关键词:经纬度坐标,平面直角坐标,空间大地坐标系,坐标系映射
一、坐标系分类
在大地测量学中,坐标系分为两大类:地心坐标系和参心坐标系
1、地心坐标系
坐标原点与地球质心重合的坐标系。
世界大地坐标系WGS-84(world geodetic system)是地心坐标系。
2、参心坐标系
坐标系原点在参考椭球体中心,不与地球质心重合。
北京54,采用前苏联的椭球体,属于参心坐标系。浅析几种常用坐标系和坐标转换
西安80,也属于参心坐标系
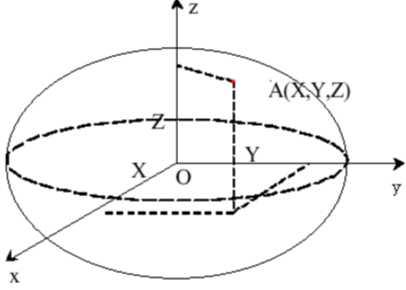
3、空间直角坐标系
空间直角坐标系的坐标原点位于参考椭球的中心,Z轴指向参考椭球的北极,X轴指向起始子午面与赤道的交点,Y轴位于赤道面上切按右手系于X轴呈90度夹角,某点中的坐标可用该点在此坐标系的各个坐标轴上的投影来表示。空间直角坐标系可用如下图所示(参考空间大地坐标系与平面直角坐标系转换公式):
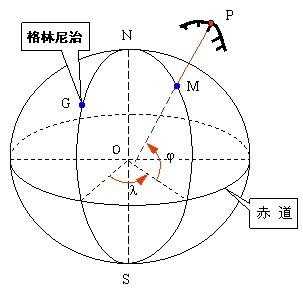
4、空间大地坐标系
大地坐标系是采用大地纬度、经度和大地高程来描述空间位置的。纬度是空间的点与参考椭球面的法线与赤道面的夹角;经度是空间的点与参考椭球的自转轴所在的面与参考椭球的起始子午面的夹角;大地高程是空间的点沿着参考椭球的法线方向到参考椭球面的距离(参考空间直角坐标系、大地坐标系、平面坐标系、高斯平面直角坐标系)。
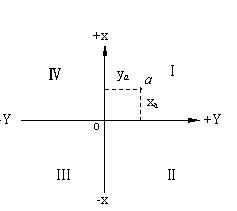
5、平面直角坐标系
平面直角坐标:如坐标原点o是任意假定的,则为独立的平面直角坐标系。
由于测量上所用的方向是从北方向(纵轴方向)起按顺时针方向以角度计值(象限也按顺时针编号)。因此,将数学上平面直角坐标系(角值从横轴正方向起按逆时针方向计值)的 x 和 y轴互换后,数学上的三角函数计算公式可不加改变直接用于测量数据的计算。
平面坐标系是利用投影变换,将空间直角坐标系或空间大地坐标系通过数学变化映射到平面上,这种变换称为投影变换。
二、坐标系转换
从空间坐标系到平面坐标系的映射方法有很多种:高斯-克吕格投影、墨卡托投影、兰伯特投影、UTM投影等。(参考地球坐标系与投影方式的理解,第9章 GPS测量数据处理,空间大地坐标系与平面直角坐标系的相互转换,坐标系统及投影概述)
三、坐标系投影的实现(source code)
1、如何将GPS坐标转换为XY平面坐标(简易转换)
本文根据《GPS经纬度坐标转平面坐标的简化计算方法及精度分析》这篇文章中的的方法将GPS经纬度坐标转换为以地平面上平面直角坐标系中的X、Y坐标。这个转换方法的前提是在一定的范围以内。具体的转化公式请参考该文,下面是坐标转换的代码:
public class PlaneCoordinate {
private static final double MACRO_AXIS = 6378137; // 赤道圆的平均半径
private static final double MINOR_AXIS = 6356752; // 半短轴的长度,地球两极距离的一半
// 返回Y坐标
private static double turnY(GePoint basePoint, GePoint point) {
double a = Math.pow(MACRO_AXIS, 2.0);
double b = Math.pow(MINOR_AXIS, 2.0);
double c = Math.pow(Math.tan(basePoint.getLatitude()), 2.0);
double d = Math.pow(1/Math.tan(basePoint.getLatitude()),2.0);
double x = a/Math.sqrt(a + b*c);
double y = b/Math.sqrt(b + a*d);
c = Math.pow(Math.tan(point.getLatitude()), 2.0);
d = Math.pow(1/Math.tan(point.getLatitude()), 2.0);
double m = a/Math.sqrt(a + b*c);
double n = b/Math.sqrt(b + a*d);
return new PePoint(x, y).distanceBetween(new PePoint(m, n));
}
// 返回X坐标
private static double turnX(GePoint basePoint, GePoint point) {
double a = Math.pow(MACRO_AXIS, 2.0);
double b = Math.pow(MINOR_AXIS, 2.0);
double c = Math.pow(Math.tan(basePoint.getLatitude()), 2.0);
double x = a/Math.sqrt(a + b*c);
return x * (point.getLongtitude() - basePoint.getLongtitude());
}
}
public class GePoint {
private double latitude; // 纬度坐标
private double longtitude; // 经度坐标
public GePoint() {
}
public GePoint(double latitude, double longtitude) {
this.latitude = latitude;
this.longtitude = longtitude;
}
public double getLatitude() {
return 2 * latitude * Math.PI / 360 ;
}
public void setLatitude(double latitude) {
this.latitude = latitude;
}
public double getLongtitude() {
return 2 * longtitude * Math.PI / 360;
}
public void setLongtitude(double longtitude) {
this.longtitude = longtitude;
}
}
2、以上代码摘自经纬度 to 平面直角坐标转换,上述代码中PePoint类没有给出,需要进一步研究得出。文中还给出了另一种复杂的实现方法,代码摘录如下:
//经纬度坐标与高斯坐标的转换代码
//没钱又丑发表于2007-12-6 13:08:00
// double y; 输入参数: 高斯坐标的横坐标,以米为单位
// double x; 输入参数: 高斯坐标的纵坐标,以米为单位
// short DH; 输入参数: 带号,表示上述高斯坐标是哪个带的
// double *L; 输出参数: 指向经度坐标的指针,其中经度坐标以秒为单位
// double *B; 输出参数: 指向纬度坐标的指针,其中纬度坐标以秒为单位
void GaussToGeo(double y, double x, short DH, double* L, double* B, double LP)
{
double l0; // 经差
double tf; // tf = tg(Bf0),注意要将Bf转换成以弧度为单位
