用的是这版本
由于逆天的语法,必须准确记清楚
目录
22-10-10
1.1Scheme语法
>、
>=、=、
<、
<=
pred1
expr1)
. . . (
pred
k
expr
k ) (else
expr))
i是一个求值结果为true或false的表达式,称为谓词
pred1,如果值为true,则cond表达式的值就
expr1的值。求值
expr1。此时无需求值其他条件或分支
pred2,如果值为true,则cond表达式的值就
expr2的值。求值
expr2。此时无需求值其他条件或分支
pred1到
pred
k的求值结果都为false,则cond表达式的值
expr的值。求值
expr
条件表达式和谓词
>=和
<=也是Scheme默认提供的过程
22.9.26(半路起步)
递归
学习阶乘概念的简单练习
第一题
(define
(f a b)
( if (= a b) b
(+ a (f (+ a 1)b))
)
)第二题
(define
(fac a b)
(if (= a b) a
(* a
(fac (+ a 1) b )
)
)
)
22-10-9
1.2递归与阶乘
1.递归与阶乘的区别
固定数目的状态变量描述, 则这个求值的过程称为迭代计算过程(iterative process)
额外保存的数字和运算, 则这个求值的过程称为递归计算过程(recursive process)
2.阶乘与递归的实例
阶乘的递归实现
(define (fac n)
(if (= n 1) 1
(* n (fac (- n 1)))
)
)
阶乘的迭代实现
神奇的情况出现了,输入以下代码,bug了
(define (fac id idbound)
(= idbound 1) 1
(* id (fac (+ 1 id) idbound))
)以下为正确表达式
result =
counter!,且counterBound总为6
a!、counter=
a,counterBound=6
a + 1)!的,因此下一行的result的值等于本行
a!
∗ (
a + 1)、
a + 1,counterBound=6
result =
counter!
counter = 6这一行时,此时
result =
counter! = 6!即为
额外引入变量和计算过
;迭代实现阶乘
;count用于计数
(define (fac count countbound result)
(if (= count countbound) result
(fac (+ count 1) countbound (* result (+ count 1)))))
;迭代算法的包装
(define (f n)
(fac 1 n 1))斐波那契数列的递归实现
(define (fib n)
(cond ( (= n 0) 0)
( (= n 1) 1)
(else
( + (fib (- n 1))
(fib (- n 2)) )
)
)
)斐波那契数列的迭代实现
(define (fib idx currValue nextValue idBound)
(if (= idx idBound) currValue
(fib (+ idx 1) nextValue (+ currValue nextValue) idBound)
