多级。 If the data your program needs are stored in a CPU register, then they can be accessed in 0 cycles during the execution of the instruction. If stored in a cache, 4 to 75 cycles. If stored in main memory, hundreds of cycles. And if stored in disk, tens of millions of cycles!
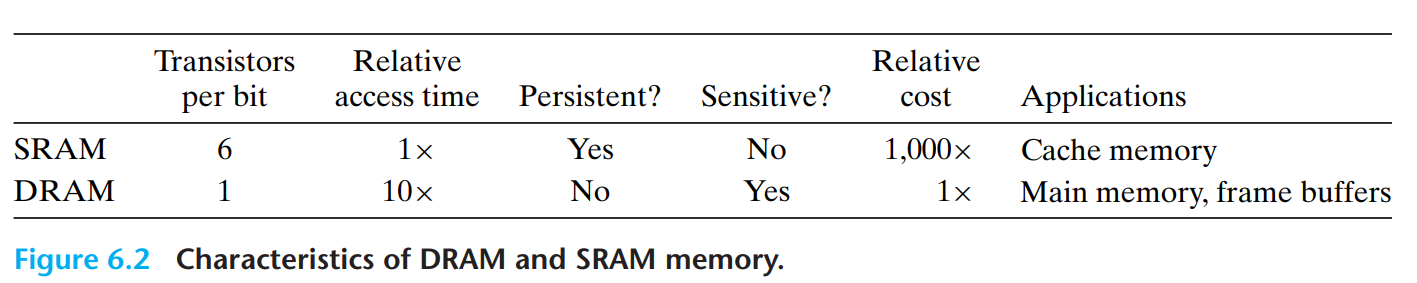
Static RAM (SRAM) is faster and significantly more expensive than dynamic RAM (DRAM).
SRAM is used for cache memories, both on and off the CPU chip.
DRAM is used for the main memory plus the frame buffer of a graphics system.
DRAM需要周期刷新,对噪声敏感。
DRAMs and SRAMs are volatile in the sense that they lose their information if the supply voltage is turned off.
There are a variety of nonvolatile memories. For historical reasons, they are referred to collectively as read-only memories (ROMs), even though some types of ROMs can be written to as well as
read.
Programs stored in ROM devices are often referred to as firmware. When a
computer system is powered up, it runs firmware stored in a ROM. Some systems
provide a small set of primitive input and output functions in firmware—for
example, a PC’s BIOS (basic input/output system) routines. Complicated devices
such as graphics cards and disk drive controllers also rely on firmware to translate
I/O (input/output) requests from the CPU.
locality的概念:
you can write your application programs so that their data items are stored higher in the hierarchy.
Programs with good locality tend to access the same set of data items over and over again, or they tend to access sets of nearby data items. Programs with good locality tend to access more data items from the upper levels of the memory hierarchy than programs with poor locality, and thus run faster.
Locality is typically described as having two distinct forms: temporal locality and spatial locality. In a program with good temporal locality, a memory location that is referenced once is likely to be referenced again multiple times in the near future. In a program with good spatial locality, if a memory location is referenced once, then the program is likely to reference a nearby memory location in the near future.
如果一个函数内的变量要么temporal locality要么spatial locality,我们认为它good locality。
操作系统层面locality的体现:
At the operating system level, the principle of locality allows the system to use the main memory as a cache of the most recently referenced chunks of the virtual address space.
在内存金字塔中,disk还不是塔底,远程服务器才是塔底。
Web browsers exploit temporal locality by caching recently referenced documents on a local disk.
此外,ssd的流行使得dram跟机械盘之间有了一个过渡。
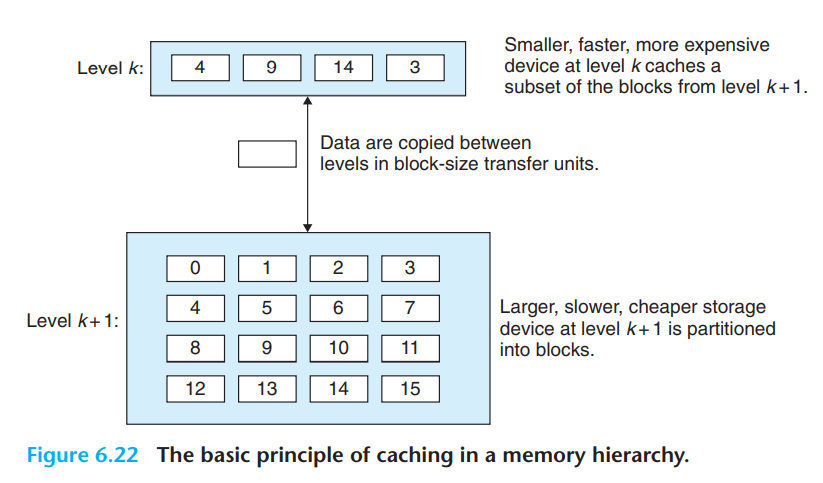
It is important to realize that while the block size is fixed between any particular pair of adjacent levels in the hierarchy, other pairs of levels can have different block sizes. In general, devices lower in the hierarchy (further from the CPU) have longer access times, and thus tend to use larger block sizes in order to amortize these longer access times.
