stringArray.length; i++) {
intArray[i]=Integer.parseInt(stringArray[i]);
}
Arrays.sort(intArray);
StringBuffer str1=new StringBuffer();
for(int i=0;i<intArray.length;i++){
str1.append(intArray[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println("升序后:"+str1);
}
}
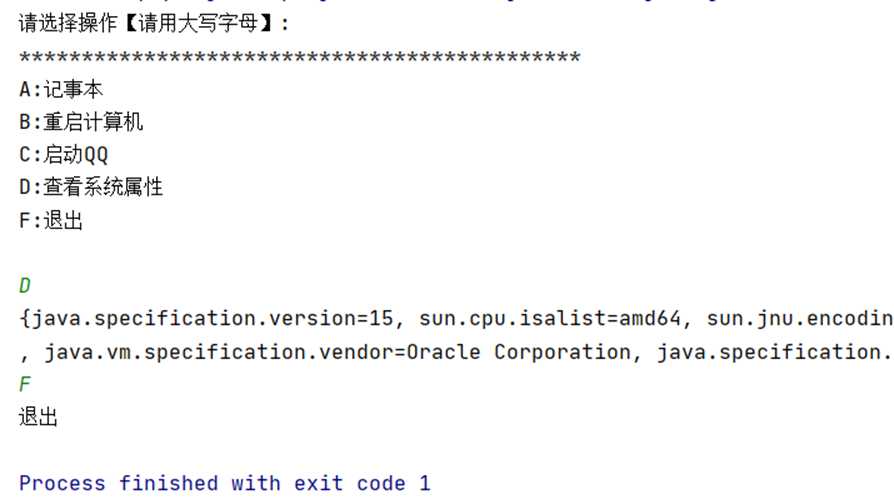
编写一个简单的程序,完成如图下图所示的功能
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class practice3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请选择操作【请用大写字母】:");
System.out.println("*********************************************");
System.out.println("A:记事本");
System.out.println("B:重启计算机");
System.out.println("C:启动QQ");
System.out.println("D:查看系统属性");
System.out.println("F:退出");
Runtime run = Runtime.getRuntime();
while (true) {
String a = sc.next();
switch (a) {
case "A":
try {
run.exec("notepad");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("启动失败");
}
break;
case "B":
try {
run.exec("shutdown -r");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("启动失败");
}
break;
case "C":
try {
run.exec("D:\\Tencent\\QQ\\Bin\\QQScLauncher.exe");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("启动失败");
}
break;
case "D":
Properties pro = System.getProperties();
System.out.println(pro);
break;
case "F":
System.out.println("退出");
System.exit(1);
break;
}
}
}
}
首先将各个指令打印到控制台。程序中需要创建一个集合作为歌曲列表,并向其添加一部分歌曲。由于控制台需要实时等待用户的输入,所以用while(true)来使程序一直处于等待用户输入指令的状态。可以通过Scanner类的nextInt()方法接受来自控制台的信息。可以使用switch语句,根据控制台传入的指令,判断应该执行的操作。通过LinkedList集合定义的方法操作歌曲列表。
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class practice1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList ll = new LinkedList();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("A.添加歌曲到列表");
System.out.println("B.将歌曲置顶");
System.out.println("C.将歌曲前移一位");
System.out.println("D.退出");
System.out.println("初始歌曲集:");
LinkedList ll2=new LinkedList();
ll2.add("关不上的窗-周传雄");
ll2.add("李白-李荣浩");
ll2.add("安和桥-宋东野");
ll2.add("当你老了-赵照");
ll2.add("父亲写的散文诗-李健");
ll2.add("再度重相逢-孙露");
ll2.add("男孩-梁博");
ll2.add("成都-赵雷");
int count=0;
for(count=0;count<8;count++){
System.out.println(count+":"+ll2.get(count));
}
Iterator it = ll.iterator();
while (it.hasNext())
System.out.println(it.next());
while (true) {
System.out.print("请输入要执行的序号[A-D]:");
String a = sc.next();
switch (a) {
case "A":
System.out.print("请输入要添加的歌曲名称:");
String b = sc.next();
count=count+1;
ll2.add(b);
System.out.println("已添加歌曲:" + b);
System.out.println("当前歌曲列表:");
for(count=0;count<ll2.size();count++){
System.out.println(count+":"+ll2.get(count));
}
break;
case "B":
System.out.print("请输入要置顶的歌曲序号:");
int c=sc.nextInt();
ll2.addFirst(ll2.get(c));
ll2.remove(c+1);
System.out.println("已将歌曲" + ll2.get(c)+"置顶");
System.out.println("当前歌曲列表:");
for(count=0;count<ll2.size();count++){
System.out.println(count+":"+ll2.get(count));
}
break;
case "C":
System.out.println("请输入要前移的歌曲序号:");
int d=sc.nextInt();
Object x=ll2.get(d);
ll2.set(d,ll2.get(d-1));
ll2.set(d-1,x);
System.out.println("已将歌曲" + ll2.get(d-1) +"前移");
System.out.println("当前歌曲列表:");
for(count=0;count<ll2.size();count++){
System.out.println(count+":"+ll2.get(count));
}
break;
case "D":
System.out.println("----------------------退出----------------------");
System.out.println("您以退出系统");
break;
}
}
}
}
请使用Map实现获取字符串“bwaerbctyxbacecrtdcvr”
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class practice2_1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str="bwaerbctyxbacecrtdcvr";
char[] arr=str.toCharArray();
int count=0;
Map<Character, Integer> tree=new TreeMap<Character,Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++)
{
if(tree.get(arr[i])==null) {
tree.put(arr[i], 1);
}
