目录
一、ODB简介
ODB是应用于C++的一个开源、跨平台、跨数据库的对象关系映射(ORM)系统。它可以让你持久化C++对象到关系数据库,而不必处理表、列或者SQL,无需手动编写任何映射代码。ODB支持MySQL,SQLite,PostgreSQL,Oracle和微软SQL Server关系数据库以及C ++98/03和C ++11语言标准。它还配备了用于Boost和Qt可选的配置文件,让你可以无缝地使用这些库持久化C++类的值类型、容器和智能指针。它有易用性,简洁的代码,安全,数据库可移植性,优良的性能,可维护性等优点。
ODB不是框架。 它并没有规定您应该如何编写应用程序。 相反,它仅通过处理C ++对象的持久性而不干扰任何其他功能而设计为适合您的样式和体系结构。只需进行少量修改就可以使现有类持久化。 特别是,可以在没有默认构造函数的情况下声明持久类,可以自动使用现有的访问器和修饰符函数来访问数据成员,并且可以将ODB编译指示移出该类并移到单独的头中,从而使对象关系 映射完全是非侵入性的。 对自动数据库模式演变的支持还使您可以像对待应用程序中的任何其他C ++类一样对待ODB持久对象。
二、Person类
1、Person.h
#ifndef PERSON_H
#define PERSON_H
#include <string>
class person
{
public:
person(void);
~person(void);
person(const std::string& first,
const std::string& last,
unsigned short age);
const std::string& first() const;
const std::string& last() const;
unsigned short age() const;
void age(unsigned short age);
private:
unsigned long id_;
std::string first_;
std::string last_;
unsigned short age_;
};
#endif
2、Person.cpp
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "person.h"
person::person(void)
{
}
person::person(const std::string& first,
const std::string& last,
unsigned short age)
: first_(first), last_(last), age_(age)
{
}
person::~person(void)
{
