前言
在本专栏【强化学习】理论知识整理汇总中提到了DQN的原理和创新点,本篇来通过Flappy Bird这个游戏实例来分析DQN的代码构成。
主要所用框架/库:pytorch、pygame、opencv
程序代码参考了github上的项目Playing-Flappy-Bird-by-DQN-on-PyTorch
游戏介绍
Flappy Bird比较流行,游戏需要控制一只不断下降的小鸟来穿越障碍物,动作选择空间为点和不点。点则让小鸟上升一段距离,不点小鸟继续下降,若小鸟碰到障碍物或地面,则游戏失败。
代码解读
我将通过主程序main.py的运行流程来简要分析DQN的运行机制。
数据预处理
在将图片输入到神经网络之前,首先需要对图片进行预处理,这里主要通过opencv的COLOR_BGR2GRAY和THRESH_BINARY将图片转成灰度并进行二值化处理,这样有利于提升计算速度。同时,还需要将图片resize成80×80的形式,以便网络输入。
# 初始操作
observation0 = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.resize(observation0, (80, 80)), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, observation0 = cv2.threshold(observation0, 1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
# 训练时操作
def preprocess(observation):
observation = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.resize(observation, (80, 80)), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, observation = cv2.threshold(observation, 1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
return np.reshape(observation, (1, 80, 80))
网络结构
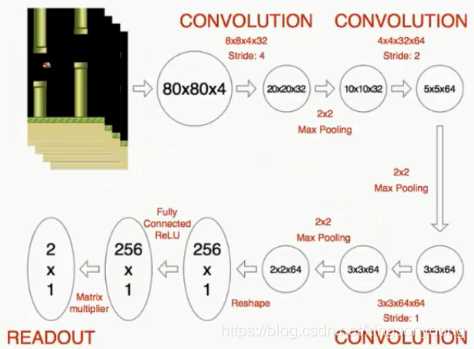
这里的网络设置成每次输入为4帧连续图片,网络结构如图所示。
图片来自强化学习—DQN训练计算机玩Flappy Bird游戏
可以看到,这里的网络使用了连续三个卷积层+两个全连接层的形式。最后输出为2个值,即动作选择。
class DeepNetWork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ):
super(DeepNetWork, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=4, out_channels=32, kernel_size=8, stride=4, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1600, 256),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.out = nn.Linear(256, 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc1(x)
return self.out(x)
数据库设置
在DQN理论介绍时提到,DQN的一大特点就是设置了数据库,后续的每次训练从数据库中抽取数据。这样可以破坏样本的连续性,使得训练更加有效。
程序中,使用了一个队列deque来当作数据库,数据库大小REPLAY_MEMORY设置为50000,如果数据库容量达到上限,将会把最先进入的数据抛出,即队列的先入先出。
# 创建数据库
self.replayMemory = deque()
# 数据库更新
self.replayMemory.append((self.currentState, action, reward, newState, terminal))
# 移除数据
if len(self.replayMemory) > REPLAY_MEMORY:
self.replayMemory.popleft()
目标网络
DQN的另一大特点是建立了两个Q网络,一个网络进行预测值的估计,另一个网络作为目标值。每个一段时间UPDATE_TIME,,目标网络需要再次复制训练网络。
# 网络构建
self.Q_net = DeepNetWork()
self.Q_netT = DeepNetWork()
# 目标值获取
QValue_batch = self.Q_netT(nextState_batch)
QValue_batch = QValue_batch.detach().numpy()
# 网络参数复制
if self.timeStep % UPDATE_TIME == 0:
self.Q_netT.load_state_dict(self.Q_net.state_dict())
self.save()
更新公式
这里的更新公式依旧是Q-Learning的更新公式,需要注意判断下一时刻是否是终止状态。
minibatch = random.sample(self.replayMemory, BATCH_SIZE)
state_batch = [data[0] for data in minibatch]
action_batch = [data[1] for data in minibatch]
reward_batch = [data[2] for data in minibatch]
nextState_batch = [data[3] for data in minibatch]
QValue_batch = self.Q_netT(nextState_batch)
QValue_batch = QValue_batch.detach().numpy()
for i in range(0, BATCH_SIZE):
terminal = minibatch[i][4]
if terminal:
y_batch[i][0] = reward_batch[i]
else:
y_batch[i][0] = reward_batch[i] + GAMMA * np.max(QValue_batch[i])
这里需要注意detach这个函数,QValue_batch是从目标网络而来,因此目标网络不参与训练的梯度更新,需要用detach来进行截断。
状态分割
值得注意的是该程序并没有一开始就进行训练,需要经历observe、explore、train三个状态。
首先前1000个时间步OBSERVE,处于观测(observe)状态,这个状态不做任何操作。
其次需要经过2000000个时间步EXPLORE,处于探索(explore)状态,这个状态随机进行动作选择,目的是给数据库增加数据。(这里我有些怀疑原作者的这个2000000是否过大,因为我尝试运行可两小时才经过50000步,需要很长时间才开始训练)
最后进入train状态,开始训练。
完整代码
这里展示的是main.py的代码,pygame游戏环境设置代码可以去原仓库下载。
import pdb
import cv2
import sys
import os
sys.path.append("game/")
import wrapped_flappy_bird as game
import random
import numpy as np
from collections import deque
import torch
from torch.autograd import Variable
import torch.nn as nn
