🌟想了解YOLO系列算法更多进阶教程欢迎订阅我的专栏🌟
基础不好的同学可以试试看一下我的《目标检测蓝皮书》🚀,里面包含超多目标检测实用知识,想速通目标检测,看这本就对了!
想了解YOLO系列算法进阶教程的同学可以关注这个专栏YOLOv5/v7 进阶实战 | 安卓部署 | PyQt5页面 | 剪枝✂️ | 蒸馏⚗️ | Flask Web部署 | 改进教程,里面包含多种手把手的部署压缩教程,除此之外还有大量的改进~
番外篇 | 20+ 种注意力机制及代码 适用于YOLOv5/v7/v8
文章目录
-
- 注意力机制介绍
- 注意力机制的分类
- 1. SE 注意力模块
- 2. CBAM 注意力模块
- 3. ECA 注意力模块
- 4. CA 注意力模块
- 5. 添加方式💡
- 6. SOCA 注意力模块
- 7. SimAM 注意力模块
- 8. S2-MLPv2 注意力模块
- 9. NAMAttention 注意力模块
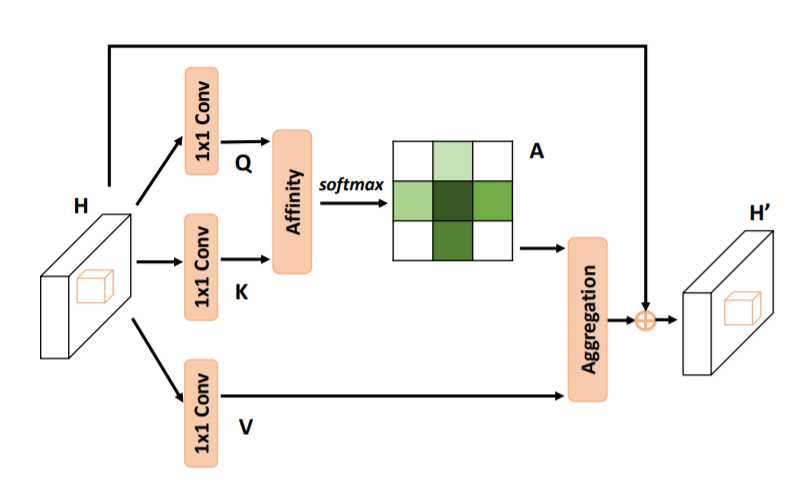
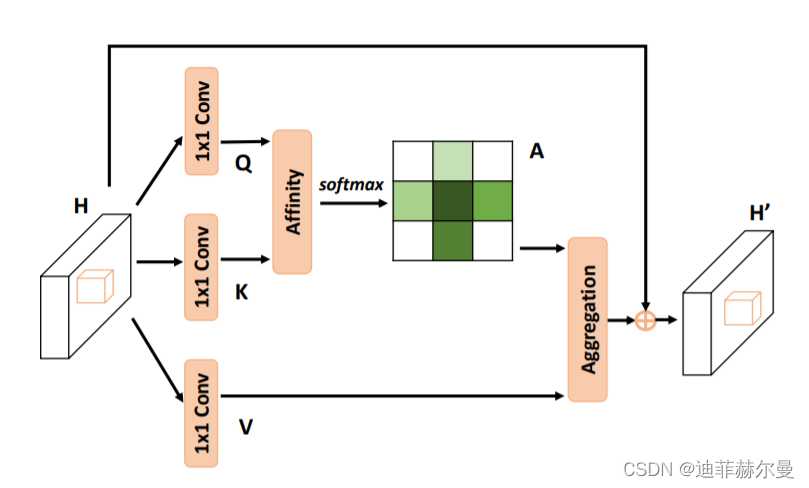
- 10. Criss-CrossAttention 注意力模块
- 11. GAMAttention 注意力模块
- 12. Selective Kernel Attention 注意力模块
- 13. ShuffleAttention 注意力模块
- 14. A2-Net 注意力模块🍀
- 15. DANPositional 注意力模块
- 16. DANChannel 注意力模块
- 17. RESNest 注意力模块
- 18. Harmonious 注意力模块
- 19. SpatialAttention 注意力模块
- 19. RANet 注意力模块
- 20. Co-excite 注意力模块
- 21. EfficientAttention 注意力模块
- 22. X-Linear 注意力模块
- 23. SlotAttention 注意力模块
- 24. Axial 注意力模块
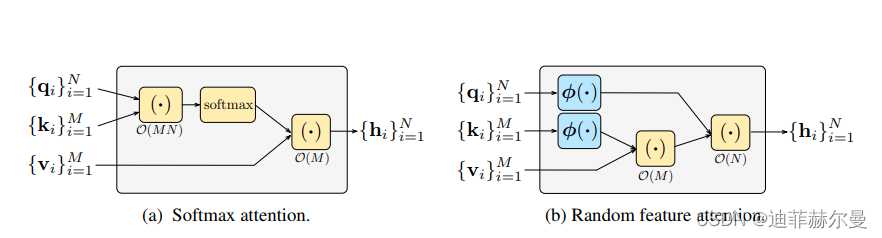
- 25. RFA 注意力模块
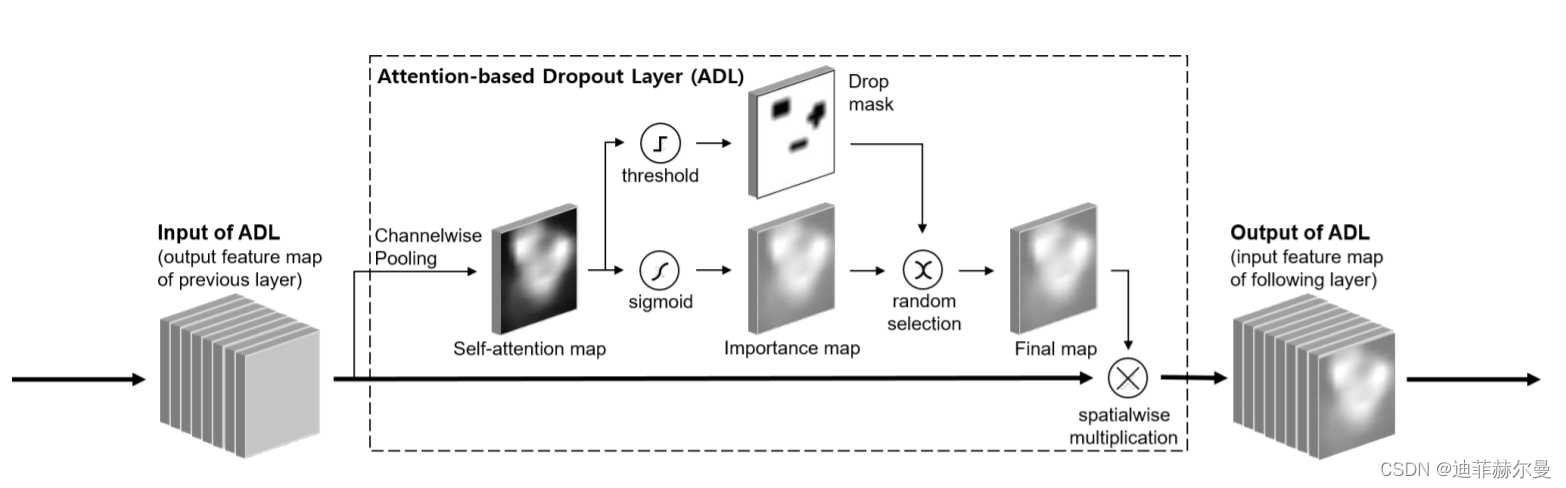
- 26. Attention-BasedDropout 注意力模块
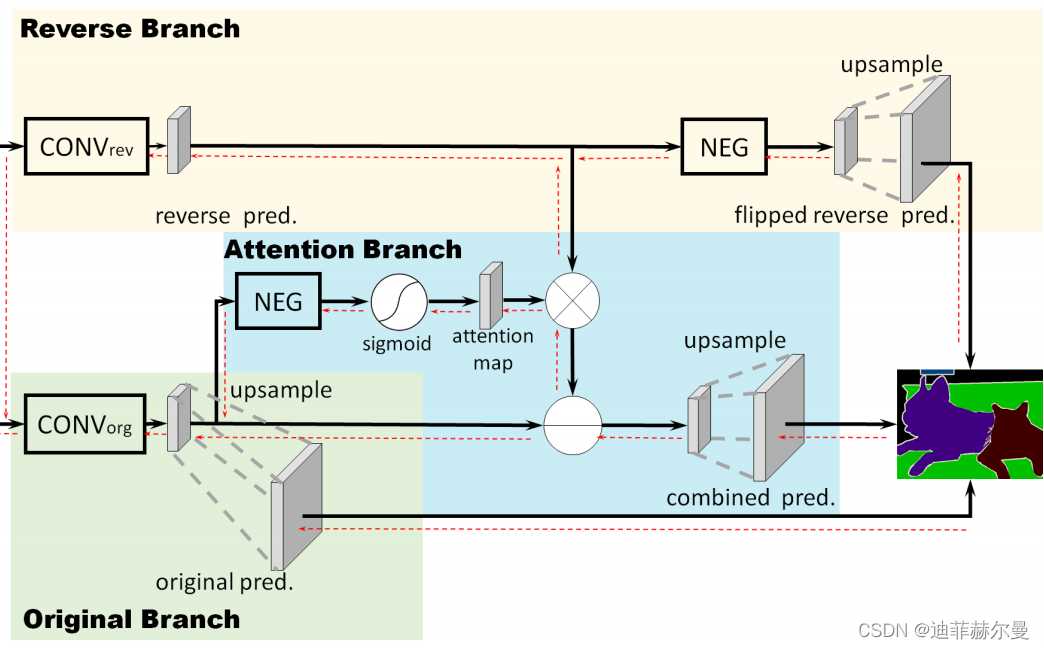
- 27. ReverseAttention 注意力模块
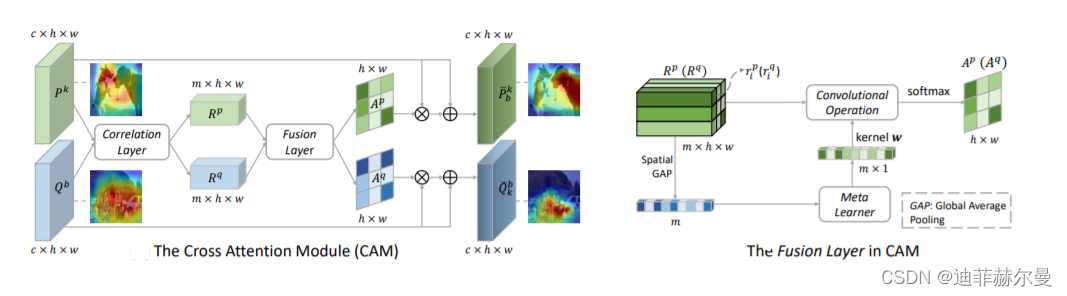
- 28. CrossAttention 注意力模块
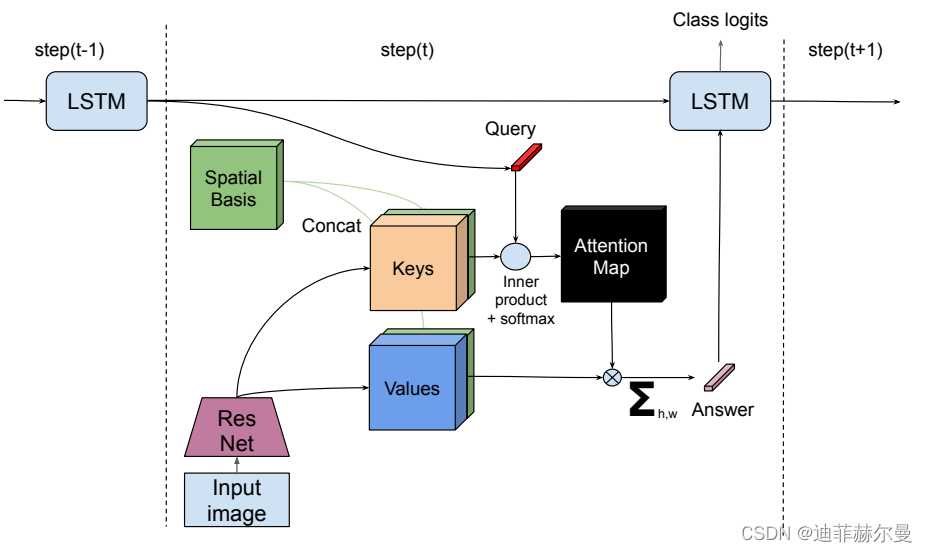
- 29. Perceiver 注意力模块
- 30. Criss-CrossAttention 注意力模块
- 31. BoostedAttention 注意力模块
- 32. Prophet 注意力模块
- 33. S3TA 注意力模块
- 34. Self-CriticAttention 注意力模块
- 35. BayesianAttentionBeliefNetworks 注意力模块
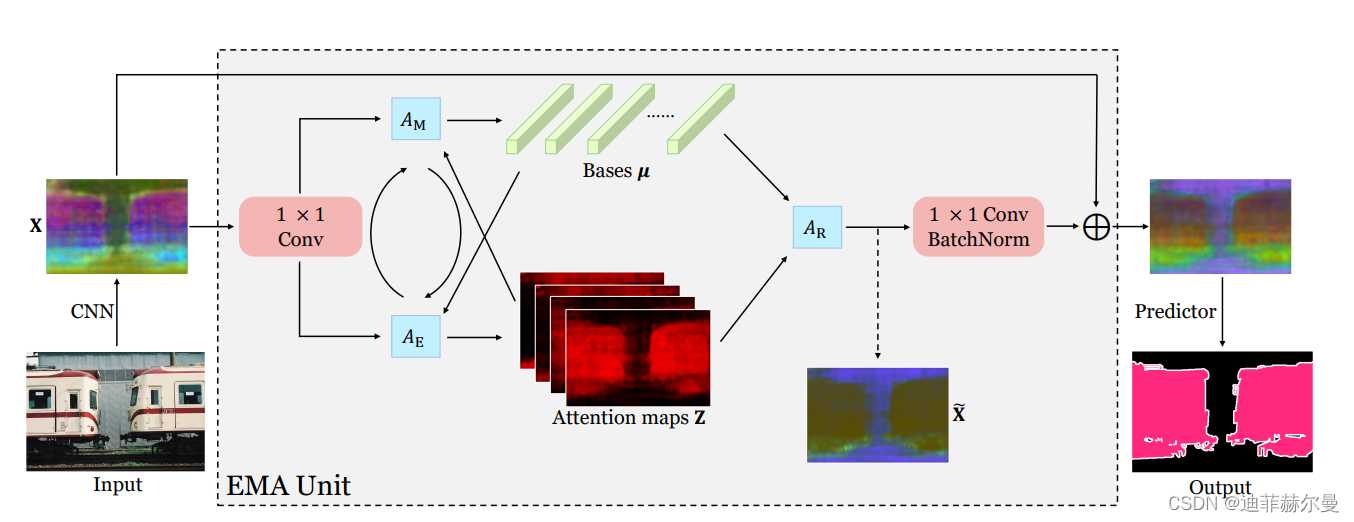
- 36. Expectation-MaximizationAttention 注意力模块
- 37. GaussianAttention 注意力模块
- 本人更多 YOLOv5/v7 实战内容导航🍀🌟🚀
注意力机制介绍
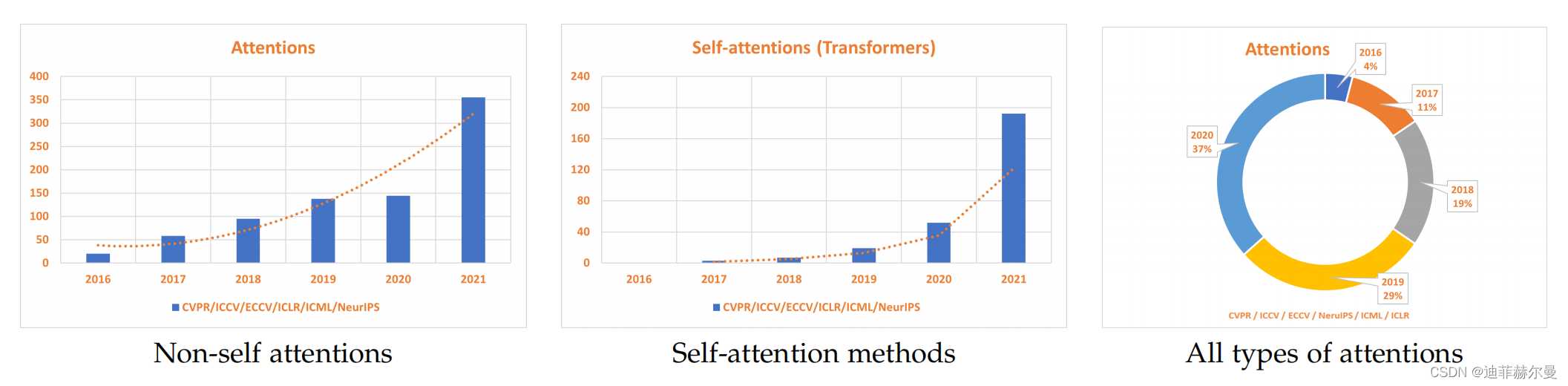
注意力机制(Attention Mechanism)源于对人类视觉的研究。在认知科学中,由于信息处理的瓶颈,人类会选择性地关注所有信息的一部分,同时忽略其他可见的信息。为了合理利用有限的视觉信息处理资源,人类需要选择视觉区域中的特定部分,然后集中关注它。例如,人们在阅读时,通常只有少量要被读取的词会被关注和处理。综上,注意力机制主要有两个方面:决定需要关注输入的哪部分;分配有限的信息处理资源给重要的部分。这几年有关attention的论文与日俱增,下图就显示了在包括CVPR、ICCV、ECCV、NeurIPS、ICML和ICLR在内的顶级会议中,与attention相关的论文数量的增加量。下面我将会分享Yolov5 v6.1如何添加注意力机制;并分享到2022年4月为止,30个顶会上提出的优秀的attention.
