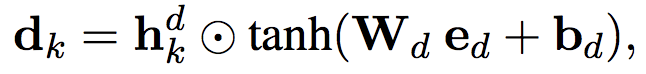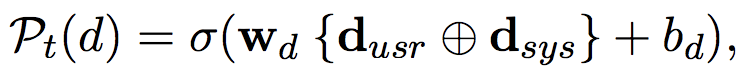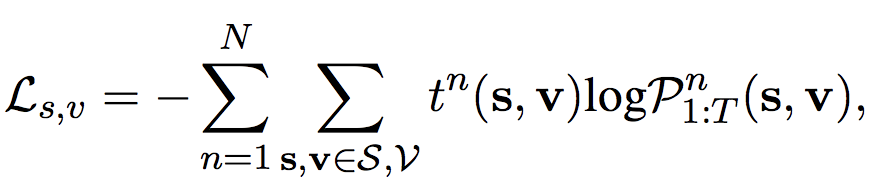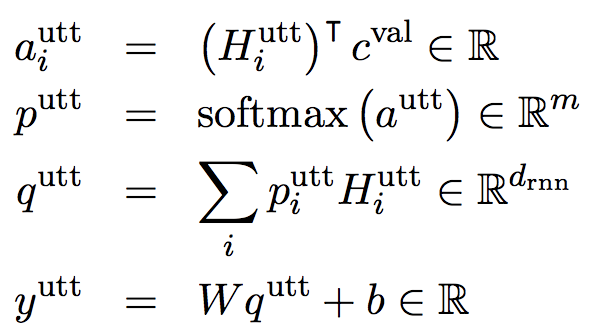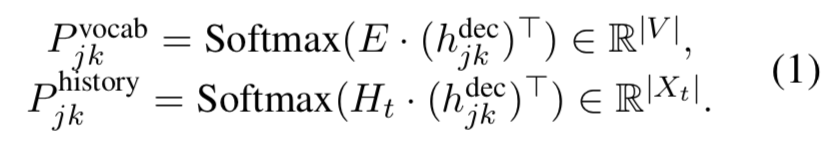DST的大多数模型是 u t u_t ut、 a n − 1 a_{n-1} an−1(或者 r t − 1 r_{t-1} rt−1)、 s l o t n − 1 slot_{n-1} slotn−1共同作为输入,判断某一个slot的value情况。本文选取18-19年几个效果较好的模型进行学习。
Large-Scale Multi-Domain Belief Tracking with Knowledge Sharing
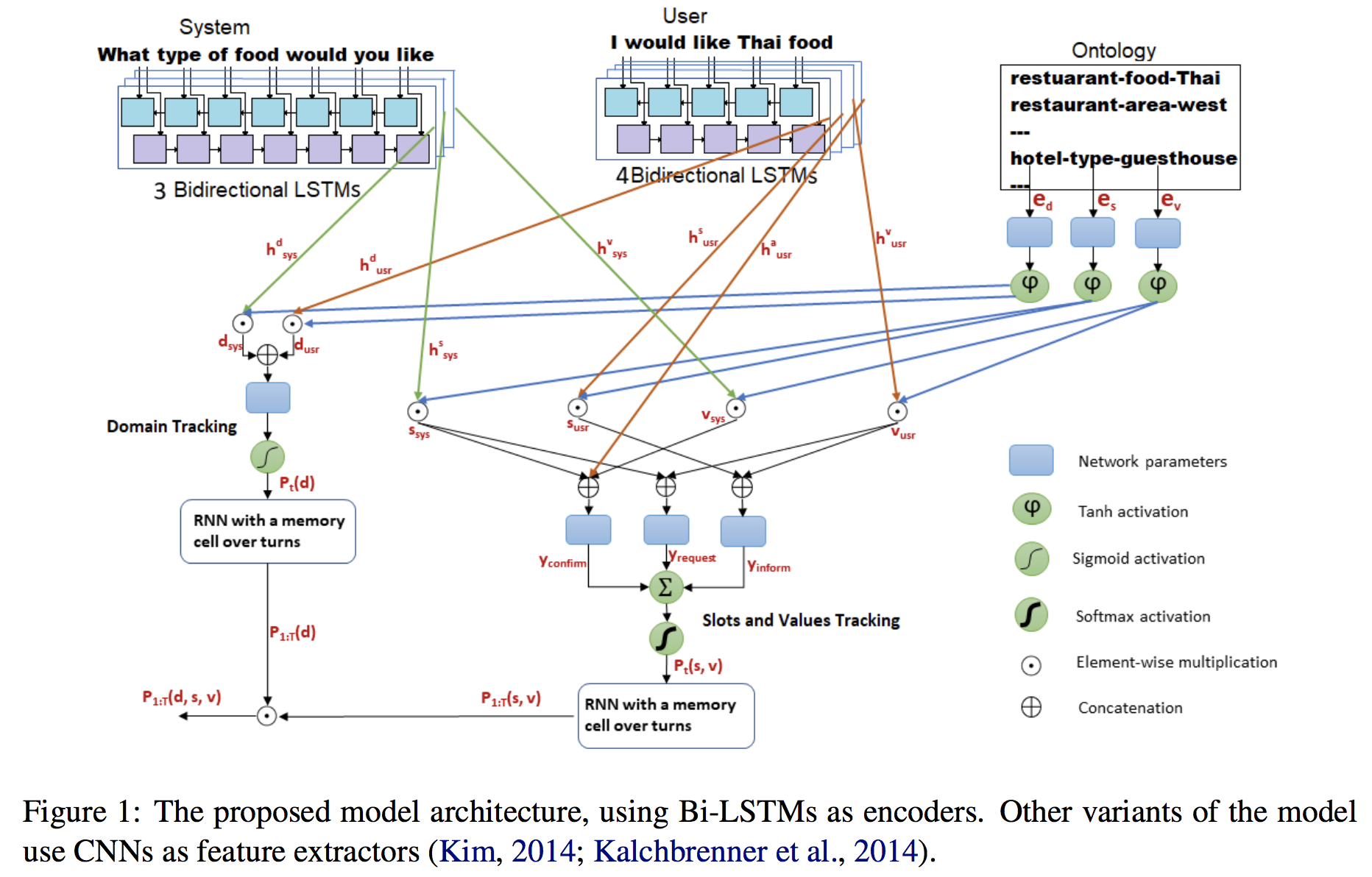
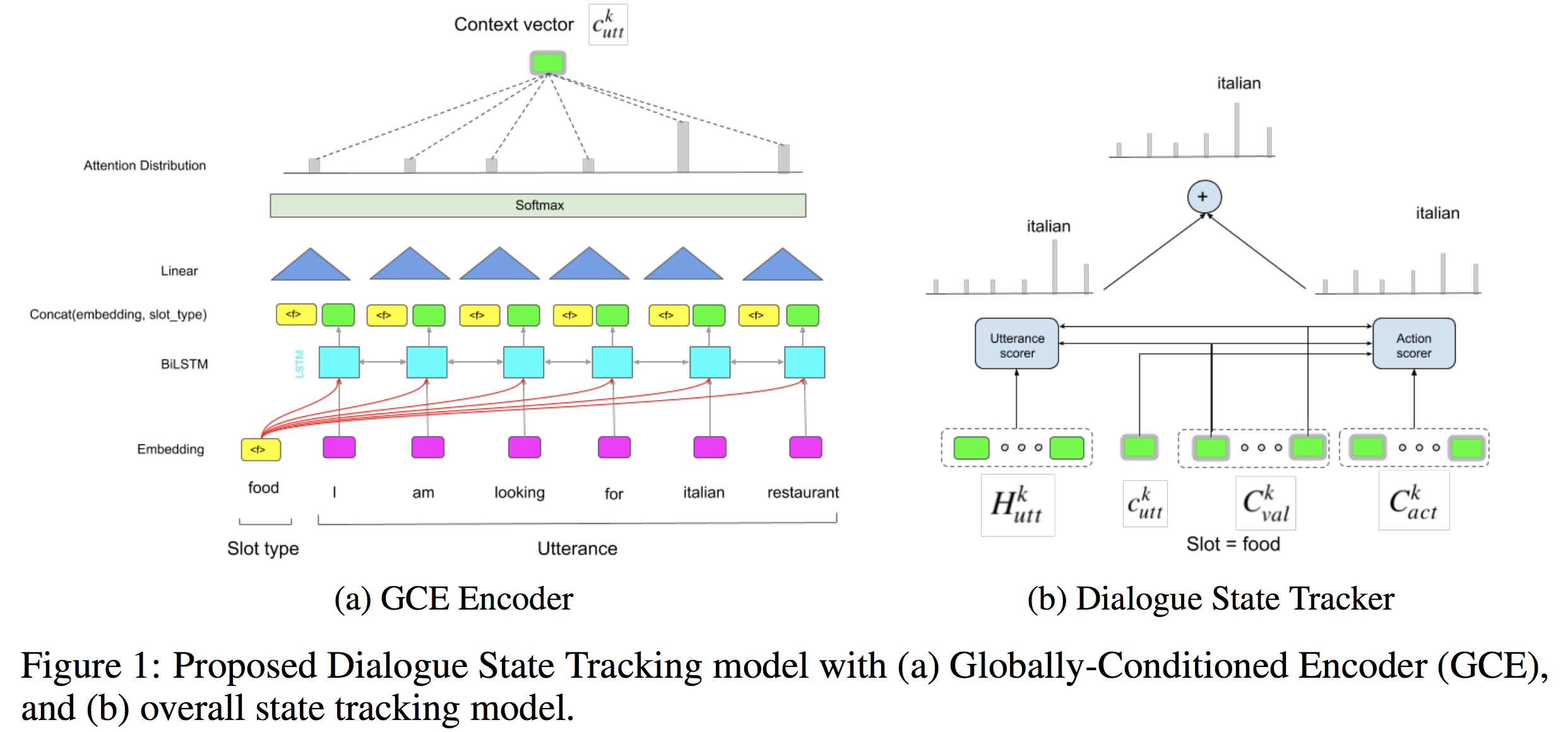
System经过三个lstm,分别提取关于slot的domain、type、value信息,
User经过四个lstm,分别提取关于slot的domain、type、value、affirm信息
(affirm代表的是User中没有slot的直接信息,是回应上一轮system,比如Would you like free parking?’, the user can either affirm positively or negatively
Ontology(整个slot的数据库)中每个选项的domain、type、value分别进行embedding,
之后进行运算
左边的domain tracking

(element-wise multiplication is used as a similarity metric)(把d换成slot的s,value 的v是一样的,如下)
右边type_value追踪,分成是三个部分,
1)Inform-’I am looking for a restaurant that serves Turkish food’
2)Request-’When do you want the taxi to arrive?’ and the user answers with ’19:30’.