GAME = 'bird' # the name of the game being played for log files
ACTIONS = 2 # number of valid actions
GAMMA = 0.99 # decay rate of past observations
OBSERVE = 1000. # timesteps to observe before training
EXPLORE = 2000000. # frames over which to anneal epsilon
FINAL_EPSILON = 0.0001 # final value of epsilon
INITIAL_EPSILON = 0.0001 # starting value of epsilon
REPLAY_MEMORY = 50000 # number of previous transitions to remember
BATCH_SIZE = 32 # size of minibatch
FRAME_PER_ACTION = 1
UPDATE_TIME = 100
width = 80
height = 80
def preprocess(observation):
observation = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.resize(observation, (80, 80)), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, observation = cv2.threshold(observation, 1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
return np.reshape(observation, (1, 80, 80))
class DeepNetWork(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, ):
super(DeepNetWork, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=4, out_channels=32, kernel_size=8, stride=4, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
)
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.fc1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1600, 256),
nn.ReLU()
)
self.out = nn.Linear(256, 2)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc1(x)
return self.out(x)
class BrainDQNMain(object):
def save(self):
print("save model param")
torch.save(self.Q_net.state_dict(), 'params3.pth')
def load(self):
if os.path.exists("params3.pth"):
print("load model param")
self.Q_net.load_state_dict(torch.load('params3.pth'))
self.Q_netT.load_state_dict(torch.load('params3.pth'))
def __init__(self, actions):
self.replayMemory = deque() # init some parameters
self.timeStep = 0
self.epsilon = INITIAL_EPSILON
self.actions = actions
self.Q_net = DeepNetWork()
self.Q_netT = DeepNetWork()
self.load()
self.loss_func = nn.MSELoss()
LR = 1e-6
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.Q_net.parameters(), lr=LR)
def train(self): # Step 1: obtain random minibatch from replay memory
minibatch = random.sample(self.replayMemory, BATCH_SIZE)
state_batch = [data[0] for data in minibatch]
action_batch = [data[1] for data in minibatch]
reward_batch = [data[2] for data in minibatch]
nextState_batch = [data[3] for data in minibatch] # Step 2: calculate y
y_batch = np.zeros([BATCH_SIZE, 1])
nextState_batch = np.array(nextState_batch) # print("train next state shape")
# print(nextState_batch.shape)
nextState_batch = torch.Tensor(nextState_batch)
action_batch = np.array(action_batch)
index = action_batch.argmax(axis=1)
print("action " + str(index))
index = np.reshape(index, [BATCH_SIZE, 1])
action_batch_tensor = torch.LongTensor(index)
QValue_batch = self.Q_netT(nextState_batch)
QValue_batch = QValue_batch.detach().numpy()
for i in range(0, BATCH_SIZE):
terminal = minibatch[i][4]
if terminal:
y_batch[i][0] = reward_batch[i]
else:
# 这里的QValue_batch[i]为数组,大小为所有动作集合大小,QValue_batch[i],代表
# 做所有动作的Q值数组,y计算为如果游戏停止,y=rewaerd[i],如果没停止,则y=reward[i]+gamma*np.max(Qvalue[i])
# 代表当前y值为当前reward+未来预期最大值*gamma(gamma:经验系数)
y_batch[i][0] = reward_batch[i] + GAMMA * np.max(QValue_batch[i])
y_batch = np.array(y_batch)
y_batch = np.reshape(y_batch, [BATCH_SIZE, 1])
state_batch_tensor = Variable(torch.Tensor(state_batch))
y_batch_tensor = Variable(torch.Tensor(y_batch))
y_predict = self.Q_net(state_batch_tensor).gather(1, action_batch_tensor)
loss = self.loss_func(y_predict, y_batch_tensor)
