背景
今天遇到了一个问题, 在写上采样 upsample的时候到底 align_corners 设为true 还是false
talk is cheap
按照pytorch doc 中的示例:
>>> input = torch.arange(1, 5, dtype=torch.float32).view(1, 1, 2, 2)
>>> input
tensor([[[[ 1., 2.],
[ 3., 4.]]]])
>>> m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
>>> m(input)
tensor([[[[ 1., 1., 2., 2.],
[ 1., 1., 2., 2.],
[ 3., 3., 4., 4.],
[ 3., 3., 4., 4.]]]])
>>> m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear') # align_corners=False
>>> m(input)
tensor([[[[ 1.0000, 1.2500, 1.7500, 2.0000],
[ 1.5000, 1.7500, 2.2500, 2.5000],
[ 2.5000, 2.7500, 3.2500, 3.5000],
[ 3.0000, 3.2500, 3.7500, 4.0000]]]])
>>> m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
>>> m(input)
tensor([[[[ 1.0000, 1.3333, 1.6667, 2.0000],
[ 1.6667, 2.0000, 2.3333, 2.6667],
[ 2.3333, 2.6667, 3.0000, 3.3333],
[ 3.0000, 3.3333, 3.6667, 4.0000]]]])
>>> # Try scaling the same data in a larger tensor
>>>
>>> input_3x3 = torch.zeros(3, 3).view(1, 1, 3, 3)
>>> input_3x3[:, :, :2, :2].copy_(input)
tensor([[[[ 1., 2.],
[ 3., 4.]]]])
>>> input_3x3
tensor([[[[ 1., 2., 0.],
[ 3., 4., 0.],
[ 0., 0., 0.]]]])
>>> m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear') # align_corners=False
>>> # Notice that values in top left corner are the same with the small input (except at boundary)
>>> m(input_3x3)
tensor([[[[ 1.0000, 1.2500, 1.7500, 1.5000, 0.5000, 0.0000],
[ 1.5000, 1.7500, 2.2500, 1.8750, 0.6250, 0.0000],
[ 2.5000, 2.7500, 3.2500, 2.6250, 0.8750, 0.0000],
[ 2.2500, 2.4375, 2.8125, 2.2500, 0.7500, 0.0000],
[ 0.7500, 0.8125, 0.9375, 0.7500, 0.2500, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]]])
>>> m = nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
>>> # Notice that values in top left corner are now changed
>>> m(input_3x3)
tensor([[[[ 1.0000, 1.4000, 1.8000, 1.6000, 0.8000, 0.0000],
[ 1.8000, 2.2000, 2.6000, 2.2400, 1.1200, 0.0000],
[ 2.6000, 3.0000, 3.4000, 2.8800, 1.4400, 0.0000],
[ 2.4000, 2.7200, 3.0400, 2.5600, 1.2800, 0.0000],
[ 1.2000, 1.3600, 1.5200, 1.2800, 0.6400, 0.0000],
[ 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000, 0.0000]]]])
具体区别呢?
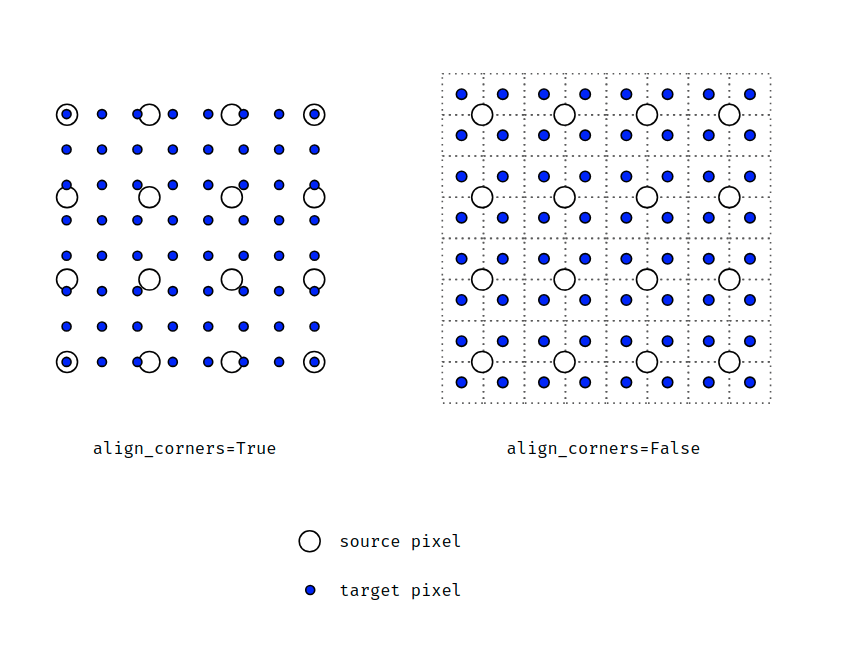
查找pytorch论坛得图
- 当**align_corners = True**时,像素被视为网格的格子上的点,拐角处的像素对齐.可知是点之间是等间距的
- 当**align_corners = False**时, 像素被视为网格的交叉线上的点, 拐角处的点依然是原图像的拐角像素,但是差值的点间却按照上图的取法取,导致点与点之间是不等距的
今天的文章pytorch 上采样 upsample 时align_corners 设为true 还是false分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/5891.html