其实我们平时最经常写的二层循环内也蕴含locality。一般把第一维的下标放在外层,第二维的下标放在内层。如果反过来,那就违背了spatial locality。
上面提到6.22中的block size是会变化的。miss之后会replace一整个block,而一个block中可能有数个相邻的data objects,因此spatial locality好的程序会更快。(比如,在访问a[0]的时候miss了,于是就replace了a[0]~a[3],因此访问a[0]-a[3]的速度会比访问四个不相干数据的速度要快。)
Loops have good temporal and spatial locality with respect to instruction fetches. The smaller the loop body and the greater the number of loop iterations, the better the locality.
locality可以用cache hits和cache misses来量化。
cache miss也可分为三类。
- cold miss
cache中没有数据。 - conflict miss
the cache is large enough to hold the referenced data objects, but because they map to the same cache block, the cache keeps missing.(以上图6.22为例,反复访问0和8时,会一直miss,0、4、8、12共享上一级cache的第一个位置。) - capacity miss
工作集比cache的容量更大。
the essence of the memory hierarchy is that the storage device at each level is a cache for the next lower level.
低级存储和高级存储之间的三种映射方法:直接映射、全相联、组相联(参考cany1000的博文)
直接映射实现简单。cache的利用率较低,就如每个人的停车位是固定分配好的,可以直接找到。适用于大容量cache。(n人共享第a个车位,这n个人的车牌号都以a结尾)
全相联,就像停车位可以大家随便停一样,停的时候简单,找车的时候需要一个一个停车位的找了。
(所有人随意使用所有车位)
组相联则是折中方案,组内全相联,组间直接映射。(n人共享第a组车位,这n个人的车牌号都以a结尾,这n个人使用第a组内的车位时,可以随意使用。这称为a路组相联)
内存金字塔中,读时是层进的hit or miss。写时,分为write-through和write-back,前者就是马上逐级下写,后者是等替换时再下写(由于temporal locality,write-back的下写次数较少)。write miss发生时,分为write-allocate和no-write-allocate。
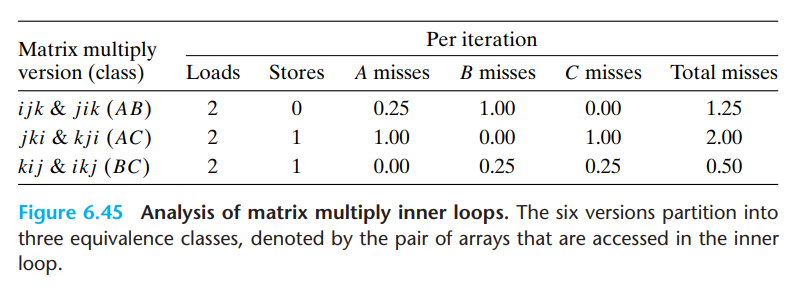
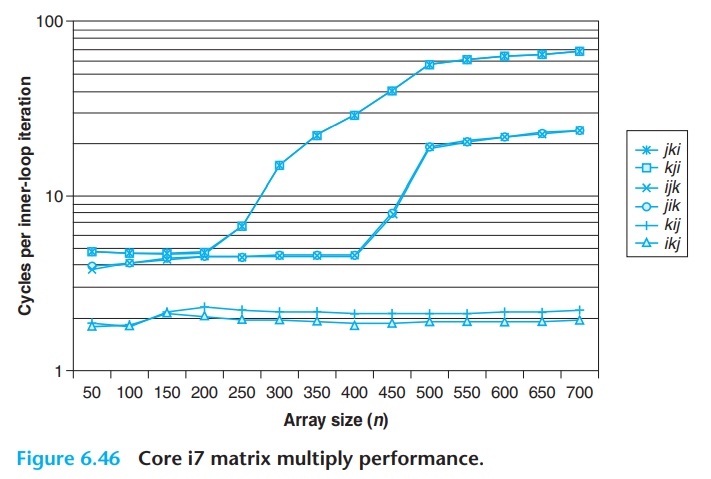
对矩阵乘法六种实现的分析:
书中提到,虽然浮点乘法的次数一样,但最好和最差之间有四十倍的差距。所以一定要充分考虑缓存对性能的影响。
从图6.46可以看出,最内层循环为BC的两种方案是最好的,并且随n的增大,优势越来越明显。
这其实还是一个spatial locality的例子,最内层循环为BC的方案(kij和ikj)是stride-1的,最内层循环所用的index出现在最后一维,所以缓存的优势很大。书中还提到,intel对stride-1做了特别的优化。
今天的文章CS:APP第六章知识总结(内存、缓存、locality)分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/60441.html