print("loss is " + str(loss))
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
if self.timeStep % UPDATE_TIME == 0:
self.Q_netT.load_state_dict(self.Q_net.state_dict())
self.save()
def setPerception(self, nextObservation, action, reward, terminal): # print(nextObservation.shape)
newState = np.append(self.currentState[1:, :, :], nextObservation,
axis=0) # newState = np.append(nextObservation,self.currentState[:,:,1:],axis = 2)
self.replayMemory.append((self.currentState, action, reward, newState, terminal))
if len(self.replayMemory) > REPLAY_MEMORY:
self.replayMemory.popleft()
if self.timeStep > OBSERVE: # Train the network
self.train()
# print info
state = ""
if self.timeStep <= OBSERVE:
state = "observe"
elif self.timeStep > OBSERVE and self.timeStep <= OBSERVE + EXPLORE:
state = "explore"
else:
state = "train"
print("TIMESTEP", self.timeStep, "/ STATE", state, "/ EPSILON", self.epsilon)
self.currentState = newState
self.timeStep += 1
def getAction(self):
currentState = torch.Tensor([self.currentState])
QValue = self.Q_net(currentState)[0]
action = np.zeros(self.actions)
if self.timeStep % FRAME_PER_ACTION == 0:
if random.random() <= self.epsilon:
action_index = random.randrange(self.actions)
print("choose random action " + str(action_index))
action[action_index] = 1
else:
action_index = np.argmax(QValue.detach().numpy())
print("choose qnet value action " + str(action_index))
action[action_index] = 1
else:
action[0] = 1 # do nothing
# change episilon
if self.epsilon > FINAL_EPSILON and self.timeStep > OBSERVE:
self.epsilon -= (INITIAL_EPSILON - FINAL_EPSILON) / EXPLORE
return action
def setInitState(self, observation):
self.currentState = np.stack((observation, observation, observation, observation), axis=0)
print(self.currentState.shape)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Step 1: init BrainDQN
actions = 2
brain = BrainDQNMain(actions) # Step 2: init Flappy Bird Game
flappyBird = game.GameState() # Step 3: play game
# Step 3.1: obtain init state
action0 = np.array([1, 0]) # do nothing
observation0, reward0, terminal = flappyBird.frame_step(action0)
observation0 = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.resize(observation0, (80, 80)), cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret, observation0 = cv2.threshold(observation0, 1, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
brain.setInitState(observation0)
print(brain.currentState.shape) # Step 3.2: run the game
while 1 != 0:
action = brain.getAction()
nextObservation, reward, terminal = flappyBird.frame_step(action)
nextObservation = preprocess(nextObservation)
# print(nextObservation.shape)
brain.setPerception(nextObservation, action, reward, terminal)
其它版本
在github上,我还找到了另一个作者用tensorflow1写的版本,这里也贴上代码以供对比(网络结构处了偏置之外基本一样)。
项目地址:https://github.com/floodsung/DRL-FlappyBird
# -----------------------------
# File: Deep Q-Learning Algorithm
# Author: Flood Sung
# Date: 2016.3.21
# -----------------------------
import tensorflow as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
import numpy as np
import random
from collections import deque
# Hyper Parameters:
FRAME_PER_ACTION = 1
GAMMA = 0.99 # decay rate of past observations
OBSERVE = 100. # timesteps to observe before training
EXPLORE = 200000. # frames over which to anneal epsilon
FINAL_EPSILON = 0.001 # 0.001 # final value of epsilon
INITIAL_EPSILON = 0.01 # 0.01 # starting value of epsilon