}
const std::string& person::first() const
{ return first_; }
const std::string& person::last() const
{ return last_; }
unsigned short person::age() const
{ return age_; }
void person::age(unsigned short age)
{ age_ = age; }三、工程修改
1、Person类修改
(1)Person.hxx
将person.h修改为person.hxx
#ifndef PERSON_CXX_H
#define PERSON_CXX_H
#include <string>
#include <odb/core.hxx> // 包含odb::access
#pragma db object // 告诉编译器这是一个 persistent class
class person
{
public:
person(void);
~person(void);
person(const std::string& first,
const std::string& last,
unsigned short age);
const std::string& first() const;
const std::string& last() const;
unsigned short age() const;
void age(unsigned short age);
private:
friend class odb::access;
#pragma db id auto
unsigned long id_;
std::string first_;
std::string last_;
unsigned short age_;
};
#endif
(2)Person.cpp修改
#include "StdAfx.h"
#include "person.hxx"
person::person(void)
{
}
person::person(const std::string& first,
const std::string& last,
unsigned short age)
: first_(first), last_(last), age_(age)
{
}
person::~person(void)
{
}
const std::string& person::first() const
{ return first_; }
const std::string& person::last() const
{ return last_; }
unsigned short person::age() const
{ return age_; }
void person::age(unsigned short age)
{ age_ = age; }2、运行odb
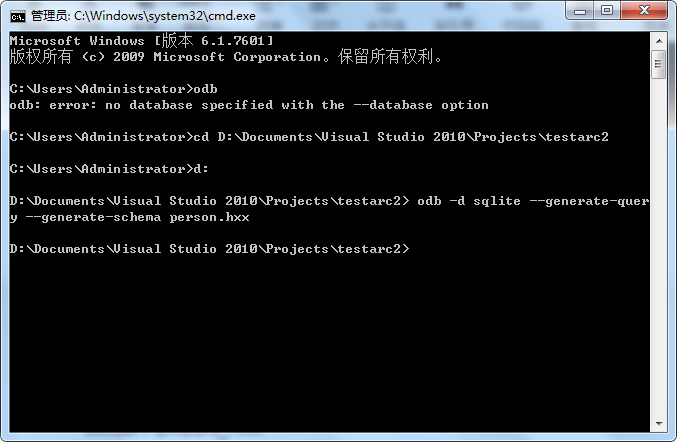
odb -d sqlite –generate-query –generate-schema person.hxx
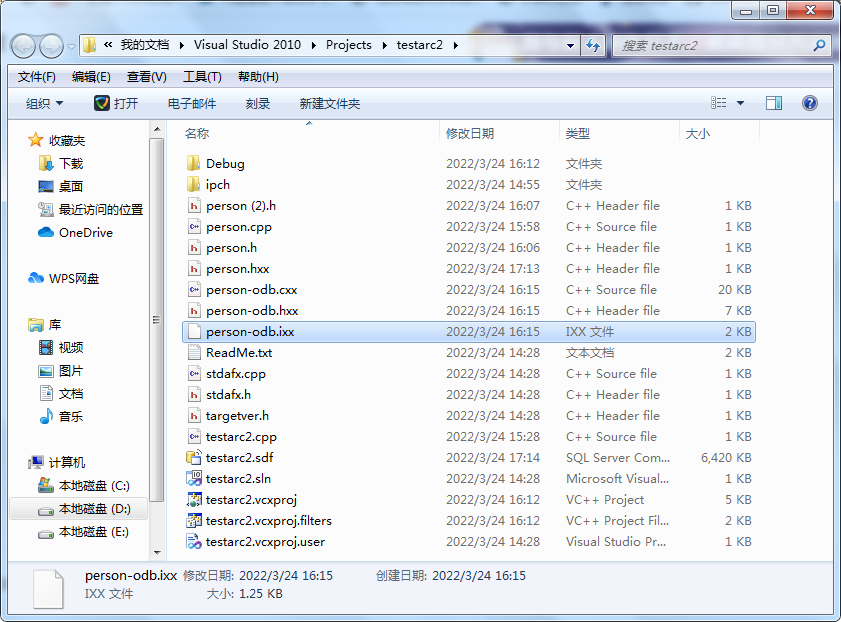
3、添加生成的文件到工程中
将生成的person-odb.hxx,person-odb.cxx和person-odb.ixx添加到项目中
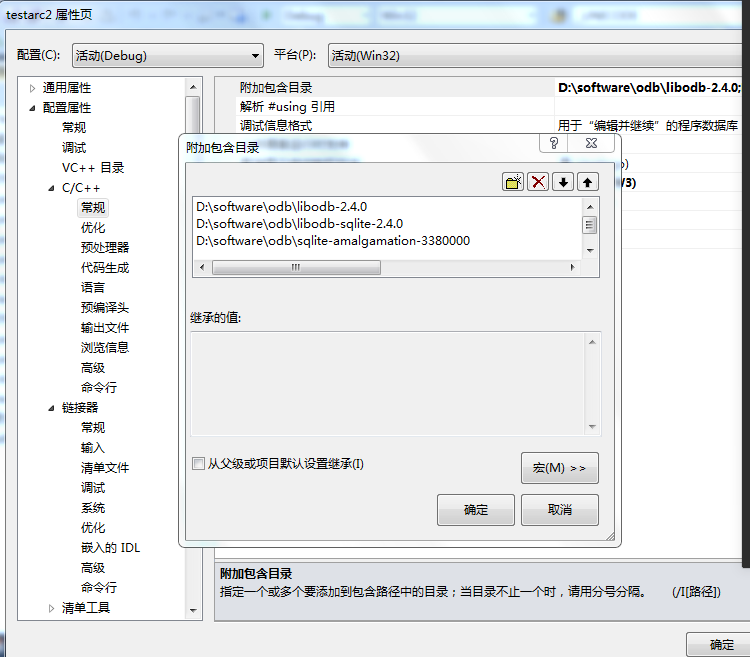
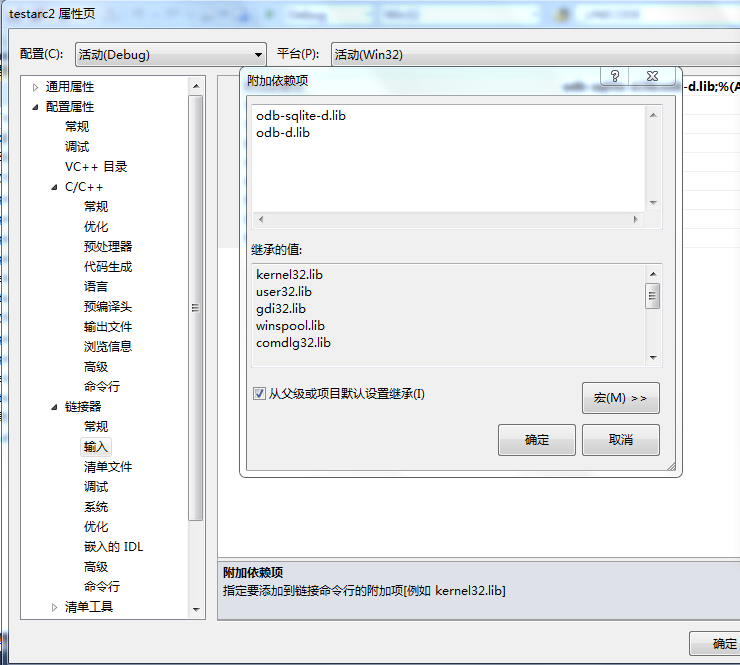
4、配置
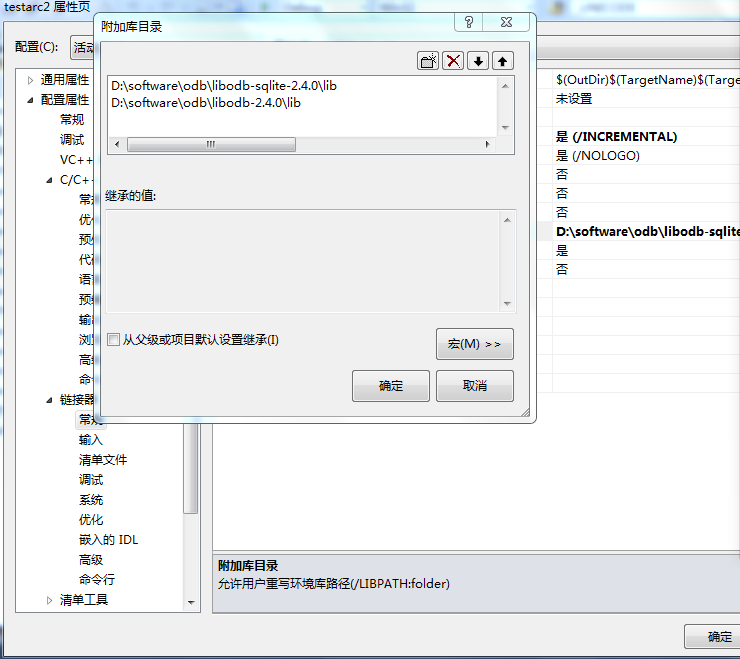
5、添加database.hxx文件到工程中
// file : hello/database.hxx
// copyright : not copyrighted - public domain
//
// Create concrete database instance based on the DATABASE_* macros.
//
#ifndef DATABASE_HXX
#define DATABASE_HXX
#include <string>
#include <memory> // std::auto_ptr
#include <cstdlib> // std::exit
#include <iostream>
#include <odb/database.hxx>
#if defined(DATABASE_MYSQL)
# include <odb/mysql/database.hxx>
#elif defined(DATABASE_SQLITE)
# include <odb/connection.hxx>
# include <odb/transaction.hxx>
# include <odb/schema-catalog.hxx>
# include <odb/sqlite/database.hxx>
#elif defined(DATABASE_PGSQL)
# include <odb/pgsql/database.hxx>
#elif defined(DATABASE_ORACLE)
# include <odb/oracle/database.hxx>
#elif defined(DATABASE_MSSQL)