可视化图表显示了顶级会议中与注意力相关的论文数量的增加量,
包括CVPR,ICCV,ECCV,NeurIPS,ICML和ICLR。
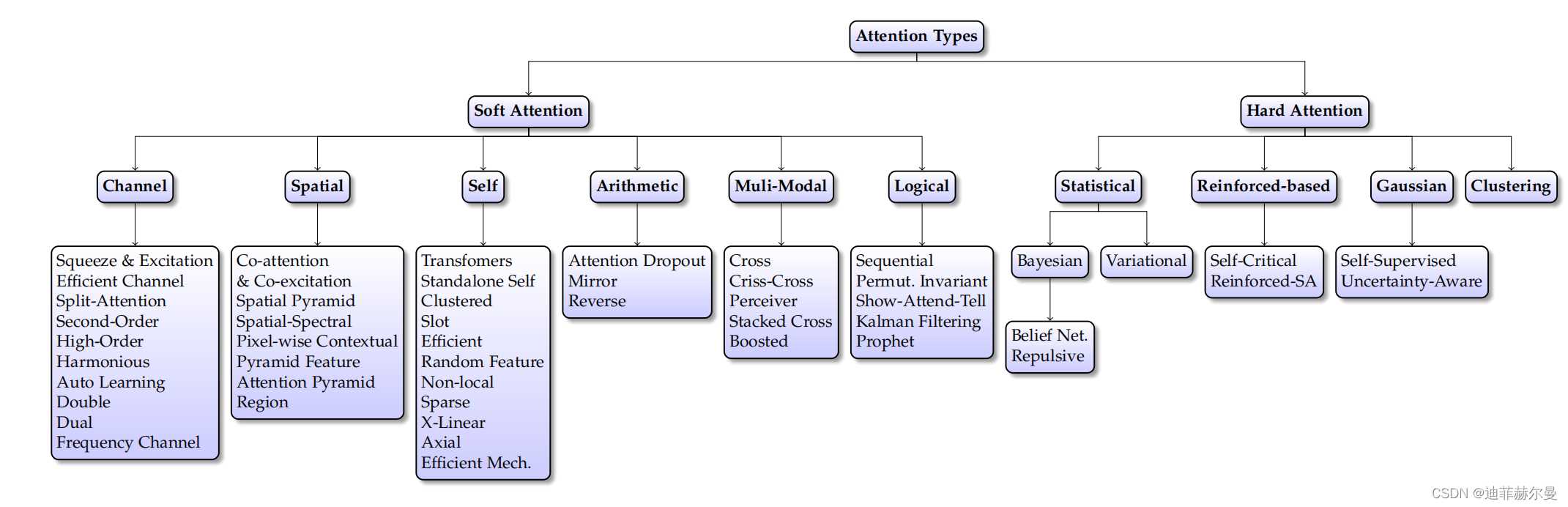
注意力机制的分类
注意力机制分类图
1. SE 注意力模块
论文名称:《Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks》
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1709.01507.pdf
代码地址: https://github.com/hujie-frank/SENet
1.1 原理
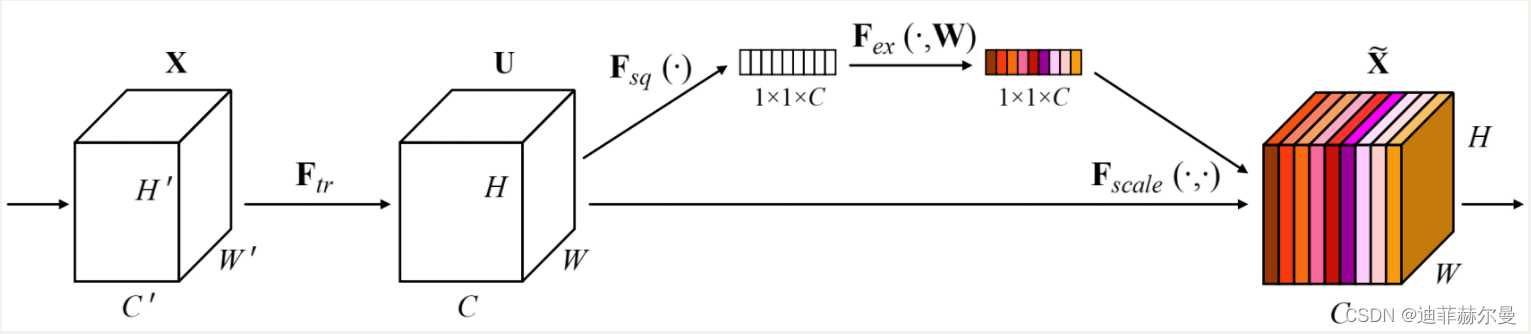
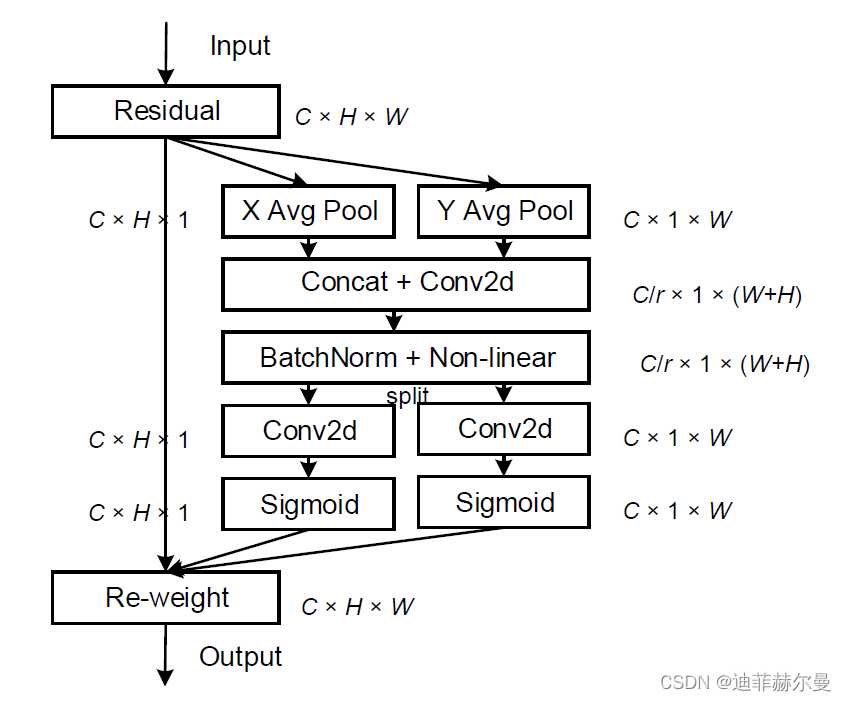
SEnet(Squeeze-and-Excitation Network)考虑了特征通道之间的关系,在特征通道上加入了注意力机制。
SEnet通过学习的方式自动获取每个特征通道的重要程度,并且利用得到的重要程度来提升特征并抑制对当前任务不重要的特征。SEnet 通过Squeeze模块和Exciation模块实现所述功能。
如图所示,首先作者通过squeeze操作,对空间维度进行压缩,直白的说就是对每个特征图做全局池化,平均成一个实数值。该实数从某种程度上来说具有全局感受野。作者提到该操作能够使得靠近数据输入的特征也可以具有全局感受野,这一点在很多的任务中是非常有用的。紧接着就是excitaton操作,由于经过squeeze操作后,网络输出了 1 ∗ 1 ∗ C 1*1*C 1∗1∗C 大小的特征图,作者利用权重 w w w 来学习 C C C 个通道直接的相关性。在实际应用时有的框架使用全连接,有的框架使用 1 ∗ 1 1*1 1∗1 的卷积实现。该过程中作者先对 C C C 个通道降维再扩展回 C C C 通道。好处就是一方面降低了网络计算量,一方面增加了网络的非线性能力。最后一个操作时将exciation的输出看作是经过特征选择后的每个通道的重要性,通过乘法加权的方式乘到先前的特征上,从事实现提升重要特征,抑制不重要特征这个功能。
1.2 代码
# SE
class SE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, ratio=16):
super(SE, self).__init__()
#c*1*1
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.l1 = nn.Linear(c1, c1 // ratio, bias=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.l2 = nn.Linear(c1 // ratio, c1, bias=False)
self.sig = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avgpool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.l1(y)
y = self.relu(y)
y = self.l2(y)
y = self.sig(y)
y = y.view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y.expand_as(x)
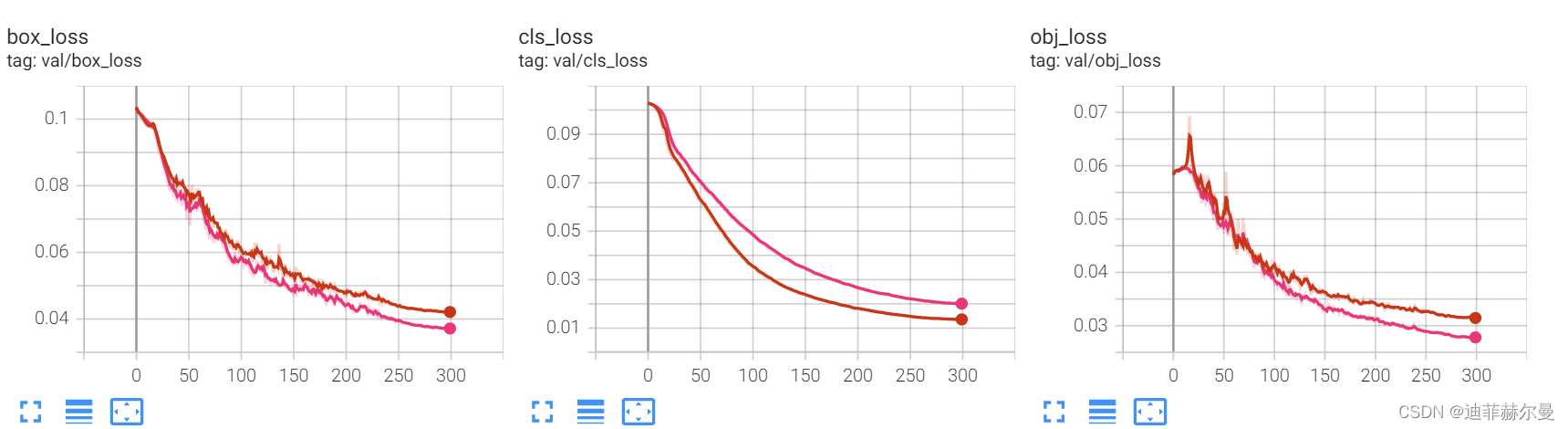
这里放上我自己做实验的截图,我就是把SE层加到了第 9 9 9 层的位置;粉红色线条代表添加了SE注意力机制。
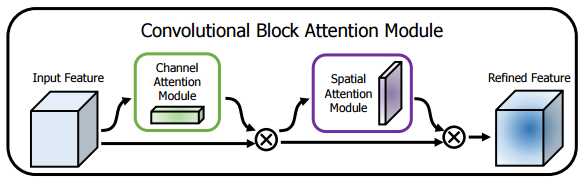
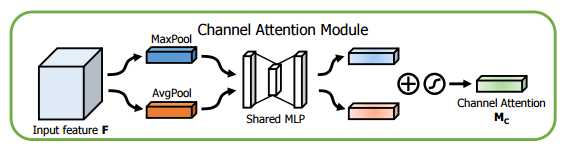
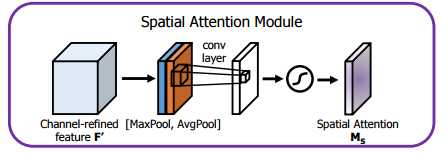
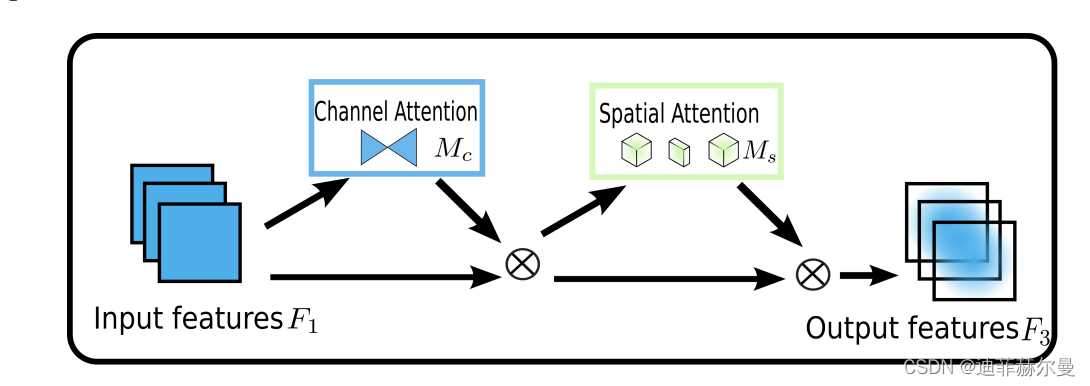
2. CBAM 注意力模块
论文题目:《CBAM: Convolutional Block Attention Module》
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1807.06521.pdf
2.1 原理
CBAM(Convolutional Block Attention Module)结合了特征通道和特征空间两个维度的注意力机制。
CBAM通过学习的方式自动获取每个特征通道的重要程度,和SEnet类似。此外还通过类似的学习方式自动获取每个特征空间的重要程度。并且利用得到的重要程度来提升特征并抑制对当前任务不重要的特征。
CBAM提取特征通道注意力的方式基本和SEnet类似,如下Channel Attention中的代码所示,其在SEnet的基础上增加了max_pool的特征提取方式,其余步骤是一样的。将通道注意力提取厚的特征作为空间注意力模块的输入。
CBAM提取特征空间注意力的方式:经过ChannelAttention后,最终将经过通道重要性选择后的特征图送入特征空间注意力模块,和通道注意力模块类似,空间注意力是以通道为单位进行最大池化和平均池化,并将两者的结果进行concat,之后再一个卷积降成 1 ∗ w ∗ h 1*w*h 1∗w∗h 的特征图空间权重,再将该权重和输入特征进行点积,从而实现空间注意力机制。
2.2 代码
# CBAM
class ChannelAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes, ratio=16):
super(ChannelAttention, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.max_pool = nn.AdaptiveMaxPool2d(1)
self.f1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, in_planes // ratio, 1, bias=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.f2 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes // ratio, in_planes, 1, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
avg_out = self.f2(self.relu(self.f1(self.avg_pool(x))))
max_out = self.f2(self.relu(self.f1(self.max_pool(x))))
out = self.sigmoid(avg_out + max_out)
return out
class SpatialAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size=7):
super(SpatialAttention, self).__init__()
assert kernel_size in (3, 7), 'kernel size must be 3 or 7'
padding = 3 if kernel_size == 7 else 1
# (特征图的大小-算子的size+2*padding)/步长+1
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(2, 1, kernel_size, padding=padding, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
# 1*h*w
avg_out = torch.mean(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
max_out, _ = torch.max(x, dim=1, keepdim=True)
x = torch.cat([avg_out, max_out], dim=1)
#2*h*w
x = self.conv(x)
#1*h*w
return self.sigmoid(x)
class CBAM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, ratio=16, kernel_size=7): # ch_in, ch_out, number, shortcut, groups, expansion
super(CBAM, self).__init__()
self.channel_attention = ChannelAttention(c1, ratio)
self.spatial_attention = SpatialAttention(kernel_size)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.channel_attention(x) * x
# c*h*w
# c*h*w * 1*h*w
out = self.spatial_attention(out) * out
return out
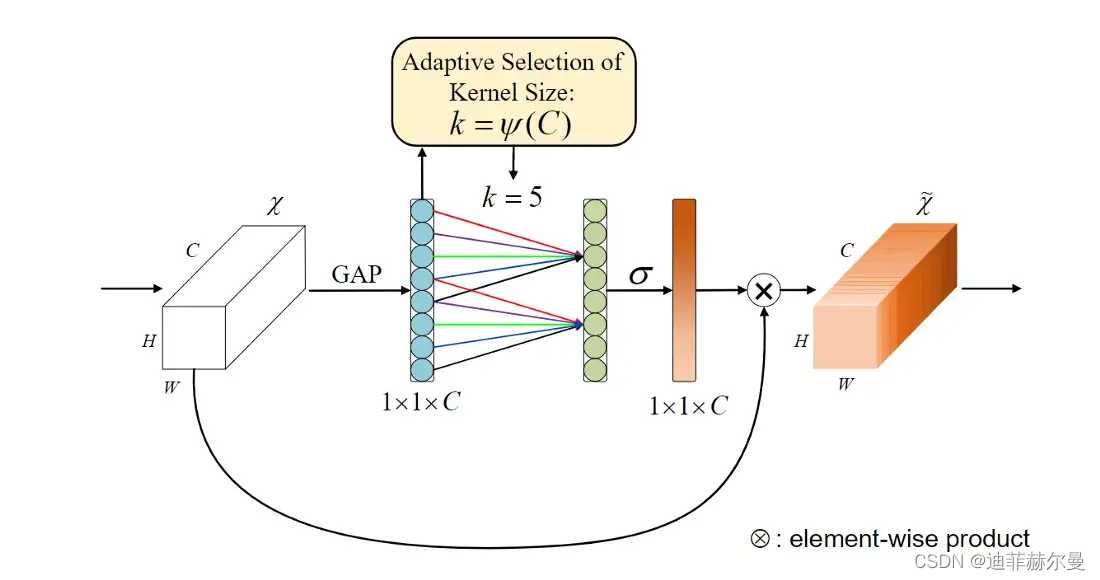
3. ECA 注意力模块
论文名称:《ECA-Net: Efficient Channel Attention for Deep Convolutional Neural Networks》
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.03151
代码地址:https://github.com/BangguWu/ECANet
3.1 原理
先前的方法大多致力于开发更复杂的注意力模块,以实现更好的性能,这不可避免地增加了模型的复杂性。为了克服性能和复杂性之间的矛盾,作者提出了一种有效的通道关注(ECA)模块,该模块只增加了少量的参数,却能获得明显的性能增益。
3.2 代码
class ECA(nn.Module):
"""Constructs a ECA module. Args: channel: Number of channels of the input feature map k_size: Adaptive selection of kernel size """
