前言
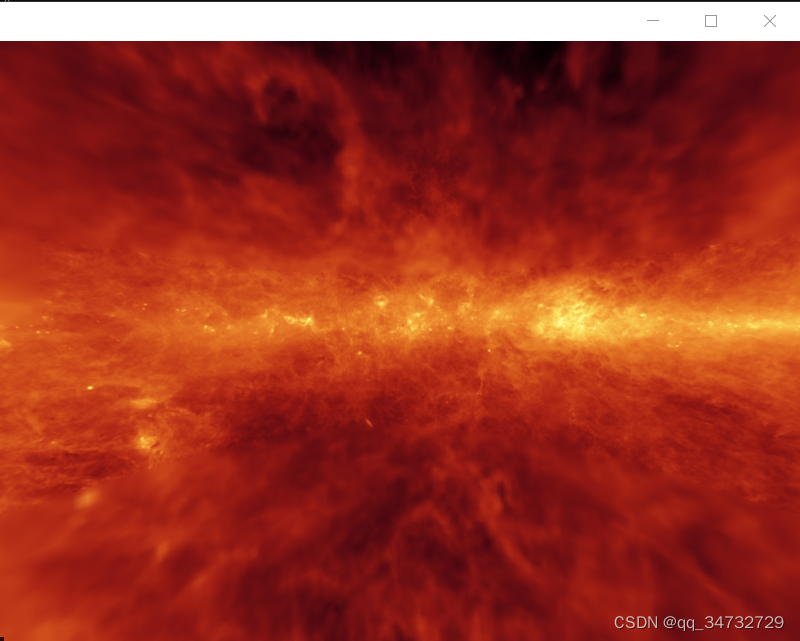
本示例分析osgearth操作深空场景,或者是银河系场景,可以想象人拿着相机站在地球表面上观看天空/银河系的场景。
重点是相机操作器的使用。
在命令框输入执行程序,在data路径下有加载的图,且被写入了earth文件。
// 两个文件仅加载图片不同
osgearth_skyviewd.exe ..\..\..\tests\skyview1.earth
osgearth_skyviewd.exe ..\..\..\tests\skyview2.earth运行结果
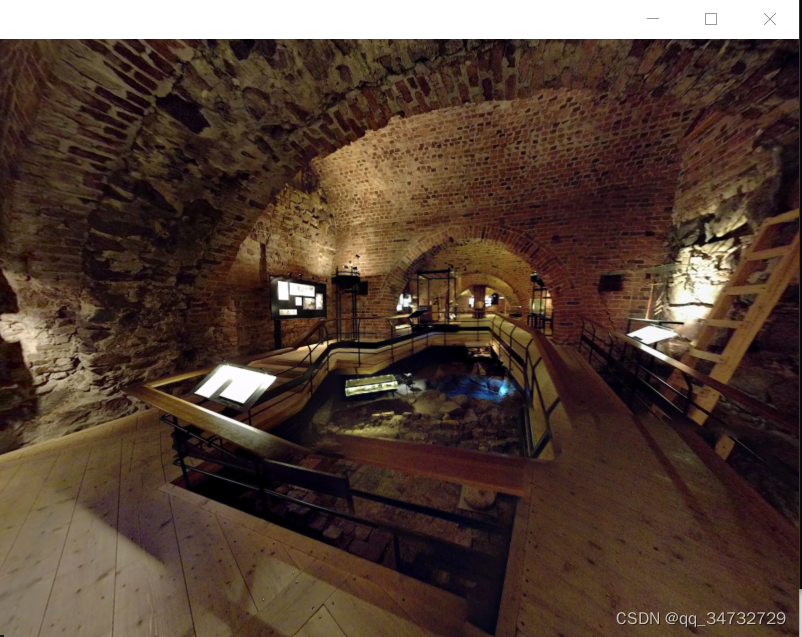
天球场景。
第三幅图,特别像带VR眼镜,周围可以看到不同的场景,相机此时像站在十字路口,看周围的场景。
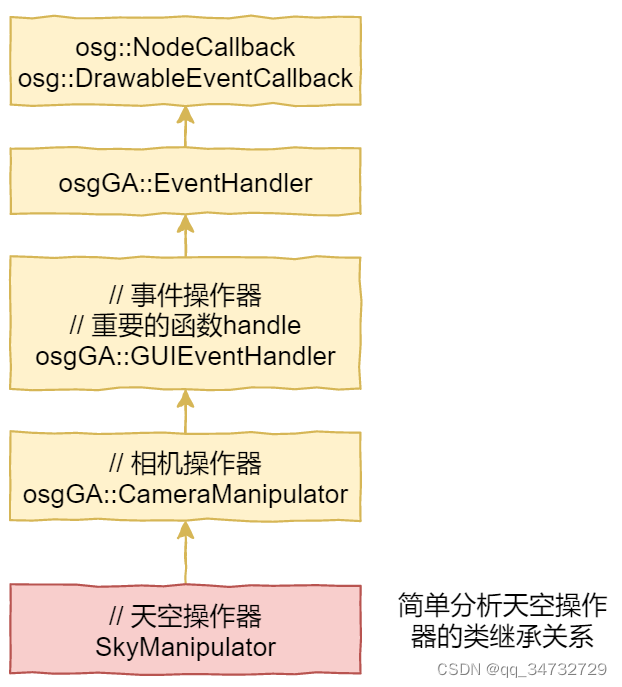
类分析
重点就是处理handle的操作器。下面4个函数,必须要重写。
virtual void setByMatrix(const osg::Matrixd& matrix);
virtual void setByInverseMatrix(const osg::Matrixd& matrix);
virtual osg::Matrixd getMatrix() const;
virtual osg::Matrixd getInverseMatrix() const;代码分析
仅将操作器的实现文件和主程序文件拷贝到此处。
osgearth_skyview.cpp文件
#include <osgViewer/Viewer>
#include <osg/CullFace>
#include <osgEarth/Notify>
#include <osgEarthUtil/ExampleResources>
#include "SkyManipulator"
#define LC "[viewer] "
using namespace osgEarth;
using namespace osgEarth::Util;
int
usage(const char* name)
{
OE_NOTICE
<< "\nUsage: " << name << " file.earth" << std::endl
<< MapNodeHelper().usage() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
int
main(int argc, char** argv)
{
osg::ArgumentParser arguments(&argc,argv);
// help?
if ( arguments.read("--help") )
return usage(argv[0]);
// Increase the fov to provide a more immersive experience.
// 增加fov值以提供更沉浸的体验。vfov:视野(Field of View),通常设置45度
// 如果想要一个末日风格的结果,可以将其设置一个更大的值
float vfov = 100.0f;
arguments.read("--vfov", vfov); // 也可以支持命令行输入
// create a viewer:
osgViewer::Viewer viewer(arguments);
// Tell the database pager to not modify the unref settings 不修改任何设置
viewer.getDatabasePager()->setUnrefImageDataAfterApplyPolicy( false, false );
// thread-safe initialization of the OSG wrapper manager. Calling this here
// prevents the "unsupported wrapper" messages from OSG
// 获取 图片 包装管理器
osgDB::Registry::instance()->getObjectWrapperManager()->findWrapper("osg::Image");
// disable the small-feature culling