double nf; // n = y * sqrt( 1 + etf ** 2) / c, 其中etf = e'**2 * cos(Bf0) ** 2
double t_l0; // l0,经差,以度为单位
double t_B0; // B0,纬度,以度为单位
double Bf0; // Bf0
double etf; // etf,其中etf = e'**2 * cos(Bf0) ** 2
double X_3;
double PI = 3.14159265358979;
double b_e2 = 0.0067385254147;
double b_c = 6399698.90178271;
X_3 = x / 1000000.00 - 3; // 以兆米()为单位
// 对于克拉索夫斯基椭球,计算Bf0
Bf0 = 27.11115372595 + 9.02468257083 * X_3 - 0.00579740442 * pow(X_3, 2)
- 0.00043532572 * pow(X_3, 3) + 0.00004857285 * pow(X_3, 4)
+ 0.00000215727 * pow(X_3, 5) - 0.00000019399 * pow(X_3, 6);
tf = tan(Bf0 * PI / 180); // tf = tg(Bf),注意这里将Bf转换成以弧度为单位
etf = b_e2 * pow(cos(Bf0 * PI / 180), 2); // etf = e'**2 * cos(Bf) ** 2
nf = y * sqrt(1 + etf) / b_c; // n = y * sqrt( 1 + etf ** 2) / c
// 计算纬度,注意这里计算出来的结果是以度为单位的
t_B0 = Bf0 - (1.0 + etf) * tf / PI * (90.0 * pow(nf, 2)
- 7.5 * (5.0 + 3 * pow(tf, 2) + etf - 9 * etf * pow(tf, 2)) * pow(nf, 4)
+ 0.25 * (61 + 90 * pow(tf, 2) + 45 * pow(tf, 4)) * pow(nf, 6));
// 计算经差,注意这里计算出来的结果是以度为单位的
t_l0 = (180 * nf - 30 * (1 + 2 * pow(tf, 2) + etf) * pow(nf, 3)
+ 1.5 * (5 + 28 * pow(tf, 2) + 24 * pow(tf, 4)) * pow(nf, 5))
/ (PI * cos(Bf0 * PI / 180));
l0 = (t_l0 * 3600.0); // 将经差转成秒
if (LP == -1000)
{
*L = (double)((DH * 6 - 3) * 3600.0 + l0); // 根据带号计算出以秒为单位的绝对经度,返回指针
}
else
{
*L = LP * 3600.0 + l0; // 根据带号计算出以秒为单位的绝对经度,返回指针
}
*B = (double)(t_B0 * 3600.0); // 将纬差转成秒,并返回指针
}
// double jd; 输入参数: 地理坐标的经度,以秒为单位
// double wd; 输入参数: 地理坐标的纬度,以秒为单位
// short DH; 输入参数: 三度带或六度带的带号
void GeoToGauss(double jd, double wd, short DH, short DH_width, double* y, double* x, double LP)
{
double t; // t=tgB
double L; // 中央经线的经度
double l0; // 经差
double jd_hd, wd_hd; // 将jd、wd转换成以弧度为单位
double et2; // et2 = (e' ** 2) * (cosB ** 2)
double N; // N = C / sqrt(1 + et2)
double X; // 克拉索夫斯基椭球中子午弧长
double m; // m = cosB * PI/180 * l0
double tsin, tcos; // sinB,cosB
double PI = 3.14159265358979;
double b_e2 = 0.0067385254147;
double b_c = 6399698.90178271;
jd_hd = jd / 3600.0 * PI / 180.0; // 将以秒为单位的经度转换成弧度
wd_hd = wd / 3600.0 * PI / 180.0; // 将以秒为单位的纬度转换成弧度
// 如果不设中央经线(缺省参数: -1000),则计算中央经线,
// 否则,使用传入的中央经线,不再使用带号和带宽参数
//L = (DH - 0.5) * DH_width ; // 计算中央经线的经度
if (LP == -1000)
{
L = (DH - 0.5) * DH_width; // 计算中央经线的经度
}
else
{
L = LP;
}
l0 = jd / 3600.0 - L; // 计算经差
tsin = sin(wd_hd); // 计算sinB
tcos = cos(wd_hd); // 计算cosB
// 计算克拉索夫斯基椭球中子午弧长X
X = 111134.8611 / 3600.0 * wd - (32005.7799 * tsin + 133.9238 * pow(tsin, 3)
+ 0.6976 * pow(tsin, 5) + 0.0039 * pow(tsin, 7)) * tcos;
et2 = b_e2 * pow(tcos, 2); // et2 = (e' ** 2) * (cosB ** 2)
N = b_c / sqrt(1 + et2); // N = C / sqrt(1 + et2)
t = tan(wd_hd); // t=tgB
m = PI / 180 * l0 * tcos; // m = cosB * PI/180 * l0
*x = X + N * t * (0.5 * pow(m, 2)
+ (5.0 - pow(t, 2) + 9.0 * et2 + 4 * pow(et2, 2)) * pow(m, 4) / 24.0
+ (61.0 - 58.0 * pow(t, 2) + pow(t, 4)) * pow(m, 6) / 720.0);
*y = N * (m + (1.0 - pow(t, 2) + et2) * pow(m, 3) / 6.0
+ (5.0 - 18.0 * pow(t, 2) + pow(t, 4) + 14.0 * et2
- 58.0 * et2 * pow(t, 2)) * pow(m, 5) / 120.0);
}3、文章经纬度坐标转换到平面坐标中给出了米勒坐标系投影和UTM坐标系投影的方法
- 米勒坐标系
package sg.edu.ntu.huangcheng;
public class MillerCoordinate {
public static double[] MillierConvertion(double lat, double lon)
{
double L = 6381372 * Math.PI * 2;//地球周长