def __init__(self, c1,c2, k_size=3):
super(ECA, self).__init__()
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.conv = nn.Conv1d(1, 1, kernel_size=k_size, padding=(k_size - 1) // 2, bias=False)
self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
# feature descriptor on the global spatial information
y = self.avg_pool(x)
y = self.conv(y.squeeze(-1).transpose(-1, -2)).transpose(-1, -2).unsqueeze(-1)
# Multi-scale information fusion
y = self.sigmoid(y)
return x * y.expand_as(x)
4. CA 注意力模块
论文名称:《Coordinate Attention for Efficient Mobile Network Design》
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.02907
4.1 原理
先前的轻量级网络的注意力机制大都采用SE模块,仅考虑了通道间的信息,忽略了位置信息。尽管后来的BAM和CBAM尝试在降低通道数后通过卷积来提取位置注意力信息,但卷积只能提取局部关系,缺乏长距离关系提取的能力。为此,论文提出了新的高效注意力机制coordinate attention(CA),能够将横向和纵向的位置信息编码到channel attention中,使得移动网络能够关注大范围的位置信息又不会带来过多的计算量。
coordinate attention的优势主要有以下几点:
- 不仅获取了通道间信息,还考虑了方向相关的位置信息,有助于模型更好地定位和识别目标;
- 足够灵活和轻量,能够简单地插入移动网络的核心结构中;
- 可以作为预训练模型用于多种任务中,如检测和分割,均有不错的性能提升。
4.2 代码
# CA
class h_sigmoid(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplace=True):
super(h_sigmoid, self).__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU6(inplace=inplace)
def forward(self, x):
return self.relu(x + 3) / 6
class h_swish(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplace=True):
super(h_swish, self).__init__()
self.sigmoid = h_sigmoid(inplace=inplace)
def forward(self, x):
return x * self.sigmoid(x)
class CoordAtt(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inp, oup, reduction=32):
super(CoordAtt, self).__init__()
self.pool_h = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((None, 1))
self.pool_w = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, None))
mip = max(8, inp // reduction)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inp, mip, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(mip)
self.act = h_swish()
self.conv_h = nn.Conv2d(mip, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv_w = nn.Conv2d(mip, oup, kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
n, c, h, w = x.size()
#c*1*W
x_h = self.pool_h(x)
#c*H*1
#C*1*h
x_w = self.pool_w(x).permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
y = torch.cat([x_h, x_w], dim=2)
#C*1*(h+w)
y = self.conv1(y)
y = self.bn1(y)
y = self.act(y)
x_h, x_w = torch.split(y, [h, w], dim=2)
x_w = x_w.permute(0, 1, 3, 2)
a_h = self.conv_h(x_h).sigmoid()
a_w = self.conv_w(x_w).sigmoid()
out = identity * a_w * a_h
return out
5. 添加方式💡
大致的修改方式如下:
在 Y O L O v 5 YOLOv5 YOLOv5 或 Y O L O v 7 YOLOv7 YOLOv7 中添加注意力机制可分为如下 5 5 5 步,以在 yolov5s 中添加 SE 注意力机制为例子:
- 在
yolov5/models文件夹下新建一个yolov5s_SE.yaml; - 将本文上面提供的
SE注意力代码添加到common.py文件末尾; - 将
SE这个类的名字加入到yolov5/models/yolo.py中; - 修改
yolov5s_SE.yaml,将SE注意力加到你想添加的位置; - 修改
train.py文件的'--cfg'默认参数,随后就可以开始训练了。
详细的修改方式如下:
- 第 1 1 1 步:在
yolov5/models文件夹下新建一个yolov5_SE.yaml,将yolov5s.yaml文件内容拷贝粘贴到我们新建的yolov5s_SE.yaml文件中等待第 4 4 4 步使用; - 第 2 2 2 步:将本文上面提供的
SE注意力代码添加到yolov5/models/common.py文件末尾;
class SE(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, c1, c2, ratio=16):
super(SE, self).__init__()
#c*1*1
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.l1 = nn.Linear(c1, c1 // ratio, bias=False)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.l2 = nn.Linear(c1 // ratio, c1, bias=False)
self.sig = nn.Sigmoid()
def forward(self, x):
b, c, _, _ = x.size()
y = self.avgpool(x).view(b, c)
y = self.l1(y)
y = self.relu(y)
y = self.l2(y)
y = self.sig(y)
y = y.view(b, c, 1, 1)
return x * y.expand_as(x)
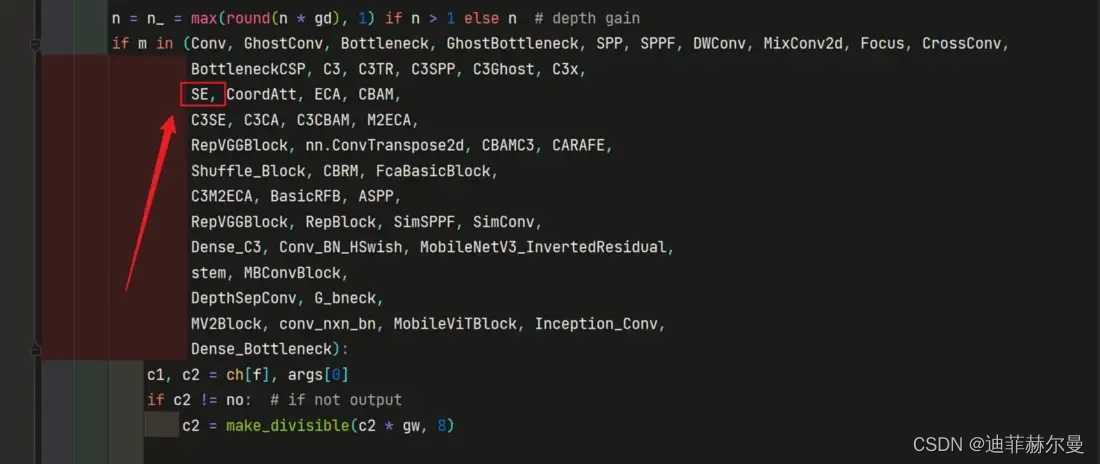
- 第 3 3 3 步:将
SE这个类的名字加入到yolov5/models/yolo.py如下位置;
你的可能和我有点区别,不用在意
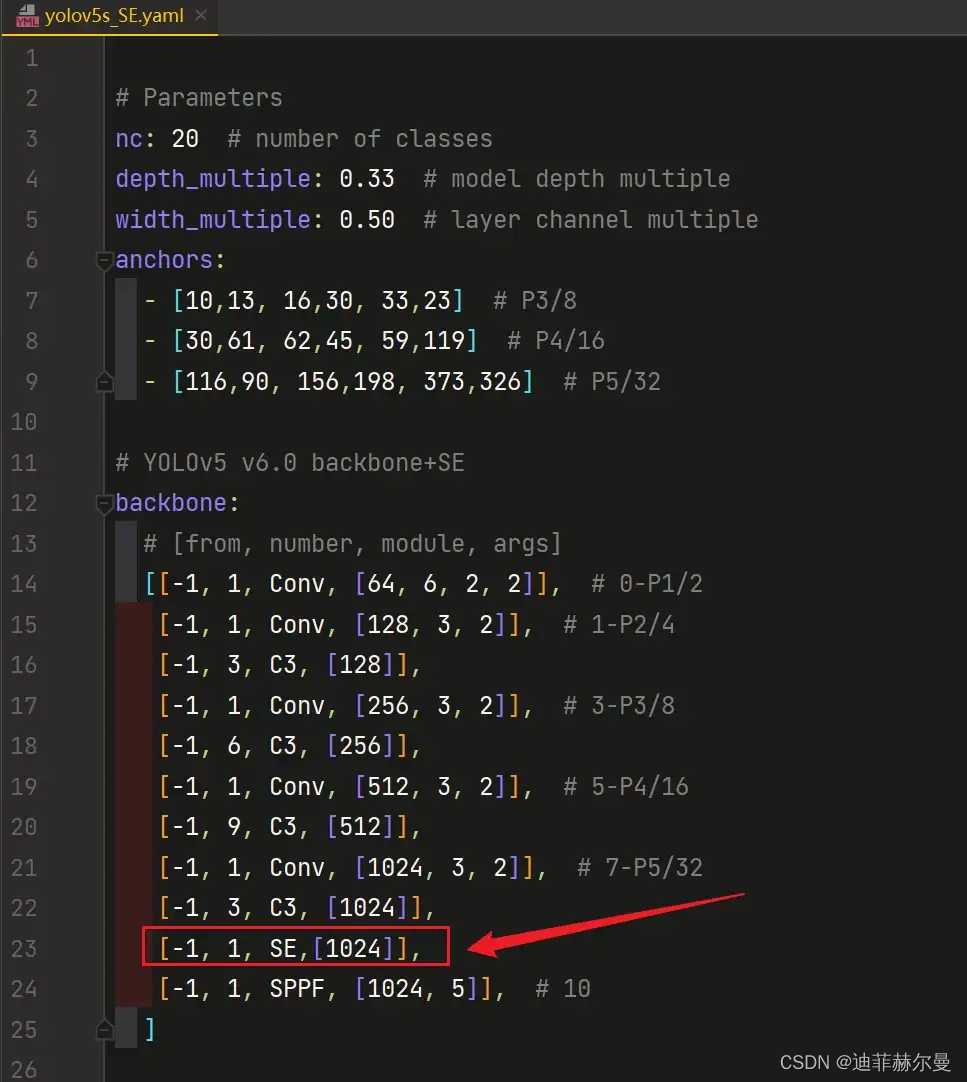
- 第 4 4 4 步:修改
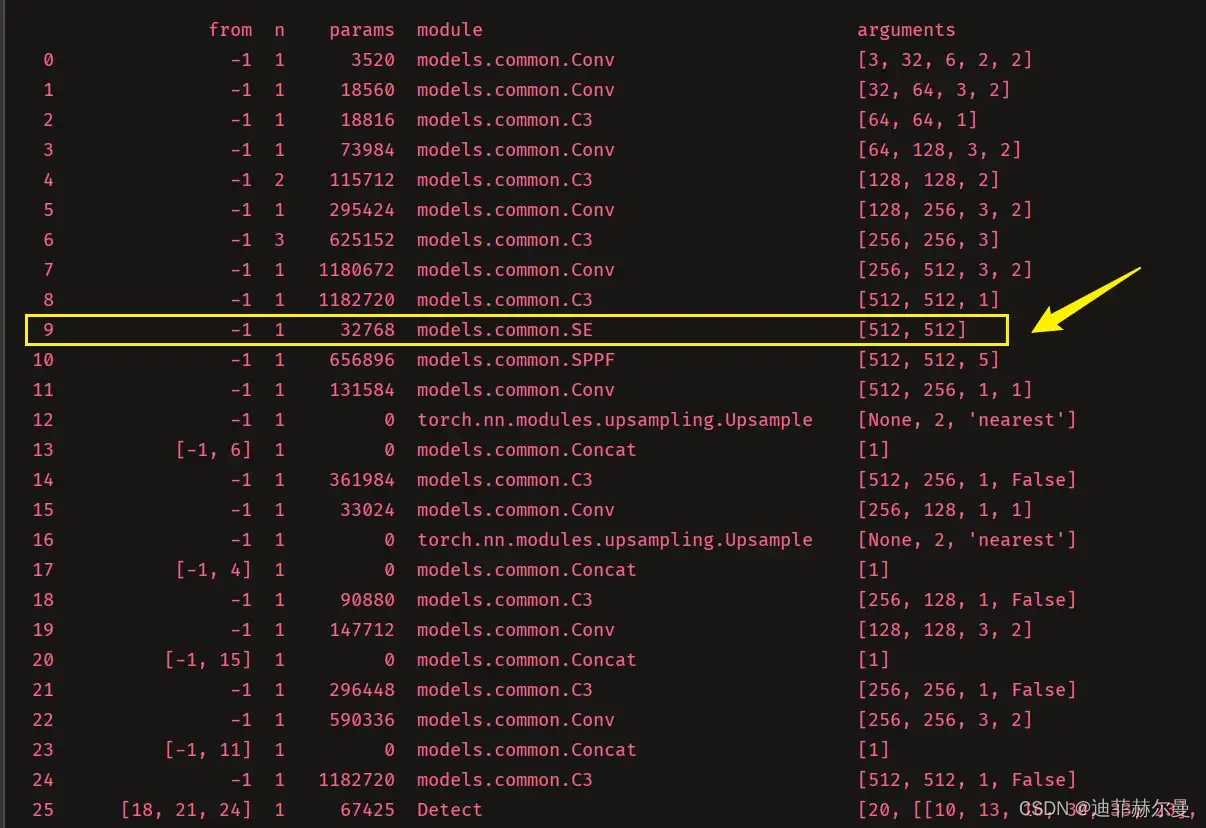
yolov5s_SE.yaml,将SE注意力加到你想添加的位置;常见的位置有 C 3 C3 C3 模块后面, N e c k Neck Neck 中,也可以在主干的 S P P F SPPF SPPF 前添加一层;我这里演示添加到 S P P F SPPF SPPF 上一层:
将[-1, 1, SE,[1024]],添加到SPPF的上一层,即下图中所示位置:
加到这里还没完,还有两个细节需要注意!🌟
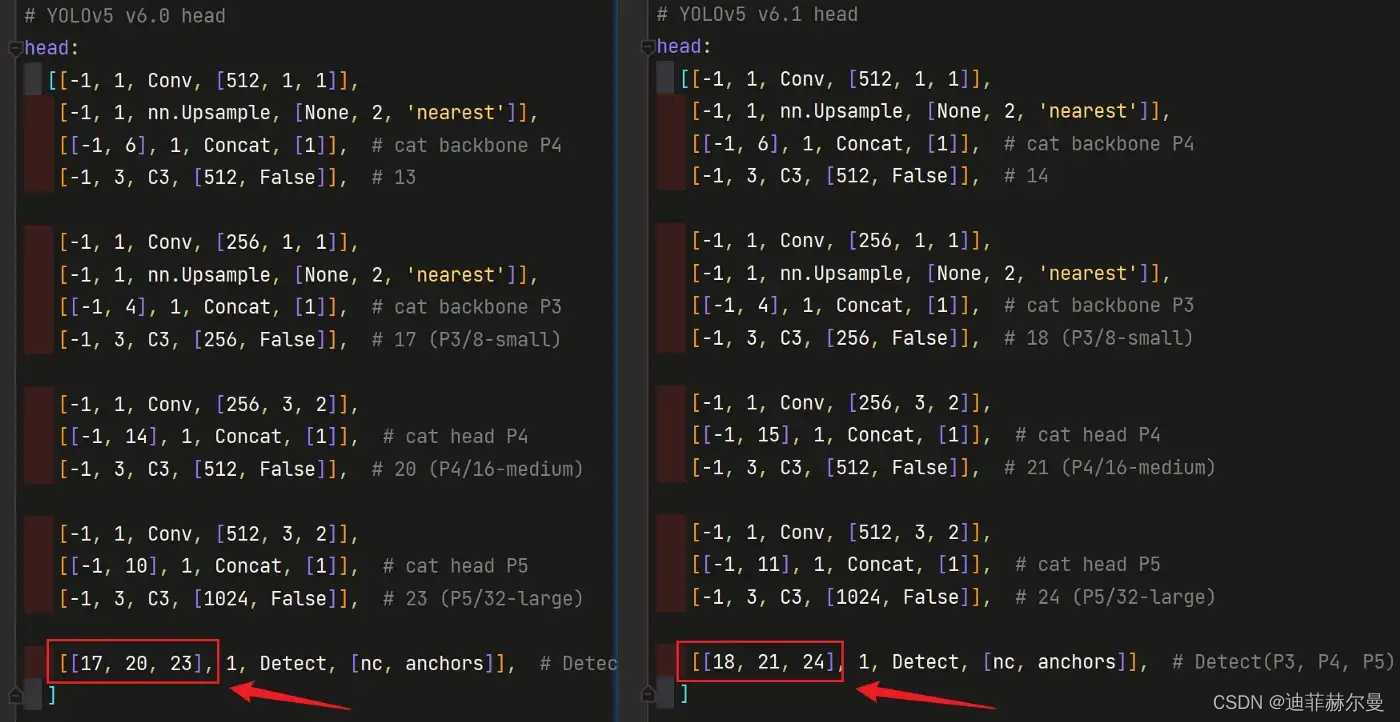
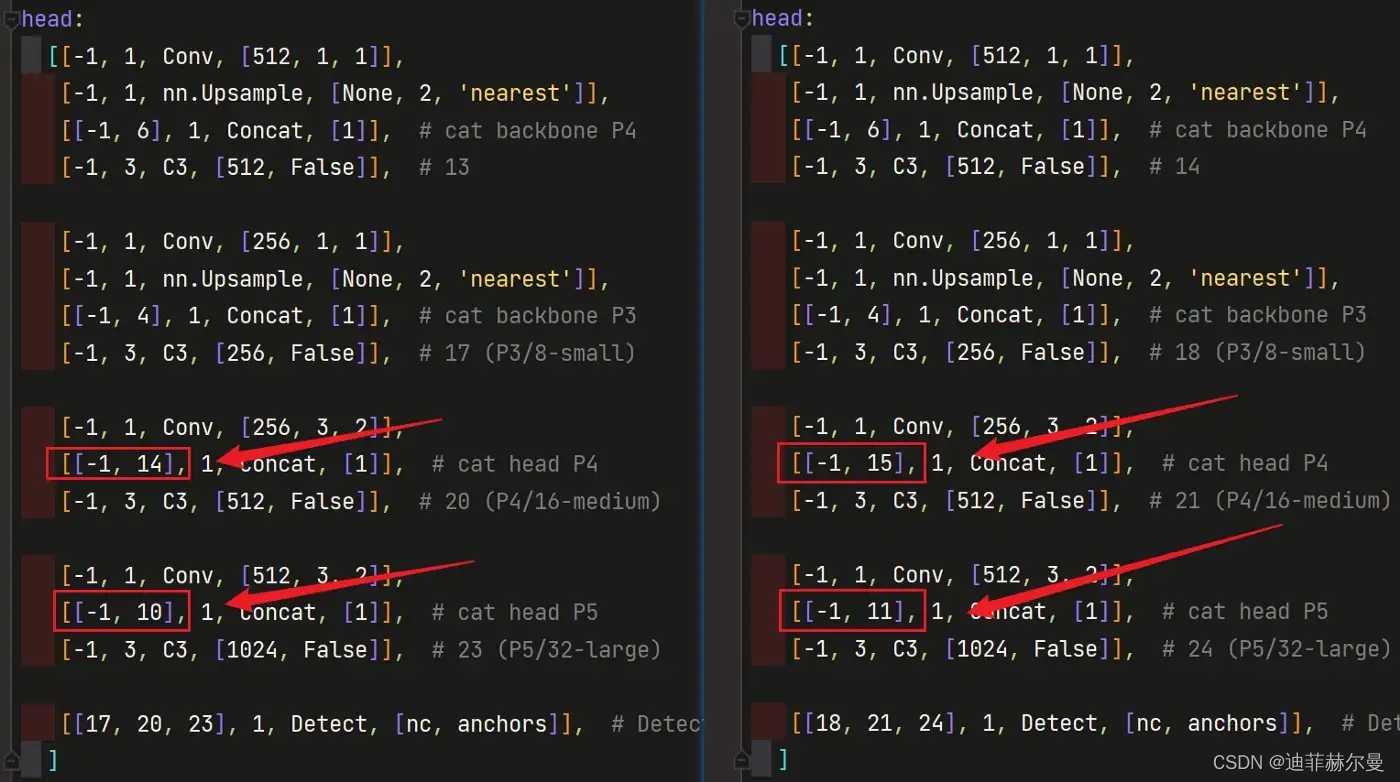
当在网络中添加了新的层之后,那么该层网络后续的层的编号都会发生改变,看下图,原本Detect 指定的是 [ 17 , 20 , 23 ] [17,20,23] [17,20,23] 层,所以在我们添加了 SE 注意力层之后也要对 Detect 的参数进行修改,即原来的 17 17 17 层变成了 18 18 18 层;原来的 20 20 20 层变成了 21 21 21 层;原来的 23 23 23 层变成了 24 24 24 层;所以 Detecet 的 from 系数要改为 [ 18 , 21 , 24 ] [18,21,24] [18,21,24]
左侧是原始的 yolov5s.yaml ,右侧为修改后的 yolov5s_SE.yaml
同样的,Concat 的 from 系数也要修改,这样才能保持原网络结构不发生特别大的改变,我们刚才把 SE 层加到了第 9 9 9 层,所以第 9 9 9 层之后的编号都会加 1 1 1 ,这里我们要把后面两个 Concat 的 from 系数分别由 [ − 1 , 14 ] , [ − 1 , 10 ] [-1,14],[-1,10] [−1,14],[−1,10] 改为 [ − 1 , 15 ] , [ − 1 , 11 ] [-1,15],[-1,11] [−1,15],[−1,11]
左侧是原始的 yolov5s.yaml ,右侧为修改后的 yolov5s_SE.yaml