viewer.getCamera()->setSmallFeatureCullingPixelSize(-1.0f);
// set a near/far ratio that is smaller than the default. This allows us to get
// closer to the ground without near clipping. If you need more, use --logdepth
viewer.getCamera()->setNearFarRatio(0.0001);
if ( vfov > 0.0 )
{
double fov, ar, n, f;
viewer.getCamera()->getProjectionMatrixAsPerspective(fov, ar, n, f);// 获取到透视矩阵的各个参数
viewer.getCamera()->setProjectionMatrixAsPerspective(vfov, ar, n, f);// 重新设置透视矩阵的各个参数
}
// load an earth file, and support all or our example command-line options
// and earth file <external> tags
osg::Node* node = MapNodeHelper().load( arguments, &viewer );
//Set our custom manipulator
viewer.setCameraManipulator(new SkyManipulator());// 天空的操作器,继承自osgGA::CameraManipulator的操作器
//viewer.setCameraManipulator( new osgGA::FirstPersonManipulator() );
if ( node )
{
// Disable backface culling
node->getOrCreateStateSet()->setMode(GL_CULL_FACE, osg::StateAttribute::OFF | osg::StateAttribute::OVERRIDE);
viewer.setSceneData( node );
while(!viewer.done())
{
viewer.frame();
}
}
else
{
return usage(argv[0]);
}
}
SkyManipulator.cpp 文件
#include "SkyManipulator"
#include <iostream>
SkyManipulator::SkyManipulator():
_heading(0.0), // 偏航角
_pitch(0.0), // 俯仰角
_distance(1.0),// 距离
_prevX(FLT_MAX),// 初始(X, Y) 坐标点值
_prevY(FLT_MAX)
{
}
void SkyManipulator::setByMatrix(const osg::Matrixd& matrix)
{
}
void SkyManipulator::setByInverseMatrix(const osg::Matrixd& matrix)
{
}
osg::Matrixd SkyManipulator::getMatrix() const
{
osg::Quat rot = getRotation();
return osg::Matrixd::translate(0,0,-_distance) *
osg::Matrixd::rotate(rot);
}
osg::Matrixd SkyManipulator::getInverseMatrix() const
{
return osg::Matrixd::inverse(getMatrix());
}
bool SkyManipulator::handle(const osgGA::GUIEventAdapter& ea, osgGA::GUIActionAdapter& aa)
{
double maxDistance = osg::WGS_84_RADIUS_EQUATOR;// 地球(赤道/长)半径
if (ea.getEventType() == osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::SCROLL)