3)Confirm-’Would you like free parking?’, Yes/No
Inform是 s u s r 、 v u s r s_{usr}、v_{usr} susr、vusr进行计算,Request是 s s y s 、 v u s r s_{sys}、v_{usr} ssys、vusr计算,Confirm是 s s y s 、 v s y s 、 h u s r a s_{sys}、v_{sys}、h_{usr}^{a} ssys、vsys、husra计算得到( h u s r a h_{usr}^{a} husra是上面usr的4th个lstm得到)
RNN with a memory cell over turns,是引入简单的memory机制,
最终 P 1 : T ( d , s , v ) = P 1 : T ( d ) P 1 : T ( s , v ) P_{1:T}(d,s,v)=P_{1:T}(d)P_{1:T}(s,v) P1:T(d,s,v)=P1:T(d)P1:T(s,v)
优化目标:
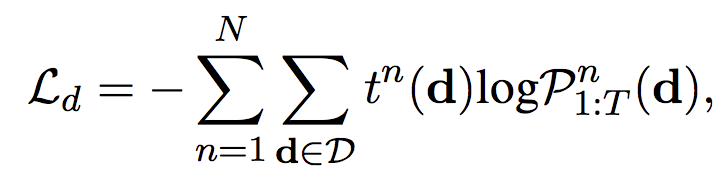
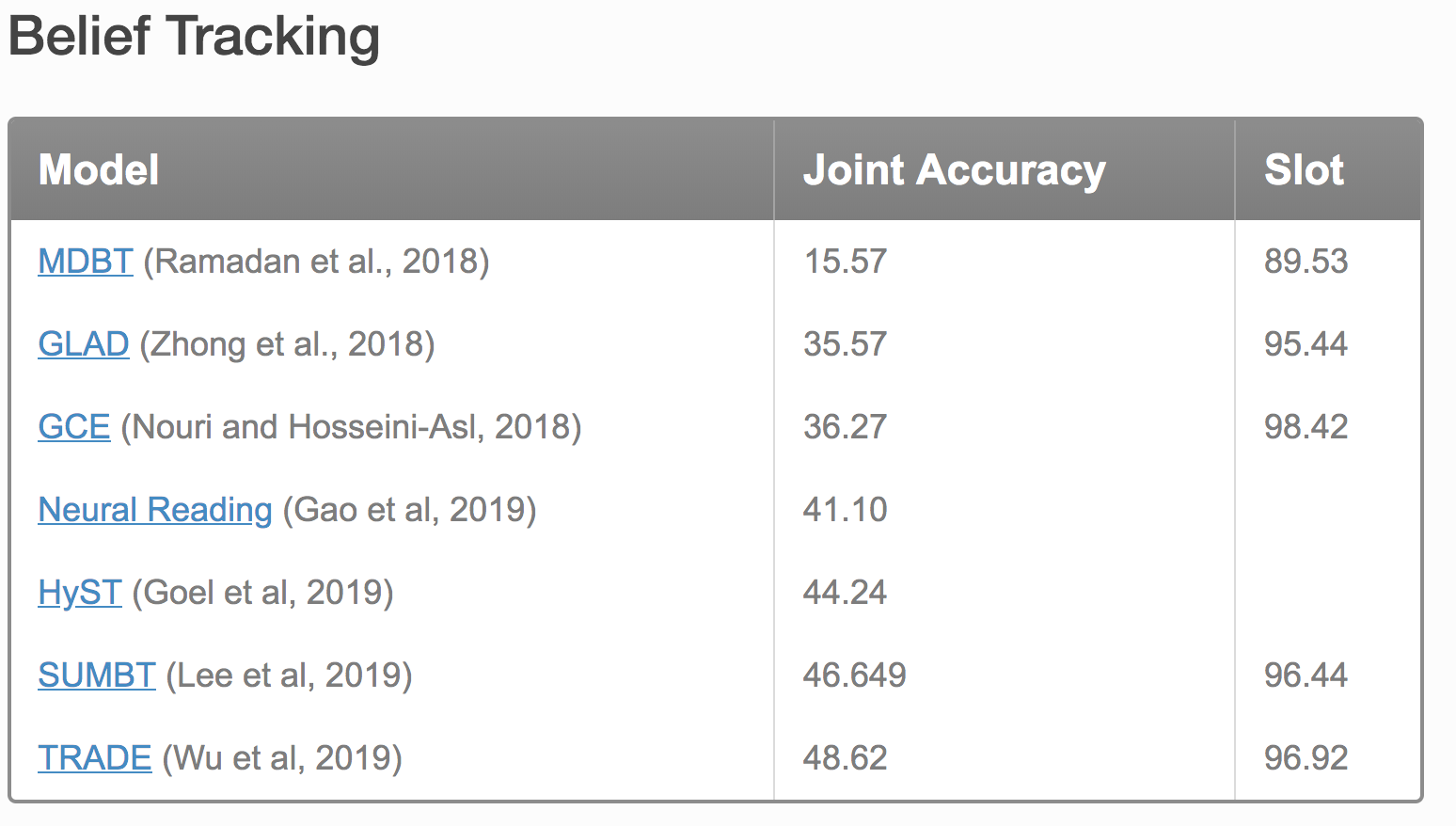
思考: 这个模型比较复杂,看起来也考虑的比较周到,但是效果相比而言不是很好。图表中数据是TRADE的模型复现的,实验设定和ontology等发生变化。
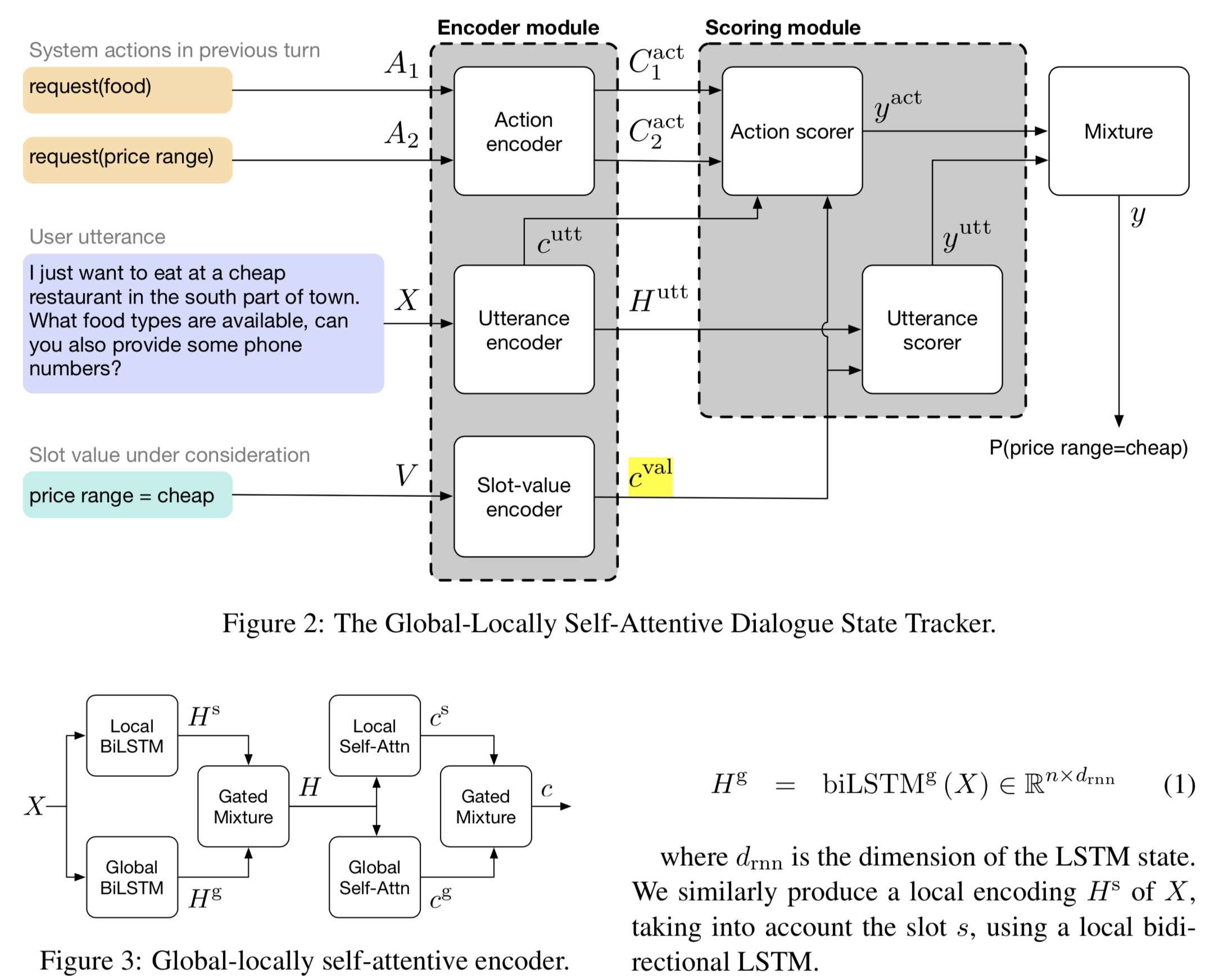
Global-Locally Self-Attentive Dialogue State Tracker
global-local的文章最近被用的很多。