如果这一步的原理大家没看懂的话,可以看看我的哔哩哔哩视频,我讲解了yaml文件的原理:点击跳转
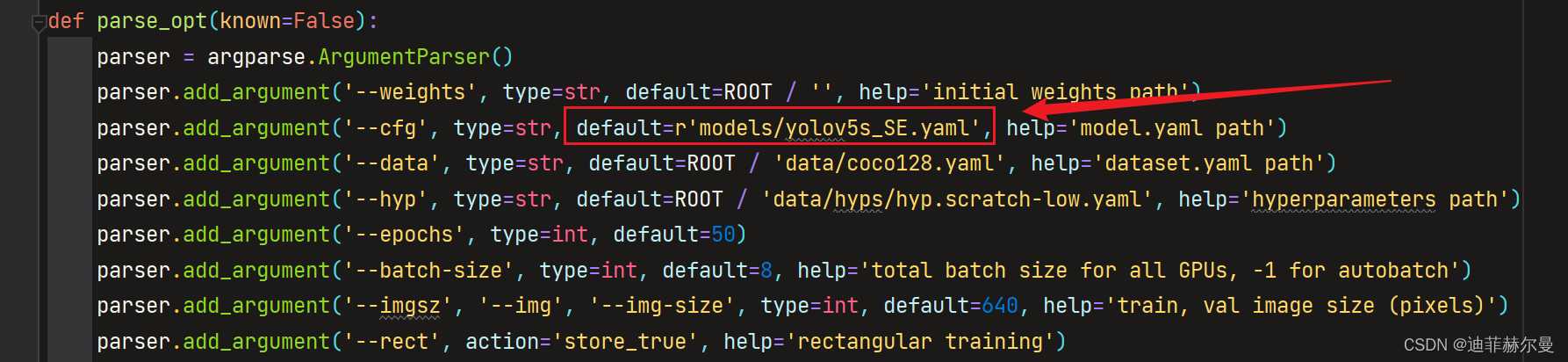
- 第 5 5 5 步:修改
train.py文件的'--cfg'默认参数,在'--cfg'后的default=后面加上yolov5s_SE.yaml的路径,随后就可以开始训练了。
在训练时会打印模型的结构,当出现下面的结构时,就代表我们添加成功了:
最后放上我加入 SE 注意力层后完整的配置文件 yolov5s_SE.yaml
# Parameters
nc: 80 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone+SE
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SE, [1024]], #SE
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 10
]
# YOLOv5+SE v6.0 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 14
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 18 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 15], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 21 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 11], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 24 (P5/32-large)
[[18, 21, 24], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
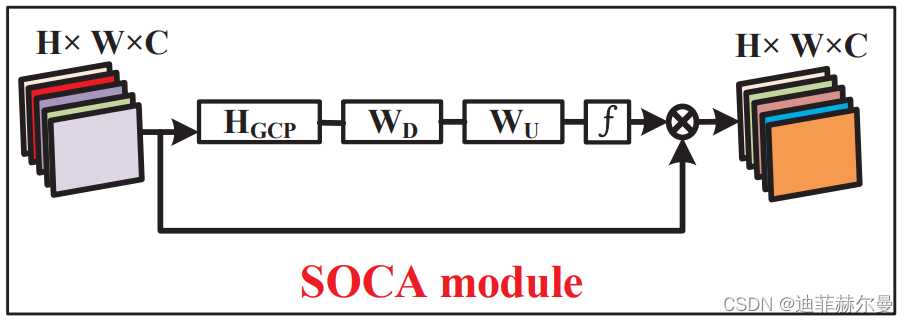
6. SOCA 注意力模块
论文地址:https://openaccess.thecvf.com.pdf
代码
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
from torch.autograd import Function
class Covpool(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input):
x = input
batchSize = x.data.shape[0]
dim = x.data.shape[1]
h = x.data.shape[2]
w = x.data.shape[3]
M = h*w
x = x.reshape(batchSize,dim,M)
I_hat = (-1./M/M)*torch.ones(M,M,device = x.device) + (1./M)*torch.eye(M,M,device = x.device)
I_hat = I_hat.view(1,M,M).repeat(batchSize,1,1).type(x.dtype)
y = x.bmm(I_hat).bmm(x.transpose(1,2))
ctx.save_for_backward(input,I_hat)
return y
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
input,I_hat = ctx.saved_tensors
x = input
batchSize = x.data.shape[0]
dim = x.data.shape[1]
h = x.data.shape[2]
w = x.data.shape[3]
M = h*w
x = x.reshape(batchSize,dim,M)
grad_input = grad_output + grad_output.transpose(1,2)
grad_input = grad_input.bmm(x).bmm(I_hat)
grad_input = grad_input.reshape(batchSize,dim,h,w)
return grad_input
class Sqrtm(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input, iterN):
x = input
batchSize = x.data.shape[0]
dim = x.data.shape[1]
dtype = x.dtype
I3 = 3.0*torch.eye(dim,dim,device = x.device).view(1, dim, dim).repeat(batchSize,1,1).type(dtype)
normA = (1.0/3.0)*x.mul(I3).sum(dim=1).sum(dim=1)
A = x.div(normA.view(batchSize,1,1).expand_as(x))
Y = torch.zeros(batchSize, iterN, dim, dim, requires_grad = False, device = x.device)
Z = torch.eye(dim,dim,device = x.device).view(1,dim,dim).repeat(batchSize,iterN,1,1)
if iterN < 2:
ZY = 0.5*(I3 - A)
Y[:,0,:,:] = A.bmm(ZY)
else:
ZY = 0.5*(I3 - A)
Y[:,0,:,:] = A.bmm(ZY)
Z[:,0,:,:] = ZY
for i in range(1, iterN-1):
ZY = 0.5*(I3 - Z[:,i-1,:,:].bmm(Y[:,i-1,:,:]))
Y[:,i,:,:] = Y[:,i-1,:,:].bmm(ZY)
Z[:,i,:,:] = ZY.bmm(Z[:,i-1,:,:])
ZY = 0.5*Y[:,iterN-2,:,:].bmm(I3 - Z[:,iterN-2,:,:].bmm(Y[:,iterN-2,:,:]))
y = ZY*torch.sqrt(normA).view(batchSize, 1, 1).expand_as(x)
ctx.save_for_backward(input, A, ZY, normA, Y, Z)
ctx.iterN = iterN
return y
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
input, A, ZY, normA, Y, Z = ctx.saved_tensors
iterN = ctx.iterN
x = input
batchSize = x.data.shape[0]
dim = x.data.shape[1]
dtype = x.dtype
der_postCom = grad_output*torch.sqrt(normA).view(batchSize, 1, 1).expand_as(x)
der_postComAux = (grad_output*ZY).sum(dim=1).sum(dim=1).div(2*torch.sqrt(normA))
I3 = 3.0*torch.eye(dim,dim,device = x.device).view(1, dim, dim).repeat(batchSize,1,1).type(dtype)
if iterN < 2:
der_NSiter = 0.5*(der_postCom.bmm(I3 - A) - A.bmm(der_sacleTrace))
else:
dldY = 0.5*(der_postCom.bmm(I3 - Y[:,iterN-2,:,:].bmm(Z[:,iterN-2,:,:])) -
Z[:,iterN-2,:,:].bmm(Y[:,iterN-2,:,:]).bmm(der_postCom))
dldZ = -0.5*Y[:,iterN-2,:,:].bmm(der_postCom).bmm(Y[:,iterN-2,:,:])
for i in range(iterN-3, -1, -1):
YZ = I3 - Y[:,i,:,:].bmm(Z[:,i,:,:])
ZY = Z[:,i,:,:].bmm(Y[:,i,:,:])
dldY_ = 0.5*(dldY.bmm(YZ) -
Z[:,i,:,:].bmm(dldZ).bmm(Z[:,i,:,:]) -
ZY.bmm(dldY))
dldZ_ = 0.5*(YZ.bmm(dldZ) -
Y[:,i,:,:].bmm(dldY).bmm(Y[:,i,:,:]) -
dldZ.bmm(ZY))
dldY = dldY_
dldZ = dldZ_
der_NSiter = 0.5*(dldY.bmm(I3 - A) - dldZ - A.bmm(dldY))
grad_input = der_NSiter.div(normA.view(batchSize,1,1).expand_as(x))
grad_aux = der_NSiter.mul(x).sum(dim=1).sum(dim=1)
for i in range(batchSize):
grad_input[i,:,:] += (der_postComAux[i] \
- grad_aux[i] / (normA[i] * normA[i])) \
*torch.ones(dim,device = x.device).diag()
return grad_input, None
def CovpoolLayer(var):
return Covpool.apply(var)
def SqrtmLayer(var, iterN):
return Sqrtm.apply(var, iterN)
class SOCA(nn.Module):
# second-order Channel attention
def __init__(self, channel, reduction=8):
super(SOCA, self).__init__()