)
)
(define (f n)
(fib 0 0 1 n)
)3.区分二者的代换过程
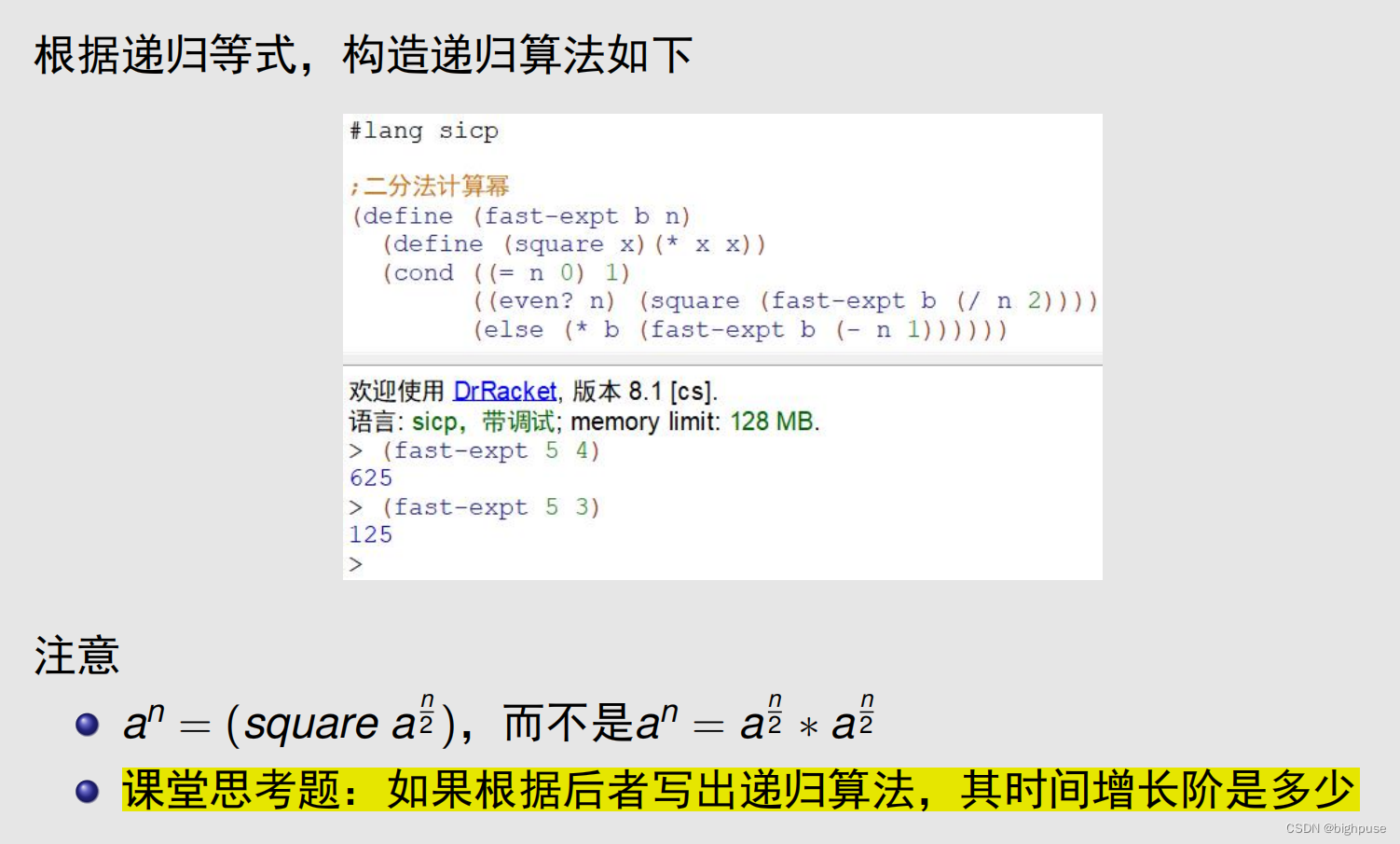
如果计算a^32,前者的代换过程需要五次乘法,而后者需要三十一次
前者的代换过程
a^32=(square a^16)
=(square (square a^8))
=(square(square(square a^4)))
=(square(square(square(square a^2))))
=(square(square(square(square(square a ))))
后者的代换过程
a^32=a^16 * a^16
=a^8 * a^8 * a^8 * a^8
……
=a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a*a
#lang sicp 自带的函数
1.DrRacket自带的abs函数(求绝对值)
2.DrRacket自带的remainder函数(求除法的余数)
22-10-18
求平方根
(define (sqrt-iter x n)
(if (good-enough? x n)
x
(sqrt-iter (improve x n) n)
)
)
(define (improve x n)
(average x (/ x n))
)
(define (average x n)
(/ (+ x n) 2)
)
(define (good-enough? x n)
(< (abs(- (square x) n)) 0.00001)
)
(define (square x)
(* x x)
)
(define (sqrt n)
(sqrt-iter 1.0 n))
1.2练习题
会发生schme死机。
因为if是特殊形式,scheme会先判断条件,再决定计算那一部分
而新编写的new-if是普通形式,scheme希望求出该函数内所有的值,最终造成无限循环。
练习1.6补充
因为lisp语言广泛使用的是应用序,也就是”先求参数值而后应用“。而if语句适用正则序
22-10-23
1.3高阶过程实现函数
1.3(1)以过程为参数的高阶过程
高阶牛顿法
;高阶过程牛顿法
(define (newtons-method g guess)
(define (good-enough? a)
(< (abs (g a))
0.0001))
(define (improve f xi)
(- xi
(/ (f xi)
(/ (- (f (+ xi 0.01)) (f xi))
0.01))))
(define (newtons-iter h x)
(if (good-enough? x)
x
(newtons-iter h (improve h x))))
(newtons-iter g guess))
(define (sqrt a)
(define (equalForSqrt x)
(- (* x x) a))
(newtons-method equalForSqrt 1.0))
高阶求和法
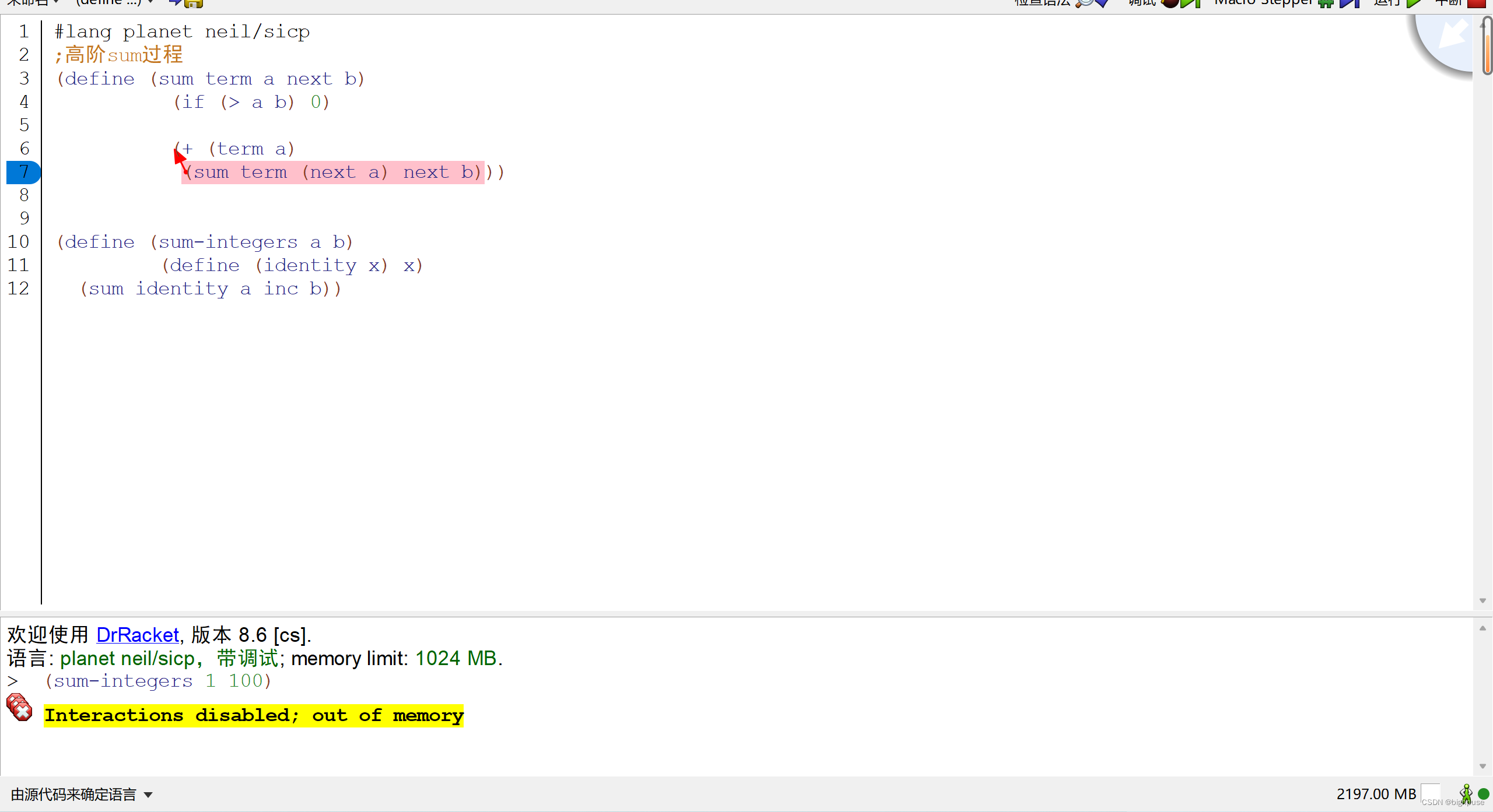
;高阶sum过程
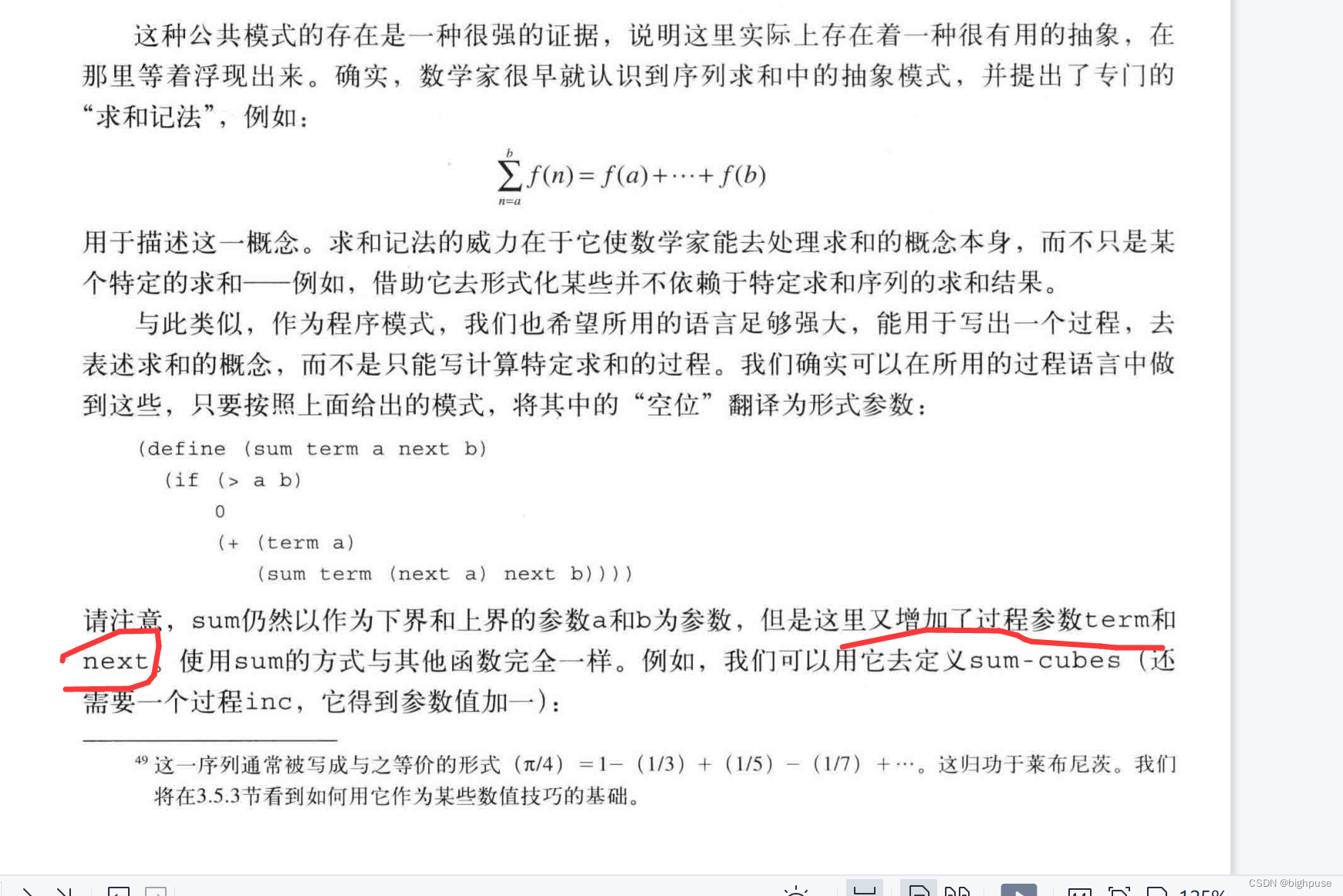