double W=L;// 平面展开后,x轴等于周长
double H=L/2;// y轴约等于周长一半
double mill=2.3;// 米勒投影中的一个常数,范围大约在正负2.3之间
double x = lon * Math.PI / 180;// 将经度从度数转换为弧度
double y = lat * Math.PI / 180;// 将纬度从度数转换为弧度
y=1.25 * Math.log( Math.tan( 0.25 * Math.PI + 0.4 * y ) );// 米勒投影的转换
// 弧度转为实际距离
x = ( W / 2 ) + ( W / (2 * Math.PI) ) * x;
y = ( H / 2 ) - ( H / ( 2 * mill ) ) * y;
double[] result=new double[2];
result[0]=x;
result[1]=y;
return result;
}
}
使用这种方法转换后的Y轴方向似乎是反的,使用的时候需要注意。
- UTM坐标系
package sg.edu.ntu.huangcheng;
/* * Author: Sami Salkosuo, sami.salkosuo@fi.ibm.com * * (c) Copyright IBM Corp. 2007 */
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class CoordinateConversion {
public CoordinateConversion()
{
}
public double[] utm2LatLon(String UTM)
{
UTM2LatLon c = new UTM2LatLon();
return c.convertUTMToLatLong(UTM);
}
public String latLon2UTM(double latitude, double longitude)
{
LatLon2UTM c = new LatLon2UTM();
return c.convertLatLonToUTM(latitude, longitude);
}
private void validate(double latitude, double longitude)
{
if (latitude < -90.0 || latitude > 90.0 || longitude < -180.0
|| longitude >= 180.0)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Legal ranges: latitude [-90,90], longitude [-180,180).");
}
}
public String latLon2MGRUTM(double latitude, double longitude)
{
LatLon2MGRUTM c = new LatLon2MGRUTM();
return c.convertLatLonToMGRUTM(latitude, longitude);
}
public double[] mgrutm2LatLon(String MGRUTM)
{
MGRUTM2LatLon c = new MGRUTM2LatLon();
return c.convertMGRUTMToLatLong(MGRUTM);
}
public double degreeToRadian(double degree)
{
return degree * Math.PI / 180;
}
public double radianToDegree(double radian)
{
return radian * 180 / Math.PI;
}
private double POW(double a, double b)
{
return Math.pow(a, b);
}
private double SIN(double value)
{
return Math.sin(value);
}
private double COS(double value)
{
return Math.cos(value);
}
private double TAN(double value)
{
return Math.tan(value);
}
private class LatLon2UTM {
public String convertLatLonToUTM(double latitude, double longitude)
{
validate(latitude, longitude);
String UTM = "";
setVariables(latitude, longitude);
String longZone = getLongZone(longitude);
LatZones latZones = new LatZones();
String latZone = latZones.getLatZone(latitude);
double _easting = getEasting();
double _northing = getNorthing(latitude);
UTM = longZone + " " + latZone + " " + ((int) _easting) + " "
+ ((int) _northing);
// UTM = longZone + " " + latZone + " " + decimalFormat.format(_easting) +
// " "+ decimalFormat.format(_northing);
return UTM;
}
protected void setVariables(double latitude, double longitude)
{
latitude = degreeToRadian(latitude);
rho = equatorialRadius * (1 - e * e)
/ POW(1 - POW(e * SIN(latitude), 2), 3 / 2.0);
nu = equatorialRadius / POW(1 - POW(e * SIN(latitude), 2), (1 / 2.0));
double var1;
if (longitude < 0.0)
{
var1 = ((int) ((180 + longitude) / 6.0)) + 1;
}
else
{
var1 = ((int) (longitude / 6)) + 31;
}
double var2 = (6 * var1) - 183;
double var3 = longitude - var2;
p = var3 * 3600 / 10000;
S = A0 * latitude - B0 * SIN(2 * latitude) + C0 * SIN(4 * latitude) - D0
* SIN(6 * latitude) + E0 * SIN(8 * latitude);
K1 = S * k0;
K2 = nu * SIN(latitude) * COS(latitude) * POW(sin1, 2) * k0 * (100000000)
