C++——多项式拟合
目标:利用C++对txt或者xml中的数据,进行高阶或低阶多项式拟合
为方便以后查找,代码以及详细资料已打包,并上传至云盘(链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1bvUBIoxv7Avxeq_Cz6xOZQ 密码:u9qe)
打包的内容如下:
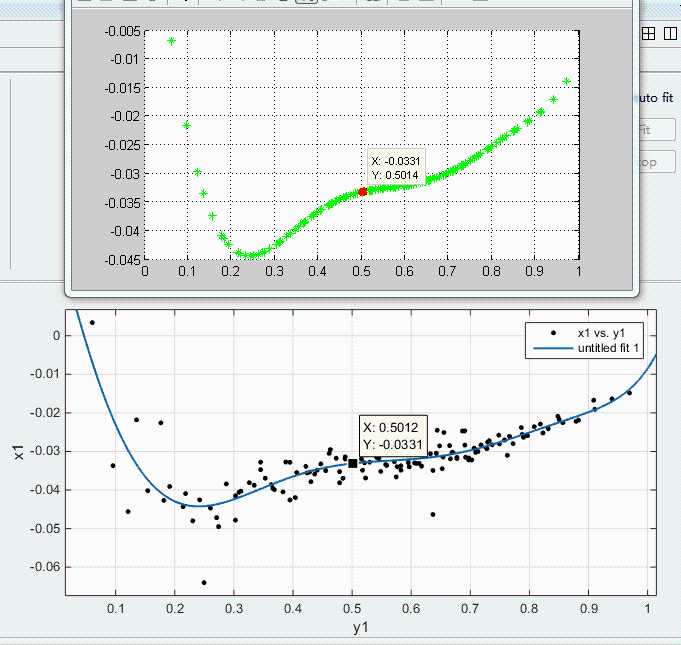
运行结果:
上图是C++代码运行的结果,在Matlab中显示的效果;下图是Matlab中利用Curve Fitting Tool拟合的效果(四阶多项式拟合)。注意横坐标与纵坐标不一样额,那是因为这里的原始数据与一般的数据不同:一个x坐标可能对应多个y值。这种情况直接将横纵坐标反着写就行了。
C++代码:
一、cpp文件
1、主函数curveFittingMain.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <Linequ.h>
#include <LS.h>
#include <Matrix.h>
#include <vector>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
vector<double> fitCurve(vector<double> arr_1, vector<double> arr_2, int n);
vector<double> getFitPoint(vector<double> coArr, vector<double> pointArr);
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
//step1: 读取txt文件中的数据
string file_x = "C:\\Users\\Zhangwei\\Desktop\\TEST\\多坐标点\\Quadrant_finalX.txt";
string file_y = "C:\\Users\\Zhangwei\\Desktop\\TEST\\多坐标点\\Quadrant_finalY.txt";
ifstream infile_x,infile_y;
infile_x.open(file_x);
infile_y.open(file_y);
if (!infile_x && !infile_y)
cout << "error" << endl;
double temp;
vector<double> Data_x, Data_y;
while (infile_x >> temp)
{
Data_x.push_back(temp);
}
while (infile_y >> temp)
{
Data_y.push_back(temp);
}
//step2:调用拟合函数
// CoArr 表示多项式拟合的系数
// myRes 表示拟合的系数与拟合前的横坐标,计算得到新的纵坐标
vector<double> CoArr = fitCurve(Data_y, Data_x, 4); //调用函数,4表示阶数,(可以随意取,1—线性拟合,2—平方拟合,3—立方拟合,>=4,高阶拟合)
vector<double> myRes = getFitPoint(CoArr, Data_y); //生成拟合数据
//step3:将myRes保存为txt文档
ofstream outfile;
outfile.open("C:\\Users\\Zhangwei\\Desktop\\TEST\\多坐标点\\Quadrant_Final.txt");
for (int j = 0; j < myRes.size(); j++)
{
outfile << myRes[j] << endl;
}
outfile.close();
//system("pause");
return 0;
}
//getFitPoint函数用于获取拟合后的数据点
vector<double> getFitPoint(vector<double> coArr, vector<double> pointArr)
{
vector<double> finalPoint;
if (pointArr.size() == 0 || coArr.size() == 0)
{
cout << "数据点有误!" << endl;
}
if (pointArr.size() > 0 && coArr.size() > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < pointArr.size(); i++)
{
double temp = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < coArr.size(); j++)
{
temp += pow(pointArr[i], j)*coArr[j];
}
finalPoint.push_back(temp);
}
}
return finalPoint;
}
//fitCurve函数用于曲线拟合
vector<double> fitCurve(vector<double> arr_1, vector<double> arr_2, int n)
{
CLS m_cls;
vector<double> coefficientsSet;
if (arr_1.size() != arr_2.size())
{
cout << " 输入数据有误!" << endl;
}
if (arr_1.size() == arr_2.size())
{
for (int i = 0; i < arr_1.size(); i++)
{
m_cls.addPoint(arr_1[i], arr_2[i]);
}
m_cls.setN(n);
m_cls.Solve();