主要创新点:Encoder中的global_LSTM和Local_LSTM, 个人觉得非常简单,他只是采用多一个lstm,参数变多从而获取了更多信息,解释性不强。文中解释为:model rare slot-value pairs by sharing parameters between each slot through global modules and learning slot-specific features through local modules
入分为了 a c t n − 1 ( 包 含 了 s l o t 信 息 ) act_{n-1}(包含了slot信息) actn−1(包含了slot信息)和 u s r n {usr}_{n} usrn,候选集中的某一项slot-value,分别对他们encode处理得到对应的context和hidden(句子长度个向量)。
之后,
Action scorer和Utterance scorer:
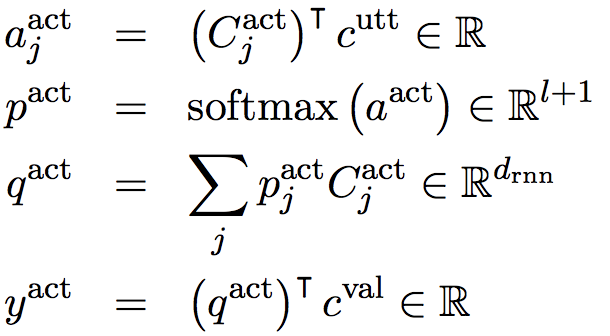
action scorer的前三步是为了计算出一个和utterance有关的综合act表示。Action scorer和Utterance scorer的计算过程不太一样,后者用到了 H i u t t H_{i}^{utt} Hiutt。最终的 y y y是 y a c t 、 y u t t y_{act}、y_{utt} yact、yutt的简单加权,表示该slot-value的概率。
Toward Scalable Neural Dialogue State Tracking Model
以前的方法GLAD,utterance representation 加入了slot values (candidate sets) and slot type。本方法值使用slot type。
论证:
(1)limitation of GLAD encoder in using slot-specific recurrent and self-attention layers in their encoders
(2)improving the latency and speed of inference by remving the
inefficient recurrent layers and self-attention layers, without degrading the performance。
(b)dialogue state tracker:
左边,user,value set输入,user对value的影响。
右边,user,value set,act_prev输入,action对value的影响
计算方式基本和GLAD相同。
题目关键词scalable阐释:没提多少次,文中说对比以前的模型去掉多余的层。
主要是改善了latency和inference time。
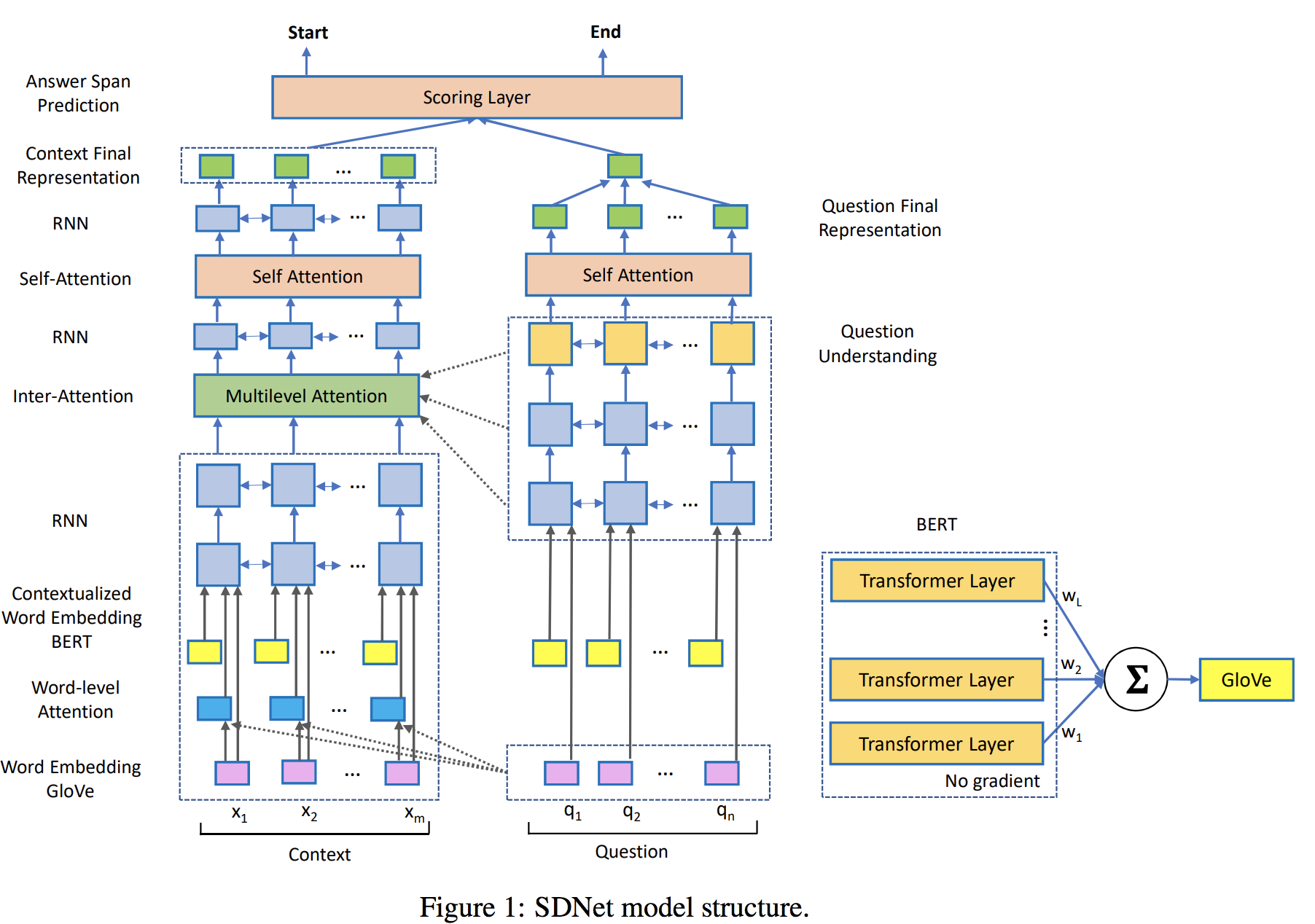
Dialog State Tracking: A Neural Reading Comprehension Approach
借鉴SDNET: CONTEXTUALIZED ATTENTION-BASED DEEP
NETWORK FOR CONVERSATIONAL QUESTION ANSWERING,大力出奇迹,如下
本文模型:
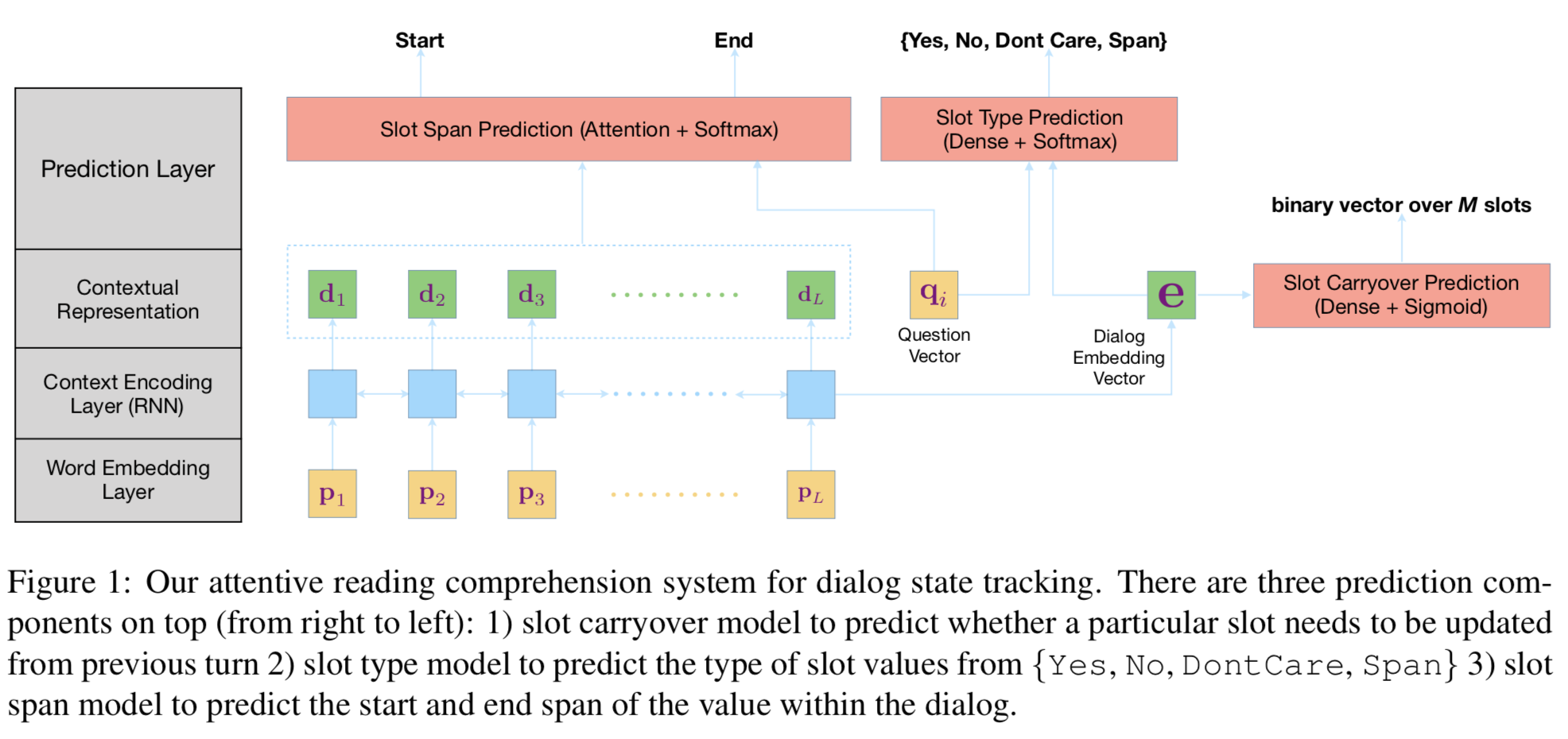
(1)把问题细分的非常厉害,Slot Carryover Prediction Model,是否与之前的belief state相同(以前有类似做法);Slot type Prediction model;Slot span Prediction model.