(define (sum term a next b)
(if (> a b) 0
(+ (term a)
(sum term (next a) next b)))
(define (sum-integers a b)
(define (identity x) x)
(sum identity a inc b))内存爆炸是因为:第四行代码最后多了一个括号。(if (> a b) 0)已经是一个独立的语句了,执行完第一个if语句后,无论什么情况一定会执行第六七行的语句,造成死循环。(可能吧,待会再问一下)
对term和next的理解
term和next只是空位,编写具体函数时,用所需的过程参数填上即可。
term和next不是scheme提供的参数。
1.3(2)以过程为结果的高阶函数
高阶逼近pai的方法
;高阶sum过程
(define (sum term a next b)
(if (> a b) 0)
(+ (term a)
(sum term (next a) next b)))
(define (pi-sum a b)
(define (pi-term x)
(/ 8 (* x (+ x 2))))
(define (pi-next x)
(+ x 4))
(sum pi-term a pi-next b))
课堂练习
#lang planet neil/sicp
(define (sum term a next b)
(if (> a b) 0
(+ (term a) (sum term (next a) next b)))
)
(define (squ-sum a b)
(define (squ-term a) (* a a))
(define (squ-next a) (+ a 2))
(sum squ-term a squ-next b)
)
(define (sos n)
(squ-sum 0 n)
)
1.3(3)匿名过程
<1>匿名过程求高阶导
正确运行
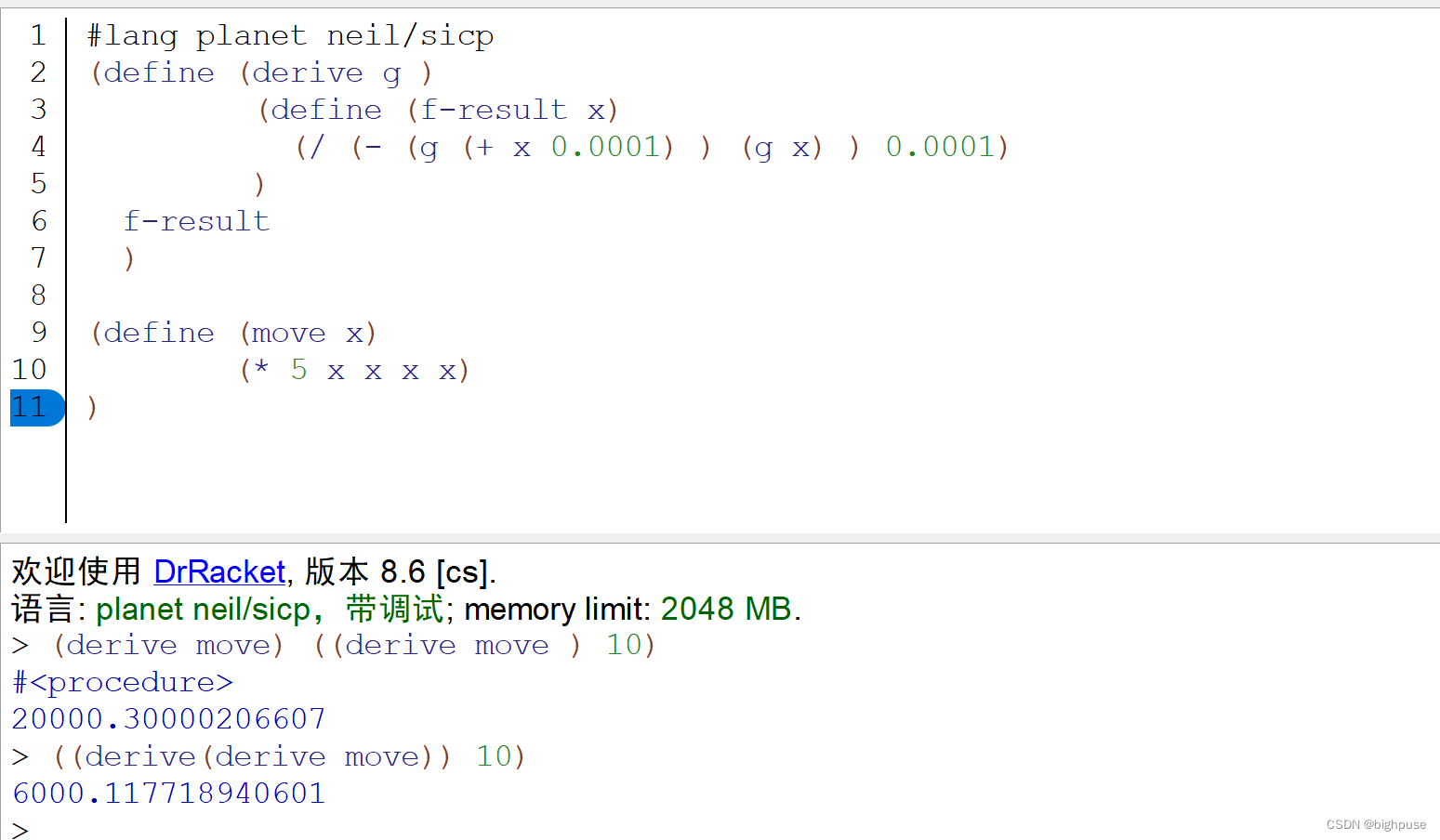
#lang planet neil/sicp
(define (derive g )
(define (f-result x)
(/ (- (g (+ x 0.0001) ) (g x) ) 0.0001)
)
f-result
)
(define (move x)
(* 5 x x x x)
)<2>匿名过程的调用
格式:(匿名过程定义 参数)
即(
(
lamda
(参数列表)
(过程体)
)
参数)
匿名g
#lang planet neil/sicp
(define (square x) (* x x))
(define (cube x) (* x x x))
(define (quad x) (* x x x x))
(define
(f x y)
(
;定义匿名过程并调用
(lambda
;匿名过程的参数列表
(a b)
;匿名过程的过程体
(+ (* 1 (quad a))
(* 2 (cube a) b)
(* 3 (square a) (square b))
(* 4 a (cube b))
(* 5 (quad b)))
)
;匿名过程的参数
(+ 2 y)
(+ 1 (square x))