double *t_paracof = m_cls.getSolution();
for (int i = 0; i < n + 1; i++)
{
coefficientsSet.push_back(t_paracof[i]); //多项式的系数项,第一项为常数项,最后一项为x^n项
}
}
return coefficientsSet;
}
2、Linequ.cpp
// Linequ.cpp: implementation of the CLinequ class.
//
//
//#include "stdafx.h"
#include "math.h"
#include "Linequ.h"
#ifdef _DEBUG
#undef THIS_FILE
static char THIS_FILE[] = __FILE__;
//#define new DEBUG_NEW
#endif
//
// Construction/Destruction
//
CLinequ::CLinequ(int dims)
{
index = dims;
sums = new double[dims];
MatrixA = new double[dims * dims];
solu = new double[dims];
}
CLinequ::~CLinequ()
{
delete[] sums;
delete[] MatrixA;
delete[] solu;
}
void CLinequ::setMatrix(double *rmatr) //设置矩阵
{
for (int i = 0; i<index*index; i++){
*(MatrixA + i) = rmatr[i]; //矩阵成员赋初值
}
}
void CLinequ::setLinequ(double *a, double *b) //设置线性方程组
{
setMatrix(a); //调用基类函数
for (int i = 0; i<index; i++)
sums[i] = b[i];
}
int CLinequ::Solve() //全选主元高斯消去法求解方程
{
int *js, l, k, i, j, is, p, q;
double d, t;
js = new int[index];
l = 1;
for (k = 0; k <= index - 2; k++){ //消去过程
d = 0.0;
for (i = k; i <= index - 1; i++)
for (j = k; j <= index - 1; j++){
t = fabs(MatrixA[i*index + j]);
if (t>d)
{
d = t; js[k] = j; is = i;
}
}
if (d + 1.0 == 1.0) l = 0;
else
{
if (js[k] != k)
for (i = 0; i <= index - 1; i++){
p = i*index + k; q = i*index + js[k];
t = MatrixA[p]; MatrixA[p] = MatrixA[q]; MatrixA[q] = t;
}
if (is != k)
{
for (j = k; j <= index - 1; j++){
p = k*index + j; q = is*index + j;
t = MatrixA[p]; MatrixA[p] = MatrixA[q]; MatrixA[q] = t;
}
t = sums[k]; sums[k] = sums[is]; sums[is] = t;
}
}
if (l == 0)
{
delete[] js;
//fail to solve
return(0);
}
d = MatrixA[k*index + k];
for (j = k + 1; j <= index - 1; j++){
p = k*index + j; MatrixA[p] = MatrixA[p] / d;
}
sums[k] = sums[k] / d;
for (i = k + 1; i <= index - 1; i++){
for (j = k + 1; j <= index - 1; j++){
p = i*index + j;
MatrixA[p] = MatrixA[p] - MatrixA[i*index + k] * MatrixA[k*index + j];
}
sums[i] = sums[i] - MatrixA[i*index + k] * sums[k];
}
}
d = MatrixA[(index - 1)*index + index - 1];
if (fabs(d) + 1.0 == 1.0)
{
delete[] js;
//fail to solve
return(0);
}
solu[index - 1] = sums[index - 1] / d; //回代过程
for (i = index - 2; i >= 0; i--){
t = 0.0;
for (j = i + 1; j <= index - 1; j++)
t = t + MatrixA[i*index + j] * solu[j];
solu[i] = sums[i] - t;
}
js[index - 1] = index - 1;
for (k = index - 1; k >= 0; k--)
if (js[k] != k)
{
t = solu[k]; solu[k] = solu[js[k]]; solu[js[k]] = t;
}
delete[] js;
return(1);
}
double *CLinequ::getSolution() const
{
return solu;
}3、LS.cpp
// LS.cpp: implementation of the CLS class.
