最长公共子串(Longest Common Substring)是一个非常经典的面试题目,在实际的程序中也有很高的实用价值,所以把该问题的解法总结在本文重。不过不单单只是写出该问题的基本解决代码而已,关键还是享受把学习算法一步步的优化,让时间和空间复杂度一步步的减少的惊喜。
概览
最长公共子串问题的基本表述为:
给定两个字符串,求出它们之间最长的相同子字符串的长度。
最直接的解法自然是找出两个字符串的所有子字符串进行比较看他们是否相同,然后取得相同最长的那个。对于一个长度为n的字符串,它有n(n+1)/2 个非空子串。所以假如两个字符串的长度同为n,通过比较各个子串其算法复杂度大致为O(n4)。这还没有考虑字符串比较所需的时间。简单想想其实并不需要取出所有的子串,而只要考虑每个子串的开始位置就可以,这样可以把复杂度减到O(n3)。
但这个问题最好的解决办法是动态规划法,在后边会更加详细介绍这个问题使用动态规划法的契机:有重叠的子问题。进而可以通过空间换时间,让复杂度优化到O(n2),代价是空间复杂度从O(1)一下子提到了O(n2)。
从时间复杂度的角度讲,对于最长公共子串问题,O(n2)已经是目前我所知最优的了,也是面试时所期望达到的。但是对于空间复杂度O(n2)并不算什么,毕竟算法上时间比空间更重要,但是如果可以省下一些空间那这个算法就会变得更加美好。所以进一步的可以把空间复杂度减少到O(n),这是相当美好了。但有一天无意间让我发现了一个算法可以让该问题的空间复杂度减少回原来的O(1),而时间上如果幸运还可以等于O(n)。
暴力解法 – 所得即所求
对于该问题,直观的思路就是问题要求什么就找出什么。要子串,就找子串;要相同,就比较每个字符;要最长就记录最长。所以很容易就可以想到如下的解法。
1 int longestCommonSubstring_n3(const string& str1, const string& str2) 2 { 3 size_t size1 = str1.size(); 4 size_t size2 = str2.size(); 5 if (size1 == 0 || size2 == 0) return 0; 6 7 // the start position of substring in original string 8 int start1 = -1; 9 int start2 = -1; 10 // the longest length of common substring 11 int longest = 0; 12 13 // record how many comparisons the solution did; 14 // it can be used to know which algorithm is better 15 int comparisons = 0; 16 17 for (int i = 0; i < size1; ++i) 18 { 19 for (int j = 0; j < size2; ++j) 20 { 21 // find longest length of prefix 22 int length = 0; 23 int m = i; 24 int n = j; 25 while(m < size1 && n < size2) 26 { 27 ++comparisons; 28 if (str1[m] != str2[n]) break; 29 30 ++length; 31 ++m; 32 ++n; 33 } 34 35 if (longest < length) 36 { 37 longest = length; 38 start1 = i; 39 start2 = j; 40 } 41 } 42 } 43 #ifdef IDER_DEBUG 44 cout<< "(first, second, comparisions) = (" 45 << start1 << ", " << start2 << ", " << comparisons 46 << ")" << endl; 47 #endif 48 return longest; 49 }
该解法的思路就如前所说,以字符串中的每个字符作为子串的端点,判定以此为开始的子串的相同字符最长能达到的长度。其实从表层上想,这个算法的复杂度应该只有O(n2)因为该算法把每个字符都成对相互比较一遍,但关键问题在于比较两个字符串的效率并非是O(1),这也导致了实际的时间复杂度应该是满足Ω(n2)和O(n3)。
动态规划法 – 空间换时间
有了一个解决问题的方法是一件很不错的事情了,但是拿着上边的解法回答面试题肯定不会得到许可,面试官还是会问有没有更好的解法呢?不过上述解法虽然不是最优的,但是依然可以从中找到一个改进的线索。不难发现在子串比较中有很多次重复的比较。
比如再比较以i和j分别为起始点字符串时,有可能会进行i+1和j+1以及i+2和j+2位置的字符的比较;而在比较i+1和j+1分别为起始点字符串时,这些字符又会被比较一次了。也就是说该问题有非常相似的子问题,而子问题之间又有重叠,这就给动态规划法的应该提供了契机。
暴力解法是从字符串开端开始找寻,现在换个思维考虑以字符结尾的子串来利用动态规划法。