/ 2;
K3 = ((POW(sin1, 4) * nu * SIN(latitude) * Math.pow(COS(latitude), 3)) / 24)
* (5 - POW(TAN(latitude), 2) + 9 * e1sq * POW(COS(latitude), 2) + 4
* POW(e1sq, 2) * POW(COS(latitude), 4))
* k0
* (10000000000000000L);
K4 = nu * COS(latitude) * sin1 * k0 * 10000;
K5 = POW(sin1 * COS(latitude), 3) * (nu / 6)
* (1 - POW(TAN(latitude), 2) + e1sq * POW(COS(latitude), 2)) * k0
* 1000000000000L;
A6 = (POW(p * sin1, 6) * nu * SIN(latitude) * POW(COS(latitude), 5) / 720)
* (61 - 58 * POW(TAN(latitude), 2) + POW(TAN(latitude), 4) + 270
* e1sq * POW(COS(latitude), 2) - 330 * e1sq
* POW(SIN(latitude), 2)) * k0 * (1E+24);
}
protected String getLongZone(double longitude)
{
double longZone = 0;
if (longitude < 0.0)
{
longZone = ((180.0 + longitude) / 6) + 1;
}
else
{
longZone = (longitude / 6) + 31;
}
String val = String.valueOf((int) longZone);
if (val.length() == 1)
{
val = "0" + val;
}
return val;
}
protected double getNorthing(double latitude)
{
double northing = K1 + K2 * p * p + K3 * POW(p, 4);
if (latitude < 0.0)
{
northing = 10000000 + northing;
}
return northing;
}
protected double getEasting()
{
return 500000 + (K4 * p + K5 * POW(p, 3));
}
// Lat Lon to UTM variables
// equatorial radius
double equatorialRadius = 6378137;
// polar radius
double polarRadius = 6356752.314;
// flattening
double flattening = 0.00335281066474748;// (equatorialRadius-polarRadius)/equatorialRadius;
// inverse flattening 1/flattening
double inverseFlattening = 298.257223563;// 1/flattening;
// Mean radius
double rm = POW(equatorialRadius * polarRadius, 1 / 2.0);
// scale factor
double k0 = 0.9996;
// eccentricity
double e = Math.sqrt(1 - POW(polarRadius / equatorialRadius, 2));
double e1sq = e * e / (1 - e * e);
double n = (equatorialRadius - polarRadius)
/ (equatorialRadius + polarRadius);
// r curv 1
double rho = 6368573.744;
// r curv 2
double nu = 6389236.914;
// Calculate Meridional Arc Length
// Meridional Arc
double S = 5103266.421;
double A0 = 6367449.146;
double B0 = 16038.42955;
double C0 = 16.83261333;
double D0 = 0.021984404;
double E0 = 0.000312705;
// Calculation Constants
// Delta Long
double p = -0.483084;
double sin1 = 4.84814E-06;
// Coefficients for UTM Coordinates
double K1 = 5101225.115;
double K2 = 3750.291596;
double K3 = 1.397608151;
double K4 = 214839.3105;
double K5 = -2.995382942;
double A6 = -1.00541E-07;
}
private class LatLon2MGRUTM extends LatLon2UTM {
public String convertLatLonToMGRUTM(double latitude, double longitude)
{
validate(latitude, longitude);
String mgrUTM = "";
setVariables(latitude, longitude);
String longZone = getLongZone(longitude);
LatZones latZones = new LatZones();
String latZone = latZones.getLatZone(latitude);
double _easting = getEasting();
double _northing = getNorthing(latitude);
Digraphs digraphs = new Digraphs();
String digraph1 = digraphs.getDigraph1(Integer.parseInt(longZone),
_easting);
String digraph2 = digraphs.getDigraph2(Integer.parseInt(longZone),
_northing);
String easting = String.valueOf((int) _easting);
if (easting.length() < 5)
{
easting = "00000" + easting;
}
easting = easting.substring(easting.length() - 5);
String northing;
northing = String.valueOf((int) _northing);