//
//
//#include "stdafx.h"
#include "LS.h"
#include "Matrix.h"
#include "Linequ.h"
#ifdef _DEBUG
#undef THIS_FILE
static char THIS_FILE[] = __FILE__;
//#define new DEBUG_NEW
#endif
//
// Construction/Destruction
//
CLS* CLS::_instance = 0;
CLS::CLS()
{
pSolution = 0;
m = 0;
n = 0;
_instance = this;
}
CLS::~CLS()
{
if (pSolution)
delete[] pSolution;
}
CLS *CLS::getInstance()
{
if (!_instance)
new CLS();
return _instance;
}
void CLS::setN(int t)
{
n = t + 1;
if (pSolution)
delete[] pSolution;
pSolution = new double[n];
}
void CLS::addPoint(double x, double y)
{
pVertex[m][0] = x;
pVertex[m][1] = y;
m++;
}
bool CLS::Solve()
{
if (m <= 0 || n <= 0)
return false;
CMatrix *A = new CMatrix(m, n);
int i, j;
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
A->setData(j, 0, 1.0);
for (i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
A->setData(j, i, A->getData(j, i - 1) * pVertex[j][0]);
}
}
CMatrix *B = A->getRev();
CMatrix *b = new CMatrix(m, 1);
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
b->setData(i, 0, pVertex[i][1]);
CMatrix *C = B->getMul(A);
CMatrix *d = B->getMul(b);
CLinequ *pL = new CLinequ(n);
pL->setLinequ(C->getMatrix(), d->getMatrix());
pL->Solve();
double *t = pL->getSolution();
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
pSolution[i] = t[i];
return true;
}
double *CLS::getSolution() const
{
return pSolution;
}
double CLS::calcY(double x)
{
double y = 0.0, temp = 1.0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
y += pSolution[i] * temp;
temp *= x;
}
return y;
}
void CLS::restart()
{
m = 0;
if (pSolution)
delete[] pSolution;
pSolution = 0;
n = 0;
}
4、Matrix.cpp
// Matrix.cpp: implementation of the CMatrix class.
//
//
//#include "stdafx.h"
#include "Matrix.h"
#ifdef _DEBUG
#undef THIS_FILE
static char THIS_FILE[] = __FILE__;
//#define new DEBUG_NEW
#endif
//
// Construction/Destruction
//
void CMatrix::setMatrix(double *rmatr) //设置矩阵
{
for (int i = 0; i < m * n; i++)
{
*(pMatrix + i) = rmatr[i]; //矩阵成员赋初值
}
}
CMatrix::CMatrix(int a, int b) //矩阵Matrix类的构造函数
{
m = a; n = b; //保护数据赋值
pMatrix = new double[m * n]; //动态分配内存
}
CMatrix::~CMatrix() //矩阵Matrix类的析构函数
{
delete[] pMatrix; //内存释放
}
CMatrix *CMatrix::getRev()
{
CMatrix *pR = new CMatrix(n, m);
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
*(pR->pMatrix + i + m * j) = *(pMatrix + i * n + j);
}
return pR;
}
CMatrix *CMatrix::getMul(CMatrix *b)
{
if (b->m != n)
return 0;
CMatrix *pR = new CMatrix(m, b->n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < b->n; j++)
{
double temp = 0.0;
for (int k = 0; k < n; k++)
temp += *(pMatrix + i * n + k) * *(b->pMatrix + k * b->n + j);
*(pR->pMatrix + i * b->n + j) = temp;
}
}
return pR;
}
int CMatrix::getM() const
{
return m;
}
int CMatrix::getN() const
{
return n;
}
double *CMatrix::getMatrix() const
{
return pMatrix;
}
double CMatrix::getData(int i, int j) const
{
if (i < m && j < n && i >= 0 && j >= 0)
return *(pMatrix + i * n + j);
else
return 0.0;
}
void CMatrix::setData(int i, int j, double t)
{
if (i < m && j < n && i >= 0 && j >= 0)
{
*(pMatrix + i * n + j) = t;
}
}二、头文件(.h文件)
1、Linequ.h
// Linequ.h: interface for the CLinequ class.