)
) <3>let语句
匿名语句可以用let语句重写,仅是格式不同。
(let (v1e1) (v2 e2) ……(vk ek) 过程体)
先将e中式子求值,再赋给变量v,最后在过程体中进行计算。
(define (square x) (* x x))
(define (cube x) (* x x x))
(define (quad x) (* x x x x))
(define
(f x y)
(let ((a (+ 2 y)) (b (+ 1(* x x))))
(+ (* 1 (quad a))
(* 2 (cube a) b)
(* 3 (square a) (square b))
(* 4 a (cube b))
(* 5 (quad b)))
)
)
let语句与lambda语法的区别在于
let把最终调用的参数放在了过程体之前,
而lambda放在最后。相对来说,let语句更加清晰
<4>高阶语句实现(不动点,牛顿法)
练习1.42
#lang sicp
(define (square n)
(* n n)
)
(define ((compose square inc) n)
(square (inc n))
)
((compose square inc) 6)22-10-20
2.1数据抽象
意识到 denom和numer两个函数并不是自带的,而是需要自己根据scheme已经提供的car和cdr进行编写的
语法
cons
,
car
,
cdr
list
,
nil
’
null?
,
pair?
,
number?
,
eq?
提供的过程
n
是否是一个序对
有理数加法的简单实现
(define (numer x)
(car x) )
(define (denom x)
(cdr x))
(define (add-rat x y)
(make-rat (+(* (numer x) (denom y))
(* (numer y) (denom x)))
(* (denom x) (denom y))
))
(define (make-rat n d )
(cons n d))教材练习2.2
障碍:
1.题目中预设接口,需要按照要求的接口去编写
2.自己编写过程中,总想着如何在运行框中输入两点坐标,之后再进行计算。网络的思路是直接定义两点坐标。目前不清楚自己的初始思路是否可行
#lang planet neil/sicp
(define
(make-segment start-point end-point )
(cons start-point end-point))
(define (start-segment seg) (car seg) )
(define (end-segment seg) (cdr seg))
(define (make-point a b) (cons a b) )
(define (point-x p) (car p))
(define (point-y p) (cdr p))
(define (midpoint-segment seg1)
(cons (/ (+ (caar seg1) (cadr seg1)) 2)
(/ (+ (cdar seg1) (cddr seg1)) 2)
))
(define (print-piont p)