self.max_pool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.conv_du = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(channel, channel // reduction, 1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(channel // reduction, channel, 1, padding=0, bias=True),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
def forward(self, x):
batch_size, C, h, w = x.shape # x: NxCxHxW
N = int(h * w)
min_h = min(h, w)
h1 = 1000
w1 = 1000
if h < h1 and w < w1:
x_sub = x
elif h < h1 and w > w1:
W = (w - w1) // 2
x_sub = x[:, :, :, W:(W + w1)]
elif w < w1 and h > h1:
H = (h - h1) // 2
x_sub = x[:, :, H:H + h1, :]
else:
H = (h - h1) // 2
W = (w - w1) // 2
x_sub = x[:, :, H:(H + h1), W:(W + w1)]
cov_mat = CovpoolLayer(x_sub) # Global Covariance pooling layer
cov_mat_sqrt = SqrtmLayer(cov_mat,5) # Matrix square root layer( including pre-norm,Newton-Schulz iter. and post-com. with 5 iteration)
cov_mat_sum = torch.mean(cov_mat_sqrt,1)
cov_mat_sum = cov_mat_sum.view(batch_size,C,1,1)
y_cov = self.conv_du(cov_mat_sum)
return y_cov*x
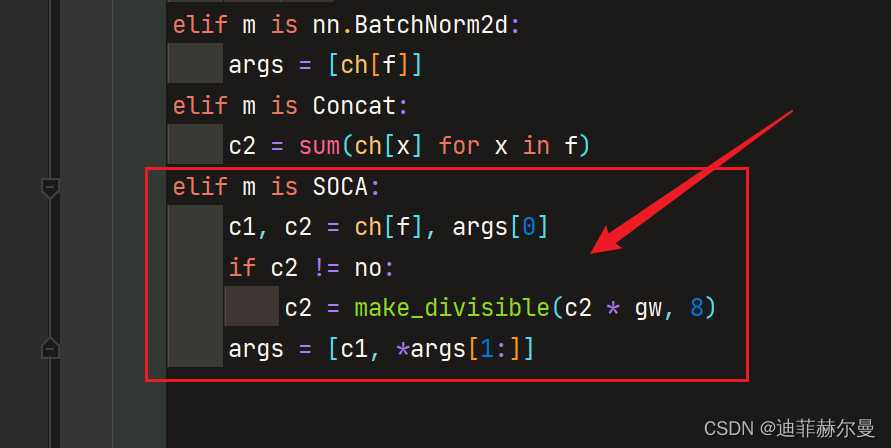
在 yolov5/models/yolo.py 的如下位置添加下面的判断语句,虽然和上面介绍的添加方式不同,但是原理都是一样的。
elif m is SOCA:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no:
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, *args[1:]]
yolov5s_SOCA.yaml
# Parameters
nc: 20 # number of classes
depth_multiple: 0.33 # model depth multiple
width_multiple: 0.50 # layer channel multiple
anchors:
- [10,13, 16,30, 33,23] # P3/8
- [30,61, 62,45, 59,119] # P4/16
- [116,90, 156,198, 373,326] # P5/32
# YOLOv5 v6.0 backbone+SE
backbone:
# [from, number, module, args]
[[-1, 1, Conv, [64, 6, 2, 2]], # 0-P1/2
[-1, 1, Conv, [128, 3, 2]], # 1-P2/4
[-1, 3, C3, [128]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]], # 3-P3/8
[-1, 6, C3, [256]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]], # 5-P4/16
[-1, 9, C3, [512]],
[-1, 1, Conv, [1024, 3, 2]], # 7-P5/32
[-1, 3, C3, [1024]],
[-1, 1, SOCA,[1024]],
[-1, 1, SPPF, [1024, 5]], # 10
]
# YOLOv5 v6.1 head
head:
[[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 6], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 14
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 1, 1]],
[-1, 1, nn.Upsample, [None, 2, 'nearest']],
[[-1, 4], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat backbone P3
[-1, 3, C3, [256, False]], # 18 (P3/8-small)
[-1, 1, Conv, [256, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 15], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P4
[-1, 3, C3, [512, False]], # 21 (P4/16-medium)
[-1, 1, Conv, [512, 3, 2]],
[[-1, 11], 1, Concat, [1]], # cat head P5
[-1, 3, C3, [1024, False]], # 24 (P5/32-large)
[[18, 21, 24], 1, Detect, [nc, anchors]], # Detect(P3, P4, P5)
]
7. SimAM 注意力模块
论文地址:http://proceedings.mlr.press/v139/yang21o/yang21o.pdf
代码
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class SimAM(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels = None,out_channels = None, e_lambda = 1e-4):
super(SimAM, self).__init__()
self.activaton = nn.Sigmoid()
self.e_lambda = e_lambda
def __repr__(self):
s = self.__class__.__name__ + '('
s += ('lambda=%f)' % self.e_lambda)
return s
@staticmethod
def get_module_name():
return "simam"
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.size()
n = w * h - 1
x_minus_mu_square = (x - x.mean(dim=[2,3], keepdim=True)).pow(2)
y = x_minus_mu_square / (4 * (x_minus_mu_square.sum(dim=[2,3], keepdim=True) / n + self.e_lambda)) + 0.5
return x * self.activaton(y)
elif m is SimAM:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no:
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, c2]
[-1, 1, SimAM, [1024]],
8. S2-MLPv2 注意力模块
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.01072
代码
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
# https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.01072
def spatial_shift1(x):
b,w,h,c = x.size()
x[:,1:,:,:c//4] = x[:,:w-1,:,:c//4]
x[:,:w-1,:,c//4:c//2] = x[:,1:,:,c//4:c//2]
x[:,:,1:,c//2:c*3//4] = x[:,:,:h-1,c//2:c*3//4]
x[:,:,:h-1,3*c//4:] = x[:,:,1:,3*c//4:]
return x
def spatial_shift2(x):
b,w,h,c = x.size()
x[:,:,1:,:c//4] = x[:,:,:h-1,:c//4]
x[:,:,:h-1,c//4:c//2] = x[:,:,1:,c//4:c//2]
x[:,1:,:,c//2:c*3//4] = x[:,:w-1,:,c//2:c*3//4]
x[:,:w-1,:,3*c//4:] = x[:,1:,:,3*c//4:]
return x
class SplitAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,channel=512,k=3):
super().__init__()
self.channel=channel
self.k=k
self.mlp1=nn.Linear(channel,channel,bias=False)
self.gelu=nn.GELU()
self.mlp2=nn.Linear(channel,channel*k,bias=False)
self.softmax=nn.Softmax(1)
def forward(self,x_all):
b,k,h,w,c=x_all.shape
x_all=x_all.reshape(b,k,-1,c)