else{
count=tree.get(arr[i]);
tree.put(arr[i],++count);
count=0;
}
}
tree.forEach((key,value)-> System.out.print(key+"("+value+")"));
}
}
用AWT和布局管理器设计如右图所示调色板界面。
import java.awt.*;
public class practice1_2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame f = new Frame("调色板");
f.setSize(600, 500);
f.setLocation(300, 200);
f.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1, 10, 20));
Panel p1 = new Panel();
Panel p2 = new Panel();
p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 4, 20, 20));
Label red = new Label("RED",Label.CENTER);
red.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG, Font.BOLD, 20));
red.setBackground(Color.red);
Button bt1=new Button("+");
bt1.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
TextField t1=new TextField("220");
t1.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,50));
Button bt5=new Button("-");
bt5.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
p1.add(red);
p1.add(bt1);
p1.add(t1);
p1.add(bt5);
Label green=new Label("GREEN",Label.CENTER);
green.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
green.setBackground(Color.green);
Button bt2=new Button("+");
bt2.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
TextField t2=new TextField("220");
t2.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,50));
Button bt6=new Button("-");
bt6.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
p1.add(green);
p1.add(bt2);
p1.add(t2);
p1.add(bt6);
Label blue=new Label("BLUE",Label.CENTER);
blue.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
blue.setBackground(Color.blue);
Button bt3=new Button("+");
bt3.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
TextField t3=new TextField("220");
t3.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,50));
Button bt7=new Button("-");
bt7.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
p1.add(blue);
p1.add(bt3);
p1.add(t3);
p1.add(bt7);
p2.setBackground(new Color(217, 80, 224));
f.add(p1);
f.add(p2);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
利用Swing包创建一个窗口,窗口位置为(220,160)、大小为320×240,并在窗口(20,80)、(120,80)、(220,80)处各安置一个按钮,按钮大小为80×40
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
public class practice2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jf=new JFrame();
jf.getContentPane().setBackground(new Color(15,217,245));
jf.setSize(320,240);
jf.setLocation(220,160);
jf.setLayout(null);
JButton j1=new JButton("红色");
j1.setBounds(20,80,80,40);
j1.setBackground(Color.red);
jf.add(j1);
JButton j2=new JButton("绿色");
j2.setBounds(120,80,80,40);
j2.setBackground(Color.green);
jf.add(j2);
JButton j3=new JButton("蓝色");
j3.setBounds(220,80,80,40);
j3.setBackground(Color.blue);
jf.add(j3);
jf.setVisible(true);
}
}
//用AWT和布局管理器设计如右图所示调色板界面。
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class practice1 {
int r,g,b;
public void practice1(){
Frame f = new Frame("调色板");
f.setSize(600, 500);
f.setLocation(300, 200);
f.setLayout(new GridLayout(2, 1, 10, 20));
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
@Override
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
Panel p1 = new Panel();
Panel p2 = new Panel();
p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 4, 20, 20));
TextField t1=new TextField("255");
t1.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,50));
TextField t2=new TextField("255");
t2.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,50));
TextField t3=new TextField("255");
t3.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,50));
r=Integer.parseInt(t1.getText());
g=Integer.parseInt(t2.getText());
b=Integer.parseInt(t3.getText());
Label red = new Label("RED",Label.CENTER);