if (northing.length() < 5)
{
northing = "0000" + northing;
}
northing = northing.substring(northing.length() - 5);
mgrUTM = longZone + latZone + digraph1 + digraph2 + easting + northing;
return mgrUTM;
}
}
private class MGRUTM2LatLon extends UTM2LatLon {
public double[] convertMGRUTMToLatLong(String mgrutm)
{
double[] latlon = { 0.0, 0.0 };
// 02CNR0634657742
int zone = Integer.parseInt(mgrutm.substring(0, 2));
String latZone = mgrutm.substring(2, 3);
String digraph1 = mgrutm.substring(3, 4);
String digraph2 = mgrutm.substring(4, 5);
easting = Double.parseDouble(mgrutm.substring(5, 10));
northing = Double.parseDouble(mgrutm.substring(10, 15));
LatZones lz = new LatZones();
double latZoneDegree = lz.getLatZoneDegree(latZone);
double a1 = latZoneDegree * 40000000 / 360.0;
double a2 = 2000000 * Math.floor(a1 / 2000000.0);
Digraphs digraphs = new Digraphs();
double digraph2Index = digraphs.getDigraph2Index(digraph2);
double startindexEquator = 1;
if ((1 + zone % 2) == 1)
{
startindexEquator = 6;
}
double a3 = a2 + (digraph2Index - startindexEquator) * 100000;
if (a3 <= 0)
{
a3 = 10000000 + a3;
}
northing = a3 + northing;
zoneCM = -183 + 6 * zone;
double digraph1Index = digraphs.getDigraph1Index(digraph1);
int a5 = 1 + zone % 3;
double[] a6 = { 16, 0, 8 };
double a7 = 100000 * (digraph1Index - a6[a5 - 1]);
easting = easting + a7;
setVariables();
double latitude = 0;
latitude = 180 * (phi1 - fact1 * (fact2 + fact3 + fact4)) / Math.PI;
if (latZoneDegree < 0)
{
latitude = 90 - latitude;
}
double d = _a2 * 180 / Math.PI;
double longitude = zoneCM - d;
if (getHemisphere(latZone).equals("S"))
{
latitude = -latitude;
}
latlon[0] = latitude;
latlon[1] = longitude;
return latlon;
}
}
private class UTM2LatLon {
double easting;
double northing;
int zone;
String southernHemisphere = "ACDEFGHJKLM";
protected String getHemisphere(String latZone)
{
String hemisphere = "N";
if (southernHemisphere.indexOf(latZone) > -1)
{
hemisphere = "S";
}
return hemisphere;
}
public double[] convertUTMToLatLong(String UTM)
{
double[] latlon = { 0.0, 0.0 };
String[] utm = UTM.split(" ");
zone = Integer.parseInt(utm[0]);
String latZone = utm[1];
easting = Double.parseDouble(utm[2]);
northing = Double.parseDouble(utm[3]);
String hemisphere = getHemisphere(latZone);
double latitude = 0.0;
double longitude = 0.0;
if (hemisphere.equals("S"))
{
northing = 10000000 - northing;
}
setVariables();
latitude = 180 * (phi1 - fact1 * (fact2 + fact3 + fact4)) / Math.PI;
if (zone > 0)
{
zoneCM = 6 * zone - 183.0;
}
else
{
zoneCM = 3.0;
}
longitude = zoneCM - _a3;
if (hemisphere.equals("S"))
{
latitude = -latitude;
}
latlon[0] = latitude;
latlon[1] = longitude;
return latlon;
}
protected void setVariables()
{
arc = northing / k0;
mu = arc
/ (a * (1 - POW(e, 2) / 4.0 - 3 * POW(e, 4) / 64.0 - 5 * POW(e, 6) / 256.0));
ei = (1 - POW((1 - e * e), (1 / 2.0)))
/ (1 + POW((1 - e * e), (1 / 2.0)));
ca = 3 * ei / 2 - 27 * POW(ei, 3) / 32.0;
cb = 21 * POW(ei, 2) / 16 - 55 * POW(ei, 4) / 32;
cc = 151 * POW(ei, 3) / 96;
cd = 1097 * POW(ei, 4) / 512;
phi1 = mu + ca * SIN(2 * mu) + cb * SIN(4 * mu) + cc * SIN(6 * mu) + cd
* SIN(8 * mu);
n0 = a / POW((1 - POW((e * SIN(phi1)), 2)), (1 / 2.0));