(newline)
(display "(")
(display (point-x p))
(display ",")
(display (point-y p))
(display ")"))
(define start (make-point 1 2))
(define end (make-point 3 4 ))
(define seg1 (make-segment start end))
(define p (midpoint-segment seg1))
教材练习2.3
作为零编程基础的初学者,确实无法解决这个问题,下面是大佬的解答。 http://t.csdn.cn/BQtlO
2.2 表(list)
1.表的基本操作
递归的构造表
构造过程:将表的每个元素写两遍
(define (f items)
(if (null? items) nil
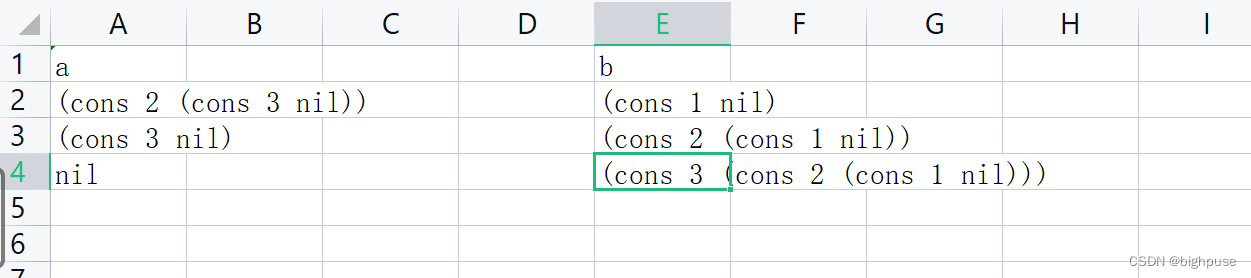
(cons (car items) (cons (car items) (f (cdr items))))))将表反转
#lang planet neil/sicp
(define (revers items)
(cond ((null? items) items)
((null? (cdr items)) items)
(else (reverse-iter (cdr items) (cons(car items) nil)))))
;a是未处理的列表,b是反转过的列表
(define (reverse-iter a b)
(if (null? a) b
(reverse-iter (cdr a) (cons (car a) b)
)))
很巧妙的代码,看来很久才看明白
整体思路是:1.取出表中第一个元素,放到新表的最后一个数字的位置上
2.对取出第一个元素后的表,重复上述操作(递归的思想),但放在倒数第二个数字的位置上
3.重复。
处理表中特定下标的元素
代码暂时存疑,询问后附上
取出表中下标为奇数的元素
#lang planet neil/sicp
(define (filterList pred? items)
;args:a为当前表格,index为当前表格的首元素在items中的下标
(define (f-rec a index)
(cond ( (null? a) nil)
( (pred? index)
(cons (car a) (f-rec (cdr a) (+ 1 index))))
( else (f-rec (cdr a) (+ 1 index)))))
(f-rec items 0))
(define (pred? index)
(if (= (remainder index 2) 0) #f
#t)
)
(filterList pred? (list 1 2 3 4))pred?过程需要自己书写,不是scheme提供的
第一次写结果为#t或#f的逻辑语句
对表的高阶过程
;表的映射-将表中每个元素都平方
(define (square-list x)
(if (null? x) nil
(cons (* (car x) (car x)) (square-list (cdr x)))
)) (define (squ-list x)