REPLAY_MEMORY = 50000 # number of previous transitions to remember
BATCH_SIZE = 32 # size of minibatch
UPDATE_TIME = 100
try:
tf.mul
except:
# For new version of tensorflow
# tf.mul has been removed in new version of tensorflow
# Using tf.multiply to replace tf.mul
tf.mul = tf.multiply
class BrainDQN:
def __init__(self, actions):
# init replay memory
self.replayMemory = deque()
# init some parameters
self.timeStep = 0
self.epsilon = INITIAL_EPSILON
self.actions = actions
self.saved = 0
# init Q network
self.stateInput, self.QValue, self.W_conv1, self.b_conv1, self.W_conv2, self.b_conv2, self.W_conv3, self.b_conv3, self.W_fc1, self.b_fc1, self.W_fc2, self.b_fc2 = self.createQNetwork()
# init Target Q Network
self.stateInputT, self.QValueT, self.W_conv1T, self.b_conv1T, self.W_conv2T, self.b_conv2T, self.W_conv3T, self.b_conv3T, self.W_fc1T, self.b_fc1T, self.W_fc2T, self.b_fc2T = self.createQNetwork()
self.copyTargetQNetworkOperation = [self.W_conv1T.assign(self.W_conv1), self.b_conv1T.assign(self.b_conv1),
self.W_conv2T.assign(self.W_conv2), self.b_conv2T.assign(self.b_conv2),
self.W_conv3T.assign(self.W_conv3), self.b_conv3T.assign(self.b_conv3),
self.W_fc1T.assign(self.W_fc1), self.b_fc1T.assign(self.b_fc1),
self.W_fc2T.assign(self.W_fc2), self.b_fc2T.assign(self.b_fc2)]
self.createTrainingMethod()
# saving and loading networks
self.saver = tf.train.Saver()
self.session = tf.InteractiveSession()
self.session.run(tf.initialize_all_variables())
checkpoint = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state("saved_networks")
if checkpoint and checkpoint.model_checkpoint_path:
checkpoint_path = checkpoint.model_checkpoint_path
self.saver.restore(self.session, checkpoint_path)
print("Successfully loaded:", checkpoint_path)
self.saved = int(checkpoint_path.split('-')[-1])
else:
print("Could not find old network weights")
def createQNetwork(self):
# network weights
W_conv1 = self.weight_variable([8, 8, 4, 32])
b_conv1 = self.bias_variable([32])
W_conv2 = self.weight_variable([4, 4, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = self.bias_variable([64])
W_conv3 = self.weight_variable([3, 3, 64, 64])
b_conv3 = self.bias_variable([64])
W_fc1 = self.weight_variable([256, 128])
b_fc1 = self.bias_variable([128])
W_fc2 = self.weight_variable([128, self.actions])
b_fc2 = self.bias_variable([self.actions])
# input layer
stateInput = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 80, 80, 4])
# hidden layers
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(self.conv2d(stateInput, W_conv1, 4) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = self.max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(self.conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2, 2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = self.max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
h_conv3 = tf.nn.relu(self.conv2d(h_pool2, W_conv3, 1) + b_conv3)
h_pool3 = self.max_pool_2x2(h_conv3)
h_conv3_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool3, [-1, 256])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_conv3_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
# Q Value layer
QValue = tf.matmul(h_fc1, W_fc2) + b_fc2
return stateInput, QValue, W_conv1, b_conv1, W_conv2, b_conv2, W_conv3, b_conv3, W_fc1, b_fc1, W_fc2, b_fc2
def copyTargetQNetwork(self):
self.session.run(self.copyTargetQNetworkOperation)
def createTrainingMethod(self):
self.actionInput = tf.placeholder("float", [None, self.actions])