r0 = a * (1 - e * e) / POW((1 - POW((e * SIN(phi1)), 2)), (3 / 2.0));
fact1 = n0 * TAN(phi1) / r0;
_a1 = 500000 - easting;
dd0 = _a1 / (n0 * k0);
fact2 = dd0 * dd0 / 2;
t0 = POW(TAN(phi1), 2);
Q0 = e1sq * POW(COS(phi1), 2);
fact3 = (5 + 3 * t0 + 10 * Q0 - 4 * Q0 * Q0 - 9 * e1sq) * POW(dd0, 4)
/ 24;
fact4 = (61 + 90 * t0 + 298 * Q0 + 45 * t0 * t0 - 252 * e1sq - 3 * Q0
* Q0)
* POW(dd0, 6) / 720;
//
lof1 = _a1 / (n0 * k0);
lof2 = (1 + 2 * t0 + Q0) * POW(dd0, 3) / 6.0;
lof3 = (5 - 2 * Q0 + 28 * t0 - 3 * POW(Q0, 2) + 8 * e1sq + 24 * POW(t0, 2))
* POW(dd0, 5) / 120;
_a2 = (lof1 - lof2 + lof3) / COS(phi1);
_a3 = _a2 * 180 / Math.PI;
}
double arc;
double mu;
double ei;
double ca;
double cb;
double cc;
double cd;
double n0;
double r0;
double _a1;
double dd0;
double t0;
double Q0;
double lof1;
double lof2;
double lof3;
double _a2;
double phi1;
double fact1;
double fact2;
double fact3;
double fact4;
double zoneCM;
double _a3;
double b = 6356752.314;
double a = 6378137;
double e = 0.081819191;
double e1sq = 0.006739497;
double k0 = 0.9996;
}
private class Digraphs {
private Map digraph1 = new Hashtable();
private Map digraph2 = new Hashtable();
private String[] digraph1Array = { "A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G", "H",
"J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V", "W", "X",
"Y", "Z" };
private String[] digraph2Array = { "V", "A", "B", "C", "D", "E", "F", "G",
"H", "J", "K", "L", "M", "N", "P", "Q", "R", "S", "T", "U", "V" };
public Digraphs()
{
digraph1.put(new Integer(1), "A");
digraph1.put(new Integer(2), "B");
digraph1.put(new Integer(3), "C");
digraph1.put(new Integer(4), "D");
digraph1.put(new Integer(5), "E");
digraph1.put(new Integer(6), "F");
digraph1.put(new Integer(7), "G");
digraph1.put(new Integer(8), "H");
digraph1.put(new Integer(9), "J");
digraph1.put(new Integer(10), "K");
digraph1.put(new Integer(11), "L");
digraph1.put(new Integer(12), "M");
digraph1.put(new Integer(13), "N");
digraph1.put(new Integer(14), "P");
digraph1.put(new Integer(15), "Q");
digraph1.put(new Integer(16), "R");
digraph1.put(new Integer(17), "S");
digraph1.put(new Integer(18), "T");
digraph1.put(new Integer(19), "U");
digraph1.put(new Integer(20), "V");
digraph1.put(new Integer(21), "W");
digraph1.put(new Integer(22), "X");
digraph1.put(new Integer(23), "Y");
digraph1.put(new Integer(24), "Z");
digraph2.put(new Integer(0), "V");
digraph2.put(new Integer(1), "A");
digraph2.put(new Integer(2), "B");
digraph2.put(new Integer(3), "C");
digraph2.put(new Integer(4), "D");
digraph2.put(new Integer(5), "E");
digraph2.put(new Integer(6), "F");
digraph2.put(new Integer(7), "G");
digraph2.put(new Integer(8), "H");
digraph2.put(new Integer(9), "J");
digraph2.put(new Integer(10), "K");
digraph2.put(new Integer(11), "L");
digraph2.put(new Integer(12), "M");
digraph2.put(new Integer(13), "N");
digraph2.put(new Integer(14), "P");
digraph2.put(new Integer(15), "Q");
digraph2.put(new Integer(16), "R");
digraph2.put(new Integer(17), "S");
digraph2.put(new Integer(18), "T");
digraph2.put(new Integer(19), "U");
digraph2.put(new Integer(20), "V");
}
public int getDigraph1Index(String letter)
{