# include <odb/mssql/database.hxx>
#else
# error unknown database; did you forget to define the DATABASE_* macros?
#endif
inline std::auto_ptr<odb::database>
create_database (int& argc, char* argv[])
{
using namespace std;
using namespace odb::core;
if (argc > 1 && argv[1] == string ("--help"))
{
cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " [options]" << endl
<< "Options:" << endl;
#if defined(DATABASE_MYSQL)
odb::mysql::database::print_usage (cout);
#elif defined(DATABASE_SQLITE)
odb::sqlite::database::print_usage (cout);
#elif defined(DATABASE_PGSQL)
odb::pgsql::database::print_usage (cout);
#elif defined(DATABASE_ORACLE)
odb::oracle::database::print_usage (cout);
#elif defined(DATABASE_MSSQL)
odb::mssql::database::print_usage (cout);
#endif
exit (0);
}
#if defined(DATABASE_MYSQL)
auto_ptr<database> db (new odb::mysql::database (argc, argv));
#elif defined(DATABASE_SQLITE)
auto_ptr<database> db (
new odb::sqlite::database (
argc, argv, false, SQLITE_OPEN_READWRITE | SQLITE_OPEN_CREATE));
// Create the database schema. Due to bugs in SQLite foreign key
// support for DDL statements, we need to temporarily disable
// foreign keys.
//
{
connection_ptr c (db->connection ());
c->execute ("PRAGMA foreign_keys=OFF");
transaction t (c->begin ());
schema_catalog::create_schema (*db);
t.commit ();
c->execute ("PRAGMA foreign_keys=ON");
}
#elif defined(DATABASE_PGSQL)
auto_ptr<database> db (new odb::pgsql::database (argc, argv));
#elif defined(DATABASE_ORACLE)
auto_ptr<database> db (new odb::oracle::database (argc, argv));
#elif defined(DATABASE_MSSQL)
auto_ptr<database> db (new odb::mssql::database (argc, argv));
#endif
return db;
}
#endif // DATABASE_HXX
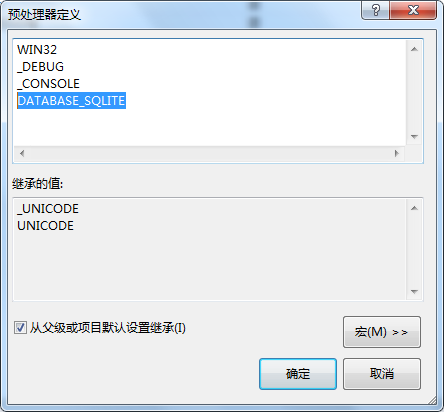
6、添加DATABASE_SQLITE宏
7、main函数
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <memory> // std::auto_ptr
#include <iostream>
#include <odb/database.hxx>
#include <odb/transaction.hxx>
#include "database.hxx" // create_database
#include "person.hxx"
#include "person-odb.hxx"
using namespace std;
using namespace odb::core;
int
main (int argc, char* argv[])
{
try
{
auto_ptr<database> db (create_database (argc, argv));
unsigned long john_id, joe_id;
// Create a few persistent person objects.
//
{
person john ("John", "Doe", 33);
person jane ("Jane", "Doe", 32);
person joe ("Joe", "Dirt", 30);
transaction t (db->begin ());
// Make objects persistent and save their ids for later use.
//
john_id = db->persist (john);
db->persist (jane);
joe_id = db->persist (joe);
t.commit ();
}
typedef odb::query<person> query;
typedef odb::result<person> result;
// Say hello to those over 30.
//
{
transaction t (db->begin ());
result r (db->query<person> (query::age > 30));
for (result::iterator i (r.begin ()); i != r.end (); ++i)
{
cout << "Hello, " << i->first () << " " << i->last () << "!" << endl;
}
t.commit ();
}
// Joe Dirt just had a birthday, so update his age.
//
{
transaction t (db->begin ());
auto_ptr<person> joe (db->load<person> (joe_id));
joe->age (joe->age () + 1);
db->update (*joe);
t.commit ();
}
// John Doe is no longer in our database.
//
{
transaction t (db->begin ());
db->erase<person> (john_id);
t.commit ();
}
}
catch (const odb::exception& e)
{
cerr << e.what () << endl;
return 1;
}
}
(1)存储
// Create a few persistent person objects.