假设两个字符串分别为s和t,s[i]和t[j]分别表示其第i和第j个字符(字符顺序从0开始),再令L[i, j]表示以s[i]和s[j]为结尾的相同子串的最大长度。应该不难递推出L[i, j]和L[i+1,j+1]之间的关系,因为两者其实只差s[i+1]和t[j+1]这一对字符。若s[i+1]和t[j+1]不同,那么L[i+1, j+1]自然应该是0,因为任何以它们为结尾的子串都不可能完全相同;而如果s[i+1]和t[j+1]相同,那么就只要在以s[i]和t[j]结尾的最长相同子串之后分别添上这两个字符即可,这样就可以让长度增加一位。合并上述两种情况,也就得到L[i+1,j+1]=(s[i]==t[j]?L[i,j]+1:0)这样的关系。
最后就是要小心的就是临界位置:如若两个字符串中任何一个是空串,那么最长公共子串的长度只能是0;当i为0时,L[0,j]应该是等于L[-1,j-1]再加上s[0]和t[j]提供的值,但L[-1,j-1]本是无效,但可以视s[-1]是空字符也就变成了前面一种临界情况,这样就可知L[-1,j-1]==0,所以L[0,j]=(s[0]==t[j]?1:0)。对于j为0也是一样的,同样可得L[i,0]=(s[i]==t[0]?1:0)。
最后的算法代码如下:
1 int longestCommonSubstring_n2_n2(const string& str1, const string& str2) 2 { 3 size_t size1 = str1.size(); 4 size_t size2 = str2.size(); 5 if (size1 == 0 || size2 == 0) return 0; 6 7 vector<vector<int> > table(size1, vector<int>(size2, 0)); 8 // the start position of substring in original string 9 int start1 = -1; 10 int start2 = -1; 11 // the longest length of common substring 12 int longest = 0; 13 14 // record how many comparisons the solution did; 15 // it can be used to know which algorithm is better 16 int comparisons = 0; 17 for (int j = 0; j < size2; ++j) 18 { 19 ++comparisons; 20 table[0][j] = (str1[0] == str2[j] ? 1 :0); 21 } 22 23 for (int i = 1; i < size1; ++i) 24 { 25 ++comparisons; 26 table[i][0] = (str1[i] == str2[0] ? 1 :0); 27 28 for (int j = 1; j < size2; ++j) 29 { 30 ++comparisons; 31 if (str1[i] == str2[j]) 32 { 33 table[i][j] = table[i-1][j-1]+1; 34 } 35 } 36 } 37 38 for (int i = 0; i < size1; ++i) 39 { 40 for (int j = 0; j < size2; ++j) 41 { 42 if (longest < table[i][j]) 43 { 44 longest = table[i][j]; 45 start1 = i-longest+1; 46 start2 = j-longest+1; 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 #ifdef IDER_DEBUG 51 cout<< "(first, second, comparisions) = (" 52 << start1 << ", " << start2 << ", " << comparisons 53 << ")" << endl; 54 #endif 55 56 return longest; 57 }
算法开辟了一个矩阵内存来存储值来保留计算值,从而避免了重复计算,于是运算的时间复杂度也就降至了O(n2)。
动态规划法优化 – 能省一点是一点
仔细回顾之前的代码,其实可以做一些合并让代码变得更加简洁,比如最后一个求最长的嵌套for循环其实可以合并到之前计算整个表的for循环之中,每计算完L[i,j]就检查它是的值是不是更长。当合并代码之后,就会发现内部循环的过程重其实只用到了整个表的相邻两行而已,对于其它已经计算好的行之后就再也不会用到,而未计算的行曽之前也不会用到,因此考虑只用两行来存储计算值可能就足够。
于是新的经过再次优化的算法就有了:
int longestCommonSubstring_n2_2n(const string& str1, const string& str2) { size_t size1 = str1.size(); size_t size2 = str2.size(); if (size1 == 0 || size2 == 0) return 0; vector<vector<int> > table(2, vector<int>(size2, 0)); // the start position of substring in original string int start1 = -1; int start2 = -1; // the longest length of common substring int longest = 0; // record how many comparisons the solution did; // it can be used to know which algorithm is better int comparisons = 0; for (int j = 0; j < size2; ++j) { ++comparisons; if (str1[0] == str2[j]) { table[0][j] = 1; if (longest == 0) { longest = 1; start1 = 0; start2 = j; } } } for (int i = 1; i < size1; ++i) { ++comparisons; // with odd/even to swith working row int cur = ((i&1) == 1); //index for current working row int pre = ((i&1) == 0); //index for previous working row table[cur][0] = 0; if (str1[i] == str2[0]) { table[cur][0] = 1; if (longest == 0) { longest = 1; start1 = i; start2 = 0; } } for (int j = 1; j < size2; ++j) { ++comparisons; if (str1[i] == str2[j]) { table[cur][j] = table[pre][j-1]+1; if (longest < table[cur][j]) { longest = table[cur][j]; start1 = i-longest+1; start2 = j-longest+1; } } else { table[cur][j] = 0; } } } #ifdef IDER_DEBUG cout<< "(first, second, comparisions) = (" << start1 << ", " << start2 << ", " << comparisons << ")" << endl; #endif return longest; }
跟之前的动态规划算法代码相比,两种解法并没有实质的区别,完全相同的嵌套for循环,只是将检查最长的代码也并入其中,然后table中所拥有的行也只剩下2个。
此解法的一些技巧在于如何交换两个行数组作为工作数组。可以交换数组中的每个元素,异或交换一对指针。上边代码中所用的方法类似于后者,根据奇偶性来决定那行数组可以被覆盖,哪行数组有需要的缓存数据。不管怎么说,该算法都让空间复杂度从O(n2)减少到了O(n),相当有效。
动态规划法再优化 – 能用一点就只用一点
最长公共子串问题的解法优化到之前的模样,基本是差不多了,Wikipedia上对于这个问题给出的解法也就到上述而已。但思考角度不同,还是有意外的惊喜的。不过要保持算法的时间复杂度不增加,算法的基本思路方针还是不能变的。
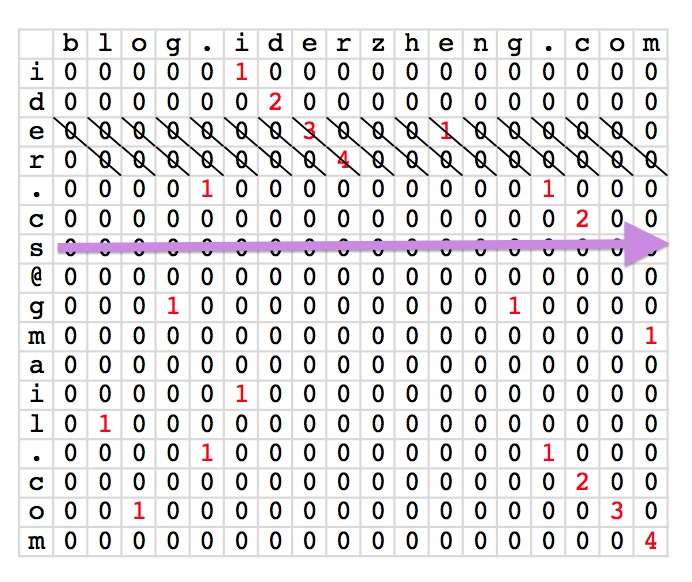
下图是上述动态规划的计算过程的示例:
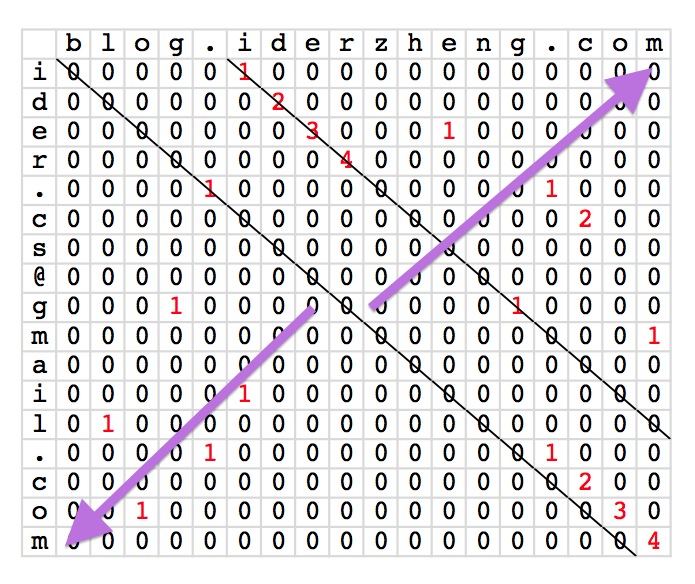
在填充这张表的过程中,算法是从上往下一行一行计算,然后每行是从左往右。对于每一格,要知道它左上格是什么值,这就导致需要保留一整行的数据信息。但如果只针对一格看,它需要知道的只是左上格,而它的左上格又只要知道左上格的左上格就足够了,于是就是一个对角线的路径。
而如若按对角线为行,一行行计算的话,其实就只需要缓存下一个数据就可以将对角线上的格子填充完毕。从字符串上讲,就是偏移一个字符串的头,然后跟另一个字符串比较看在如此固定的位置下能找到最长的公共子串是多长。
解释可能有点不清,程序员可能还是从代码更能看懂算法的意思:
1 int longestCommonSubstring_n2_1(const string& str1, const string& str2) 2 { 3 size_t size1 = str1.size(); 4 size_t size2 = str2.size(); 5 if (size1 == 0 || size2 == 0) return 0; 6 7 // the start position of substring in original string 8 int start1 = -1; 9 int start2 = -1; 10 // the longest length of common substring 11 int longest = 0; 12 13 // record how many comparisons the solution