for (int i = 0; i < digraph1Array.length; i++)
{
if (digraph1Array[i].equals(letter))
{
return i + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public int getDigraph2Index(String letter)
{
for (int i = 0; i < digraph2Array.length; i++)
{
if (digraph2Array[i].equals(letter))
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public String getDigraph1(int longZone, double easting)
{
int a1 = longZone;
double a2 = 8 * ((a1 - 1) % 3) + 1;
double a3 = easting;
double a4 = a2 + ((int) (a3 / 100000)) - 1;
return (String) digraph1.get(new Integer((int) Math.floor(a4)));
}
public String getDigraph2(int longZone, double northing)
{
int a1 = longZone;
double a2 = 1 + 5 * ((a1 - 1) % 2);
double a3 = northing;
double a4 = (a2 + ((int) (a3 / 100000)));
a4 = (a2 + ((int) (a3 / 100000.0))) % 20;
a4 = Math.floor(a4);
if (a4 < 0)
{
a4 = a4 + 19;
}
return (String) digraph2.get(new Integer((int) Math.floor(a4)));
}
}
private class LatZones {
private char[] letters = { 'A', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'J', 'K',
'L', 'M', 'N', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W', 'X', 'Z' };
private int[] degrees = { -90, -84, -72, -64, -56, -48, -40, -32, -24, -16,
-8, 0, 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 84 };
private char[] negLetters = { 'A', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'J', 'K',
'L', 'M' };
private int[] negDegrees = { -90, -84, -72, -64, -56, -48, -40, -32, -24,
-16, -8 };
private char[] posLetters = { 'N', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W',
'X', 'Z' };
private int[] posDegrees = { 0, 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 84 };
private int arrayLength = 22;
public LatZones()
{
}
public int getLatZoneDegree(String letter)
{
char ltr = letter.charAt(0);
for (int i = 0; i < arrayLength; i++)
{
if (letters[i] == ltr)
{
return degrees[i];
}
}
return -100;
}
public String getLatZone(double latitude)
{
int latIndex = -2;
int lat = (int) latitude;
if (lat >= 0)
{
int len = posLetters.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (lat == posDegrees[i])
{
latIndex = i;
break;
}
if (lat > posDegrees[i])
{
continue;
}
else
{
latIndex = i - 1;
break;
}
}
}
else
{
int len = negLetters.length;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
if (lat == negDegrees[i])
{
latIndex = i;
break;
}
if (lat < negDegrees[i])
{
latIndex = i - 1;
break;
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
}
if (latIndex == -1)
{
latIndex = 0;
}
if (lat >= 0)
{
if (latIndex == -2)
{
latIndex = posLetters.length - 1;
}
return String.valueOf(posLetters[latIndex]);
}
else
{
if (latIndex == -2)
{
latIndex = negLetters.length - 1;
}
return String.valueOf(negLetters[latIndex]);
}
}
}
}3、另外,文章墨卡托投影C#实现给出了墨卡托投影的C#实现方法,摘录如下:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MRP
{
public class ClassMct {
static public int __IterativeTimes = 10; //反向转换程序中的迭代次数
static public double __IterativeValue = 0; //反向转换程序中的迭代初始值
static public double __A = 6378.137; //椭球体长轴,千米
static public double __B = 6356.752314; //椭球体短轴,千米
static public double __B0 = 0; //标准纬度,弧度
static public double __L0 = 0; //原点经度,弧度
//角度到弧度的转换
static public double DegreeToRad(double degree)
{