(2)不太明白slot type中的yes,no,的含义,
(3)需要自己生成question,作为q的输入,
(4)p1,p2,,pL,是到t轮的全部语句单词,user和agent之间会用[u]和[a]作为区分,使用bert为word embedding,而输入到lstm中,而不是直接bert encoder,没有给出原因,可能是lstm反而照顾后面的结果,而bert是整个句子每个单词都attention。
(4)
- 目前大多数模型是输出概率分布。本文将DST问题化为阅读理解(RC)问题,之前有类似模型是判断start和end(但是没有和RC结合), 主要是它设计了question这样说成阅读理解名正言顺,确实阅读理解里简单的单词问答应该很容易。但是question还要经过lstm进行解析,我认为是多此一举,直接输入slot本身不就可以了?question的表述what is the value for slot i?没有任何提示性和信息
思考:模型产生多个start-end选项,增加参数,
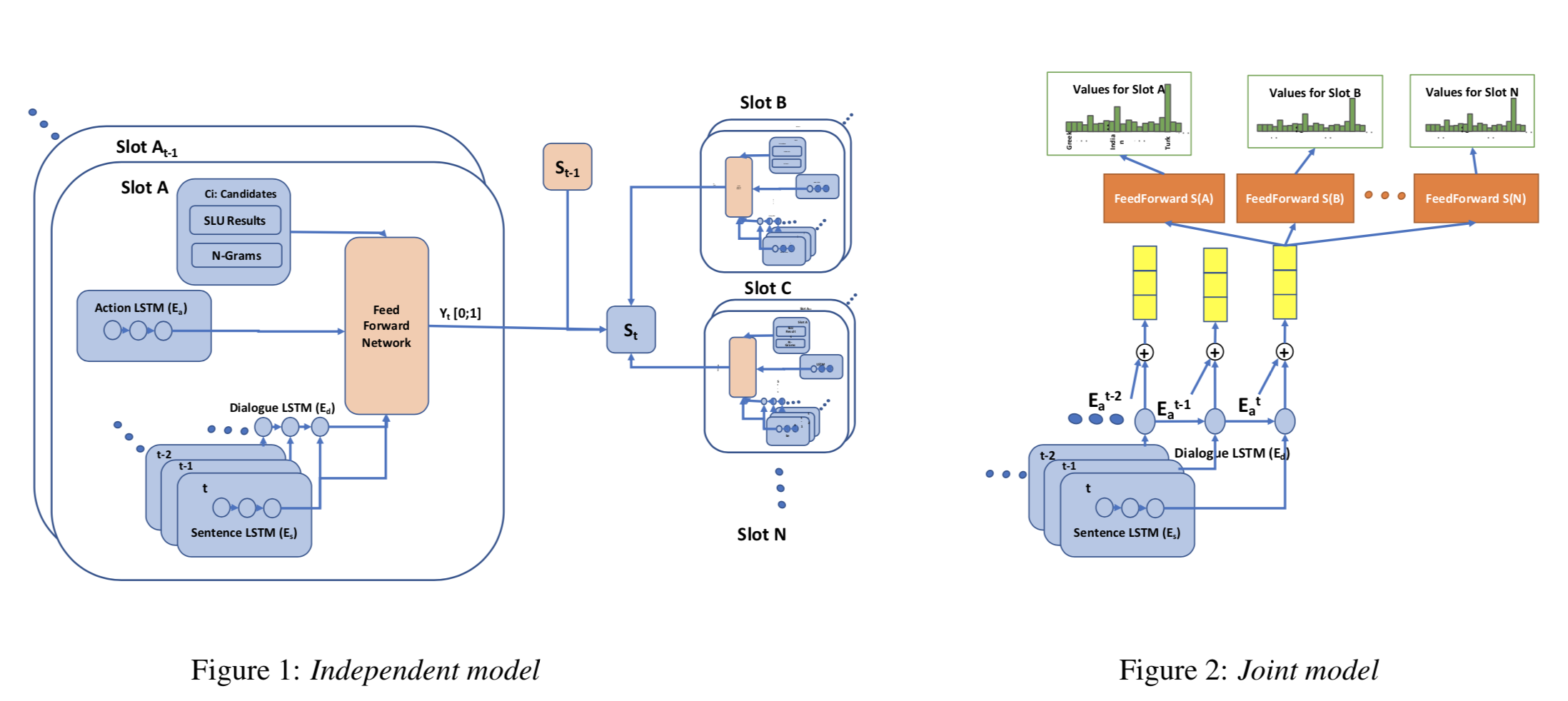
HyST: A Hybrid Approach for Flexible and Accurate Dialogue State Tracking
过去的模型:
a) estimate a probability distribution over all possible slot values——-》do not scale for large value sets commonly present in real-life applications and are not ideal for tracking slot values that were not observed in the training set
b) candidate-generation-based approach estimate a set of values that are possible at each turn based on the conversation history and/or language understanding outputs——-》 hence enable state tracking over unseen values and large value sets however, they fall short in terms of performance in comparison to the first group