a=torch.sum(torch.sum(x_all,1),1)
hat_a=self.mlp2(self.gelu(self.mlp1(a)))
hat_a=hat_a.reshape(b,self.k,c)
bar_a=self.softmax(hat_a)
attention=bar_a.unsqueeze(-2)
out=attention*x_all
out=torch.sum(out,1).reshape(b,h,w,c)
return out
class S2Attention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels=512 ):
super().__init__()
self.mlp1 = nn.Linear(channels,channels*3)
self.mlp2 = nn.Linear(channels,channels)
self.split_attention = SplitAttention()
def forward(self, x):
b,c,w,h = x.size()
x=x.permute(0,2,3,1)
x = self.mlp1(x)
x1 = spatial_shift1(x[:,:,:,:c])
x2 = spatial_shift2(x[:,:,:,c:c*2])
x3 = x[:,:,:,c*2:]
x_all=torch.stack([x1,x2,x3],1)
a = self.split_attention(x_all)
x = self.mlp2(a)
x=x.permute(0,3,1,2)
return x
elif m is S2Attention:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no:
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
[-1, 1, S2Attention, [1024]],
9. NAMAttention 注意力模块
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.12419
代码
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
from torch.nn import functional as F
class Channel_Att(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, t=16):
super(Channel_Att, self).__init__()
self.channels = channels
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.channels, affine=True)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
x = self.bn2(x)
weight_bn = self.bn2.weight.data.abs() / torch.sum(self.bn2.weight.data.abs())
x = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).contiguous()
x = torch.mul(weight_bn, x)
x = x.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
x = torch.sigmoid(x) * residual #
return x
class NAMAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, out_channels=None, no_spatial=True):
super(NAMAttention, self).__init__()
self.Channel_Att = Channel_Att(channels)
def forward(self, x):
x_out1=self.Channel_Att(x)
return x_out1
elif m is NAMAttention:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no:
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, *args[1:]]
[-1, 1, NAMAttention, [1024]],
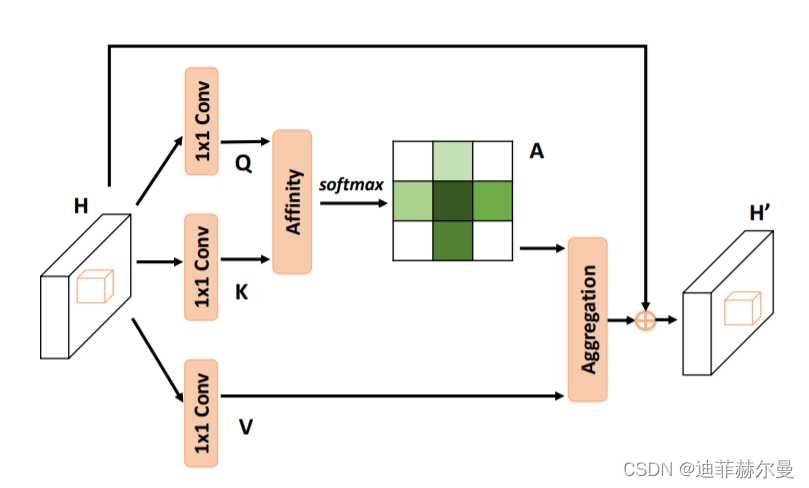
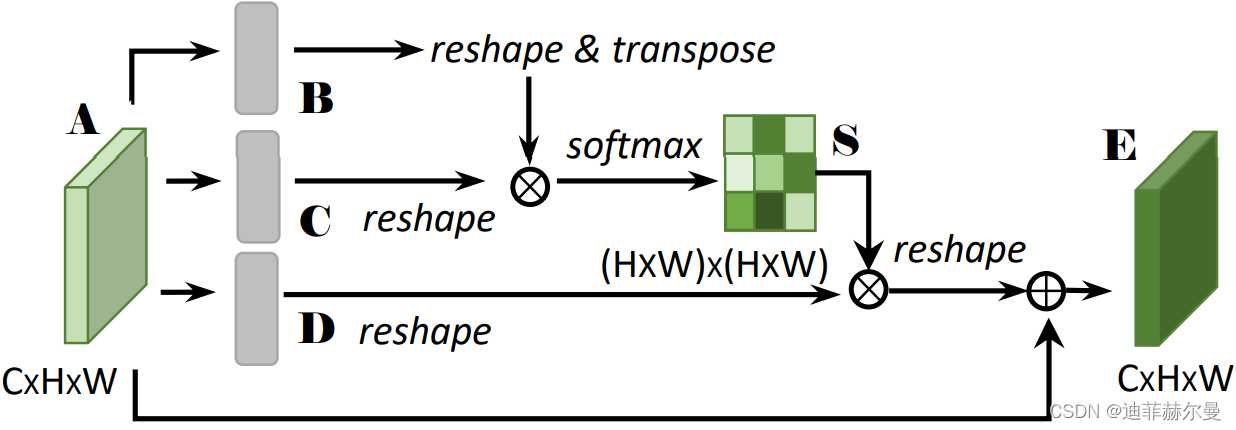
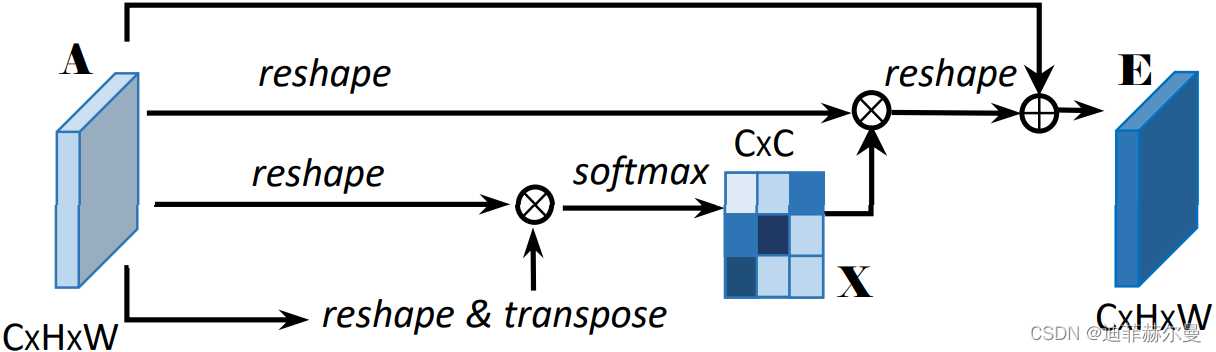
10. Criss-CrossAttention 注意力模块
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/1811.11721
代码
''' This code is borrowed from Serge-weihao/CCNet-Pure-Pytorch '''
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.nn import Softmax
def INF(B,H,W):
return -torch.diag(torch.tensor(float("inf")).repeat(H),0).unsqueeze(0).repeat(B*W,1,1)
class CrissCrossAttention(nn.Module):
""" Criss-Cross Attention Module"""
def __init__(self, in_dim):
super(CrissCrossAttention,self).__init__()
self.query_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim//8, kernel_size=1)
self.key_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim//8, kernel_size=1)
self.value_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_dim, out_channels=in_dim, kernel_size=1)
self.softmax = Softmax(dim=3)
self.INF = INF
self.gamma = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1))
def forward(self, x):
m_batchsize, _, height, width = x.size()
proj_query = self.query_conv(x)
proj_query_H = proj_query.permute(0,3,1,2).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*width,-1,height).permute(0, 2, 1)
proj_query_W = proj_query.permute(0,2,1,3).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*height,-1,width).permute(0, 2, 1)
proj_key = self.key_conv(x)
proj_key_H = proj_key.permute(0,3,1,2).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*width,-1,height)
proj_key_W = proj_key.permute(0,2,1,3).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*height,-1,width)
proj_value = self.value_conv(x)
proj_value_H = proj_value.permute(0,3,1,2).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*width,-1,height)
proj_value_W = proj_value.permute(0,2,1,3).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*height,-1,width)
energy_H = (torch.bmm(proj_query_H, proj_key_H)+self.INF(m_batchsize, height, width)).view(m_batchsize,width,height,height).permute(0,2,1,3)
energy_W = torch.bmm(proj_query_W, proj_key_W).view(m_batchsize,height,width,width)
concate = self.softmax(torch.cat([energy_H, energy_W], 3))
att_H = concate[:,:,:,0:height].permute(0,2,1,3).contiguous().view(m_batchsize*width,height,height)
#print(concate)
#print(att_H)
att_W = concate[:,:,:,height:height+width].contiguous().view(m_batchsize*height,width,width)
out_H = torch.bmm(proj_value_H, att_H.permute(0, 2, 1)).view(m_batchsize,width,-1,height).permute(0,2,3,1)
out_W = torch.bmm(proj_value_W, att_W.permute(0, 2, 1)).view(m_batchsize,height,-1,width).permute(0,2,1,3)