(map (lambda (x) (* x x)) x))作业题
第一题: 实现过程(last-part n items),返回由表items的最后n个元素构成的表。例如,(last-part 3 (list 2 8 1 10 5 20))的求值结果为(10 5 20)。当n大于表的长度时,(last-part n items)的求值结果为items。
分析:输出最后n个元素组成的表,即输出第leng-n+1到第leng个元素。
解决方法:
①求出items长度leng
②当n大于leng时,输出items
③否则,遍历数组,找到第leng-n+1个元素,并逐次输出其后所有元素直到表结束。
#lang sicp
(define (length items)
(if (null? items)
0
(+ 1 (length (cdr items)))
)
)
(define (last-part n items)
(define (get-last n items idx leng)
(if (>= n (length items))
items
(if (> idx (- leng n)) (car items)
(get-last n (cdr items) idx leng)
)
)
)
(get-last n items 1 (length items))
)
(last-part 3 (list 1 3 5 7 9))第二题: 实现过程(plus-index items),给定表items作为参数,求值结果是这样一张表,其元素数目和items的元素数目相同,并且每个元素 = items中对应元素+下标。我们认为一个表的首元素下标为0。 例如,(plus-index (list 1 8 2 12 6 3 4 5)) = (1 9 4 15 10 8 10 12)。 其中,1(右边)=1(左边)+0,9(右边)=8(左边)+1,4(右边)=2(左边)+2,...
错误实例:(原因未知)
#lang sicp
(define (length items)
(if (null? items)
0
(+ 1 (length (cdr items))
)
)
)
(define (plus-index items)
(define (plus items idx leng)
(if (null? items) items
(if(> idx leng) nil
(cons (+ idx (car items)) (plus (cdr items) (+ idx 1)(length items)) )
)
)
)
(plus items 0 (length items))
)
(plus-index (list 1 3 5 7 9));第二题:
;实现过程(plus-index items),给定表items作为参数,求值结果是这样一张表,其元素数目和items的元素数目相同,并且每个元素 = items中对应元素+下标。我们认为一个表的首元素下标为0。
;例如,(plus-index (list 1 8 2 12 6 3 4 5)) = (1 9 4 15 10 8 10 12)。
;其中,1(右边)=1(左边)+0,9(右边)=8(左边)+1,4(右边)=2(左边)+2,...