该方法: aims to learn what method to rely on for each slot type
左边的是candidate set,右边的是all possible slot value,
而且两边的方法不一样,Slot A t − 1 A_{t-1} At−1的作用?怎么插入,公式中没有显示,(可能我看的不够认真)
我认为他只是提出了joint model。两种方法都训练,然后验证时选择平均起来相对当前slot效果更好的一个模型。
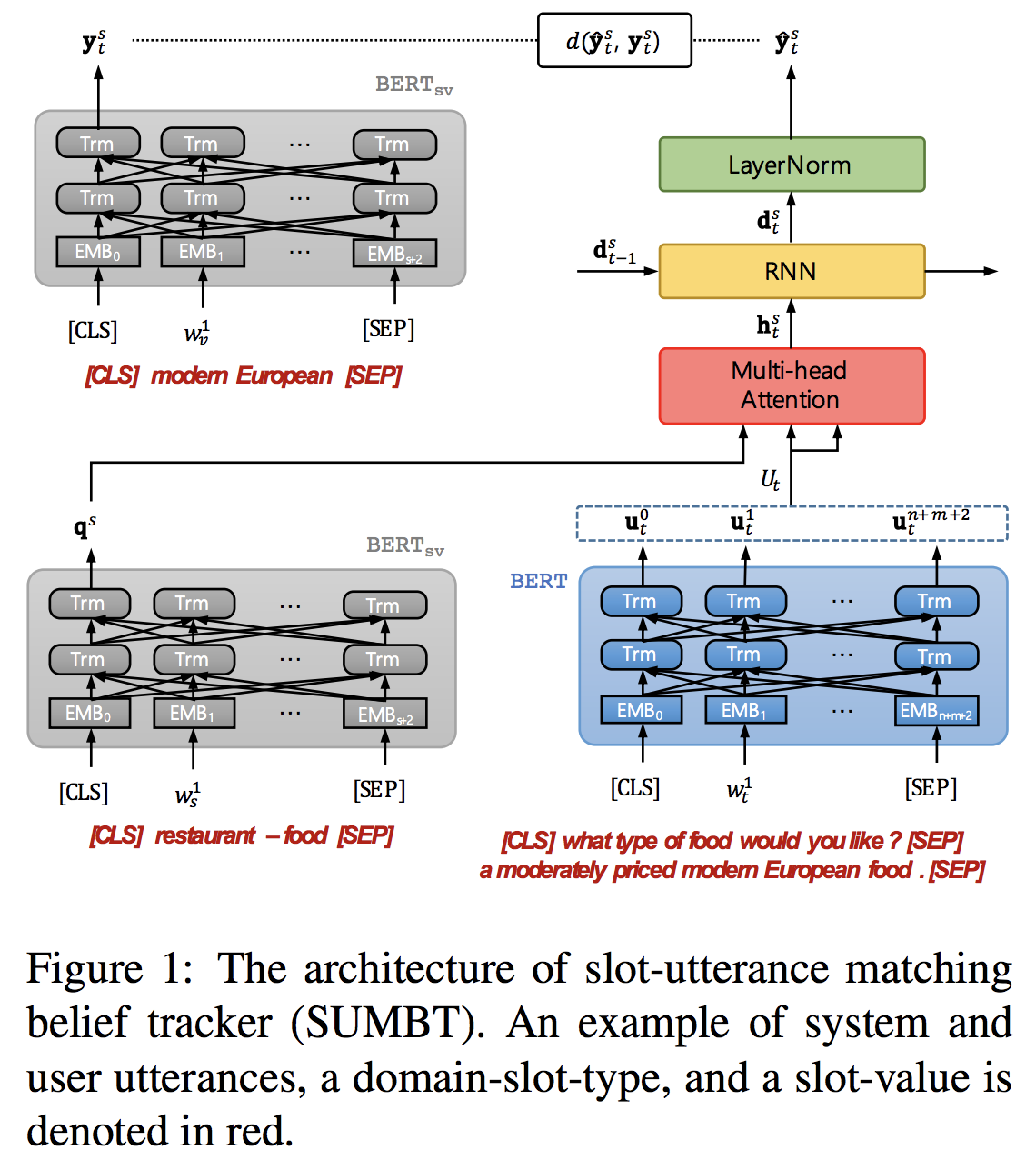
SUMBT: Slot-Utterance Matching for Universal and Scalable Belief Tracking
该模型的主要亮点在使用bert然后使用attention机制形成一个对话flow,三个输入中有针对某个slot的slot-type和slot-candidate,所以一次只能计算一个slot。
methods either individually model each domain and/or slot (GLAD; Ren et al., 2018; HyST)(没懂) or have difficulty in adding new slot-values that are not defined in the ontology(就是slot对应的value集合发生变化怎么办)
同样借助阅读理解,将slot-type考虑为question。
强调:The model predicts the slot-value label in a non-parametric way ,就是除了bert和attention以外没有参数,based on a certain metric, which enables the model architecture not to structurally depend on domains and slot-types.