#print(out_H.size(),out_W.size())
return self.gamma*(out_H + out_W) + x
elif m is CrissCrossAttention:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no:
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, *args[1:]]
[-1, 1, CrissCrossAttention, [1024]],
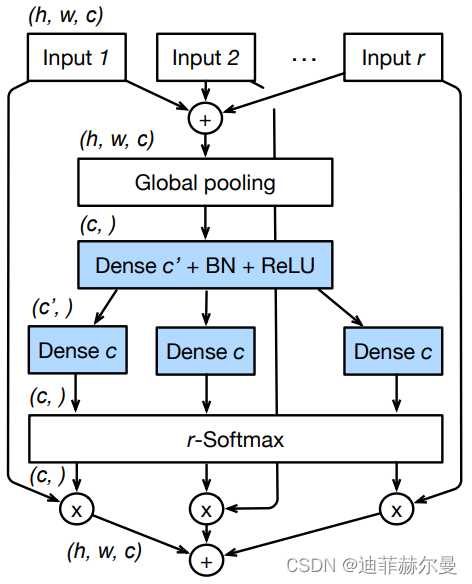
11. GAMAttention 注意力模块
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2112.05561v1.pdf
代码
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
class GAMAttention(nn.Module):
#https://paperswithcode.com/paper/global-attention-mechanism-retain-information
def __init__(self, c1, c2, group=True,rate=4):
super(GAMAttention, self).__init__()
self.channel_attention = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(c1, int(c1 / rate)),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(int(c1 / rate), c1)
)
self.spatial_attention = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(c1, c1//rate, kernel_size=7, padding=3,groups=rate)if group else nn.Conv2d(c1, int(c1 / rate), kernel_size=7, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(int(c1 /rate)),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(c1//rate, c2, kernel_size=7, padding=3,groups=rate) if group else nn.Conv2d(int(c1 / rate), c2, kernel_size=7, padding=3),
nn.BatchNorm2d(c2)
)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
x_permute = x.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(b, -1, c)
x_att_permute = self.channel_attention(x_permute).view(b, h, w, c)
x_channel_att = x_att_permute.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
x = x * x_channel_att
x_spatial_att = self.spatial_attention(x).sigmoid()
x_spatial_att=channel_shuffle(x_spatial_att,4) #last shuffle
out = x * x_spatial_att
return out
def channel_shuffle(x, groups=2): ##shuffle channel
#RESHAPE----->transpose------->Flatten
B, C, H, W = x.size()
out = x.view(B, groups, C // groups, H, W).permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4).contiguous()
out=out.view(B, C, H, W)
return out
elif m is GAMAttention:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no:
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
[-1, 1, GAMAttention, [1024,1024]],
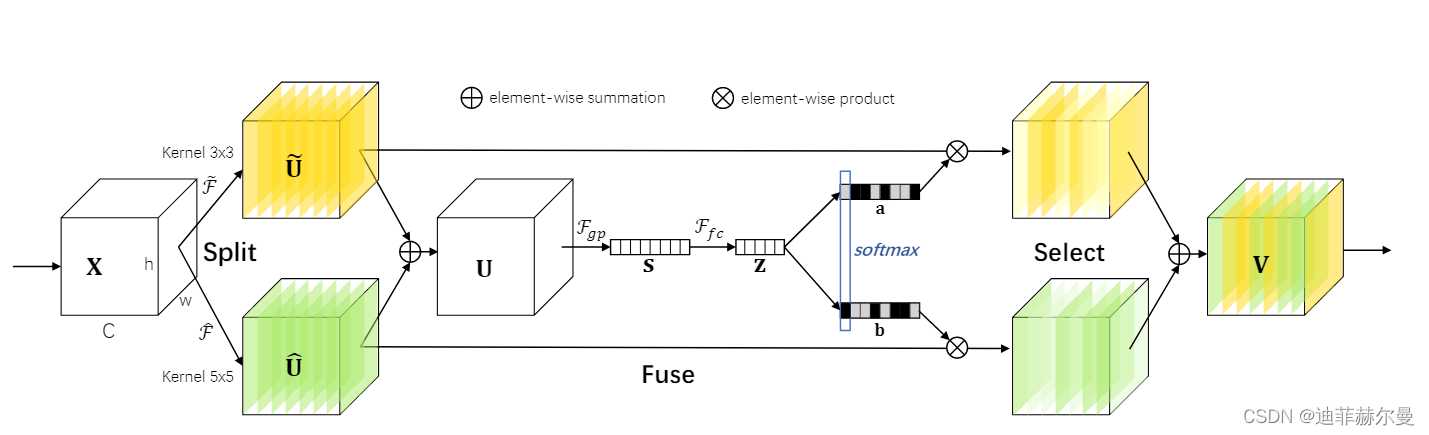
12. Selective Kernel Attention 注意力模块
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1903.06586.pdf
代码
class SKAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel=512,kernels=[1,3,5,7],reduction=16,group=1,L=32):
super().__init__()
self.d=max(L,channel//reduction)
self.convs=nn.ModuleList([])
for k in kernels:
self.convs.append(
nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
('conv',nn.Conv2d(channel,channel,kernel_size=k,padding=k//2,groups=group)),
('bn',nn.BatchNorm2d(channel)),
('relu',nn.ReLU())
]))
)
self.fc=nn.Linear(channel,self.d)
self.fcs=nn.ModuleList([])
for i in range(len(kernels)):
self.fcs.append(nn.Linear(self.d,channel))
self.softmax=nn.Softmax(dim=0)
def forward(self, x):
bs, c, _, _ = x.size()
conv_outs=[]
### split
for conv in self.convs:
conv_outs.append(conv(x))
feats=torch.stack(conv_outs,0)#k,bs,channel,h,w
### fuse
U=sum(conv_outs) #bs,c,h,w
### reduction channel
S=U.mean(-1).mean(-1) #bs,c
Z=self.fc(S) #bs,d
### calculate attention weight
weights=[]
for fc in self.fcs:
weight=fc(Z)
weights.append(weight.view(bs,c,1,1)) #bs,channel
attention_weughts=torch.stack(weights,0)#k,bs,channel,1,1
attention_weughts=self.softmax(attention_weughts)#k,bs,channel,1,1
### fuse
V=(attention_weughts*feats).sum(0)
return V
elif m is SKAttention:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no:
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, *args[1:]]
[-1, 1, SKAttention, [1024]],
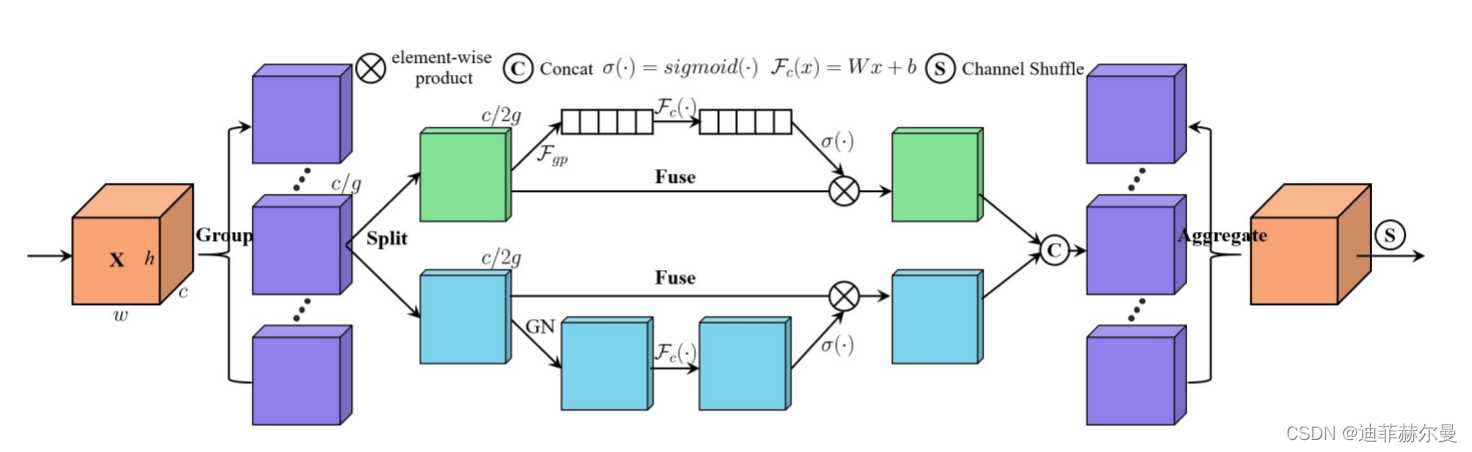
13. ShuffleAttention 注意力模块
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.00240.pdf
代码
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
# https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.00240.pdf
class ShuffleAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel=512,reduction=16,G=8):
super().__init__()
self.G=G
self.channel=channel
self.avg_pool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1)
self.gn = nn.GroupNorm(channel // (2 * G), channel // (2 * G))
self.cweight = Parameter(torch.zeros(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.cbias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.sweight = Parameter(torch.zeros(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.sbias = Parameter(torch.ones(1, channel // (2 * G), 1, 1))
self.sigmoid=nn.Sigmoid()
def init_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