#lang sicp
(define (length items)
(if (null? items)
0
(+ 1 (length (cdr items))
)
)
)
(define (plus-index items)
(define (plus items idx leng)
(if (null? items) items
(if(> idx leng) nil
(cons (+ idx (car items)) (plus (cdr items) (+ idx 1) leng) )
)
)
)
(plus items 0 (length items))
)
(plus-index (list 1 3 5 7 9))对树的操作
1.递归的拆开树
;返回树的叶节点个数
(define (count-leaves items)
(cond
((null? items) 0)
((not (pair? items)) 1)
(else (+ (count-leaves (car items))
(count-leaves (cdr items))
)
)
)
)错误:前后函数名不一致导致“未定义”
#lang planet neil/sicp
;返回树的叶节点数字的和
(define (sum-leaves items)
(cond
((null? items) 0)
((not (pair? items)) items)
(else (+ (sum-leaves (car items))
(sum-leaves (cdr items))
)
)
)
)2.对树的映射
一种实现的方法
#lang planet neil/sicp
(define
(map-tree square items )
(cond ((null? items ) nil)
((not (pair? items)) (square items))
(else (cons (map-tree square (car items) )
(map-tree square (cdr items) ))
)
)
)
(define (square x) (* x x))
(map-tree square (list (list 1 2) (list 3 4)) )另一种方式(间接递归)实现树的映射
22-11-6proc未定义,如何实现?
#lang planet neil/sicp
;用另一种方式实现对树的映射
(define (map-tree2 proc items)
(map (lambda (subTree)
(if (pair? subTree)
(map-tree2 proc subTree)
(proc subTree)))
items))自己编写proc即可实现
;用另一种方式实现对树的映射
;间接递归,即map-tree2调用map,而map在匿名过程中调用map-tree2
(define (map-tree2 proc items)
(map (lambda (subTree)
(if (pair? subTree)
(map-tree2 proc subTree)
(proc subTree)))
items))
(define (proc a)
(* a a)
)
(map-tree2 proc (list (list 1 2) (list 3 4)))构造函数fring,把树拍扁
例如 (fringe (list 1 2 )3 (list 4 5)) =(1 2 3 4 5)
#lang planet neil/sicp
;拍扁树
(define (fringe items)
(cond ((null? items) items)
(else (cons (car items) (fringe (cdr items))))
)
)
(fringe (list (list 1 2) 3 (list 4 5)))一个失败的尝试,为什么多出这么多括号
这个似乎正确
(define (fringe items)
(cond ((null? items) items)
((not (pair? items)) (list items))
(else (append (fringe (car items)) (fringe (cdr items))))))
(fringe (list (list 1 2) 3 (list 4 5)))22-11-12
2.3符号数据
‘操作
1.由scheme提供
2.求值时将后面内容视为文字而不是变量
判断字符串的相同
(eq? a b)函数
1.由scheme提供
2.a,b都是字符串,判断a,b内容是否相同
#lang planet neil/sicp
;在表x中搜寻目标元素items
(define (memq items x )
(cond ((null? x) false)
((eq? (car x) items) x)
(else (memq items (cdr x)))
)
)
(memq 'a '(b a e f))实例:符号求导
思想:愿望思维和递归
问题分析:1.exp=constant,0
2.exp是否是单个变量,分两种情况,exp与var相同或不同
3.exp是否是加法
4.exp是否是乘法
#lang sicp
(define (deriv exp var)
(cond ((number? exp) 0 )
((variable? exp)
(if (same-variable? exp var) 1 0))
;sum
((sum? exp)
(make-sum (deriv (addend exp) var)
(deriv (augend exp) var))
)
;multiply
((product? exp)
(make-sum
(make-product (deriv (multiplier exp) var) multiplicand)
(make-product (multiplier exp) (deriv (multiplicand exp) var)))
)
)
; (else error "error in deriv")
)
;variable
(define (variable? x)
(symbol? x))
(define (same-variable? a b)
(and (eq? a b) (variable? a ) (variable? b))
)
;sum
(define (sum? x)
(and (pair? x) (eq? '+ (car x))))
(define (addend x)
(car x))
(define (augend x)
(cdr x))
(define (make-sum a b)
(list '+ a b))
;product
(define (product? x)
(eq? '* (car x)))
(define (make-product a b)
(list '* a b))
(define (multiplier x)
(cadr x))
(define (multiplicand x)
(caddr x))
(deriv '(+ x 3) 'x)
(deriv '(* x y) 'x)
(deriv '(* (* x y) (+ x 3)) 'x)
(deriv '(* x (* x x)) 'x)
(deriv '(* x 3) 'x)
自己写的问题:
1.忽略” ‘ “的在sum? product?中的作用
2.不清楚exp的储存形式(’+ x x)=>写加法,乘法的分步处理时错用为car和cdr
3.是否为同一变量的条件语句:写的不充分
明日再改
22-11-13
成功!!!!