return Math.PI * degree / 180;
}
//弧度到角度的转换
static public double RadToDegree(double rad)
{
return (180 * rad) / Math.PI;
}
//设定__A与__B
static public void SetAB(double a, double b)
{
if (a <= 0 || b <= 0)
{
return;
}
__A = a;
__B = b;
}
//设定__B0
static public void SetLB0(double pmtL0, double pmtB0)
{
double l0 = DegreeToRad(pmtL0);
if (l0 < -Math.PI || l0 > Math.PI)
{
return;
}
__L0 = l0;
double b0 = DegreeToRad(pmtB0);
if (b0 < -Math.PI / 2 || b0 > Math.PI / 2)
{
return;
}
__B0 = b0;
}
/******************************************* 经纬度转XY坐标 pmtLB0: 参考点经纬度 pmtLB1: 要转换的经纬度 返回值: 直角坐标,单位:公里 *******************************************/
static public PointXY LBToXY(PointLB pmtLB0, PointLB pmtLB1)
{
SetLB0(pmtLB0.lon, pmtLB0.lat);
double B = DegreeToRad(pmtLB1.lat);
double L = DegreeToRad(pmtLB1.lon);
PointXY xy = new PointXY();
xy.x = 0; xy.y = 0;
double f/*扁率*/, e/*第一偏心率*/, e_/*第二偏心率*/, NB0/*卯酉圈曲率半径*/, K, dtemp;
double E = Math.Exp(1);
if (L < -Math.PI || L > Math.PI || B < -Math.PI / 2 || B > Math.PI / 2)
{
return xy;
}
if (__A <= 0 || __B <= 0)
{
return xy;
}
f = (__A - __B) / __A;
dtemp = 1 - (__B / __A) * (__B / __A);
if (dtemp < 0)
{
return xy;
}
e = Math.Sqrt(dtemp);
dtemp = (__A / __B) * (__A / __B) - 1;
if (dtemp < 0)
{
return xy;
}
e_ = Math.Sqrt(dtemp);
NB0 = ((__A * __A) / __B) / Math.Sqrt(1 + e_ * e_ * Math.Cos(__B0) * Math.Cos(__B0));
K = NB0 * Math.Cos(__B0);
xy.x = K * (L - __L0);
xy.y = K * Math.Log(Math.Tan(Math.PI / 4 + (B) / 2) * Math.Pow((1 - e * Math.Sin(B)) / (1 + e * Math.Sin(B)), e / 2));
double y0 = K * Math.Log(Math.Tan(Math.PI / 4 + (__B0) / 2) * Math.Pow((1 - e * Math.Sin(__B0)) / (1 + e * Math.Sin(__B0)), e / 2));
xy.y = xy.y - y0;
xy.y = -xy.y;//正常的Y坐标系(向上)转程序的Y坐标系(向下)
return xy;
}
/******************************************* XY坐标转经纬度 pmtLB0: 参考点经纬度 pmtXY: 要转换的XY坐标,单位:公里 返回值: 经纬度 *******************************************/
static public PointLB XYtoLB(PointLB pmtLB0, PointXY pmtXY)
{
SetLB0(pmtLB0.lon, pmtLB0.lat);
double X = pmtXY.x;
double Y = -pmtXY.y;//程序的Y坐标系(向下)转正常的Y坐标系(向上)
double B = 0, L = 0;
PointLB lb = new PointLB();
lb.lat = 0; lb.lon = 0;
double f/*扁率*/, e/*第一偏心率*/, e_/*第二偏心率*/, NB0/*卯酉圈曲率半径*/, K, dtemp;
double E = Math.Exp(1);
if (__A <= 0 || __B <= 0)
{
return lb;
}
f = (__A - __B) / __A;
dtemp = 1 - (__B / __A) * (__B / __A);
if (dtemp < 0)
{
return lb;
}
e = Math.Sqrt(dtemp);
dtemp = (__A / __B) * (__A / __B) - 1;
if (dtemp < 0)
{
return lb;
}
e_ = Math.Sqrt(dtemp);
NB0 = ((__A * __A) / __B) / Math.Sqrt(1 + e_ * e_ * Math.Cos(__B0) * Math.Cos(__B0));
K = NB0 * Math.Cos(__B0);
double y0 = K * Math.Log(Math.Tan(Math.PI / 4 + (__B0) / 2) * Math.Pow((1 - e * Math.Sin(__B0)) / (1 + e * Math.Sin(__B0)), e / 2));
Y = Y + y0;
L = X / K + __L0;
B = __IterativeValue;
for (int i = 0; i < __IterativeTimes; i++)
{
B = Math.PI / 2 - 2 * Math.Atan(Math.Pow(E, (-Y / K)) * Math.Pow(E, (e / 2) * Math.Log((1 - e * Math.Sin(B)) / (1 + e * Math.Sin(B)))));
}
lb.lon = RadToDegree(L);
lb.lat = RadToDegree(B);
return lb;
}
}
}4、开源坐标和投影转换库:Proj4
四、坐标系投影的工具
这里介绍几款坐标转换的工具
1、Excel转换工具GeogTools
2、GPS工具箱 (坐标转换,线路设计)
今天的文章经纬度坐标映射到平面直角坐标系的方法_经纬坐标如何转换平面坐标「建议收藏」分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/86762.html