did; 14 // it can be used to know which algorithm is better 15 int comparisons = 0; 16 17 for (int i = 0; i < size1; ++i) 18 { 19 int m = i; 20 int n = 0; 21 int length = 0; 22 while(m < size1 && n < size2) 23 { 24 ++comparisons; 25 if (str1[m] != str2[n]) 26 { 27 length = 0; 28 } 29 else 30 { 31 ++length; 32 if (longest < length) 33 { 34 longest = length; 35 start1 = m-longest+1; 36 start2 = n-longest+1; 37 } 38 } 39 40 ++m; 41 ++n; 42 } 43 } 44 45 // shift string2 to find the longest common substring 46 for (int j = 1; j < size2; ++j) 47 { 48 int m = 0; 49 int n = j; 50 int length = 0; 51 while(m < size1 && n < size2) 52 { 53 ++comparisons; 54 if (str1[m] != str2[n]) 55 { 56 length = 0; 57 } 58 else 59 { 60 ++length; 61 if (longest < length) 62 { 63 longest = length; 64 start1 = m-longest+1; 65 start2 = n-longest+1; 66 } 67 } 68 69 ++m; 70 ++n; 71 } 72 } 73 74 #ifdef IDER_DEBUG 75 cout<< "(first, second, comparisions) = (" 76 << start1 << ", " << start2 << ", " << comparisons 77 << ")" << endl; 78 #endif 79 80 return longest; 81 }
算法中两个for循环都嵌套着一个while循环,但实际时间复杂度是跟原来一致依然是O(n2)而不是翻倍(当然翻倍了O还是一样的),因为每个for其实都只遍历原表的一半区域而已。
看看这两个for实在是不欢喜,循环内的代码除了头两行对m和n的初始化值不同以外,其它代码全都一模一样。对于这种冗余的代码是程序员极为不满的,所以我们应该合并它们,一种方法就是把代码封装到方法中,在两个for循环里调用方法即可。不过我用来一些非常规的技巧和C++的引用类型特性来合并两个for循环:
1 int longestCommonSubstring_n2_1(const string& str1, const string& str2) 2 { 3 size_t size1 = str1.size(); 4 size_t size2 = str2.size(); 5 if (size1 == 0 || size2 == 0) return 0; 6 7 // the start position of substring in original string 8 int start1 = -1; 9 int start2 = -1; 10 // the longest length of common substring 11 int longest = 0; 12 13 // record how many comparisons the solution did; 14 // it can be used to know which algorithm is better 15 int comparisons = 0; 16 17 int indices[] = {0, 0}; 18 int sizes[] = {size1, size2}; 19 20 // shift strings to find the longest common substring 21 for (int index = 0; index < 2; ++index) 22 { 23 indices[0] = 0; 24 indices[1] = 0; 25 26 // i is reference to the value in array 27 int &i = indices[index]; 28 int size = sizes[index]; 29 30 // this is tricky to skip comparing strings both start with 0 for second loop 31 i = index; 32 for (; i < size; ++i) 33 { 34 int m = indices[0]; 35 int n = indices[1]; 36 int length = 0; 37 38 // with following