{
double speed = 0.1;
double diff = (maxDistance - _distance) * speed;
if (ea.getScrollingMotion() == osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::SCROLL_UP)
{
_distance += diff; // 滚轮向上
}
else
{
_distance -= diff; // 滚轮向下
}
_distance = osg::clampBetween(_distance, 0.0, maxDistance);
return true;
}
else if (ea.getEventType() == osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::DRAG)// 拖拽
{
if (_prevX != FLT_MAX && _prevY != FLT_MAX)
{
float dx = ea.getX() - _prevX;
float dy = ea.getY() - _prevY;
double maxSpeed = osg::PI * 2.0 / 300.0;
double minSpeed = osg::PI * 2.0 / 30000.0;
// _distance距离较远时,速度大;_distance距离较近时,速度减小
double speed = minSpeed + (1.0 - _distance / maxDistance) * (maxSpeed - minSpeed);
_heading -= dx * speed;
_pitch -= dy * speed;
}
_prevX = ea.getX();
_prevY = ea.getY();
return true;
}
else if (ea.getEventType() == osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::PUSH)// 获取坐标位置
{
_prevX = ea.getX();
_prevY = ea.getY();
}
else if (ea.getEventType() == osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::RELEASE)//释放鼠标后,两个点位置还原
{
_prevX = FLT_MAX;
_prevY = FLT_MAX;
}
else if (ea.getEventType() == osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::KEYDOWN)
{
if (ea.getKey()== osgGA::GUIEventAdapter::KEY_Space)// 空格键,回到home位置
{
home(0.0);
}
}
return false;
}
// 得到旋转角
osg::Quat SkyManipulator::getRotation() const
{
osg::Quat azim_q ( _heading, osg::Vec3d(0,0,1) );
osg::Quat pitch_q( -_pitch-osg::PI_2, osg::Vec3d(1,0,0) );
osg::Matrix newRot = osg::Matrixd( azim_q * pitch_q );
return osg::Matrixd::inverse(newRot).getRotate();
}
void
SkyManipulator::home(double unused)
{
_heading = 0.0;
_pitch = 0.0;
_distance = 0.0;
}
void
SkyManipulator::home(const osgGA::GUIEventAdapter& ,osgGA::GUIActionAdapter& us)
{
home( 0.0 );
us.requestRedraw();
}今天的文章osgEarth示例分析——osgearth_skyview分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/63084.html