目录
一.关系运算符
等于: ==
不等于: !=
大于:>
小于: <
大于等于: >=
小于等于: <=
二.逻辑运算符
并且(与):&&
或者(或): ||
三.IF条件语句
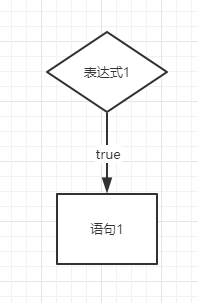
示例一:单个if表达式
if(表达式1){
语句1;
}
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
//如果成立就打印yes
if( a == b ){
System.out.println("yes");
}
}
}
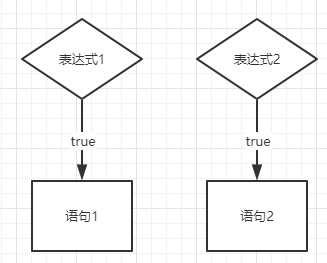
示例二:多个if表达式
if(表达式1){
语句1;
}
if(表达式2){
语句2;
}
当表达式1的判断为真(正确/true)
就执行语句1
当表达式2的判断为真(正确/true)
就执行语句2
(两个if没有任何关系)
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
int b = 1;
//如果成立就打印yes1
if( a == b ){
System.out.println("yes1");
}
//如果成立就打印yes2
if( a == 1){
System.out.println("yes2");
}
}
}
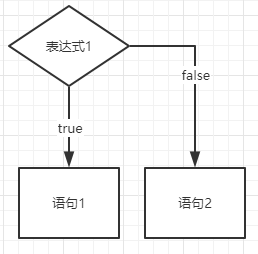
示例三:if else表达式
if(表达式1){
语句1;
}else{
语句2;
}
当表达式1的判断为真(正确/true)
就执行语句1
否则
就执行语句2
(不执行1就执行2)
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 1;
if( a == 0){
System.out.println("yes1");
}else{
System.out.println("yes2");
}
}
}
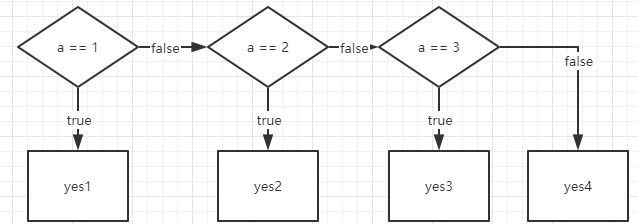
示例四:if else if 表达式
if(表达式1){
语句1;
}else if(表达式2){
语句2;
}else{
语句3;
}
当表达式1的判断为真(正确/true)
就执行语句1
否则 当表达式2的判断为真
就执行语句2
否则
就执行语句3
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 3;
if( a == 1 ){
System.out.println("yes1");
} else if( a == 2){
System.out.println("yes2");
} else if( a == 3){
System.out.println("yes3");
} else{
System.out.println("yes4");
}
}
}
示例五:if表达式中使用关系运算符
小于:<
大于等于:>=
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 3;
if( a == 1 ){
System.out.println("yes1");
} else if( a < 2){
System.out.println("yes2");
} else if( a >= 3){
System.out.println("yes3");
} else{
System.out.println("yes4");
}
}
}
示例六:if表达式中使用逻辑运算符
并且(与):&&
或者(或): ||
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 3;
int b = 2
if( a == 1 && b == 2){
System.out.println("yes1");
} else if( a < 2 || b > 3){
System.out.println("yes2");
} else if( a >= 3 && b == 2){
System.out.println("yes3");
} else{
System.out.println("yes4");
}
}
}
以上if表达式中使用的都是数字判断,字符串的判断有较大的区别。
补充:字符串的判断
错误的字符串判断相等(字符串的判断不能使用 “==” )
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = new String("张三");
if( name == "王五" ){
System.out.println("yes1");
} else if( name == "赵四"){
System.out.println("yes2");
} else if( name == "张三"){
System.out.println("yes3");
} else{
System.out.println("yes4");
}
}
}
正确的字符串判断相等(使用 “equal”)
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = new String("张三");
if( name.equals("王五")){
System.out.println("yes1");
} else if( "赵四".equals(name)){
System.out.println("yes2");
} else if( name.equals("张三")){
System.out.println("yes3");
} else{
System.out.println("yes4");
}
}
}
三、补充for循环语句:连续输出十句话
不使用for循环
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("这是第"+1+"句话");
System.out.println("这是第"+2+"句话");
System.out.println("这是第"+3+"句话");
System.out.println("这是第"+4+"句话");
System.out.println("这是第"+5+"句话");
System.out.println("这是第"+6+"句话");
System.out.println("这是第"+7+"句话");
System.out.println("这是第"+8+"句话");
System.out.println("这是第"+9+"句话");
System.out.println("这是第"+10+"句话");
}
}
使用for循环
public class HelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
System.out.println("这是第"+i+"句话");
}
}
}
今天的文章java if判断条件_ifelseifelse执行顺序「建议收藏」分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/68466.html