#lang sicp
(define (deriv exp var)
(cond ((number? exp) 0 )
((variable? exp)
(if (same-variable? exp var) 1 0))
;sum
((sum? exp)
(make-sum (deriv (addend exp) var)
(deriv (augend exp) var))
)
;multiply
((product? exp)
(make-sum
(make-product (deriv (multiplier exp) var) (multiplicand exp))
(make-product (multiplier exp) (deriv (multiplicand exp) var)))
)
(else error "error in deriv"))
)
;variable
(define (variable? x)(symbol? x))
(define (same-variable? a b)
(and (variable? a) (variable? b) (eq? a b)))
;sum
(define (sum? x)
(and (pair? x) (eq? '+ (car x))))
(define (addend x)
(cadr x))
(define (augend x)
(caddr x))
(define (make-sum a b)
(list '+ a b))
;product
(define (product? x)
(eq? '* (car x)))
(define (make-product a b)
(list '* a b))
(define (multiplier x)
(cadr x))
(define (multiplicand x)
(caddr x))
;EXAMPLE
(deriv '(+ x 3) 'x)
(deriv '(* x y) 'x)
(deriv '(* (* x y) (+ x 3)) 'x)
(deriv '(* x (* x x)) 'x)
(deriv '(* x 3) 'x)
(deriv '(- x 3) 'x)
收获:
1.递归思想,抽象屏障的理解更加深刻
2.” ‘ “符号的应用,表达式的储存格式
3.如何判断exp是否含乘法,加法
4.如何判断是否是变量,常数
求导结果的化简
虽然得到了正确的结果,但是很多冗余的式子。
(+ (* 1 y) (* x 0))应该直接写为y
化简结果的代码
#lang sicp
;化简
(define (deriv exp var)
(cond ((number? exp) 0 )
((variable? exp)
(if (same-variable? exp var) 1 0))
;sum
((sum? exp)
(make-sum (deriv (addend exp) var)
(deriv (augend exp) var))
)
;multiply
((product? exp)
(make-sum
(make-product (deriv (multiplier exp) var) (multiplicand exp))
(make-product (multiplier exp) (deriv (multiplicand exp) var)))
)
(else error "error in deriv"))
)
;variable
(define (variable? x)(symbol? x))
(define (same-variable? a b)
(and (variable? a) (variable? b) (eq? a b)))
;化简加法
(define (sum? x)
(and (pair? x) (eq? '+ (car x))))
(define (addend x)
(cadr x))
(define (augend x)
(caddr x))
(define (make-sum a b)
(cond ( (=number? a 0) b)
( (=number? b 0) a)
( (and (number? a) (number? b))
(+ a b))
(else (list '+ a b))))
(define (=number? a b)
(and (number? a) (= a b)))
;化简乘法
(define (product? x)
(eq? '* (car x)))
(define (make-product a b)
(cond ((or (=number? a 0) (=number? b 0)) 0)
((=number? a 1) b)
((=number? b 1) a)
(else (list '* a b))
)
)
(define (multiplier x)
(cadr x))
(define (multiplicand x)
(caddr x))
;EXAMPLE
(deriv '(+ x 3) 'x)
(deriv '(* x y) 'x)
(deriv '(* (* x y) (+ x 3)) 'x)
(deriv '(* x (* x x)) 'x)
(deriv '(* x 3) 'x)
(deriv '(- x 3) 'x)
集合的表示
集合作为抽象数据,给用户提供接口方便操作
1.求两个集合的交集
2.求两个集合的并集
3.判断元素是否在集合内部
4.把元素插入集合内部
共有三种方法
1.使用未排序的表实现集合
2.使用排序的表实现集合
3.使用二叉树实现集合
方法一:使用未排序的表实现集合
错误示例:
#lang sicp
;求两个集合的交集(intersection)
(define (intersection a b)
(cond ((or (null? a) (null? b)) nil)
((element-of-x? (car a) b )
(cons (car a) (intersection (cdr a) b)))
(intersection (cdr a) b)
)
)
(define (element-of-x? element x)
(cond ((null? x) false)
( (equal? element (car x)) true)
(element-of-x? element (cdr x))
))
(intersection (list 1 2) (list 2 3))错误原因:cond语法格式错误
(intersection (cdr a) b)
(element-of-x? element (cdr x))
这两个语句在cond内单独出现,缺乏执行的条件
正确:
在上述两句执行语句之前加上else并在该行之前加()即可
(else (intersection (cdr a) b))
(else (element-of-x? element (cdr x)) )
#lang sicp
;求两个集合的交集(intersection)
(define (intersection a b)
(cond ((or (null? a) (null? b)) nil)
((element-of-x? (car a) b )
(cons (car a) (intersection (cdr a) b)))
(else (intersection (cdr a) b))
)
)
(define (element-of-x? element x)
(cond ((null? x) false)
( (equal? element (car x)) true)
(else (element-of-x? element (cdr x)) )
))
(intersection (list 1 2) (list 2 3))求两个集合的并集
#lang sicp
;求两个集合的并集(union-set)
(define (union a b)
(cond ( (null? a) b)
( (null? b) a)
((element-of-x? (car a) b)
(union (cdr a) b))
(else
(cons (car a)
(union (cdr a) b) ))
))
(define (element-of-x? element x)
(cond ((null? x) false)
( (equal? element (car x)) true)
(else (element-of-x? element (cdr x)) )
))
(union (list 1 2) (list 2 3))自己写的过程中总会出现:cond分支语句少了最后一个“)”的问题
SICP 练习2.56
exponentiation:指数运算
base:基底
exponent:指数
2.使用排序的表实现集合
今天的文章SICP(计算机程序构造与解释)学习笔记(lisp语言实现)分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/79862.html