//
//
#if !defined(AFX_LINEQU_H__3673E7FC_1154_436A_9D22_B472DD858F13__INCLUDED_)
#define AFX_LINEQU_H__3673E7FC_1154_436A_9D22_B472DD858F13__INCLUDED_
#if _MSC_VER > 1000
#pragma once
#endif // _MSC_VER > 1000
class CLinequ
{
public: //外部接口
CLinequ(int dims = 2); //构造函数
virtual ~CLinequ(); //析构函数
void setLinequ(double *a, double *b); //方称赋值
void setMatrix(double *rmatr);
int Solve(); //全选主元高斯消去法求解方程
double *getSolution() const;
private:
double *sums; //方程右端项
double *MatrixA;
double *solu; //方程的解
int index;
};
#endif // !defined(AFX_LINEQU_H__3673E7FC_1154_436A_9D22_B472DD858F13__INCLUDED_)
2、LS.h
// LS.h: interface for the CLS class.
//
//
#if !defined(AFX_LS_H__208D279A_F391_4DA8_BBE3_3895A9800FFE__INCLUDED_)
#define AFX_LS_H__208D279A_F391_4DA8_BBE3_3895A9800FFE__INCLUDED_
#if _MSC_VER > 1000
#pragma once
#endif // _MSC_VER > 1000
class CLS
{
private:
static CLS *_instance;
double pVertex[2000][2];//最多可以拟合2000个点
int m; //点的个数
int n; //多项式次数
double *pSolution; //多项式系数
public:
CLS();
virtual ~CLS();
static CLS *getInstance();
void setN(int t); //n次多项式拟合
void addPoint(double x, double y); //添加一个点
void restart();
bool Solve();
double *getSolution() const; //获得多项式系数
double calcY(double x); //根据x坐标计算y
};
#endif // !defined(AFX_LS_H__208D279A_F391_4DA8_BBE3_3895A9800FFE__INCLUDED_)
3、Matrix.h
// Matrix.h: interface for the CMatrix class.
//
//
#if !defined(AFX_MATRIX_H__AEE89FA3_05E2_44AC_AA96_5FBCB3608C13__INCLUDED_)
#define AFX_MATRIX_H__AEE89FA3_05E2_44AC_AA96_5FBCB3608C13__INCLUDED_
#if _MSC_VER > 1000
#pragma once
#endif // _MSC_VER > 1000
class CMatrix
{
public:
CMatrix(int a = 2, int b = 2);
virtual ~CMatrix();
void setMatrix(double *rmatr);
CMatrix *getRev();
CMatrix *getMul(CMatrix *b);
int getM() const; //获得行数
int getN() const; //获得列数
double getData(int i, int j) const;
void setData(int i, int j, double t);
double *getMatrix() const; //获得矩阵
protected:
int m, n;
double *pMatrix;
};
#endif // !defined(AFX_MATRIX_H__AEE89FA3_05E2_44AC_AA96_5FBCB3608C13__INCLUDED_)
今天的文章C++——多项式拟合分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/72770.html