self.yInput = tf.placeholder("float", [None])
Q_Action = tf.reduce_sum(tf.mul(self.QValue, self.actionInput), reduction_indices=1)
self.cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(self.yInput - Q_Action))
self.trainStep = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-6).minimize(self.cost)
def trainQNetwork(self):
# Step 1: obtain random minibatch from replay memory
minibatch = random.sample(self.replayMemory, BATCH_SIZE)
state_batch = [data[0] for data in minibatch]
action_batch = [data[1] for data in minibatch]
reward_batch = [data[2] for data in minibatch]
nextState_batch = [data[3] for data in minibatch]
# Step 2: calculate y
y_batch = []
QValue_batch = self.QValueT.eval(feed_dict={
self.stateInputT: nextState_batch})
for i in range(0, BATCH_SIZE):
terminal = minibatch[i][4]
if terminal:
y_batch.append(reward_batch[i])
else:
y_batch.append(reward_batch[i] + GAMMA * np.max(QValue_batch[i]))
self.trainStep.run(feed_dict={
self.yInput: y_batch,
self.actionInput: action_batch,
self.stateInput: state_batch
})
# save network every 100000 iteration
if self.timeStep % 100 == 0:
self.saver.save(self.session, 'saved_networks/' + 'network' + '-dqn',
global_step=(self.saved + self.timeStep))
if self.timeStep % UPDATE_TIME == 0:
self.copyTargetQNetwork()
def setPerception(self, nextObservation, action, reward, terminal):
# newState = np.append(nextObservation,self.currentState[:,:,1:],axis = 2)
newState = np.append(self.currentState[:, :, 1:], nextObservation, axis=2)
self.replayMemory.append((self.currentState, action, reward, newState, terminal))
if len(self.replayMemory) > REPLAY_MEMORY:
self.replayMemory.popleft()
if self.timeStep > OBSERVE:
# Train the network
self.trainQNetwork()
# print info
state = ""
if self.timeStep <= OBSERVE:
state = "observe"
elif self.timeStep > OBSERVE and self.timeStep <= OBSERVE + EXPLORE:
state = "explore"
else:
state = "train"
print("TIMESTEP", (self.saved + self.timeStep), "/ STATE", state, \
"/ EPSILON", self.epsilon)
self.currentState = newState
self.timeStep += 1
def getAction(self):
QValue = self.QValue.eval(feed_dict={
self.stateInput: [self.currentState]})[0]
action = np.zeros(self.actions)
action_index = 0
if self.timeStep % FRAME_PER_ACTION == 0:
if random.random() <= self.epsilon:
action_index = random.randrange(self.actions)
action[action_index] = 1
else:
action_index = np.argmax(QValue)
action[action_index] = 1
else:
action[0] = 1 # do nothing
# change episilon
if self.epsilon > FINAL_EPSILON and self.timeStep > OBSERVE:
self.epsilon -= (INITIAL_EPSILON - FINAL_EPSILON) / EXPLORE
return action
def setInitState(self, observation):
self.currentState = np.stack((observation, observation, observation, observation), axis=2)
def weight_variable(self, shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.01)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(self, shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.01, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(self, x, W, stride):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, stride, stride, 1], padding="SAME")
def max_pool_2x2(self, x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding="SAME")
总结
这个示例我没有完全跑完,预计获得一个较好结果预估需要训练数天时间。通过代码,能够对DQN有进一步的认识。
今天的文章【强化学习】DQN:Flappy Bird实例分析分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读,如果确实帮到您,您可以动动手指转发给其他人。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:http://bianchenghao.cn/30596.html