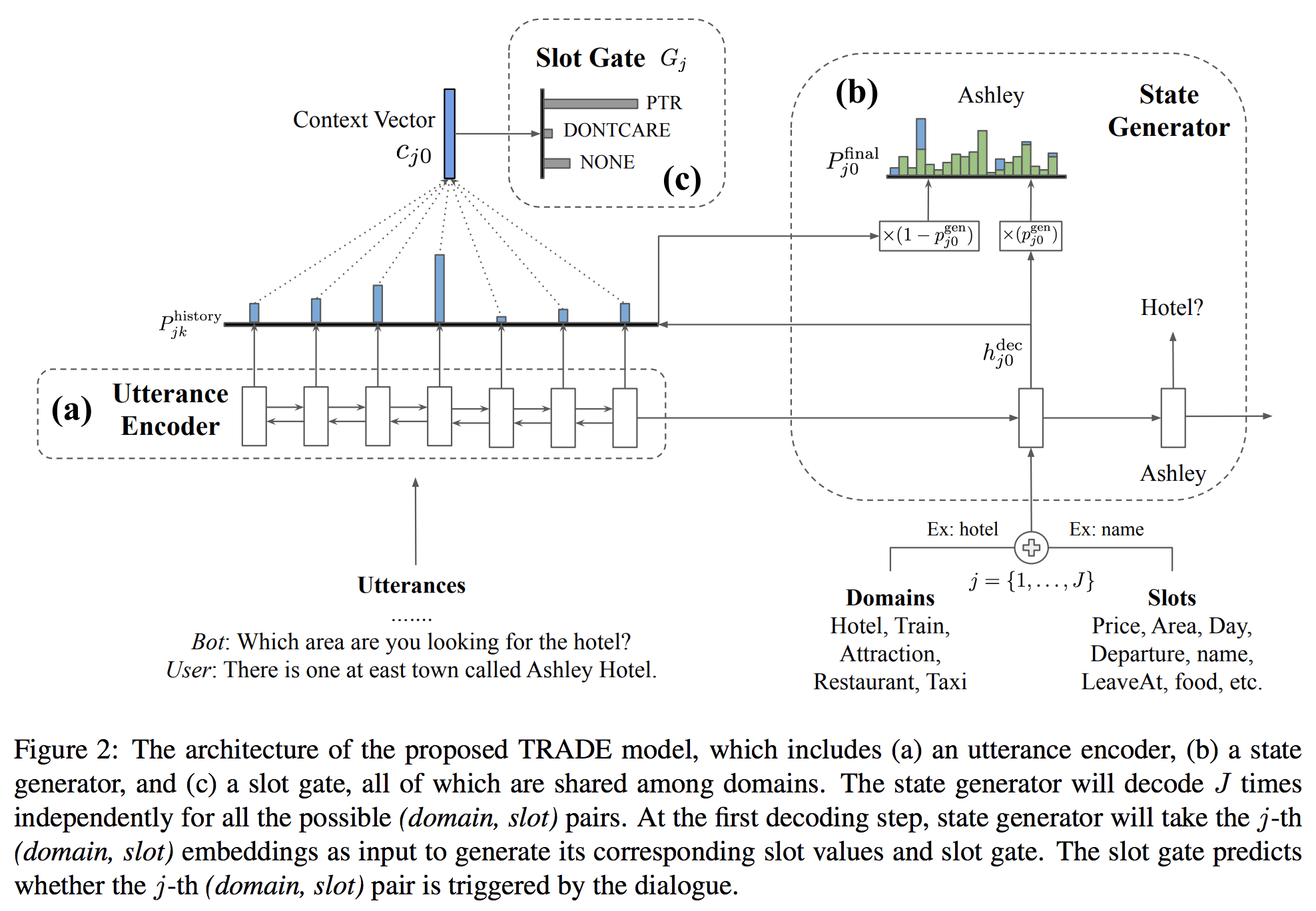
Transferable Multi-Domain State Generator for Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems
效果惊人
不光是模型,论文中还提到如何Transfer的问题,使用旧方法,
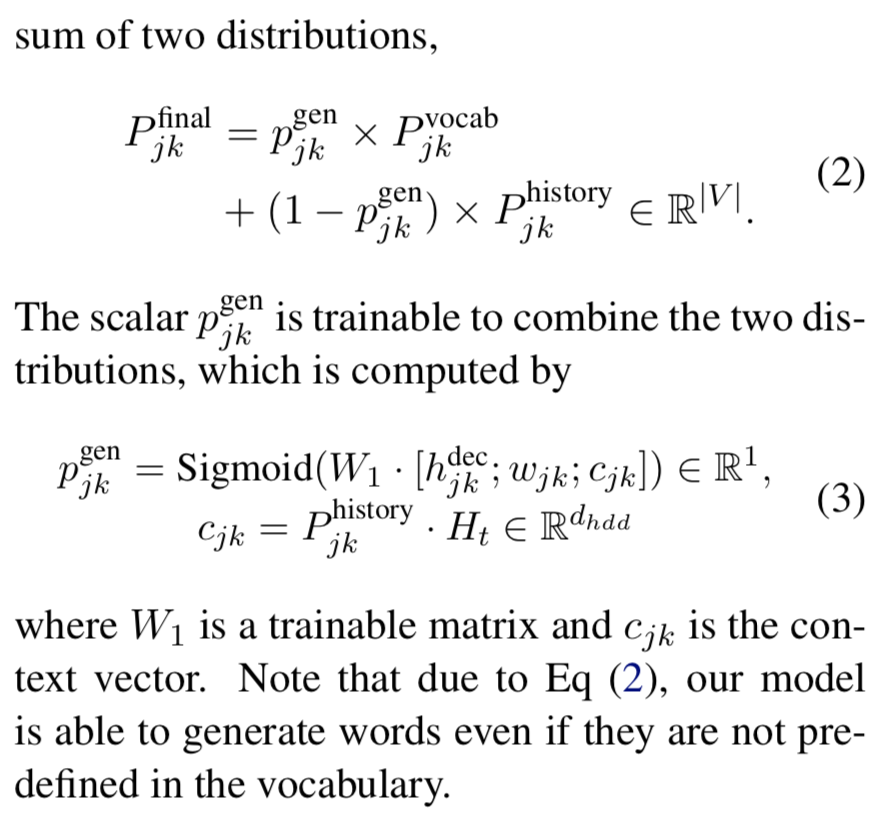
目前就图而言,厉害的地方在于有vocab和context两个地方提取value相关信息。
除了pointer network,我认为lstm的decoder结构也是一个创新点,p_vocab的形成有大量参数,是不是帮助了效果。
Ht是句子的每步hidden集合, h j k d e c h_{jk}^{dec} hjkdec是decoder过程中对于 S l o t j Slot_j Slotj第k步产生的hidden向量.
pointer network真的是对变量进行很紧很深的交互,引入很多参数,
以后写感想要加入自己的想法,对于这个模型可以怎样删改,
今天的文章DST文章学习分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/66811.html