red.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG, Font.BOLD, 20));
red.setBackground(Color.red);
Button bt1=new Button("+");
bt1.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
bt1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(r>=255)
r=0;
else
r++;
t1.setText(r+"");
p2.setBackground(new Color(r,g,b));
}
});
Button bt5=new Button("-");
bt5.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int r=Integer.parseInt(t1.getText());
if(r<=0)
r=255;
else
r--;
t1.setText(r+"");
p2.setBackground(new Color(r,g,b));
}
});
bt5.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
p1.add(red);
p1.add(bt1);
p1.add(t1);
p1.add(bt5);
Label green=new Label("GREEN",Label.CENTER);
green.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
green.setBackground(Color.green);
Button bt2=new Button("+");
bt2.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
bt2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(g>=255)
g=0;
else
g++;
t2.setText(g+"");
p2.setBackground(new Color(r,g,b));
}
});
Button bt6=new Button("-");
bt6.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
bt6.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int r=Integer.parseInt(t1.getText());
if(g<=0)
g=255;
else
g--;
t2.setText(g+"");
p2.setBackground(new Color(r,g,b));
}
});
p1.add(green);
p1.add(bt2);
p1.add(t2);
p1.add(bt6);
Label blue=new Label("BLUE",Label.CENTER);
blue.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
blue.setBackground(Color.blue);
Button bt3=new Button("+");
bt3.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
bt3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(b>=255)
b=0;
else
b++;
t3.setText(b+"");
p2.setBackground(new Color(r,g,b));
}
});
Button bt7=new Button("-");
bt7.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,20));
bt7.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int r=Integer.parseInt(t1.getText());
if(b<=0)
b=255;
else
b--;
t3.setText(b+"");
p2.setBackground(new Color(r,g,b));
}
});
p1.add(blue);
p1.add(bt3);
p1.add(t3);
p1.add(bt7);
p2.setBackground(new Color(r, g, b));
f.add(p1);
f.add(p2);
f.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
practice1 p=new practice1();
p.practice1();
}
}
//利用Swing包创建一个窗口,窗口位置为(220,160)、大小为320×240,并在窗口(20,80)、(120,80)、(220,80)处各安置一个按钮,按钮大小为80×40。点击左按钮将窗口背景的红色分量增加10,点击中间按钮将窗口背景的绿色分量增加10,点击右按钮将窗口背景的蓝色分量增加10,上述三种分量大于255时变成0,下面面板的颜色同步改变,三种颜色初始值都为5,点击窗口关闭按钮时退出程序运行
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
public class practice2 {
JFrame f;
int r,g,b;
JButton bt1,bt2,bt3;
public void practice2(){
r=5;g=5;b=5;
f=new JFrame();
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setBounds(220,160,320,240);
Container cont=f.getContentPane();
cont.setBackground(new Color(r,g,b));
f.setLayout(null);
bt1=new JButton("红色");
bt1.setBackground(Color.red);
bt1.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG, Font.BOLD, 15));
bt1.setBounds(20,80,80,40);
bt1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(r>=255)
r=0;
else
r+=10;
cont.setBackground(new Color(r,g,b));
}
});
bt2=new JButton("绿色");
bt2.setBackground(Color.GREEN);
bt2.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG, Font.BOLD, 15));
bt2.setBounds(120,80,80,40);
bt2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(g>=255)
g=0;
else
g+=10;
cont.setBackground(new Color(r,g,b));
}
});
bt3=new JButton("蓝色");
bt3.setBackground(Color.blue);
bt3.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG, Font.BOLD, 15));
bt3.setBounds(220,80,80,40);
bt3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
if(b>=255)
b=0;
else
b+=10;
cont.setBackground(new Color(r,g,b));
}
});