//
{
person john ("John", "Doe", 33);
person jane ("Jane", "Doe", 32);
person joe ("Joe", "Dirt", 30);
transaction t (db->begin ());
// Make objects persistent and save their ids for later use.
//
john_id = db->persist (john);
db->persist (jane);
joe_id = db->persist (joe);
t.commit ();
}(2)查询
// Say hello to those over 30.
//
{
transaction t (db->begin ());
result r (db->query<person> (query::age > 30));
for (result::iterator i (r.begin ()); i != r.end (); ++i)
{
cout << "Hello, " << i->first () << " " << i->last () << "!" << endl;
}
t.commit ();
}(3)更新
// Joe Dirt just had a birthday, so update his age.
//
{
transaction t (db->begin ());
auto_ptr<person> joe (db->load<person> (joe_id));
joe->age (joe->age () + 1);
db->update (*joe);
t.commit ();
}(4)删除
// John Doe is no longer in our database.
//
{
transaction t (db->begin ());
db->erase<person> (john_id);
t.commit ();
}8、copy dll
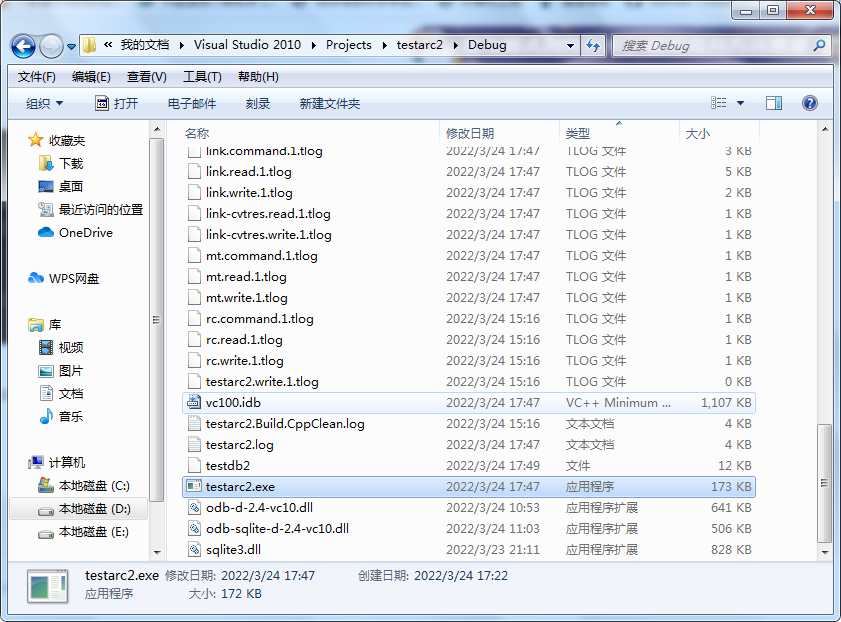
copy odb-d-2.4-vc10.dll,odb-sqlite-d-2.4-vc10.dll和sqlite3.dll到debug目录下
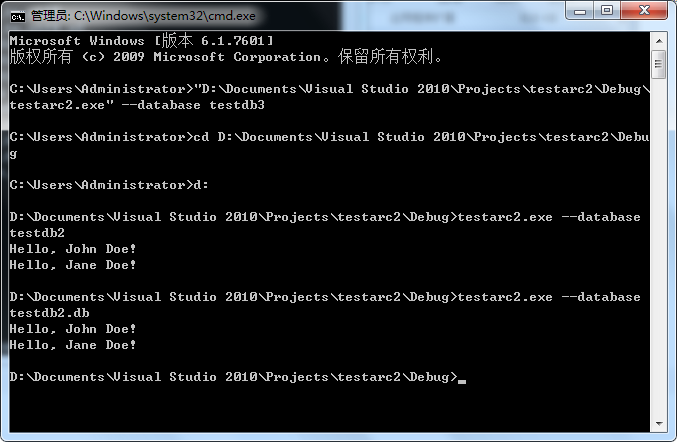
9、运行
今天的文章跨数据库join_oracle跨数据库查询分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/83859.html