@staticmethod
def channel_shuffle(x, groups):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
x = x.reshape(b, groups, -1, h, w)
x = x.permute(0, 2, 1, 3, 4)
# flatten
x = x.reshape(b, -1, h, w)
return x
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.size()
#group into subfeatures
x=x.view(b*self.G,-1,h,w) #bs*G,c//G,h,w
#channel_split
x_0,x_1=x.chunk(2,dim=1) #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
#channel attention
x_channel=self.avg_pool(x_0) #bs*G,c//(2*G),1,1
x_channel=self.cweight*x_channel+self.cbias #bs*G,c//(2*G),1,1
x_channel=x_0*self.sigmoid(x_channel)
#spatial attention
x_spatial=self.gn(x_1) #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
x_spatial=self.sweight*x_spatial+self.sbias #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
x_spatial=x_1*self.sigmoid(x_spatial) #bs*G,c//(2*G),h,w
# concatenate along channel axis
out=torch.cat([x_channel,x_spatial],dim=1) #bs*G,c//G,h,w
out=out.contiguous().view(b,-1,h,w)
# channel shuffle
out = self.channel_shuffle(out, 2)
return out
elif m is ShuffleAttention:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no:
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
[-1, 1, ShuffleAttention, [1024]],
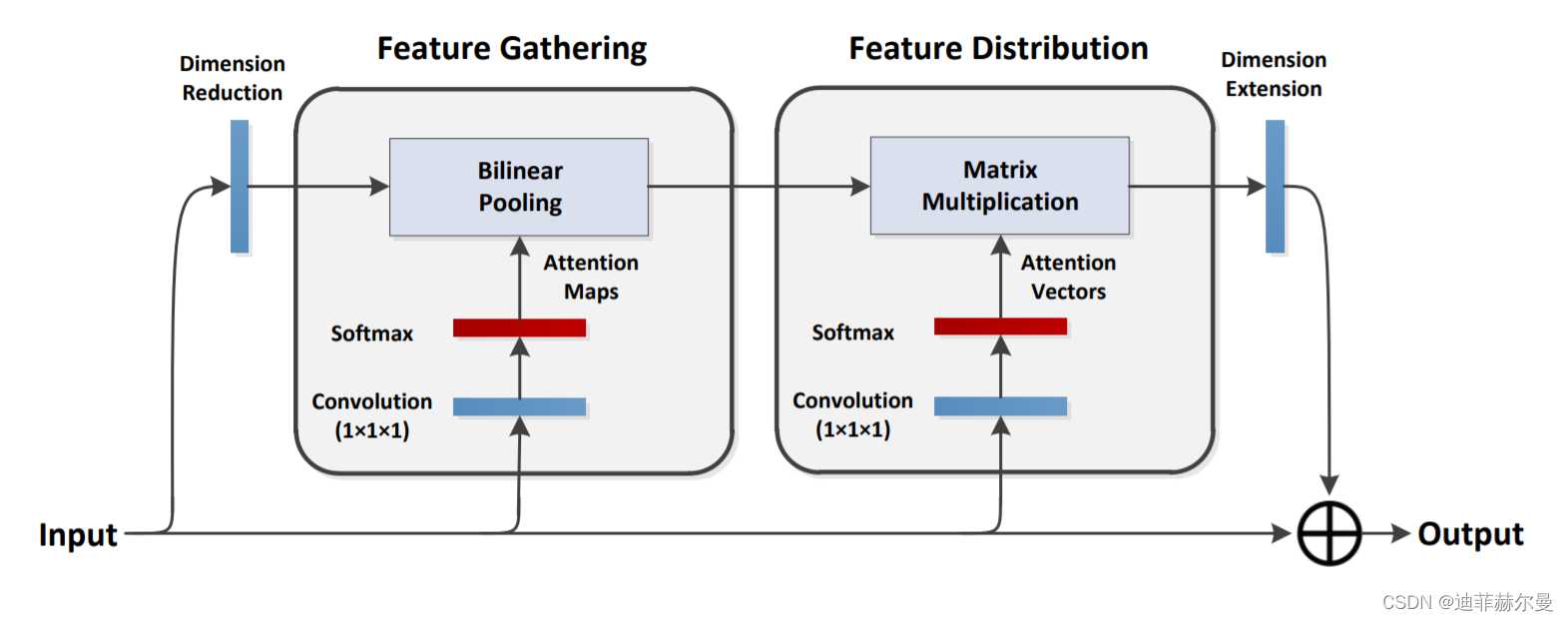
14. A2-Net 注意力模块🍀
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.11579.pdf
代码
from torch.nn import init
class DoubleAttention(nn.Module):
""" A2-Nets: Double Attention Networks. NIPS 2018 """
def __init__(self, in_channels, c_m, c_n, reconstruct=True):
super().__init__()
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.reconstruct = reconstruct
self.c_m = c_m
self.c_n = c_n
self.convA = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c_m, 1)
self.convB = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c_n, 1)
self.convV = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, c_n, 1)
if self.reconstruct:
self.conv_reconstruct = nn.Conv2d(c_m, in_channels, kernel_size=1)
self.init_weights()
def init_weights(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out')
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
init.normal_(m.weight, std=0.001)
if m.bias is not None:
init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
b, c, h, w = x.shape
assert c == self.in_channels
A = self.convA(x) # b,c_m,h,w
B = self.convB(x) # b,c_n,h,w
V = self.convV(x) # b,c_n,h,w
tmpA = A.view(b, self.c_m, -1)
attention_maps = F.softmax(B.view(b, self.c_n, -1), dim=1)
attention_vectors = F.softmax(V.view(b, self.c_n, -1), dim=1)
# step 1: feature gating
global_descriptors = torch.bmm(tmpA, attention_maps.permute(0, 2, 1)) # b.c_m,c_n
# step 2: feature distribution
tmpZ = global_descriptors.matmul(attention_vectors) # b,c_m,h*w
tmpZ = tmpZ.view(b, self.c_m, h, w) # b,c_m,h,w
if self.reconstruct:
tmpZ = self.conv_reconstruct(tmpZ)
return tmpZ
elif m is DoubleAttention:
c1, c2 = ch[f], args[0]
if c2 != no: # if not output
c2 = make_divisible(c2 * gw, 8)
args = [c1, c2, *args[1:]]
[-1, 1, DoubleAttention,[1024,256,256]],
更多注意力代码欢迎关注我的《目标检测蓝皮书》💖
番外篇 | 20+ 种注意力机制及代码 适用于YOLOv5/v7/v8
15. DANPositional 注意力模块
16. DANChannel 注意力模块
17. RESNest 注意力模块
18. Harmonious 注意力模块
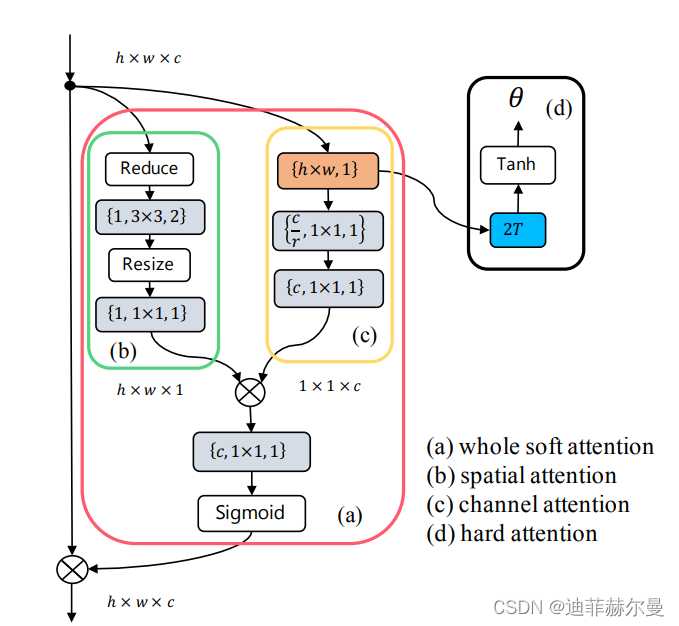
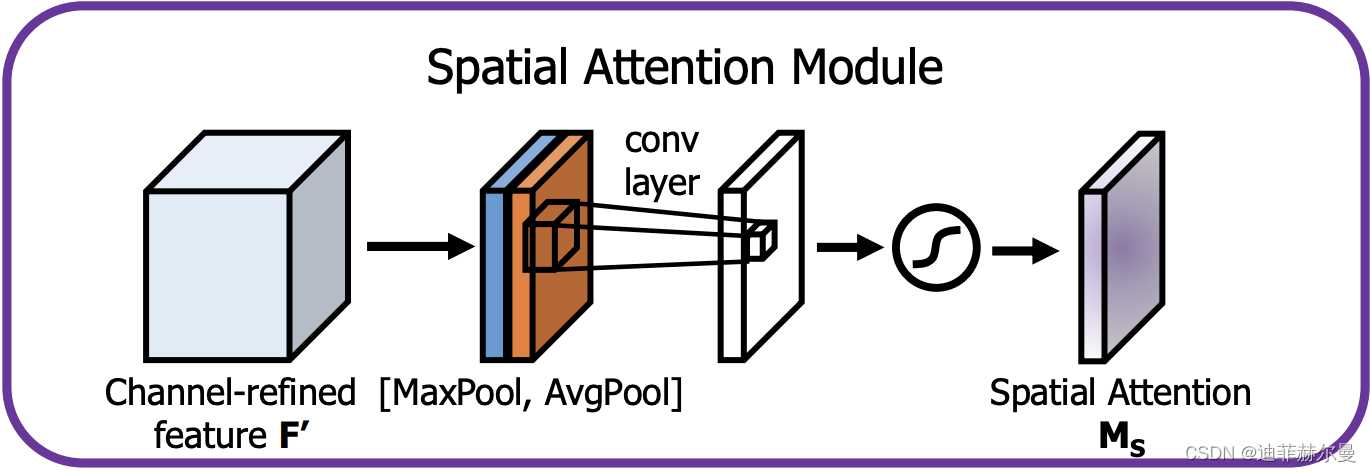
19. SpatialAttention 注意力模块
19. RANet 注意力模块
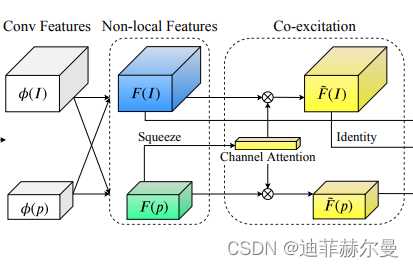
20. Co-excite 注意力模块
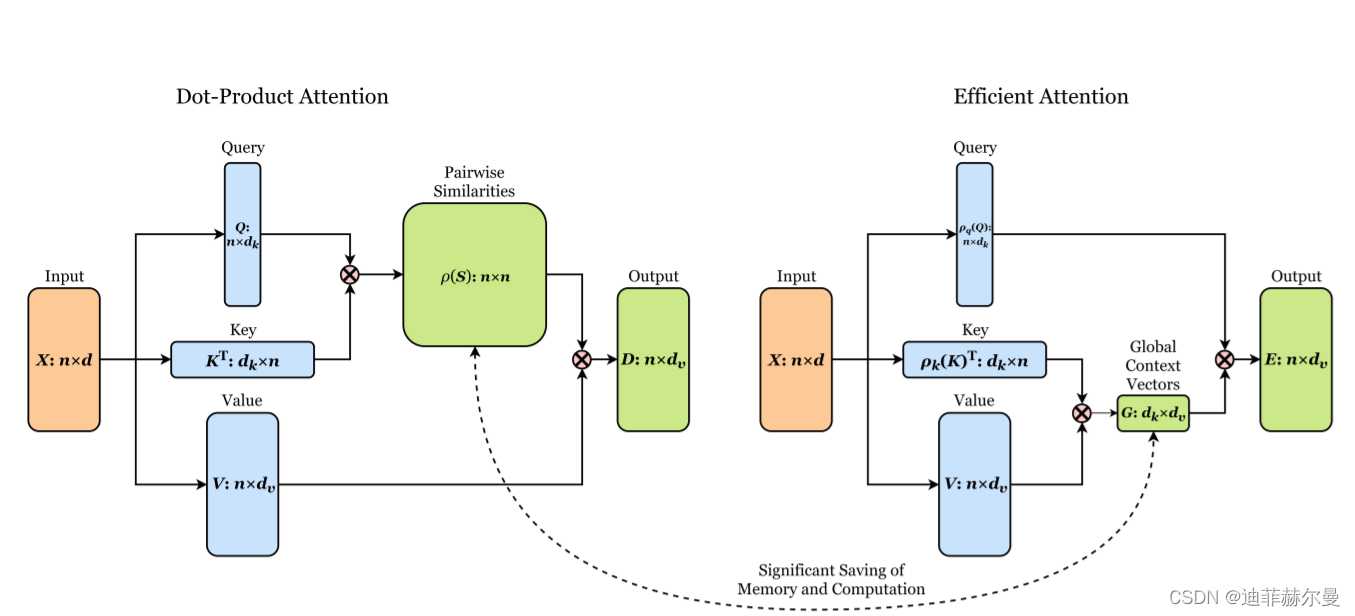
21. EfficientAttention 注意力模块
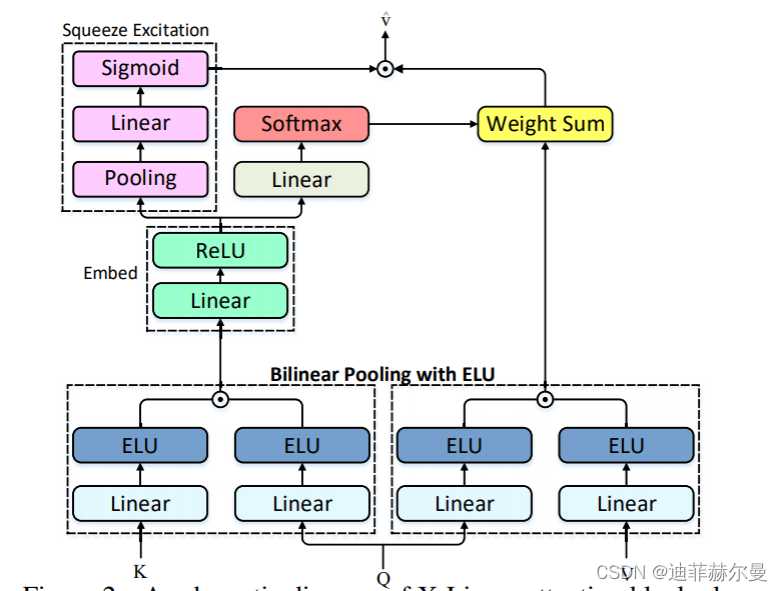
22. X-Linear 注意力模块
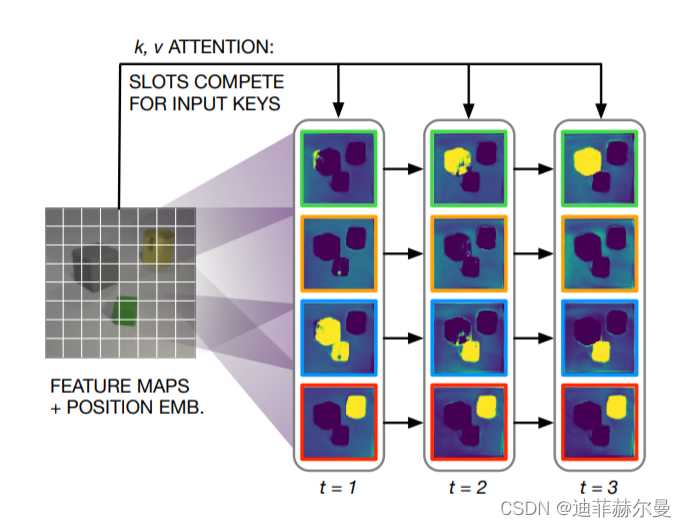
23. SlotAttention 注意力模块
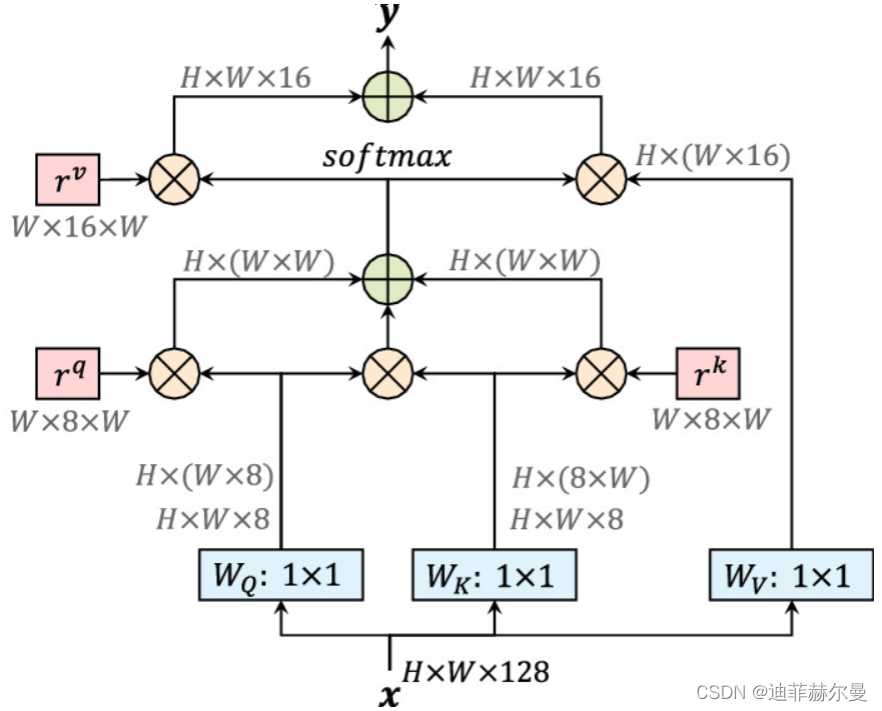
24. Axial 注意力模块
25. RFA 注意力模块
26. Attention-BasedDropout 注意力模块
27. ReverseAttention 注意力模块
28. CrossAttention 注意力模块
29. Perceiver 注意力模块
30. Criss-CrossAttention 注意力模块
31. BoostedAttention 注意力模块
32. Prophet 注意力模块
33. S3TA 注意力模块
34. Self-CriticAttention 注意力模块
35. BayesianAttentionBeliefNetworks 注意力模块
36. Expectation-MaximizationAttention 注意力模块
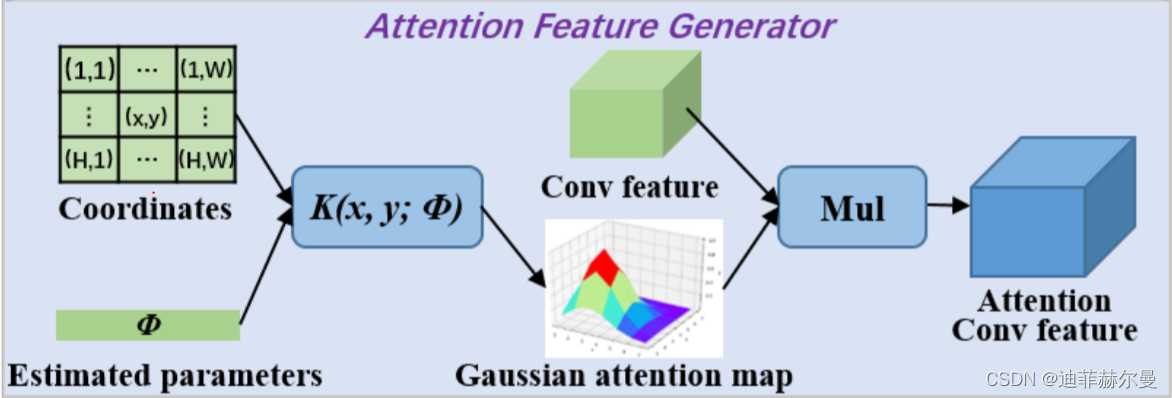
37. GaussianAttention 注意力模块
代码持续更新中。。。
本人更多 YOLOv5/v7 实战内容导航🍀🌟🚀
-
手把手带你YOLOv5/v7 (v5.0-v7.0)添加注意力机制(一)(并附上30多种顶会Attention原理图)🌟强烈推荐🍀新增8种
-
空间金字塔池化改进 SPP / SPPF / SimSPPF / ASPP / RFB / SPPCSPC / SPPFCSPC🚀
2022/10/30更新日志:新增加8种注意力机制源码(6-13),完美适配YOLO系列算法,感谢CSDN芒果汁没有芒果为本文提供技术支持。
2023/01/07更新日志:修改了文章结构,对部分章节增加了更加详细的解释。
2023/02/011更新日志:增加了A2-Net注意力代码。🍀
有问题欢迎大家指正,如果感觉有帮助的话请点赞支持下👍📖🌟
!!转载请注明出处!!
今天的文章手把手带你YOLOv5/v7 添加注意力机制(并附上30多种顶会Attention原理图)2023/2/11更新分享到此就结束了,感谢您的阅读。
版权声明:本文内容由互联网用户自发贡献,该文观点仅代表作者本人。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。如发现本站有涉嫌侵权/违法违规的内容, 请发送邮件至 举报,一经查实,本站将立刻删除。
如需转载请保留出处:https://bianchenghao.cn/13232.html