f.add(bt1);f.add(bt2);f.add(bt3);
f.setVisible(true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
practice2 test=new practice2();
test.practice2();
}
}
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.util.Stack;
import javax.swing.*;
class MyException extends Exception{
public MyException() {
super();
}
public MyException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
class SwingConsole{
public static void run(final JFrame f,final int width,final int height){
SwingUtilities.invokeLater(new Runnable(){
public void run(){
JMenuBar mb;
JMenu m1,m2,m3;
f.setTitle("计算器");
f.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
f.setSize(width,height);
f.setVisible(true);
mb=new JMenuBar();
m1=new JMenu("查看(V)");
m1.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,15));
m2=new JMenu("编辑(E)");
m2.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,15));
m3=new JMenu("帮助(H)");
m3.setFont(new Font(Font.DIALOG,Font.BOLD,15));
mb.add(m1);mb.add(m2);mb.add(m3);
f.setJMenuBar(mb);
}
});
}
}
class MyCalculator extends JFrame{
private JTextField textField;
private String input;
private String operator;
public MyCalculator() {
input = "";
operator = "";
Container container = this.getContentPane();
JPanel panel = new JPanel();
textField = new JTextField(30);
textField.setHorizontalAlignment(JTextField.LEFT);
textField.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(200,30));
container.add(textField, BorderLayout.NORTH);
String[] name= {"7","8","9","+","4","5","6","-","1","2","3","*","0","C","=","/"};
panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4,4,1,1));
for(int i=0;i<name.length;i++) {
JButton button = new JButton(name[i]);
button.addActionListener(new MyActionListener());
panel.add(button);
}
container.add(panel,BorderLayout.CENTER);
}
class MyActionListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int cnt=0;
String actionCommand = e.getActionCommand();
if(actionCommand.equals("+") || actionCommand.equals("-") || actionCommand.equals("*")
|| actionCommand.equals("/")) {
input += " " + actionCommand + " ";
}
else if(actionCommand.equals("C")) {
input = "";
}
else if(actionCommand.equals("=")) {
try {
input+= "="+calculate(input);
} catch (MyException e1) {
if(e1.getMessage().equals("Infinity"))
input+= "=" + e1.getMessage();
else
input = e1.getMessage();
}
textField.setText(input);
input="";
cnt = 1;
}
else
input += actionCommand;
if(cnt == 0)
textField.setText(input);
}
}
private String calculate(String input) throws MyException{
String[] comput = input.split(" ");
Stack<Double> stack = new Stack<>();
Double m = Double.parseDouble(comput[0]);
stack.push(m);
for(int i = 1; i < comput.length; i++) {
if(i%2==1) {
if(comput[i].equals("+"))
stack.push(Double.parseDouble(comput[i+1]));
if(comput[i].equals("-"))
stack.push(-Double.parseDouble(comput[i+1]));
if(comput[i].equals("*")) {
Double d = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
stack.push(d*Double.parseDouble(comput[i+1]));
}
if(comput[i].equals("/")) {
double help = Double.parseDouble(comput[i+1]);
if(help == 0)
throw new MyException("Infinity");
double d = stack.peek();
stack.pop();
stack.push(d/help);
}
}
}
double d = 0d;
while(!stack.isEmpty()) {
d += stack.peek();
stack.pop();
}
String result = String.valueOf(d);
return result;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SwingConsole.run(new MyCalculator(), 250, 300);
}
}
设计出如图所示Windows操作系统附带的小应用-计算器样式的简单计算器。(只需要实现简单的加减乘除功能。菜单内容和样式如同系统自带计算器,但功能只需实现退出系统功能。) |
今天的文章Java实验报告分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读,如果确实帮到您,您可以动动手指转发给其他人。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/33707.html