check to reduce some more comparisons 39 if (size1-m <= longest || size2-n <= longest) 40 break; 41 42 while(m < size1 && n < size2) 43 { 44 ++comparisons; 45 if (str1[m] != str2[n]) 46 { 47 length = 0; 48 } 49 else 50 { 51 ++length; 52 if (longest < length) 53 { 54 longest = length; 55 start1 = m-longest+1; 56 start2 = n-longest+1; 57 } 58 } 59 60 ++m; 61 ++n; 62 } 63 } 64 } 65 66 #ifdef IDER_DEBUG 67 cout<< "(first, second, comparisions) = (" 68 << start1 << ", " << start2 << ", " << comparisons 69 << ")" << endl; 70 #endif 71 72 return longest; 73 }
在上述代表中,有一个语句if (size1-m <= longest || size2-n <= longest) 会break循环,其中的条件其实是检查剩下子串长度是否小于或等于跟最长公共子串的长度,如果是那么剩下的可定不足以构建出更长的子串。这对于当一个字符串是另一个字符串的子串是可以减少很多的比较,这也是之前在提到:在幸运的时候运算时间复杂度可以有O(n)。对于这样的微小优化也可以在之前的几个算法中使用。
测试案例及结果
最后贴上一些测试随机生成的测试案例已经调用每个算法所得到的结果和运算需要的“量”。打包的所有代码都可以在这里下载,欢迎测试并给出一些建议和优化方案。
YXXXXXY (7) YXYXXYYYYXXYYYYXYYXXYYXXYXYYYYYYXYXYYXYXYYYXXXXXX (49) (first, second, comparisions) = (0, 42, 537) 6 (first, second, comparisions) = (0, 42, 343) 6 (first, second, comparisions) = (0, 42, 343) 6 (first, second, comparisions) = (0, 42, 316) 6 XXYXYYYXXYXYYYYXYXYYYXYYYYYXYX (30) XYY (3) (first, second, comparisions) = (3, 0, 127) 3 (first, second, comparisions) = (3, 0, 90) 3 (first, second, comparisions) = (3, 0, 90) 3 (first, second, comparisions) = (3, 0, 12) 3 XXYXXYYYXYXYYXXYYYYYXXYXXXYXXYXYXXXXYXXYYYXYYXYXYXXXYYXXXYYXYYXYXYXYXXXXXXXXXYXXXX (82) YYYYYXYYYXYYXXXYYYXXYYXXYXXXYYYYYYYYXXYXYYYYXYXYYXYX (52) (first, second, comparisions) = (5, 41, 7911) 9 (first, second, comparisions) = (5, 41, 4264) 9 (first, second, comparisions) = (5, 41, 4264) 9 (first, second, comparisions) = (18, 20, 4183) 9 X (1) XXYYYYYYXYYXYXXXYYXXXYYYYYYXYYYXYYXXYYYYXXXYXXXXXXXYXYXYXYYYYYYYYXYXYXXX (72) (first, second, comparisions) = (0, 0, 72) 1 (first, second, comparisions) = (0, 0, 72) 1 (first, second, comparisions) = (0, 0, 72) 1 (first, second, comparisions) = (0, 0, 1) 1 (0) XYXXYYYXXXYYXXYYYYXXYYYXYYYXXXXXYYXXYXYXXXYY (44) 0 0 0 0
从见过可以看出所有方法的计算应该都是正确并且一致的,也不难看出对于经典的动态规划的两个方法需要的比较时间正式两个字符串长度的乘积。另一个问题如果不旦旦只有长度而要找出最长子串来,算法给出的答案就有可能不同,因为两个字符串中可能存在多个不同的最长公共子串。
今天的文章最长公共子序列优化算法_最长连续子串最大和分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读,如果确实帮到您,您可以动动手指转发给其他人。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/47921.html